Out of the Box Test - NR SA
The purpose of this tutorial is to show you how to establish NR SA connectionbetween a UE and Amari Callbox. It is assumed that you don't have any previous experience with Amari callbox.
SA stands for "Stand Alone". "Stand Alone" in NR SA implies two things as below
- It support NR without any help of other technology (e.g, LTE)
- It supports NR Core Network and NR RAN directly connected to NR Core network.
According to NR deployment options described in RP-161266, NR SA corresponds to Option 2) as highlighted in green box below (
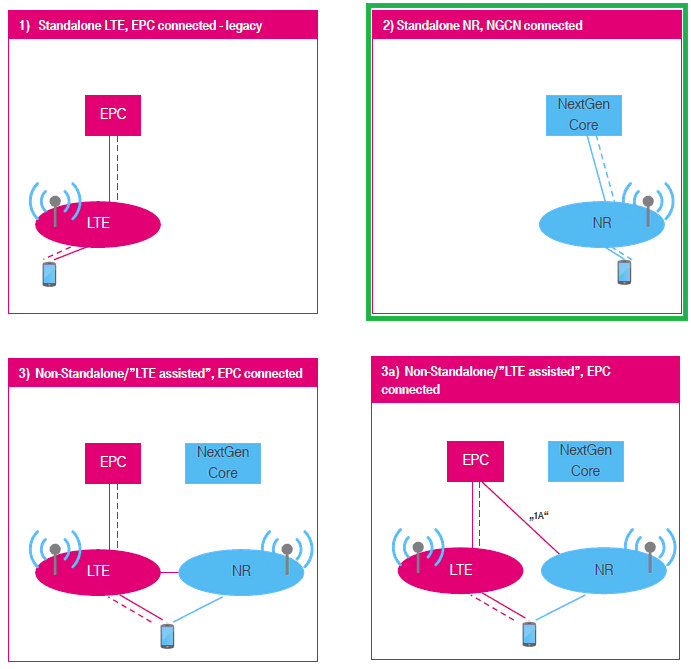
In terms of the frequency and bands, Amarisoft Callbox (gNB) support all the frequencies and bands that are specified in 3GPP. In terms of bandwidth, Amarisoft Callbox (gNB) support any 3gpp defined band upto 100Mhz per component carrieras of now.
Table of Contents
- Out of the Box Test - NR SA
- Introduction
- Summary of the Tutorial
- Test Setup
- Key Configuration Parameters
- Configuration
- Check if LTE service is Running
- Perform the Test
- Log Analysis
- RRC / NAS Signaling
- SIB1
- RrcSetup
- Registration Request
- Registration Accept
- PDU Session Establishment Request
- PDU Session Establishment Accept
- Troubleshoot
Introduction
The evolution of mobile communication networks has reached a pivotal point with the deployment of 5G New Radio (NR) Standalone (SA) architecture, which enables end-to-end 5G connectivity without reliance on legacy technologies such as LTE. NR SA represents a significant advancement over previous deployment options, as it leverages a dedicated NR Core Network (5GC) and NR Radio Access Network (NR RAN), facilitating low latency, high throughput, and network slicing capabilities fundamental to next-generation applications. In this context, the Amari Callbox by Amarisoft emerges as a versatile and powerful solution for testing, validating, and experimenting with NR SA connections. The Amari Callbox integrates a software-defined radio platform capable of emulating both the NR RAN (gNB) and the NR Core Network, supporting all 3GPP-specified frequency bands and bandwidths up to 100 MHz per component carrier. This enables comprehensive end-to-end testing of User Equipment (UE) in a controlled environment, accelerating development cycles and ensuring conformance to industry standards. By establishing an NR SA connection between a UE and the Amari Callbox, users can gain practical insight into 5G protocols, signaling procedures, and network behavior, which are critical for engineers, researchers, and network operators involved in the 5G ecosystem. The tutorial provides a step-by-step guide for users with no prior experience with the Amari Callbox, demystifying the setup and configuration required to achieve a successful NR SA connection and illustrating the broader implications of standalone 5G deployments in real-world scenarios.
-
Context and Background
- 5G NR SA Overview: Standalone (SA) mode in 5G NR refers to a network architecture where both the Radio Access Network (gNB) and the Core Network (5GC) are based on 5G technologies, without dependency on LTE EPC or eNodeB.
- Industry Relevance: NR SA (Option 2) is widely recognized for enabling the full suite of 5G features, such as network slicing, ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC), and massive machine-type communications (mMTC).
