SDR Check Up
The purpose of this tutorial is to shows how to check basic status and information about sdr cards installed on the callbox PC. This will help you to find root cause or troubleshoot for the sdr card related problems that you may face.
SDR stands for Software Defined Radio. The SDR card is the hardware card placed in PCI slots of the Callbox or UEsim. Each of the cards has multiple RF port (SMA type) where you connect antenna or coex cables. There are not so many cases where you need to check on SDR. But there are a few cases where it is worth checking SDR status/functionality.
Whenever you think you have any issues with sdr card (e.g, UE does not seem to receive any signal from Callbox), first suggestion is always to tweak the power of RF ports using tx_gain, rx_gain, t spl
If you end up with failure with the teaking the power tuning, it is not easy to confirm whether you have any issues with sdr power issue or timing/sync issue. so more practical advise would be ' do some sdr check up as in this tutorial whenever you have some problem and have done all other software related troubleshooting)
Table of Contents
- SDR Check Up
- Introduction
- Summary of the Tutorial
- Test Setup
- Key Command Line
- Check Up #1 : Errors / Warnings
- Check Up #2 : Check SDR Status with sdr_util
- Check SDR Status
- ./sdr_util -c all version
- ./sdr_util -c all sync_state
- ./sdr_util -c all gps_state
- ./sdr_util -c all clock_tune
- ./sdr_util -c all temp
- Sync with GPS
- Check Up #3 : Check SDR power with sdr_spectrum
- Check Up #4 : Running LTE on different sdr cards
- Check Up #5 : Clock Calibration
- Check Up #6 : Checkup for underflow/overflow
- Check Up #7 : Hardware Check-Up
- Additional Information
Introduction
Software Defined Radio (SDR) technology represents a transformative approach to radio communication systems by enabling the majority of radio functions, such as modulation, demodulation, and signal processing, to be implemented in software rather than hardware. SDR cards, which are specialized hardware modules typically installed in PCIe slots within systems like Callbox or UEsim, serve as highly flexible radio front-ends. Each SDR card is designed with multiple RF ports (commonly SMA type connectors), allowing for diverse connectivity options including antennas and coaxial cables. These cards interface directly with system software, facilitating real-time RF signal transmission and reception, and supporting a broad range of cellular and wireless standards. Within the Callbox ecosystem, SDR cards are pivotal for emulating network environments, running protocol stacks, and conducting comprehensive testing of wireless devices. Their configurability enables dynamic adjustment of RF parameters such as gain, frequency, and bandwidth, making them essential for troubleshooting and root cause analysis in laboratory and field scenarios. Understanding and monitoring the status of SDR cards is crucial for maintaining optimal system performance, diagnosing hardware or synchronization issues, and ensuring accurate test outcomes. This tutorial provides a systematic approach to checking the basic status and health of SDR cards installed on a Callbox PC, empowering engineers and technicians to efficiently identify and resolve SDR-related problems as part of broader troubleshooting workflows.
-
Context and Background
- SDR cards are integral hardware components in platforms such as Callbox and UEsim, providing the physical layer interface for wireless signal processing.
- The technology decouples radio functions from fixed hardware, allowing updates and adjustments via software, which supports rapid prototyping, testing, and deployment of new wireless standards.
- In a typical Callbox setup, each SDR card manages multiple RF ports, facilitating simultaneous multi-channel operation and extensive connectivity options.
-
Relevance and Importance of This Tutorial
- SDR card status directly impacts the fidelity and reliability of wireless testing environments, making regular health checks vital for consistent operation.
- Troubleshooting SDR cards helps in isolating hardware issues from software misconfigurations, streamlining the resolution process in complex test setups.
- This tutorial enables users to proactively identify potential SDR hardware faults or misconfigurations before they escalate into critical system failures.
-
Learning Outcomes
- Gain the ability to check and interpret basic SDR card status and health indicators on the Callbox PC.
- Understand the typical symptoms and scenarios where SDR card checks are necessary, such as unexpected signal loss or suspected hardware malfunction.
- Acquire practical troubleshooting skills for distinguishing between software and hardware-related RF issues.
- Learn to utilize key command-line utilities and logs relevant to SDR monitoring and diagnostics.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge and Skills
- Familiarity with the Callbox or UEsim test environments and their hardware architecture.
- Basic understanding of RF concepts, including signal gain, synchronization, and antenna connectivity.
- Experience with command-line interfaces in a Linux or Windows environment.
- General troubleshooting methodology for wireless communication systems.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial provides a comprehensive set of check-up and troubleshooting procedures for SDR (Software Defined Radio) card functionality in a test setup environment. The following summarizes each test procedure, step-by-step methodologies, and essential checks described in the document:
-
Test Setup
- Connect antennas or RF cables to as many SDR cards as required for your testing scenario.
