Out of the Box Test - Command Line Commands
The purpose of this tutorial is to give you tips on how to best utilize the command line commands in Amari callbox / UE sim screen to operate the box or analyze / troubleshoot various issues. This tutorial assumes that you are already familiar with the basic operation of the callbox software (e.g, start/restart the service and launching the screen). If you are not familiar with this very basic operation, refer to this tutorial first. You don't have to read and memorize all the commands listed here. Just use this as a cheatsheet and check it out when you are not sure of which command you need to use and what is the syntax of the command.
Command Line Command is at the core of utilizing Amarisoft Product (both eNB/gNB and UEsim) and the more you know of those commands and the better you can use or troubleshoot the product. So the command line tool would be the first thing you need to learn from Day 1 and the thing you have to live forever with the Amarisoft Product. It may be a little bit intimidating to use the command line tool but we would get used to the power of the command line tool as you play more with it. There are a few categories of the operations you can do with the command line command as listed below.
- Getting the real time status and statistics : You can get various configuration information and statistics. I think this category is what you get the most familiar with. t , t spl, t cpu, tx_gain, rx_gain, rf_info , cell, cell_phy are the commands that belong to this category. These are the commands that I am personally using everytime when I use Amarisoft product.
- Changing Configuration : You can change the configuration while you are running the callbox (eNB/gNB) or UEsim. Most of the configurations are static and should be configured in *.cfg files for each components but there are some of the commands that can be changed dynamically via command line tool. tx_gain, rx_gain, log are some of the examples in this category. tx_gain, rx_gain would be the commands that you would use most frequently.
You can use the command line commands in a few different ways as listed below.
- In [screen] window : Probably you would use this way most of the time. run 'screen -x' and run the commands in the screen window as explained in this tutorial .
- Command line tool in WebGUI : Not so frequently used, but you may want to use this way if you likes to do more in WebGUI without switching back to Screen window. As shown here, you can run a command line window from WebGUI and run all the commands as you do in the [screen] window.
Table of Contents
- Out of the Box Test - Command Line Commands
Introduction
Amarisoft Callbox and UE Simulator are sophisticated test platforms designed for wireless network development, validation, and troubleshooting. At the heart of these products lies a powerful command line interface (CLI), which provides direct, granular control over both the base station (eNB/gNB) and UE simulation environments. The CLI exposes commands for real-time monitoring, dynamic configuration adjustments, and comprehensive diagnostics, enabling users to interact with the underlying software stack, radio hardware, and protocol layers. This flexibility is essential in the context of 4G LTE and 5G NR research, interoperability testing, and field troubleshooting, where rapid insight and control can dramatically accelerate development cycles. The CLI operates as a bridge between the user and the Amarisoft software architecture, interfacing with modular components such as protocol stacks, PHY/MAC layers, and radio frontends. Due to its central role, mastering the command line is fundamental for maximizing the effectiveness of Amarisoft products. Through targeted commands, users can query status, gather statistics, modify operational parameters, and investigate abnormal behaviors, making the CLI indispensable for both routine operation and advanced problem analysis. This tutorial focuses on practical usage patterns, best practices, and troubleshooting strategies related to the Amari Callbox/UEsim CLI, equipping users with the expertise necessary to fully leverage these tools in real-world scenarios.
-
Context and Overview
- Amarisoft Callbox and UE Simulator are used in wireless network R&D, providing a flexible software-defined environment for 4G/5G testing.
- The command line interface is the primary means to interact with the system's core components, offering immediate access to configuration, status, and diagnostic data.
- CLI usage spans a range of activities, from daily operation and configuration to deep troubleshooting and performance analysis.
-
Relevance and Importance
- Efficient use of CLI commands is crucial for rapid prototyping, debugging, and maintenance in both lab and field settings.
- Understanding CLI operations enables users to react promptly to network events, analyze protocol behaviors, and optimize system performance.
- The CLI is often required for tasks that cannot be performed through graphical interfaces, especially in headless or automated deployments.
-
Learning Outcomes
- Gain hands-on experience with essential CLI commands for monitoring system status, gathering real-time statistics, and modifying configurations.
- Develop troubleshooting skills by interpreting command outputs and identifying common issues in wireless network operation.
