eSIM
This tutorial shows how to use eSIM for the test with Amarisoft Callbox. The concept of eSIM has been there long time, but we start seeing the wide scale adoption of it relatively recently. With this wide employment of the technology, Amarisoft evaluated the technology and proved working.
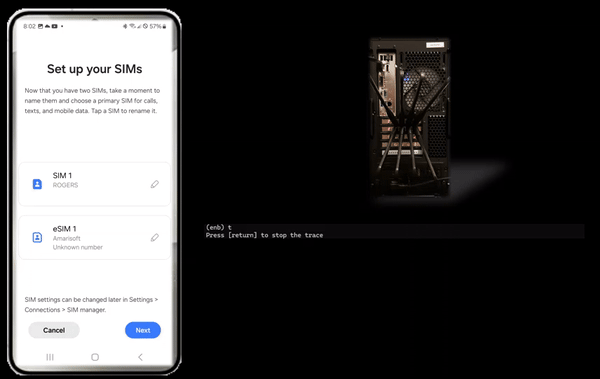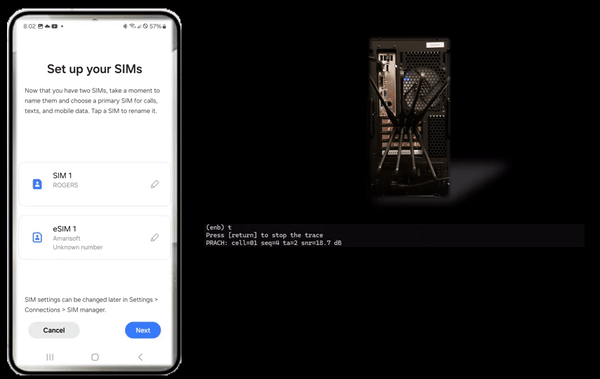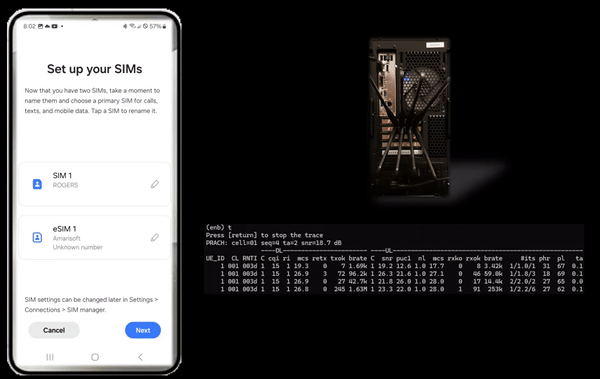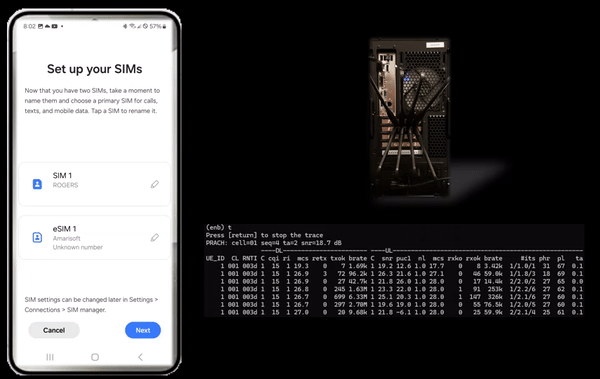
Table of Contents
Introduction
Embedded SIM (eSIM) technology represents a significant evolution in mobile device connectivity, providing a programmable, rewritable alternative to traditional removable SIM cards. eSIMs are hardware components soldered directly onto a device's motherboard, allowing users to download and manage multiple carrier profiles over-the-air without the need for physical card swaps. This advancement facilitates seamless carrier switching, improved device design, and enhanced security, making eSIM an essential component for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, smartphones, wearables, and industrial applications. In the broader telecommunications ecosystem, eSIM adoption streamlines subscriber management, reduces logistical overhead, and enables new business models for network operators and device manufacturers. The Amarisoft Callbox, a comprehensive LTE/5G test platform, enables engineers and researchers to test, evaluate, and validate eSIM workflows in controlled environments. Although eSIM functionality is managed entirely on the User Equipment (UE) at the application level and does not directly interact with 3GPP authentication algorithms or core network processes, understanding how to utilize eSIMs in conjunction with the Amarisoft Callbox is crucial for validating device compliance and ensuring robust interoperability in modern networks.