Key command-line utilities used:
- sdr_util
- sdr_test
- sdr_spectrum
Common sdr_util commands include:
- ./sdr_util -c all version
- ./sdr_util -c all sync_state
- ./sdr_util -c all gps_state
- ./sdr_util clock_tune
- ./sdr_util -c all temp
-
Check Up #1: Errors / Warnings
- Investigate explicit errors or warnings related to SDR cards (such as initialization failures, clock source issues, GPS synchronization errors, temperature alarms, or system errors).
- Do not proceed until the root cause of the error or warning is resolved.
-
Check Up #2: Check SDR Status with sdr_util
- Use sdr_util to check the status of installed SDR cards.
- Ensure LTE service is stopped before executing these commands (use service lte stop).
- Commands and their purposes:
- ./sdr_util -c all version: Lists basic information about all detected SDR cards; if any card is missing, perform a hardware checkup.
- ./sdr_util -c all sync_state: Verifies synchronization status, sync source, and clock source of each card. By default, SDR 0 is sync master and others are slaves.
- ./sdr_util -c all gps_state: Checks GPS status. If the GPS antenna is connected, look for 'GPS locked(active)'; otherwise, 'GPS not locked' indicates no GPS signal.
- ./sdr_util -c all clock_tune: Shows current clock drift. A value of 0 may indicate factory tuning has not been performed.
- ./sdr_util -c all temp: Reports temperature of each SDR card; if high temperature is reported, reboot and recheck before concluding an issue.
- Synchronizing with GPS: If a GPS antenna is connected, synchronize the SDR card with the GPS clock to improve performance (e.g., reduce BLER).
-
Check Up #3: Check SDR Power with sdr_spectrum
- Transmit a known reference signal from SDR and measure RF output power.
- Use a spectrum analyzer or another SDR card as a spectrum analyzer if dedicated equipment is unavailable.
- Refer to a separate tutorial for detailed steps on generating OFDM signals and measuring with sdr_spectrum.
-
Check Up #4: Running LTE on Different SDR Cards
- Troubleshoot attachment issues by running LTE (or NR) using only one SDR card at a time.
- Modify a copy of the configuration file (enb.default.cfg) for each SDR card under test.
- Restart LTE service, check SDR info using rf_info, and attempt to attach UE. Successful attachment and traffic indicate the SDR card is functioning.
- Repeat the procedure for each SDR card in the system.
- For multi-SDR configurations (e.g., running one NR cell on two SDRs for higher bandwidth), refer to the referenced tutorial.
-
Check Up #5: Clock Calibration
- If all previous checkups (particularly #1, #2, and #6) pass but issues persist, consider calibrating the SDR card clock to a GPS clock.
- Refer to the specified wiki for clock calibration procedures.
- Situations warranting calibration include long-term use (oscillator drift), synchronizing with other equipment, or excessive Carrier Frequency Offset (CFO) in UEsim scenarios.
-
Check Up #6: Checkup for Underflow/Overflow
- If underflow or overflow errors persist after prior checkups, consult the provided wiki for further troubleshooting steps.
-
Check Up #7: Hardware Check-Up
- If SDRs fail to work despite passing basic checkups, investigate hardware issues.
- Steps include:
- Remove all SDR cards; insert one card into a PCI slot and test individually using Checkup #2, Checkup #6, and by running LTE service with a single cell configuration. Repeat for each card.
- Identify working SDR cards.
- Install multiple confirmed-working cards, connect sync cables securely, and test multi-card operation (Checkup #2, #6, and LTE service with multi-cell configuration).
- If problems persist in multi-card setup, suspect sync cable or connection issues rather than the SDR cards themselves.
-
Additional Information: Max Power
- Maximum transmit power depends on frequency, bandwidth, and TX gain.
- Consult the appropriate documentation for SDR50 or SDR100 regarding measurement conditions and maximum power specifications.
This summary captures the stepwise diagnostic and validation process for SDR card operation, focusing on command-line checks, hardware verification, and systematic troubleshooting. Individual configuration parameters and commands are highlighted where essential for following the test procedures.
Test Setup
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below. I would suggest you to connect antenna (or RF cables) to as many sdr cards as possible as per your needs.
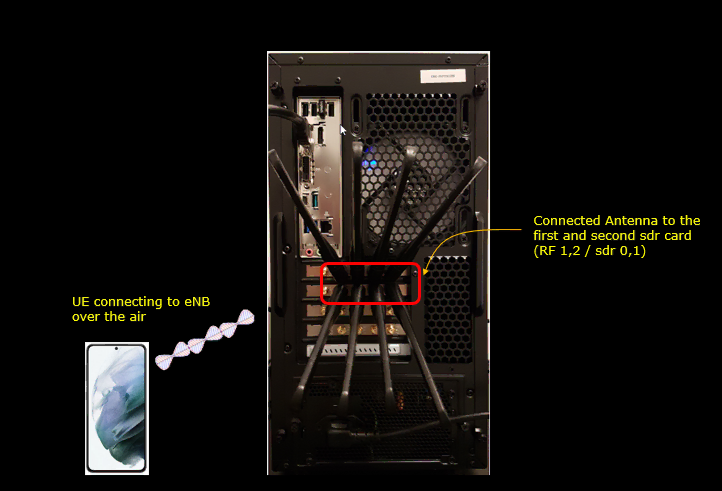
Key Command Line
Followings are the list of the important command used in this tutorial.