- Learn best practices for command line usage in both screen-based and WebGUI-integrated environments.
- Understand command categories and their application in everyday workflow and advanced scenarios.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge
- Familiarity with basic operation of Amarisoft Callbox/UEsim software (e.g., starting/restarting services, accessing screen sessions).
- General understanding of LTE/5G network architecture and protocol layers.
- Basic proficiency with Linux shell environments and command line interfaces.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial provides procedures and methodologies for using command line commands to test, monitor, and troubleshoot a cellular test setup involving eNB/gNB, MME/AMF, and UEsim components. The summary below outlines the key test and monitoring steps as described for each system element, focusing on the use of command line utilities and their intended diagnostic or configuration functions.
-
Test Setup
- Default configuration file used; no changes made for out-of-the-box testing.
- Standard SIM card provided with the system utilized.
- Configuration changes, if necessary, are referenced in a separate configuration guide.
-
(enb) Command Procedures
- help: Lists all available commands and descriptions to assist with operation navigation.
- t: Prints logs with UE and cell info, signal quality, data rate, and CRC errors for troubleshooting.
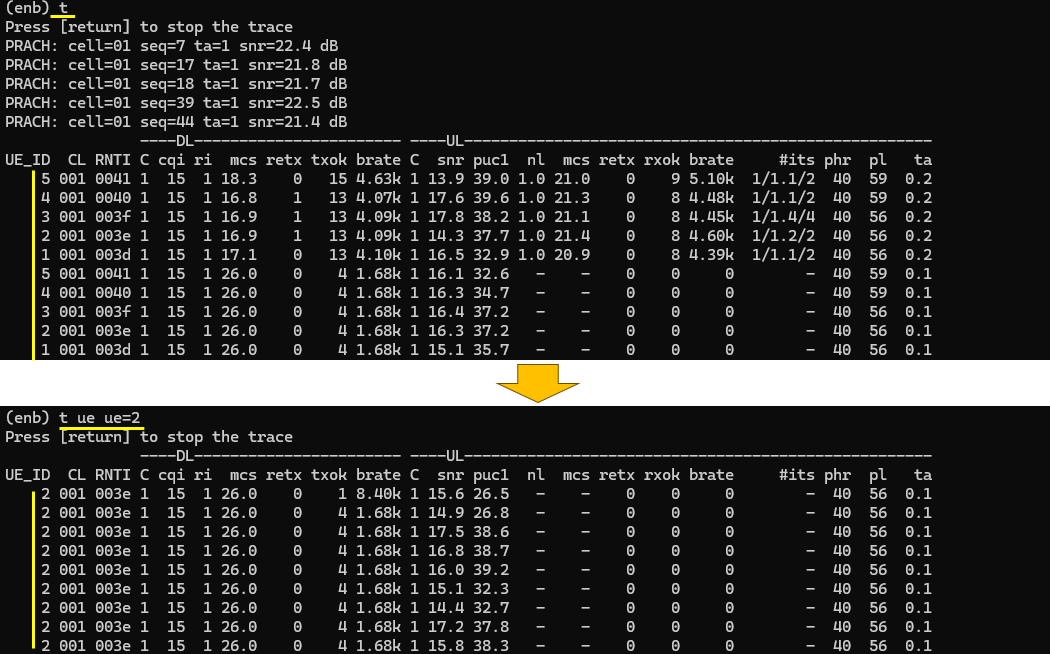
- t ue [interval] [UE_ID]: Similar to 't', but can filter logs by UE or set log print intervals for specific UEs.
- t cpu: Displays CPU utilization and real-time processing status; high values (>100%) indicate multicore usage.
- t g: Shows global statistics including some RRC/UE information.
- cell: Displays brief info about configured cells.
- cell phy: Shows PHY-layer details for cells.
- cell main: Provides info about the main cell; generally matches 'cell' command output.
- ue: Lists UEs currently in communication with the eNB/gNB (attached and not in idle).
- m2: Executes as shown for additional monitoring (details referenced in images).
- hwcaps: Summarizes the call box hardware capabilities.
- s1: Shows core (MME/AMF) connections for eNB, listing all configured servers.
- ng: Displays core (MME/AMF) connections for gNB; not populated in NSA configurations.
- rf_info: Provides status and information of SDR cards in use.
- t spl: Monitors per-port TX/RX power in dBFS; helps detect RX chain saturation (recommend reducing rx_gain if RX MAX is 0).
- t spl dbm: Like 't spl', but outputs power in dBm (converted from dBFS).
- rx_gain: Views or sets RX gain per port or channel; essential for resolving high BLER in the receive path. Can be specified globally or per channel.
- tx_gain: Views or sets TX gain for all or individual TX ports, useful for troubleshooting downlink BLER issues. Syntax varies for command line versus configuration file use.
- cell_gain: Adjusts cell power via software (callbox), not SDR chipset. Used for multi-cell SDR scenarios.
- handover: Triggers handover between cells; requires at least two cells configured and UE in connected mode.
- pcap: Starts and stops PCAP capture (LTE only). Used to log traffic for further analysis.
-
(mme) Command Procedures
- help: Lists all supported commands and descriptions for the current software version.
- ue: Lists UEs attached to the core network, even if in RRC idle, including assigned IPs.
- ng_ran: Lists all gNBs connected to the core network (AMF).
- enb: Lists all eNBs connected to the core network (MME).
-
(UEsim) Command Procedures
- help: Lists all available commands for UEsim control and monitoring.
- t: Prints trace logs with detailed UE status; columns defined in documentation. Includes indicators like RSRP, HARQ stats, CFO, SRO.
- cells: Lists all configured cells; missing PCI implies a cell is configured but not synchronized.
- t spl: Prints TX/RX power per TRX port in dBFS; RX MAX value of 0 indicates saturation, suggesting to reduce rx_gain. Also monitors DAC saturation events via the 'SAT' column.
-
For high TX power or nonzero SAT count:
- Enable power_control_enabled
- Adjust tx_gain_offset
- t spl dbm: Outputs TX/RX power in dBm for each TRX port.
- ue: Lists status for each UE, indicating RRC and EMM state.
- t cpu: Monitors CPU utilization and real-time processing (values >100% indicate multicore operation).
The tutorial focuses on utilizing command line interfaces for configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting of different network functions. It emphasizes step-by-step procedures for each command, their intended outputs, and practical considerations for interpreting results or resolving common issues.
Test Setup
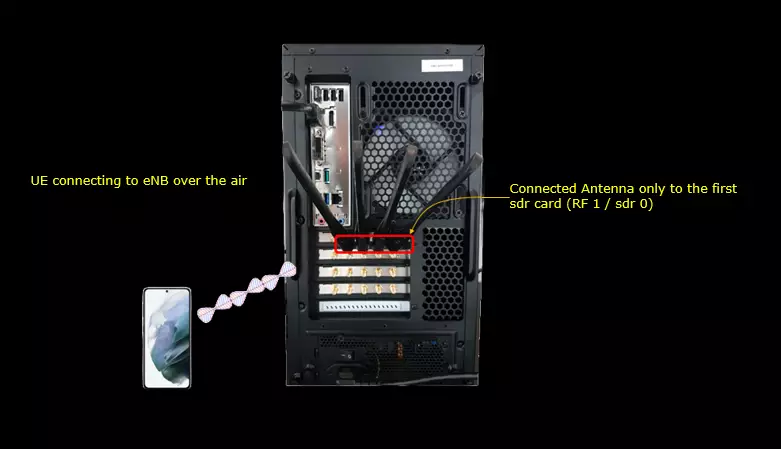
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below. (NOTE : Basically it doesn't matter with exact hardware setup to utilize the Command Line Commands. You can use the information in this page for any test setup you are using)
- Since this test is for Out of the box testing, I used the default configuration(cfg) file without changing anything in it
- SIM Card used in this tutorial is the one delivered with the system as it is.
- If you want to change the configuration, The tutorial Information_Config_Guide.pdf would help