-
Context of eSIM and Amarisoft Callbox
- eSIM technology provides a digital, embedded alternative to traditional SIM cards, enabling remote provisioning and management of mobile network profiles.
- Amarisoft Callbox is an advanced test platform for LTE and 5G networks, widely used for device validation, protocol analysis, and interoperability testing.
- With the proliferation of eSIM-capable devices, integrating and testing eSIM workflows is increasingly important in network development and device certification processes.
-
Relevance and Importance of This Tutorial
- Demonstrates practical steps to leverage eSIM technology for testing using the Amarisoft Callbox environment.
- Clarifies key distinctions: eSIM is managed on the device (UE) at the application layer and does not require modifications or special handling on the Amarisoft side or within 3GPP authentication workflows.
- Empowers engineers, researchers, and testers to efficiently evaluate eSIM-enabled devices and ensure seamless network integration.
-
What Learners Will Gain
- Understanding of eSIM architecture, provisioning mechanisms, and workflow integration with Amarisoft Callbox.
- Step-by-step guidance for configuring and conducting eSIM-based tests in a controlled lab environment.
- Insight into best practices for troubleshooting and validating eSIM functionality on the UE side.
- Awareness of available resources, application notes, and avenues for acquiring test eSIMs.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge and Skills
- Familiarity with LTE/5G network concepts and architecture.
- Basic understanding of SIM and eSIM technologies, including provisioning and profile management.
- Experience with Amarisoft Callbox or similar cellular test platforms is beneficial.
- General competence in device configuration and network testing procedures.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial details the procedures for performing out-of-the-box eSIM testing on a UE (User Equipment) using Amarisoft Callbox, focusing on both LTE and NR/NSA connectivity. The test process involves the following key steps:
-
Test Setup:
- Use a single cell LTE and single cell NR/NSA configuration as provided by the default installation packages (enb.default.cfg for LTE, gnb-nsa.cfg for NR/NSA).
- eSIM used is the one delivered with the system, without modifications.
- No specific requirements for callbox configuration, except ensuring correct USIM parameter settings for the eSIM profile.
-
eSIM Configuration and Installation:
- Ensure the UE supports eSIM functionality (example device: Samsung Galaxy 24).
- Install the eSIM profile on the UE by navigating to ‘Settings’ > ‘Connection’ > ‘SIM manager’ > ‘Add eSIM’.
- Use the QR code method for eSIM installation (as supported by the test device).
- Select the primary SIM after installation and manage SIM activation as required.
-
APN Setting:
- Configure APN(s) for IP traffic functionality. At minimum, set up the ‘default’ APN; recommended to add 'default', 'internet', and 'ims' for comprehensive IP testing.
-
LTE Test Procedure:
- Use the enb.default.cfg file for basic LTE cell configuration (example: LTE Band 7, 5MHz bandwidth, PLMN 00101).
- Power on the UE with the installed eSIM and confirm successful initial attach and data traffic using the provided logs.
-
NR/NSA Test Procedure:
- Use the gnb-nsa.cfg file for NR/NSA testing (example: LTE band 1, 20MHz; NR n78, 40MHz bandwidth; PLMN 00101).
- Power on the UE with the installed eSIM and confirm initial attach and data traffic for NR/NSA mode.
- Note: In this specific test, NR/SA was not supported by the test device with a test SIM.
-
IP Traffic Test:
- Verify IP traffic capability (e.g., browsing, YouTube, iperf) after APN configuration to ensure data services are operational over eSIM.