- sdr_util
- ./sdr_util -c all version
- ./sdr_util -c all sync_state
- ./sdr_util -c all gps_state
- ./sdr_util clock_tune
- ./sdr_util -c all temp
- sdr_test
- sdr_spectrum
Check Up #1 : Errors / Warnings
When you have explicit errors or warnings about sdr cards. Some example of this kind of errors are as follows : ( NOTE : The full set of error/warning list is much longer than this, but I just tried to put some of the errors that most commonly happen. If you want to get the full list of error/warning, check out this file)
In most cases when you have these kinds of error, you are not allowed to proceed any further. So the first step is to find the root cause of the error / warning and remove the error / warning.
- "*** Can't initialize phy ***"
- "Clock of device 'DDD' is not master - please check cables"
- "Clock of device 'DDD' is not slave - please check cables"
- Clock source of SDR device DDD should be set as master for the first one and slave for the others
- "Error: Timeout while waiting for the PPS"
- Timeout waiting for a valid SYNC signal (PPS).
- "Error: GPS time not available for sync"
- Sync is set as GPS but no signal received.
- "Can't init thread"
- Fatal system error
- "ERROR: OverTemp on 'DDD': FPGA:FFF░ RFIC:RRR░"
- Temperature is above threshold for device DDD
- Low level internal error: retry
Check Up #2 : Check SDR Status with sdr_util
If you don't have any specific warnings or errors and are still suspicious whether a sdr_card is functioning OK or not.
Check SDR Status
You may check on some basic status of sdr card using sdr_util.
Go to the directory /root/trx_sdr as shown below

NOTE : Make it sure that lte service is not running before you run any of the commands shown in this test (just do { service lte stop })
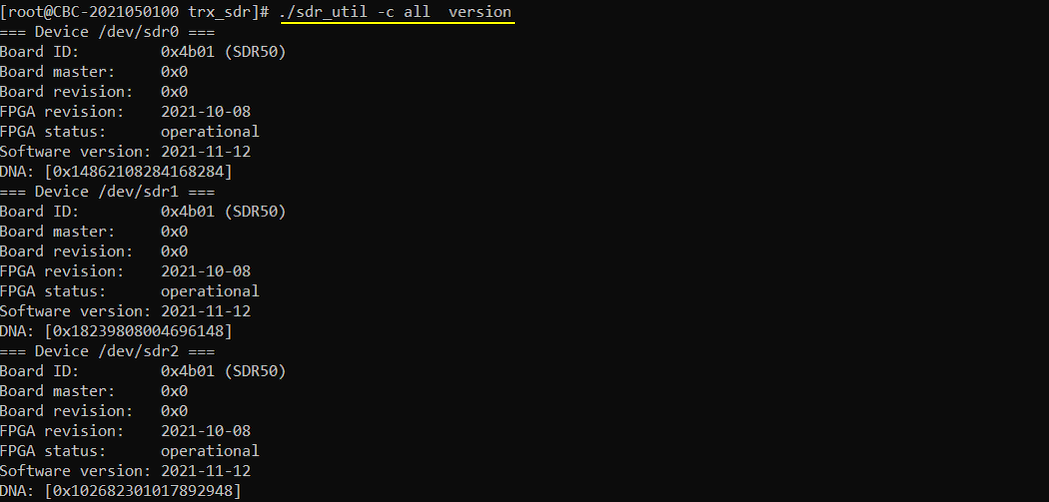
Check how many SDR cards are installed and basic information of each cards. run ./sdr_util -c all version
./sdr_util -c all version
: returns Basic informations of all sdr cards detected from the system
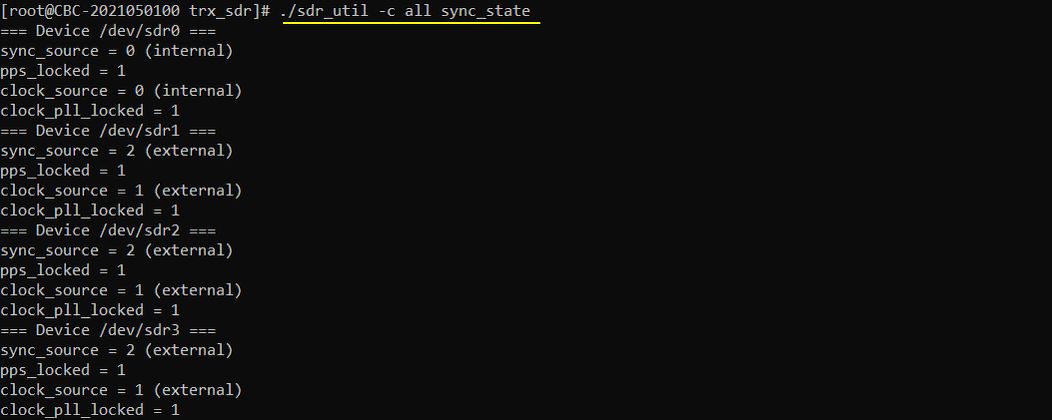
./sdr_util -c all sync_state
: check if each of the sdr cards are synched and prints sync_src, clock_source etc
SDR50: In case of SDR50, one of the cards are configured as sync master and the other cards are configured as sync slave. Usually the card with sync_source = 0 functions as sync master that provides sync signal to other cards with sync_source != 0. The sync ports on every sdr cards are cable-connected and by default sdr 0 is configured to be sync_source(sync master, internal) and other sdr cards are configured to be sync_sinc (sync slave, external). If you are not using sdr0 and using other cards only, the cards that you are using is configured to be sync source (internal). Even in this case, sdr0 always remain as (internal).