(enb) commands
In this section, I will show some examples of command line commands used in (enb) mode.
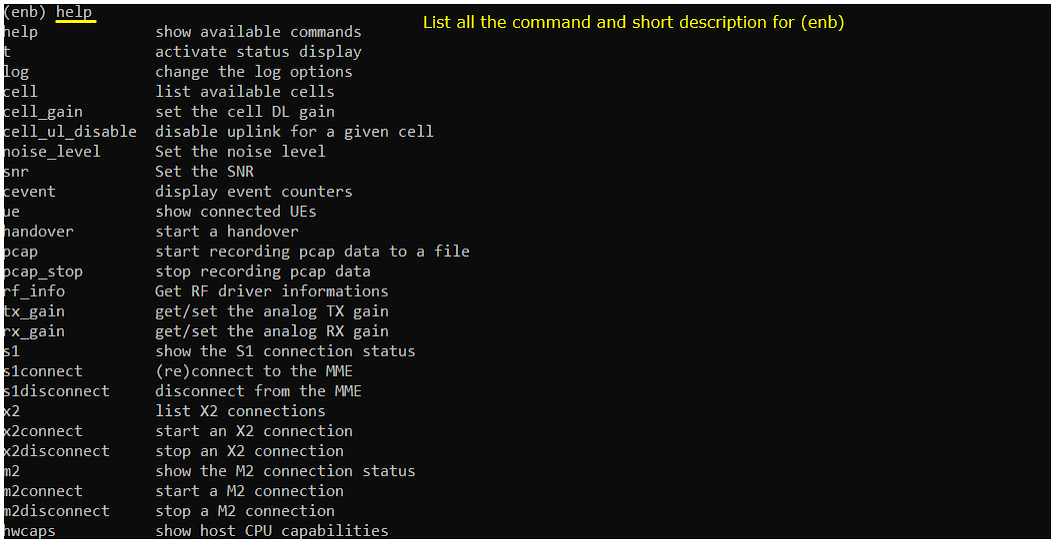
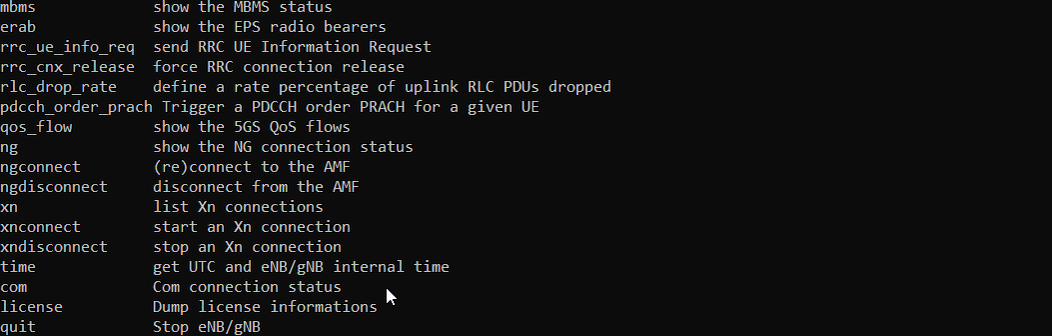
help
this command list all the commands you can use and short descriptions about the command.
t
't' means 'trace'. it print out logs showing ue and cell information, signal quality, data rate, crc error etc. this is the most commonly used command and you can do a lot of troubleshooting just with this command.
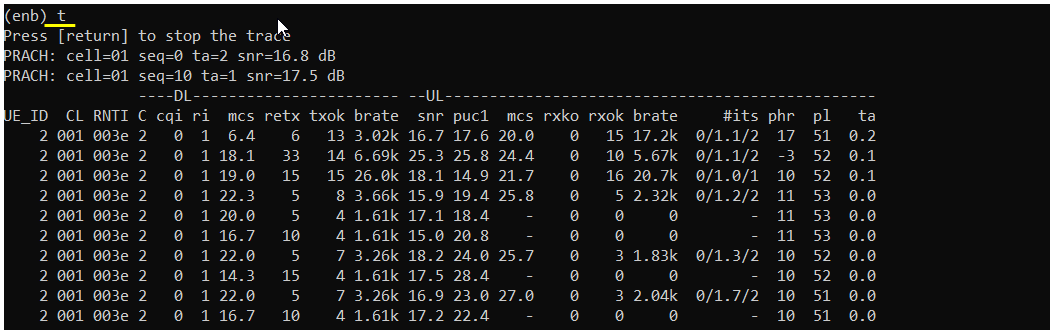
You can use the result of this command and do various troubleshoot as shown below.
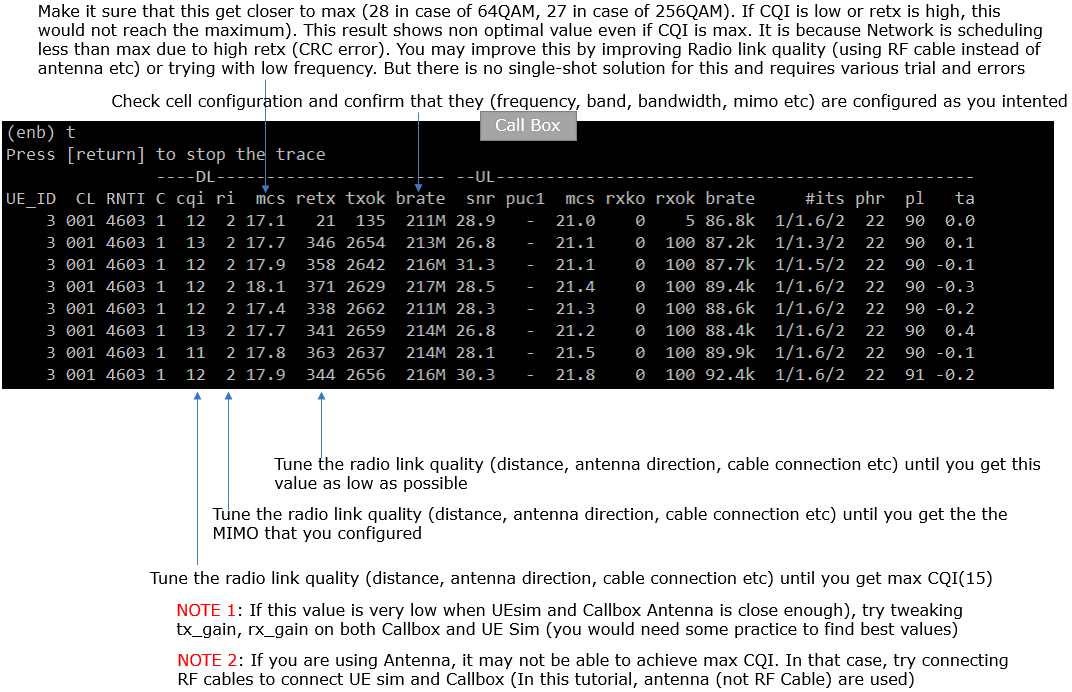
t ue
this is a variation of 't' command shown above. Unless you specify a specific UE ID, the result of this command would be similar to 't'
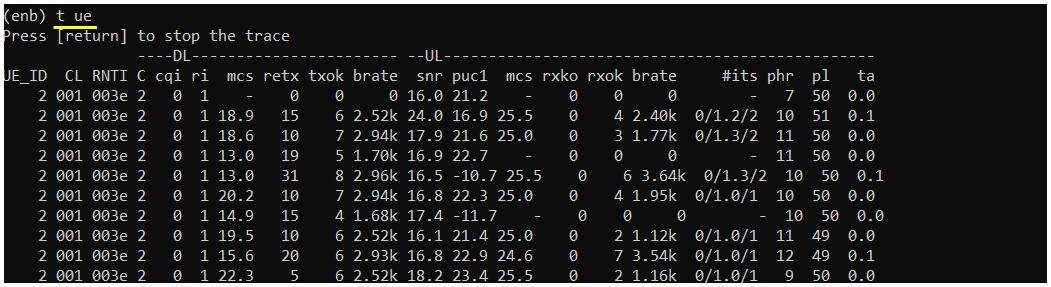
: you can control trace log print interval by specifying the interval (in sec) after t ue command as shown below. 't ue 2' mean update the log for all UEs at every 2 seconds
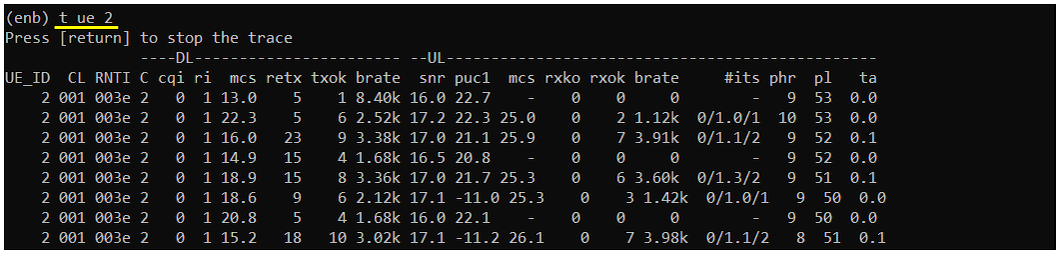