-
Log Collection:
- Logs are collected for both LTE and NR/NSA attach procedures to demonstrate successful test execution. Detailed log analysis is outside the scope of this tutorial.
The overall methodology emphasizes using default configurations for both the callbox and eSIM, with primary attention to eSIM profile installation and minimal APN setup to validate network registration and data connectivity for LTE and NR/NSA modes.
Test Setup
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below. Since eSIM is just a UE side feature, it doesn't matter much with what type of test setup to be used. In this tutorial, I used the setup shown here because I wanted to test at least about single cell LTE and single cell NR/NSA.
- Since this test is for Out of the box testing, I used the default nsa configuration(gnb-nsa.cfg) file without changing anything in it
- SIM Card used in this tutorial is the one delivered with the system as it is.
- If you want to change the configuration, The tutorial Configuration Guide would help
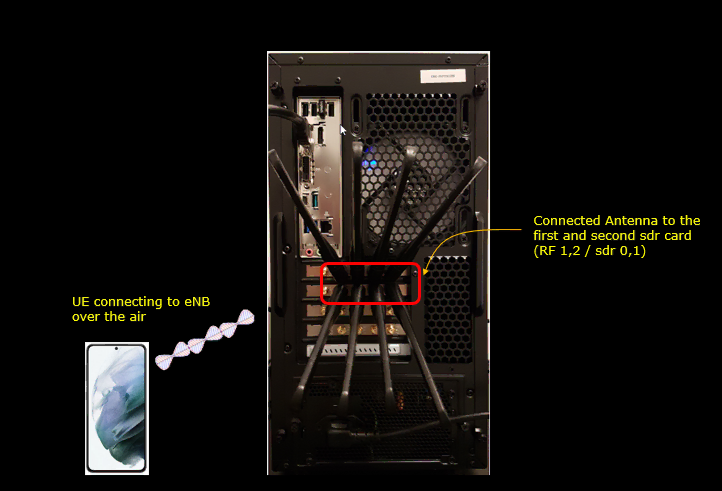
Configuration
In this application, you don't need to care much about callbox configuration. You can use whatever configuration that you want to use. The only point you need to pay attention to is about SIM parameter setting because eSIM by definition is all about SIM parameter. Most part of the configuration you need to care about is how to install an eSIM profile on your UE(phone).
Callbox
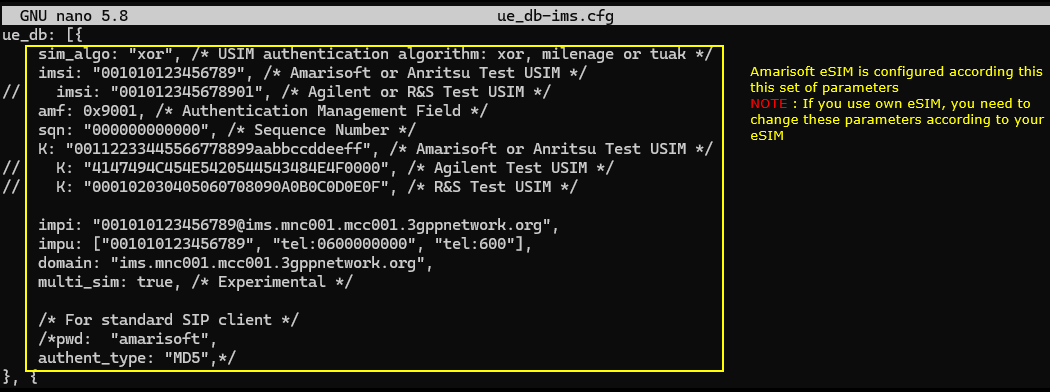
As mentioned above, the only configuration that you need to consider in relation to eSIM is the USIM parameters. The USIM parameter is configured in Callbox by default is ue_db-ims.cfg which are located in /root/mme/config directory.