NOTE : Refer to sdr50 user manual for the details of hardware form factor and structure
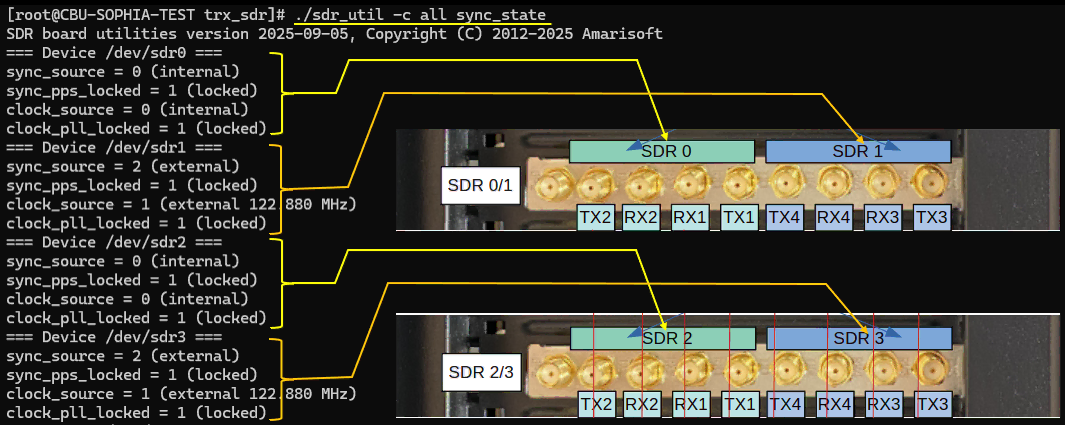
SDR100: In case of SDR100, Each SDR card (SDR Hardware module) can run independantly with its own internal clock/sync source. But within a SDR card are two sets of sdrs where the first sdr act as a master and the other sdr act as slave. An example of sync_state output for SDR100 is as shown below.
./sdr_util -c all gps_state
: Check gps status of all sdr cards (You will get the following result { GPS not locked } if GPS port on SDR card is not connected to GPS antenna)
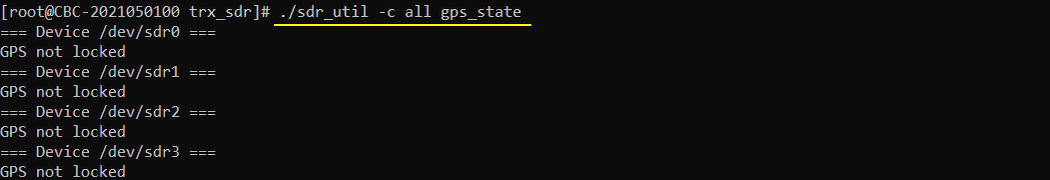
If your SDR card is connected with GPS Antenna, check if the GPS signal is properly detected.
If sdr 0 is connected with GPS antenna, you can check the gps_state only for sdr 0 by running ./sdr_util -c 0 gps_state
If the GPS signal is properly detected, you will get the message 'GPS locked(active)' as shown below.
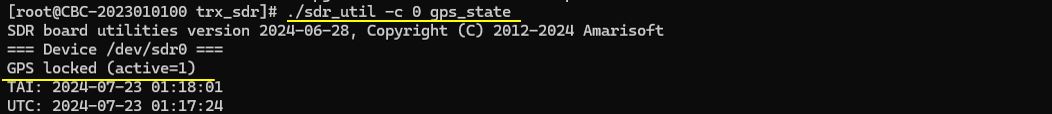
If the GPS signal is not detected, you will get the message 'GPS not locked'.