: If you specific UE_ID, you can print the log only for the UE that you specified. This can be useful for the case where multiple UEs are connected and you want to print out the log for a specific UE that you are interested.'
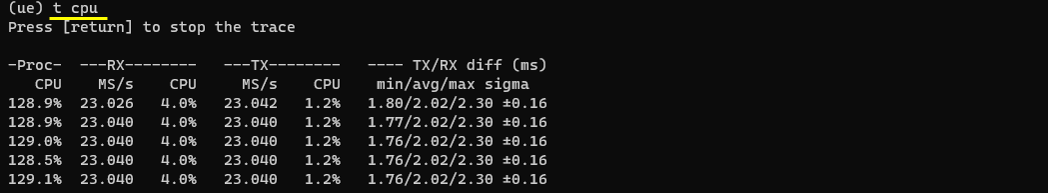
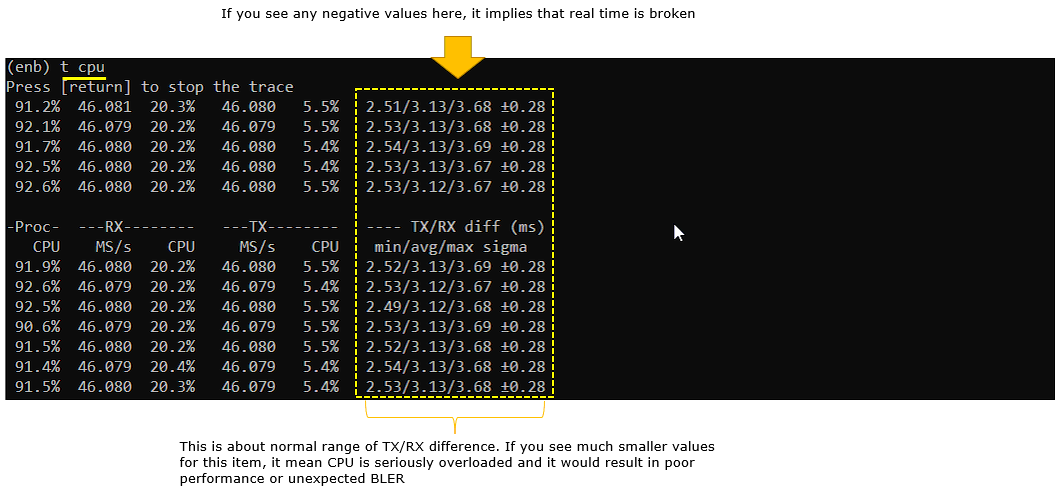
t cpu
This is a good indicator showing the CPU utilization and real-time processing status. (NOTE : sometimes you would see CPU utilization goes above 100%. Even if it goes over 100%, it is completely normal. It just indicates that more than one CPU is being used. For example, if it is 210%, it mean 3 CPU cores are being used)
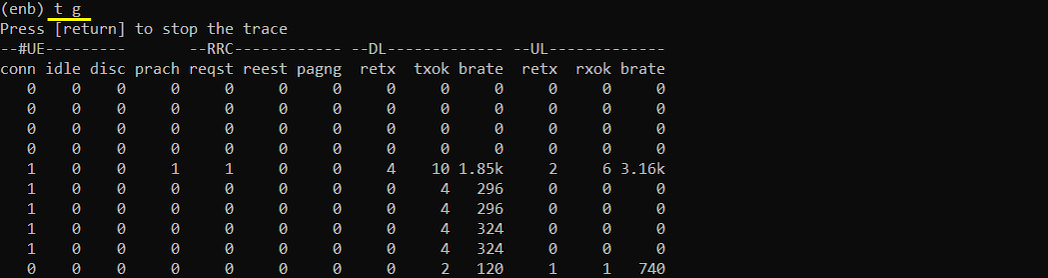
t g
This shows a list of general statistics (global statistics) as shown below. It carries some information like 't' command and some additional information like RRC / UE information.
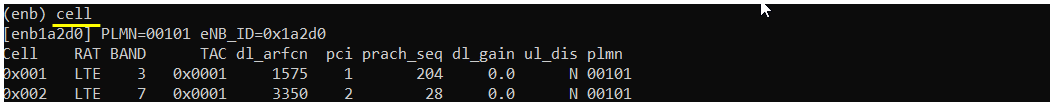
cell
this commands show you the brief information about the cells that are configured.
cell phy
This an variation of 'cell' command and it give more of phy related information.