If you use Amarisoft eSIM, you don't have to change anything because it is configured to match Amarisoft default configuration. If you are using an eSIM from other sources, you need to know all the SIM parameters and configure those parameters in ue_db configuration file.
UE(Mobile phone)
Installation of eSIM on UE(mobile phone) would vary depending on each specific UE model and some phone (mostly old model) would not support eSIM at all. So the first thing you need to check is to figure out whether your UE support eSIM or not.
eSIM Setting
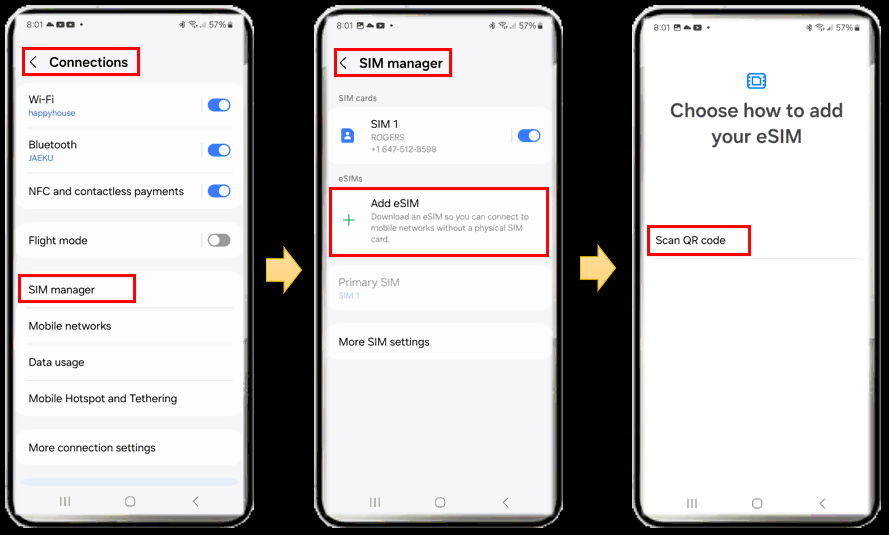
First go to 'Settings' tool and get to 'Connection'. And then select 'SIM manager' and hit 'Add eSIM'. There can be multiple ways of adding eSIM (e.g, QR code, LPA string etc), but SamSung g24 support QR code only. So just hit 'Scan QR code'.