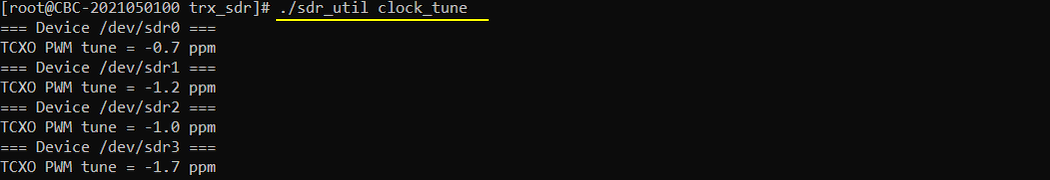
./sdr_util -c all clock_tune
This gives you the current drift applied. If it is 0, it is likely the factory process was not applied yet on this board. (
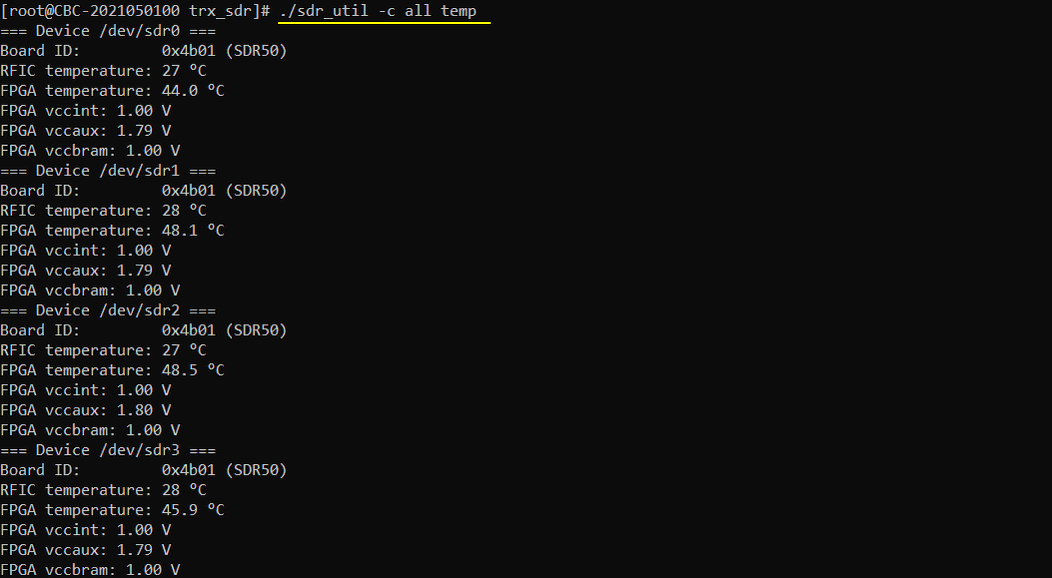
./sdr_util -c all temp
Check temperature of all sdr cards. (
Sync with GPS
If you have GPS antenna connected to GPS input port on SDR card, you may improve the performance (possibly reduce BLER) by synchronizing the SDR card with gps clock.
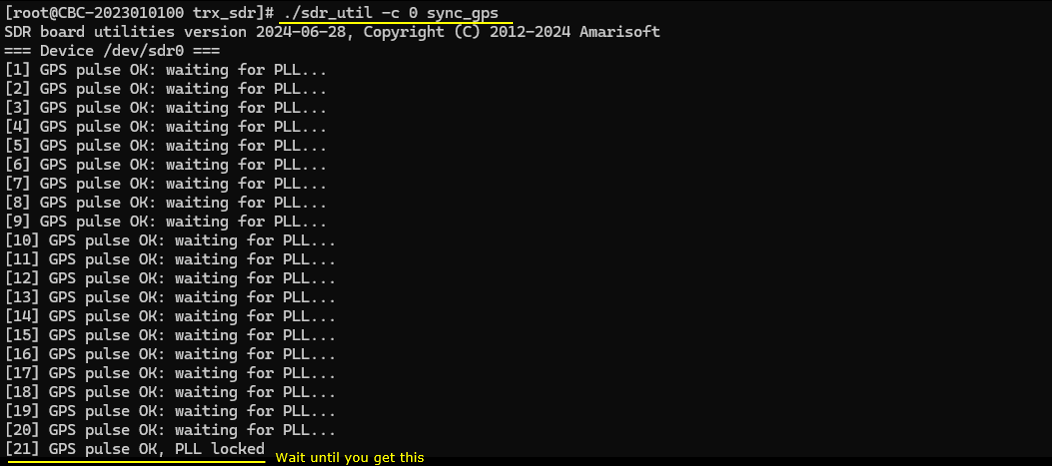
Check Up #3 : Check SDR power with sdr_spectrum
If you don't find any outstanding issues in previous checkup, next step I want to suggest is to let the sdr transmit a known signal and check out the power coming out of the RF port of the sdr.