cell main
This command shows the cell information about the main cell. In most case, this shows the same result as cell;

ue
This shows the list of UEs that is in communication with eNB/gNB. If UE is not attached or attached but in RRC idle state, you would not see the UE here.

m2

hwcaps
This shows the brief information of hardware capabilities of the call box

s1
This command shows that the list of core (mme or amf) that the eNB connected to. In most case you would see only one servers shown here but if you configure the eNB to multiple mme, you will get multiple items as the result of this command.

ng
This command shows that the list of core (mme or amf) that the gNB connected to. In most case you would see only one servers shown here but if you configure the gNB to multiple mme, you will get multiple items as the result of this command.
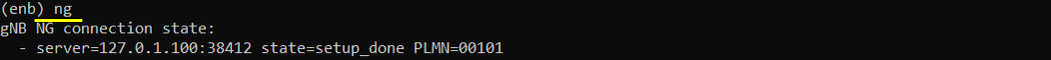
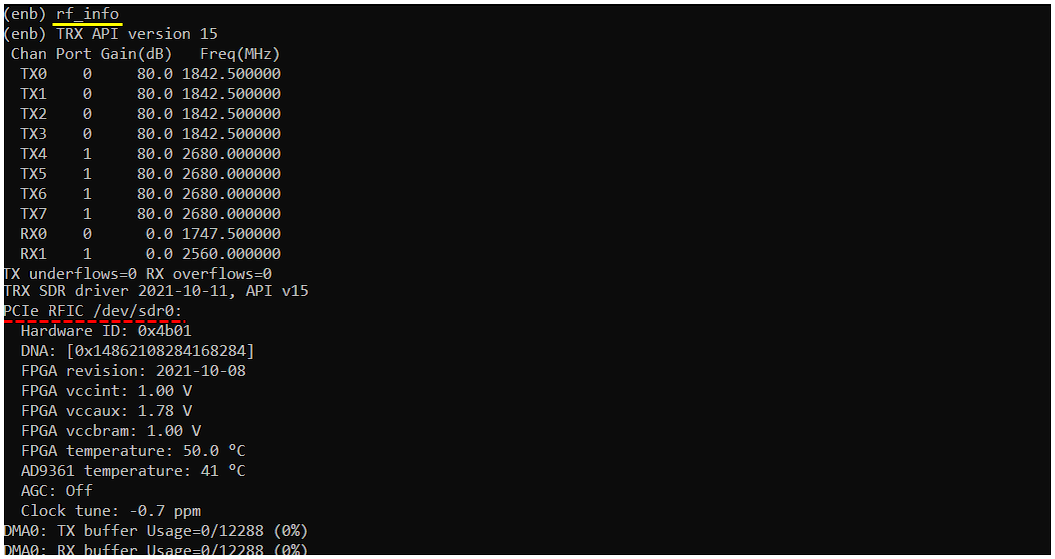
rf_info
this command shows you about the information / status of the sdr cards that are being used.
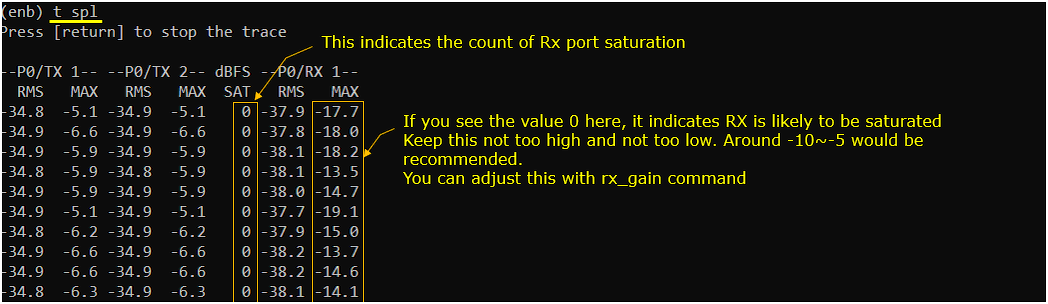
t spl
this command shows you the power related information for each and every Tx/Rx port. This is also one of the most frequently used commands. If you see 0 in RX MAX power, it indicates the RX chain is saturated and it may lead to high BLER for the received physical channel. In this case, it is recommended to tweak rx_gain to get the RX MAX to go below 0. (
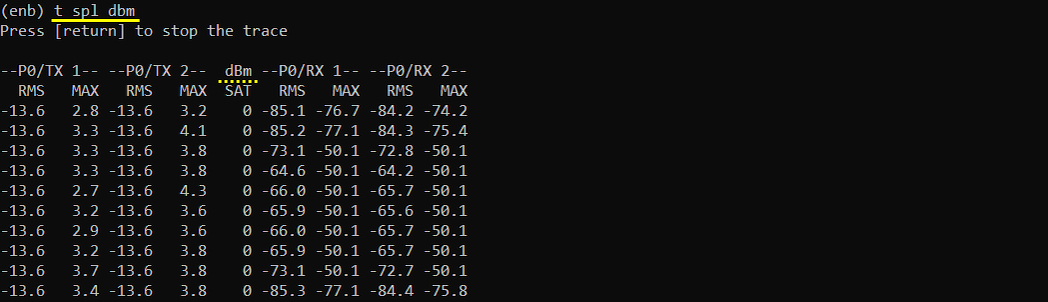
t spl dbm
The role / meaning of this command is exactly same as 't spl' command shown above, the only difference is the unit of the power value. This command shows the power in the unit of dBm. (
rx_gain
This command is used to view or set rx_gain. this is the most commonly used command for troubleshooting high BLER issues for the received physical channel.
If you use rx_gain without parameter, it views (prints) the current settings of rx_gain for each RX ports.