If you purchase an eSIM, the eSIM will be delivered in the form of a document with a QR code. Scan the QR code in Camera App and add it to your phone.
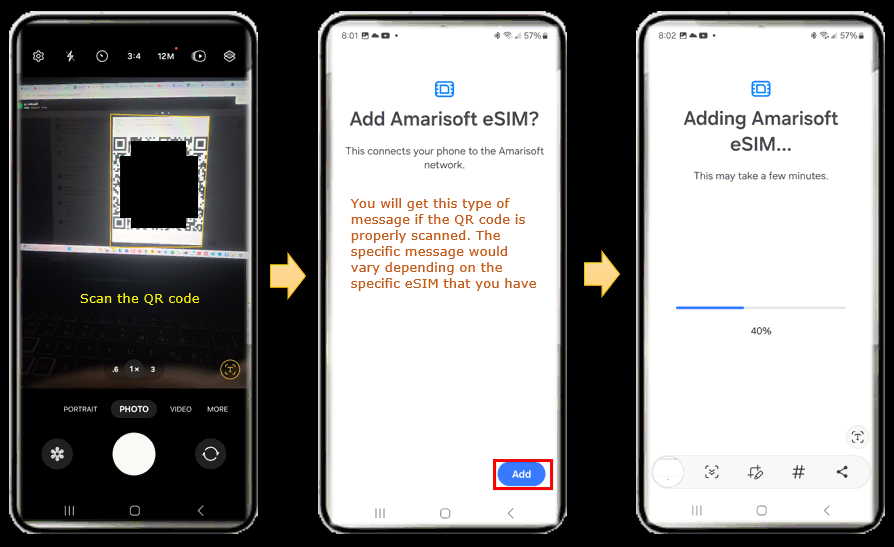
Once the installation is done, select which SIM is used as Primary SIM
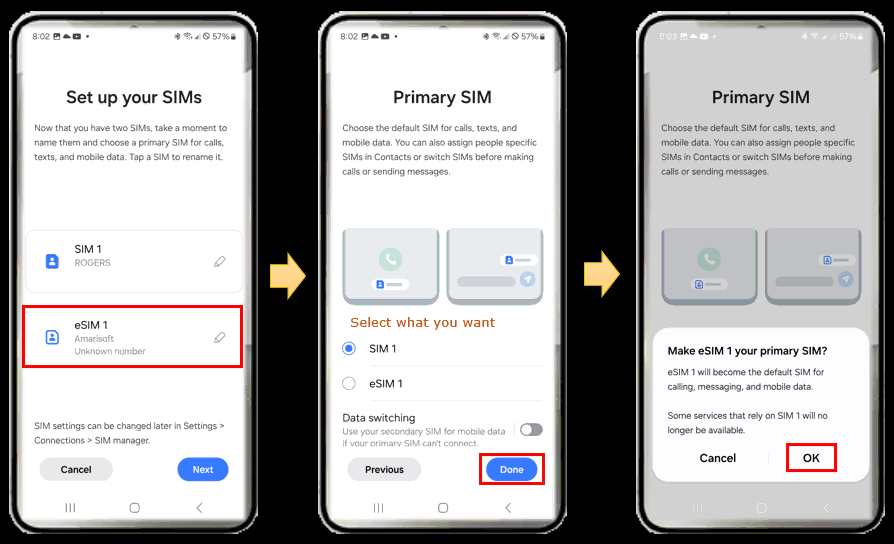
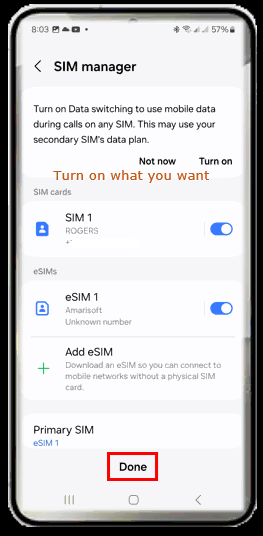
Then you can turn ON or OFF the SIM you want. You can turn on all SIMs or turn off all of them or turn on only specific SIM that you want.
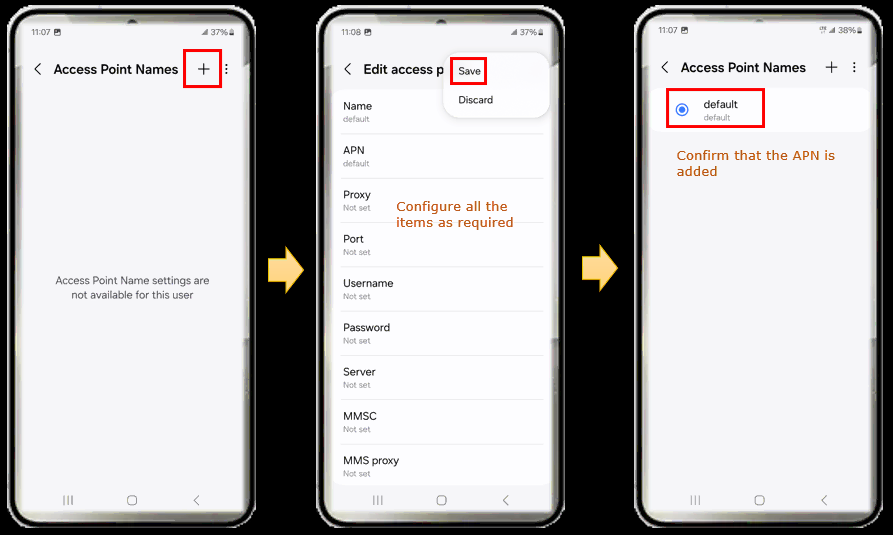
APN Setting
APN setting is not directly associated with eSIM configuration, but proper APN setting would be required to make the UE work with IP traffic (e.g, browsing, YouTube etc). I added 'default' APN to make the Amarisoft eSIM for IP traffic as a minimum setting. But it would be good to have three basic APNs (default, internet,ims) to cover most of the IP related test.