You can generate a predefined reference signal from a SDR card and check out the power from the RF port. If you have any spectrum analyzer, you can use it. If you don't have any spectrum analyer, you can use another SDR card installed on your system as a spectrum analyzer.
Check out this tutorial for the details : sdr_test-generated OFDM signal on sdr 0 and sdr_spectrum on sdr 1
Check Up #4 : Running LTE on different sdr cards
This is mainly for troubleshooting when you have multiple SDR cards and UE is not attaching to the cell even after you did all other procedure / checkups (e.g, the procedure described in lteenb.pdf - 6.5).
The idea is to run simple LTE(or NR) requiring only one SDR card on different SDR card one by one.
Running on sdr 0
In this test, I run an LTE cell on sdr0 and then run it on sdr1. If UE can attach to both cards, you can say both SDR cards are functioning OK. I used the configuration file enb.default.cfg as the baseline and modified it for this test as follows.
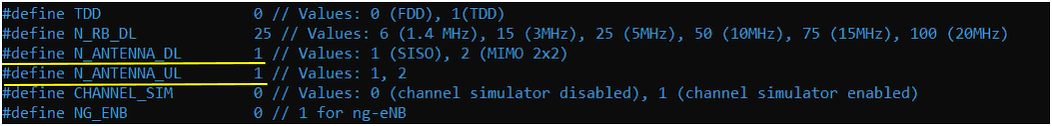
I have added the following configurations.

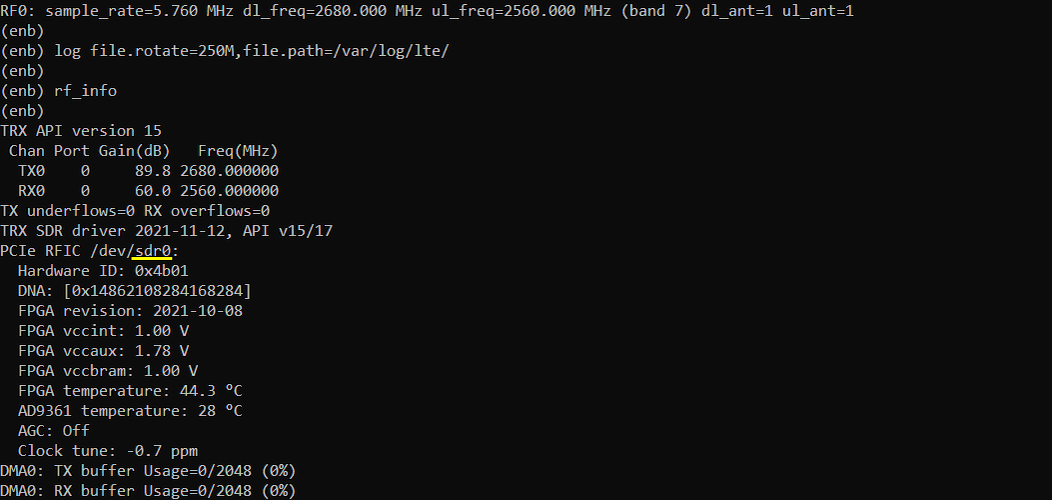
Restart the lte service (service lte restart) and launch screen (screen -r) and check rf_info in (enb) window. It will show you the sdr information as shown below.
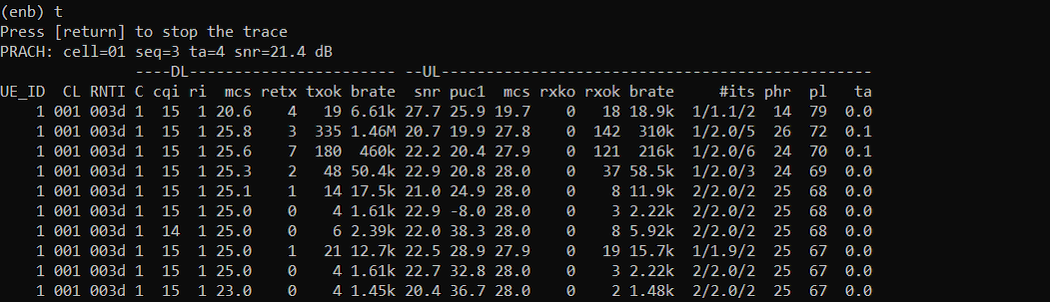
Now run trace command and get UE attached to the cell as shown below. If UE successfully attaches and you see some traffic, it would be a good indicator that the sdr is functioning properly (NOTE : even if UE successfully attaches and gives you some traffic, there still be some possibility of sdr card problems like problem with a certain bandwidth, frequency etc, but at least you can say there is no crtical problems with the sdr card)
Running on sdr 1
In this test, I run an LTE cell on sdr0 and then run it on sdr1. If UE can attach to both cards, you can say both SDR cards are functioning OK. I used the configuration file enb.default.cfg as the baseline and modified it for this test as follows.

I have added the following configurations.