If you use rx_gain with the value, it changes the gains of all RX ports.

If you want to change rx_gain for multiple channels, you can change the gain for all channels simultaneously or separately as shown below.
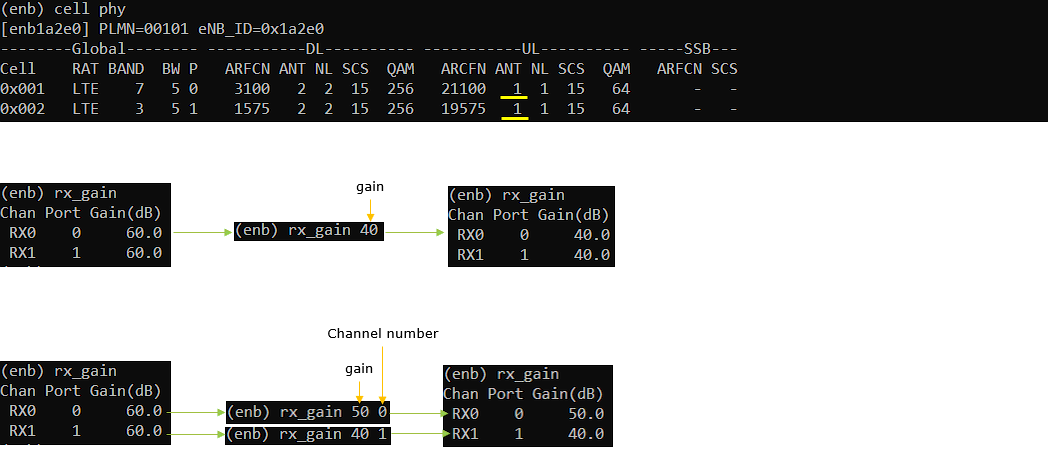
In case of command line
Specify in the form of 'rx_gain [gain] [channel' (Example, rx_gain 40, 0 ==> set rx gain 40 to the first channel/first antenna, rx_gain 40, 1 ==> set rx gain 40 to the second channel/second antenna)
For 4 cells with 1 UL antenna and 2 DL antenna as an example
rx_gain : [Cell0Ant1, Cell1Ant1, Cell2Ant1, Cell3Ant1]
tx_gain : [Cell0Ant1, Cell0Ant2, Cell1Ant1, Cell1Ant2, Cell2Ant1, Cell2Ant2, Cell3Ant1, Cell3Ant2]
tx_gain
this is used to view or print the gain (tx power) of all the tx ports being used. This would impact decoding performance on UE. If you see high BLER (high retransmission) for downlink data, usually we try tweaking this value for troubleshoot.
: If you use tx_gain without additional parameter, it prints out the gain of all the TX ports being used.

: if you use tx_gain with the value, it changes the gains of all TX ports.