Perform the test
As I keep saying, eSIM is just about USIM and it get involved only in authentication processes. So you can test it with any test that perform initial registration procedure. In this tutorial, I tested with one basic LTE and one basic NR/NSA.
LTE
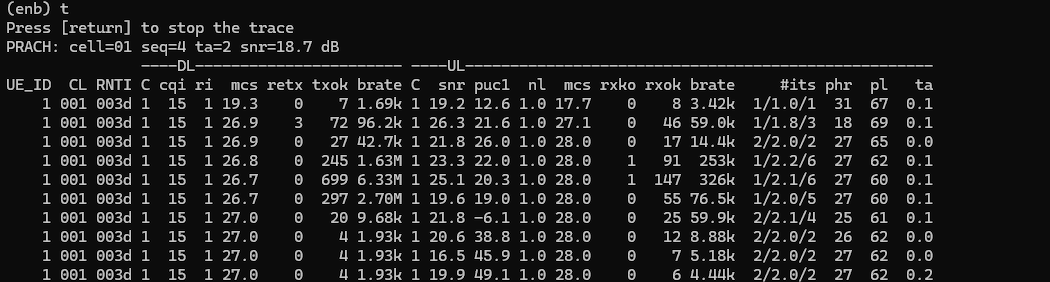
For LTE, I just tested with the most basic configuration provided by installation package, which is enb.default.cfg (
The cell configuration is as shown below (LTE Band 7 and 5Mhz channel bandwidth, PLMN 00101)
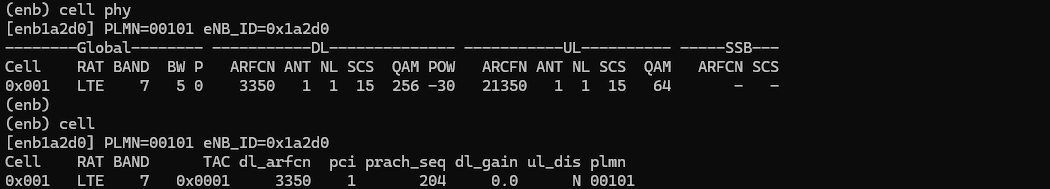
Then I turned on Radio with eSIM that I installed and confirmed the initial attach and data traffic as shown below.
NR/NSA
For NR, I used the most basic NR/NSA test configuration that comes with installation package. It is gnb-nsa.cfg (
Cell configuration is as shown below (LTE band 1, 20Mhz Bandwidth and PLMN 00101, NR n78 and 40Mhz Bandwidth).
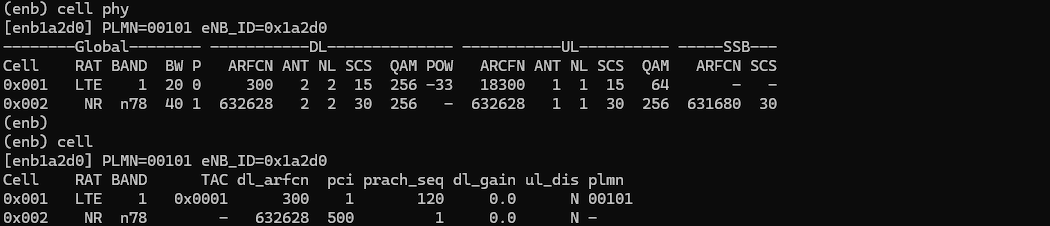
Then I turned on Radio with eSIM that I installed and confirmed the initial attach and data traffic as shown below.