Restart the lte service (service lte restart) and launch screen (screen -r) and check rf_info in (enb) window. It will show you the sdr information as shown below.
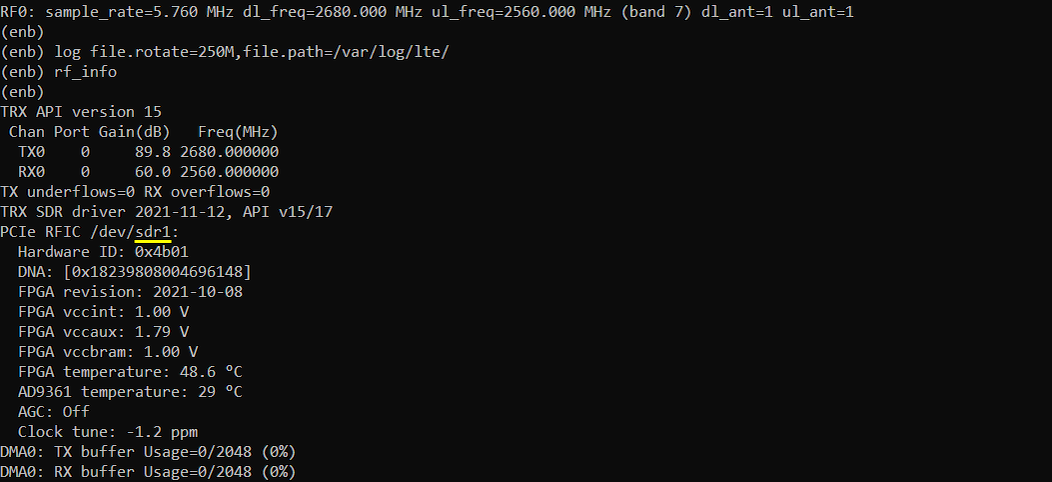
Now run trace command and get UE attached to the cell as shown below. If UE successfully attaches and you see some traffic, it would be a good indicator that the sdr is functioning properly (NOTE : even if UE successfully attaches and gives you some traffic, there still be some possibility of sdr card problems like problem with a certain bandwidth, frequency etc, but at least you can say there is no crtical problems with the sdr card)

Running one cell(one NR Cell) on 2 x sdr 20
In some cases, an sdr would work fine but you may see some issues when you combine multiple sdr cards to run one cell (e.g, achieving wider bandwidth than single sdr bandwidth). For this operation, refer to this tutorial.
Check Up #5 : Clock Calibration
If all of the check up mentioned above (probably except Check Up #4) did not show any conspicuous (outstanding) problem and still an SDR does not work, you may think of the possibility of Clock Calibration. Clock Calibration in this context mean to tune up an SDR card clock to GPS clock.
Regarding how to do clock calibration, refer to this wiki.
Amarisoft deliver SDR card with factory calibration. So it is less likely for you to have clock calibration issue, but you may consider trying this calibration in some situation exampled below.
- It has been used over long time (months/years) and the internal oscillator might have drifted
- You want to synchronize our enb/gnb with a other test equipment
- If you are using SDR card on UEsim and notice the CFO is too high (NOTE : if abs(CFO) > SCS (in Hz), it is strongly suggested to try clock calibration. this criteria is based on assumption that there is no clock issue on gNB/eNB side)
Check Up #6 : Checkup for underflow/overflow
When you have 'underflow / overflow' even after all the previous checkup has passed, I would suggest you to check out this wiki.
Check Up #7 : Hardware Check-Up
There are some cases where most of the basic checkup (e.g, checkup 1, 2, 6) passed but still fails to get SDR working for the complete call connection. In this case, you would need to check on the possible hardware issues. However, there is no simple and clear way to identify the root cause of hardware issues. It is good time for you to get a chance to open up the Chassis of the PC and play with sdr cards and slots. Since there is no determistic ways to trace out the root cause of the hardware issues, I will try to consolidate various trials based on cases that I personally came across.
Check if each individual sdr card works
For SDR 50
First, take out all the sdr card. You would get the empty PCI slots as shown below (

Pick any one PCI slot and plug in only one of your sdr cards and check if it works. And then check if the card works with no problem. For this checking, I would try followings
- i) Perform Checkup #2
- ii) Perform Checkup #6
- iii) Run lte service with any single cell configuration (e.g, enb.default.cfg or gnb-sa.cfg) and check if the initial attach with UE complete successfully
- iv) If there is no problem with step i),ii),iii), pull out the sdr cards, plug in another sdr cards and repeat the step i), ii), iii)
- v) Identify all the sdr cards that is working OK.

Check if Multiple cards works
For SDR 50
If you have multiple sdr cards that is confirmed working at previous step, check if those cards works OK in multi sdr configuration.