If you want to change tx_gain for multiple channels, you can change the gain for all channels simultaneously or separately as shown below.
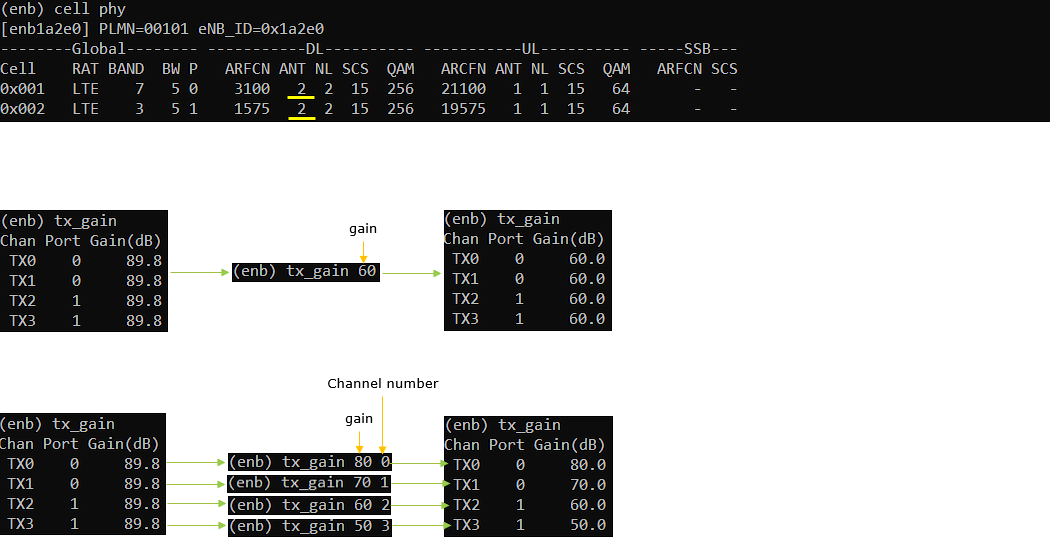
In case of command line
Specify in the form of 'tx_gain [gain] [channel' (Example, tx_gain 40, 0 ==> set tx gain 40 to the first channel/first antenna, tx_gain 40, 1 ==> set tx gain 40 to the second channel/second antenna)
For 4 cells with 1 UL antenna and 2 DL antenna as an example
rx_gain : [Cell0Ant1, Cell1Ant1, Cell2Ant1, Cell3Ant1]
tx_gain : [Cell0Ant1, Cell0Ant2, Cell1Ant1, Cell1Ant2, Cell2Ant1, Cell2Ant2, Cell3Ant1, Cell3Ant2]
cell_gain
Change the gain of a specified cell. This is done by callbox software, not by the sdr card.
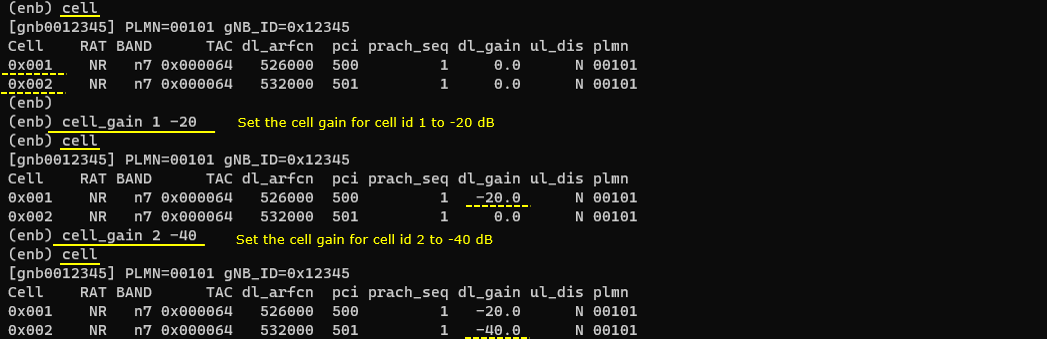
- tx_gain change tx power by Analog Device Chipset, but cell_gain change cell power by callbox software
- tx_gain changes broadcasting cell reference power in SIB message (check this out on how cell reference power works)
handover
Trigger handover. There should be at least two cells configured and UE should be in connected mode before running this command.
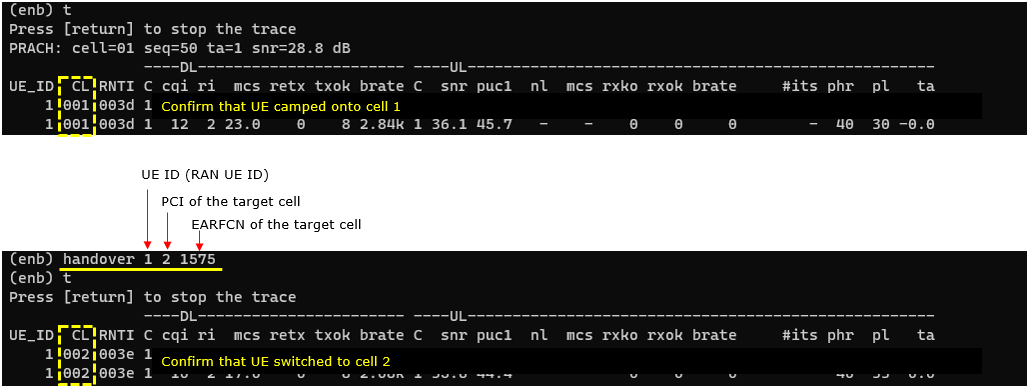
pcap
Start Capturing a Pcap file (

Stop Capturing

Confirm that the file is properly stored

(mme) commands
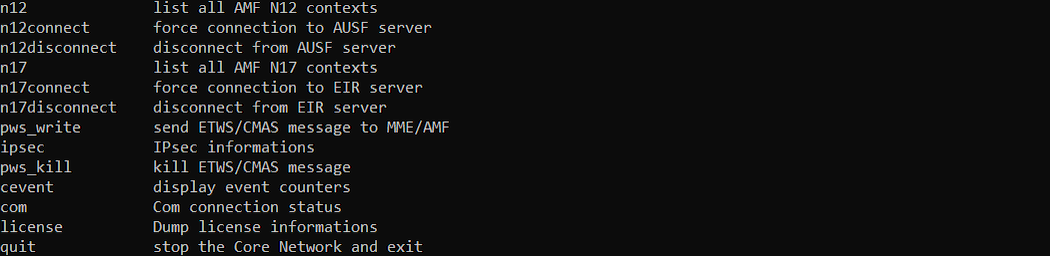
help
This will give you the list of all the commands and short descriptions that you can use in (mme). (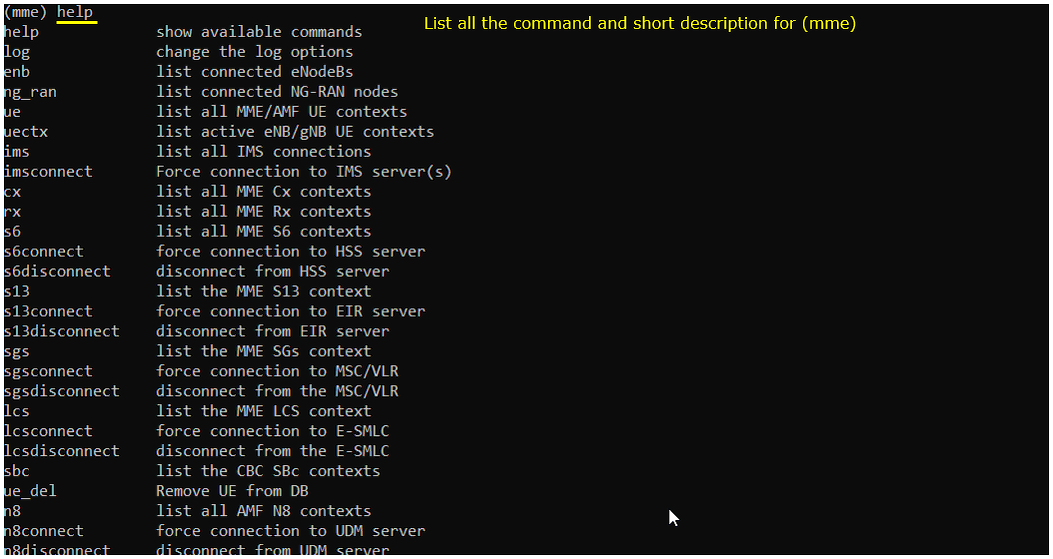
ue
: This will give you the list of UEs that are connected to core network. Even when UE gets in Idle mode in RRC, this would still show you the UE that completed the initial attach. This may be the most commonly used command in (mme) because you would want to check the IP assigned to the UE.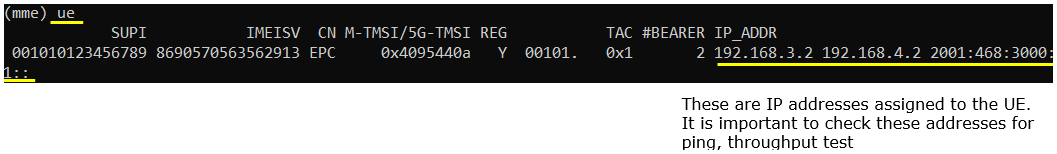
ng_ran
: this will give you the list of gNB that are connected to core network(AMF).