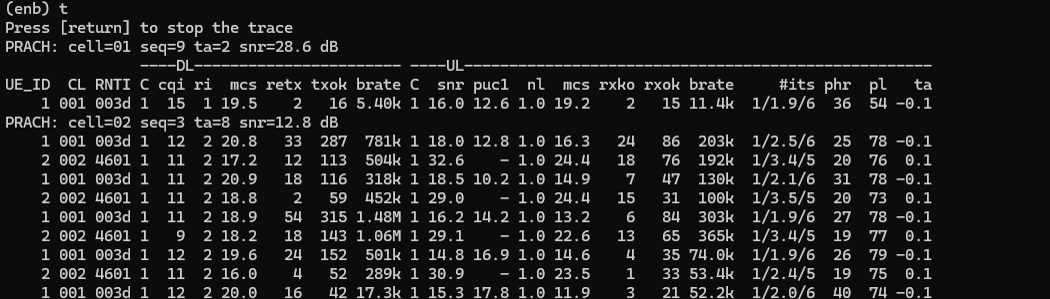
IP Traffic
This is not strictly associated with eSIM feature, it is more about APN setting. Try IP traffic (e.g, Browsing/ YouTube or iperf etc). In this tutorial, I tried YouTube (
Log Analysis
Detailed Log analysis is not the purpose of this tutorial because the log itself is very basic and the analysis was done in other tutorial. I am just providing the log that I collected from the eSIM test just as a proof that eSIM worked as expected.
LTE
A LTE test log is shared as below. For the analysis, refer to this.
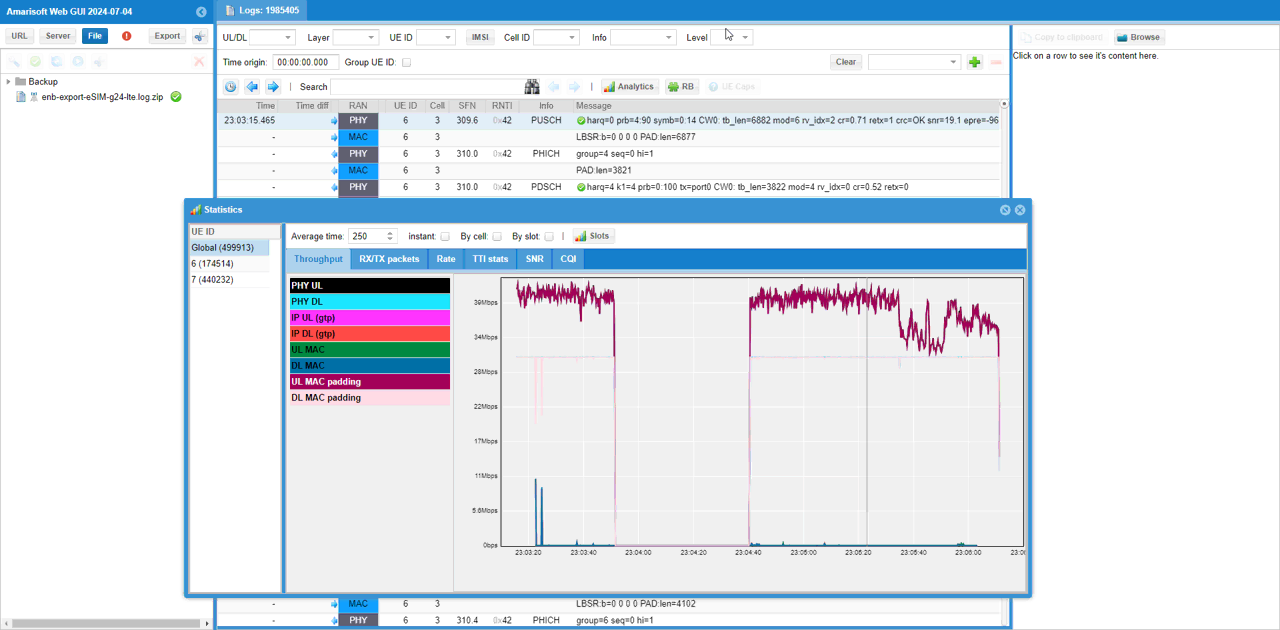
NR/NSA
A NR test log is shared as below. For the analysis, refer to this.