Plug in two sdr cards in two PCI slots and connect Sync cable as shown below (

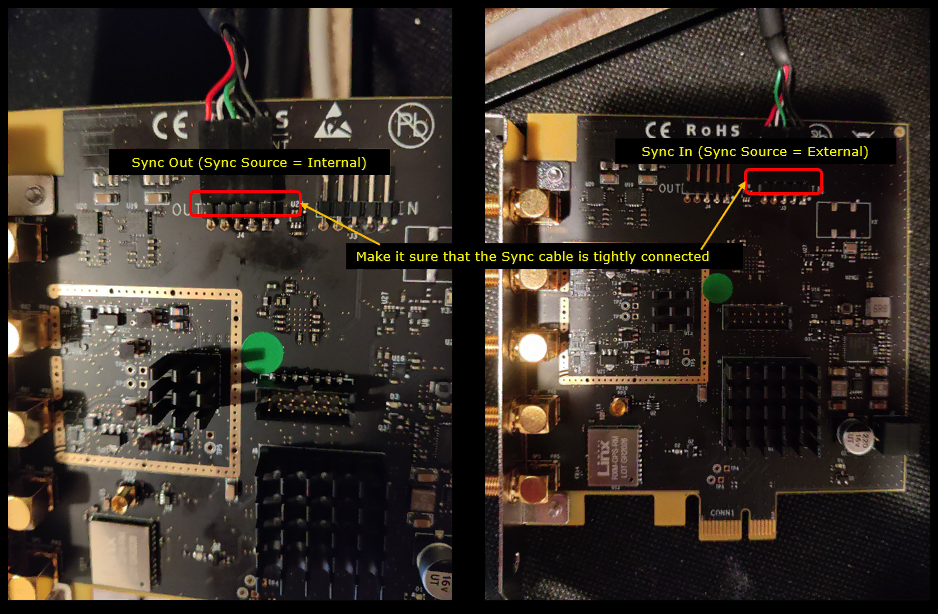
Make it sure that you get green LED lit on each of the cards.

Now check out if the sdr cards work with multi card configuration as follows :
- i) Perform Checkup #2
- ii) Perform Checkup #6
- iii) Run lte service with any two cell configuration (e.g, enb-2cell-ho.cfg) and check if the initial attach with UE complete successfully
For SDR 100
Even though each SDR card 100 can work independantly with it's own internal clock, one of them should work as Master and the others work as Slave when they are used in multi card setting (e.g, Carrier Aggregation, Handover etc). In this case, the first thing to do is to check the Clock cables are properly connected as shown below. (
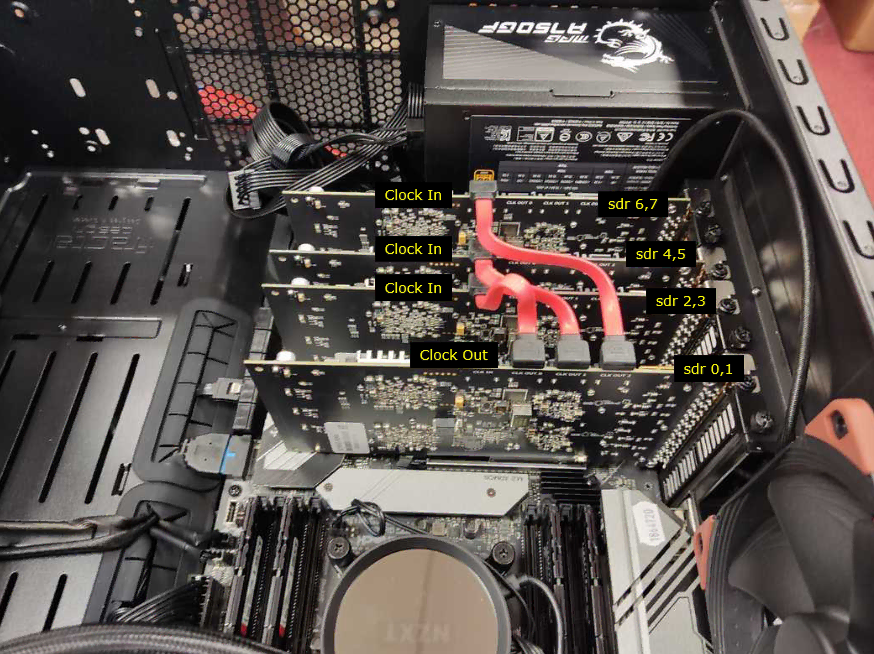
Now check out if the sdr cards work with multi card configuration as follows :
- i) Perform Checkup #2
- ii) Perform Checkup #6
- iii) Run lte service with any two cell configuration (e.g, enb-2cell-ho.cfg) and check if the initial attach with UE complete successfully
Additional Information
Max Power
the max power would vary depending on frequency, bandwidth and tx_gain. The measurement condition for the documentation is a little different between SDR 50 and SDR100. You need to refer to different document depending on the type of SDR card you are using.
- For SDR 100, refer to this document
- For SDR 50, refer to this document