enb
: this will give you the list of eNB that are connected to core network(MME).

(UEsim) commands
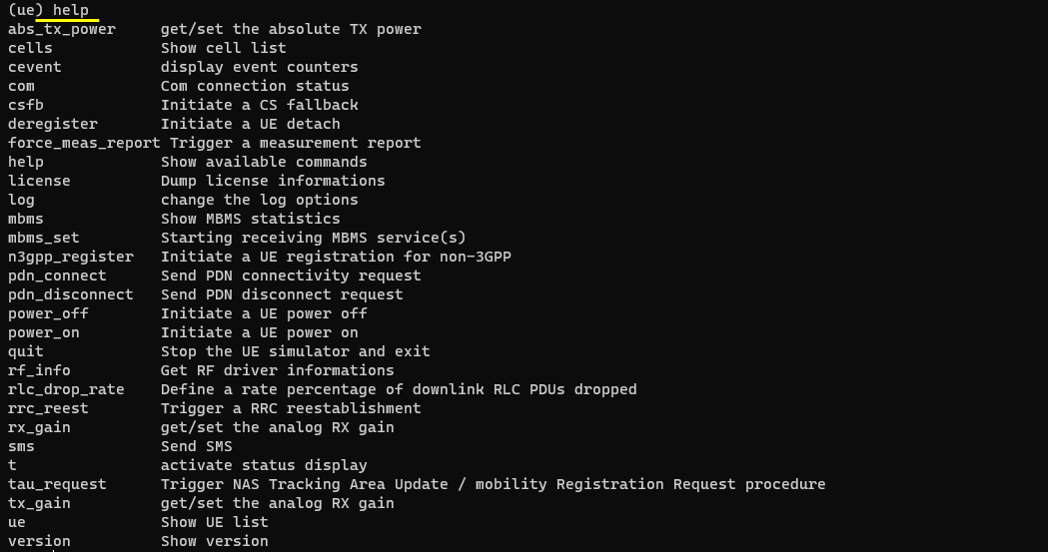
help
list all the commands available.
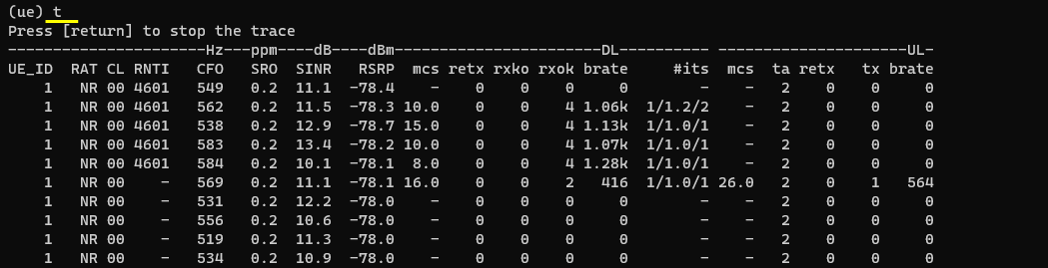
t
prints trace log.
Meaning of each column is described in UEsim doc. (
cells
list all the configured cells. If PCI is missing in the print, it mean that the cell is configured but not detected (i.e, not synched)

t spl
print TX/RX power for each TRX port in dBFS scale. The important part is RX MAX value. If you see 0 for any of the RX MAX column, it mean that the RX port got saturated. I would suggest you to reduce rx_gain value until you get the value around -5 ~ -10.

The sat column counts the number of times the UE simulator had to limit the TX power of an uplink signal (e.g. PUCCH or PUSCH) so that it does not give a saturated output on the DAC. These saturations do not degrade the signal as the saturation at the sample level (see t spl monitor command) but they indicate that the UE received power at the eNodeB will be lower than expected by the channel simulator.
- enable power_control_enabled
- set tx_gain_offset
t spl dbm
print TX/RX power for each TRX port in dbm.

ue
lists status of every configured UEs. RRC STATE indicates the status with RAN(i.e, eNB / gNB) and EMM_STATE indicates the status with corenetwork.

t cpu
This is a good indicator showing the CPU utilization and real-time processing status. (NOTE : sometimes you would see CPU utilization goes above 100%. Even if it goes over 100%, it is completely normal. It just indicates that more than one CPU is being used. For example, if it is 210%, it mean 3 CPU cores are being used)