- Amari Callbox Solution: The Amari Callbox is a self-contained, software-defined radio platform supporting both LTE and NR core networks, capable of emulating any 3GPP-defined frequency band up to 100 MHz per component carrier.
-
Relevance and Importance of the Tutorial
- Hands-on Experience: Guides users through practical steps to establish and troubleshoot NR SA connectivity, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world application.
- Accelerated Development: Enables rapid prototyping, validation, and debugging of 5G NR features using a flexible test platform.
- Industry Alignment: Prepares engineers and researchers for evolving 5G standards and deployment models adopted globally.
-
What Learners Will Gain
- Technical Proficiency: Understanding of NR SA architecture, protocol stack, and signaling flows between UE and 5G core network.
- Practical Skills: Step-by-step instructions for configuring Amari Callbox, initiating NR SA connections, and interpreting diagnostic information.
- Troubleshooting Techniques: Ability to diagnose and resolve common issues encountered during NR SA connection attempts.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge and Skills
- Basic Networking Concepts: Familiarity with IP addressing, network interfaces, and general connectivity principles is helpful but not required.
- 5G NR Fundamentals: Prior knowledge of 5G NR concepts is beneficial but the tutorial is structured to accommodate users new to Amari Callbox and NR SA deployments.
- System Access: Access to Amari Callbox hardware/software and a compatible 5G NR-capable UE are required for hands-on exercises.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial outlines the procedures for conducting an "Out of the Box" Standalone (SA) NR test using Amarisoft equipment and default configurations. The steps cover setup, execution, logging, log analysis, signaling review, and troubleshooting. The following summarizes the key test procedures and methodologies described:
-
Test Setup and Configuration
- Use the default configuration file gnb-sa.cfg for the gNB, with no modifications.
- Utilize the SIM card provided with the system as-is.
- Key configuration parameters include nr_cell_list.band, dl_nr_arfcn, subcarrier_spacing, ssb_pos_bitmap, nr_cell_default.bandwidth, n_antenna_dl, n_antenna_ul, tdd_ul_dl_config, and ssb_period.
- To apply the desired configuration, set up symbolic links:
- In /root/enb/config, link enb.cfg to gnb-sa.cfg using
ln -sf gnb-sa.cfg enb.cfg. - In /root/mme/config, ensure ims.cfg points to ims.default.cfg and mme.cfg to mme-ims.cfg via symbolic links.
- In /root/enb/config, link enb.cfg to gnb-sa.cfg using
- Restart the callbox to apply new configurations using
service lte restart. - Verify LTE service status with
service lte statusbefore proceeding.
-
Test Execution
- Access the call box interface using
screen -rto monitor and interact with network components (MME, ENB, IMS, MBMSGW). - Switch to the ENB component using Ctrl + A + 1 for detailed RF and network status.
- Begin trace logging by pressing t prior to powering on the User Equipment (UE) to capture the full attach sequence, including PRACH attempts.
- Power on the UE and allow it to complete initial attach and SA establishment.
- Stop trace logging by pressing the Enter key and return to the command prompt for further actions.
- Access the call box interface using
-
Log Analysis
- Open the generated log file (e.g., /tmp/gnb0.log) using a text editor.
- Verify the presence and sequence of key signaling messages:
- Check for RRC Setup Request and RRC Setup to confirm successful cell search and PRACH completion.
- Ensure RRC Setup Complete is received, indicating the UE completed setup.
- Monitor for authentication messages; analyze Authentication Response or Failure for SIM parameter mismatches.
- Confirm NAS and RRC security completion via Security mode complete messages.
- Check for RRC Reconfiguration and Reconfiguration Complete.
- Verify 5GMM: Registration complete and PDU Session Establishment procedures, including correct IP and DNS assignment to UE.
- For detailed analysis, use the WebGUI as recommended.
-
Signaling and Message Structure Review
- Sample structures of SIB1, RRC Setup, Registration Request/Accept, and PDU Session Establishment Request/Accept messages are provided for reference.
- Identify and interpret important Information Elements (IEs) for troubleshooting and validation of the signaling flow.
-
Troubleshooting Procedures
- If UE fails to camp on SA, perform the following checks:
- Test with NSA mode to validate UE capability.
- Review UE capability information from LTE/NSA logs for NR SA support.
- Compare supported bandwidth and subcarrier spacing with configuration files.
- Investigate known commercial UE issues related to SA operation, especially with test USIMs.
- Reference provided signaling IEs and troubleshooting guides for further diagnosis of registration or attach failures.
- If UE fails to camp on SA, perform the following checks:
This procedure ensures a comprehensive, step-by-step validation of Standalone NR operation using Amarisoft solutions in an out-of-the-box configuration, with guidance on configuration, execution, logging, analysis, and troubleshooting.