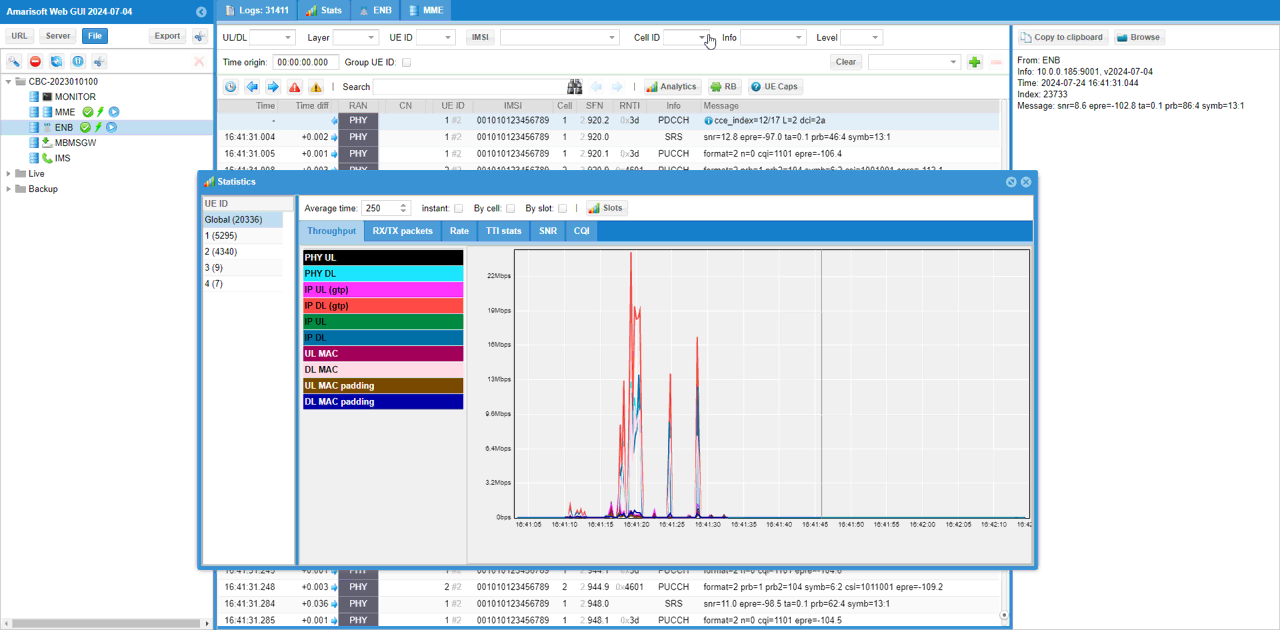
FAQ
Q1 : How many different eSIM profile we can purchase from Amarisoft ?
A1 : As of now, Amarisoft sells only one eSIM profile as described here. Currently we don't have any immediate plan to extend this.
Q2 : When we(the end user) wants to change eSIM profile that we purchased, does need to provide new QR code (automatic profile update not possible) ?
A2 : Since Amarisoft seels only one eSIM profile, the exact method for profile change is not investigated yet (Just issuing new QR code would be the simplest way, but automatic update may be possible as well depending on the technical support of eSIM provider)
Q3 : Does Amarisoft run the eSIM server (SM-DP + Server) ?
Q3 : No, the server is not Amarisoft product (i.e, Amarisoft is not running the server), Amarisoft partners with a third party service provider for the server and Amarisoft just provide one specific eSIM profile that is provided by the provider.