Test Setup
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below.
- Since this test is for Out of the box testing, I used the SA default configuration(gnb-sa.cfg) file without changing anything in it
- SIM Card used in this tutorial is the one delivered with the system as it is.
- If you want to change the configuration, The tutorial Configuration Guidewould help

Key Configuration Parameters
Followings are important configuration parameters for this tutorial. You may click on the items for the descriptions from Amarisoft documents.
Configuration
In this section, I would show you how to change the configuration file that is used by eNB/gNB. But in this very basic tutorial (Out of the Box Test), I would not try to change the detailed configuration within the file and will just replace the enb.cfg with another file.
Go to eNB/gNB configuration directory

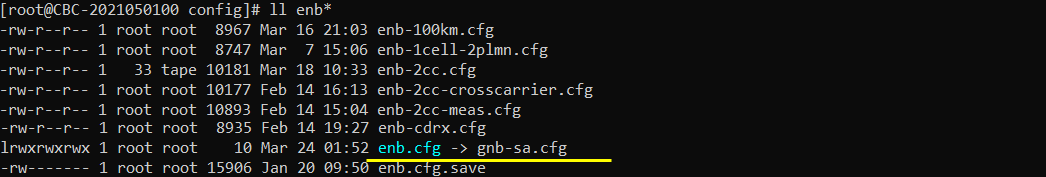
Change the symbolic link so that enb.cfg points to { enb.cfg -> gnb-sa.cfg }using the command : "ln -sf gnb-sa.cfg enb.cfg"

Now you should see the enb.cfg is linked to gnb-sa.cfg as shown below.(
Now go to the directory /root/mme/config. You should see the configuration files as below. (
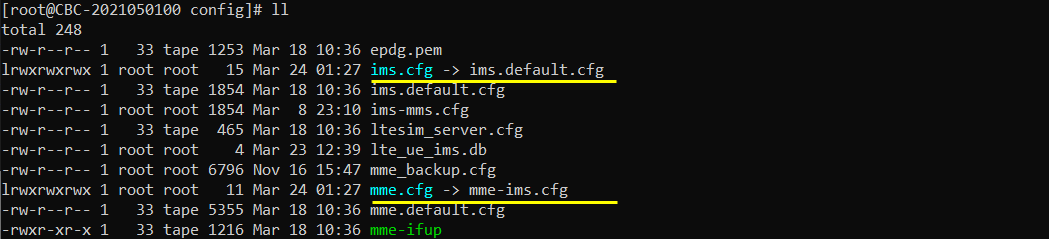
If ims.cfg and mme.cfg is not linked to the files as shown above, you may run following commands to make proper link : "ln -sf ims.default.cfg ims.cfg" and "ln -sf mme-ims.cfg mme.cfg
![]()
Restart the callbox so that the new configuration file is applied : try with 'service lte restart'

Check if LTE service is Running
Whatever you want to test, the first thing you need to do is that call box program (LTE Service) is running. You can check on the execution status of the call box program by running following command and you should get the result as shown below
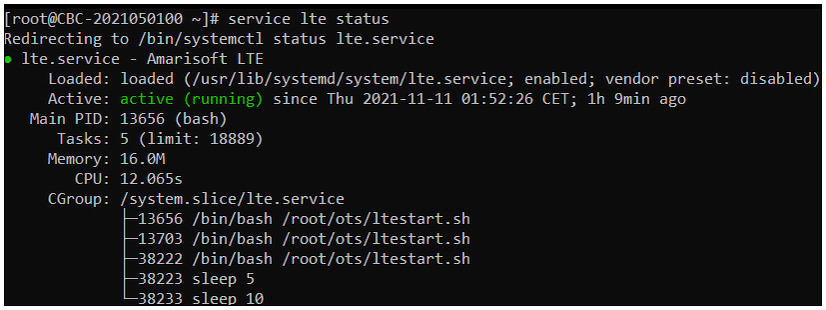
# service lte status
Run service lte status, which redirects to systemctl status lte.service. If the output shows Active: active (running), the LTE service is up. The same screen also shows whether it is enabled at boot (Loaded ... enabled), the main PID, and the child processes under the service, which helps quick troubleshooting.
# service lte restart
Perform the Test
If it is confirmed that the lte service is running, go to screen mode by running 'screen -r' and follow through the steps as shown below. The steps shown here is the procedure that you would use for almost every test and it is highly recommended to get familiar with these steps. For further commands you can use in this screen mode, refer to the tutorial : Command Line Command
Run following command : "screen -r"
This command reattaches your terminal to an existing GNU Screen session, so you can view and interact with the already-running process instead of starting a new one. If there is a detached session, it will bring you directly into that session. If there are multiple sessions, Screen will list them so you can pick the one to reattach.

You will get the screen as shown below
This screen shows all the network components installed in the callbox. In this tutorial, it indicates MME, ENB, IMS, MBMSGW are installed in the callbox. You would see a number before each component name. With Ctrl+A and the number before the component name, you can switch to command line window for the specific component. For example, if you press Ctrl+A+1, the command line window switches to ENB and if you press Ctrl+A+0, the command line window switches to MME and so on.
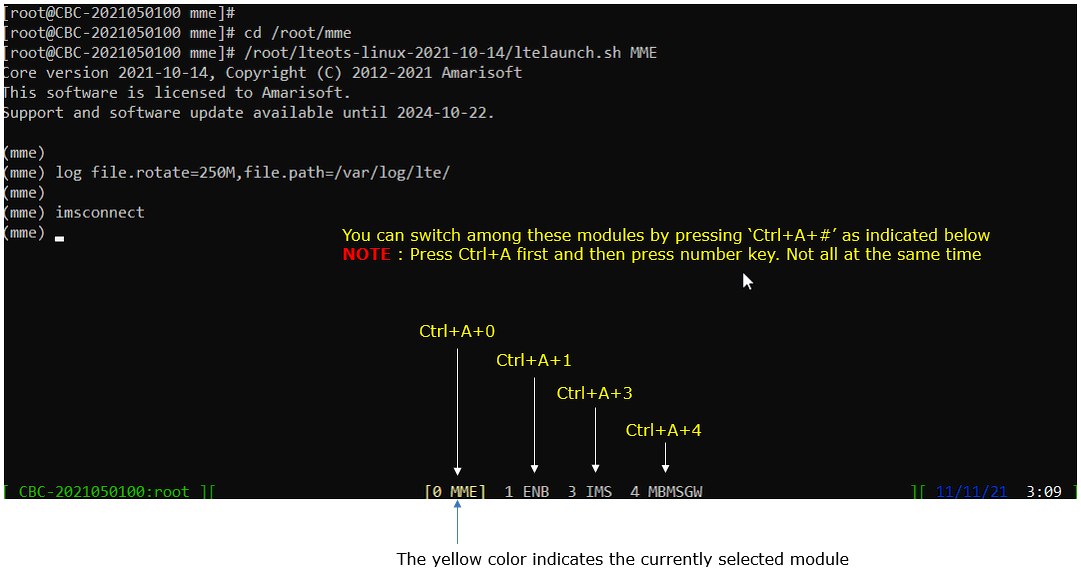
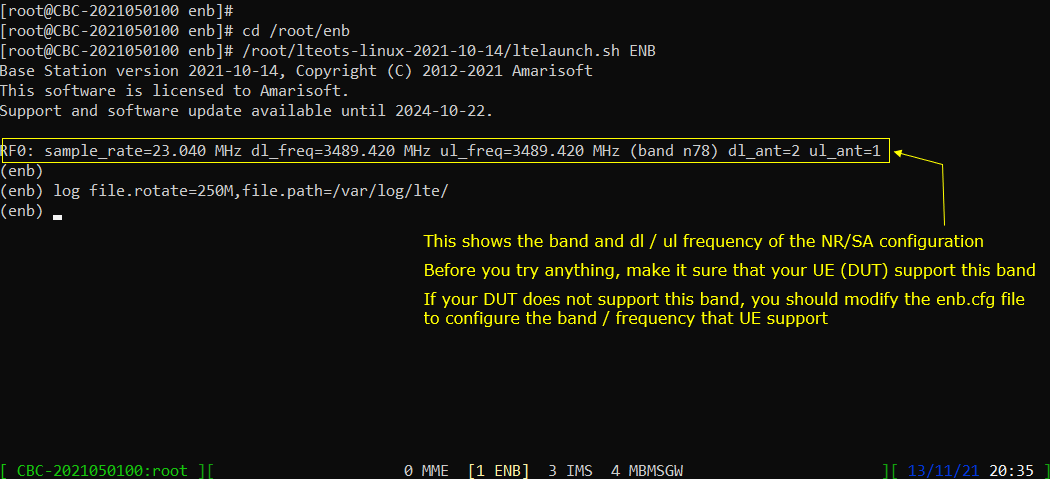
Switch to [ENB] by pressing ‘Ctrl + A + 1’. You will get the screen as shown below.
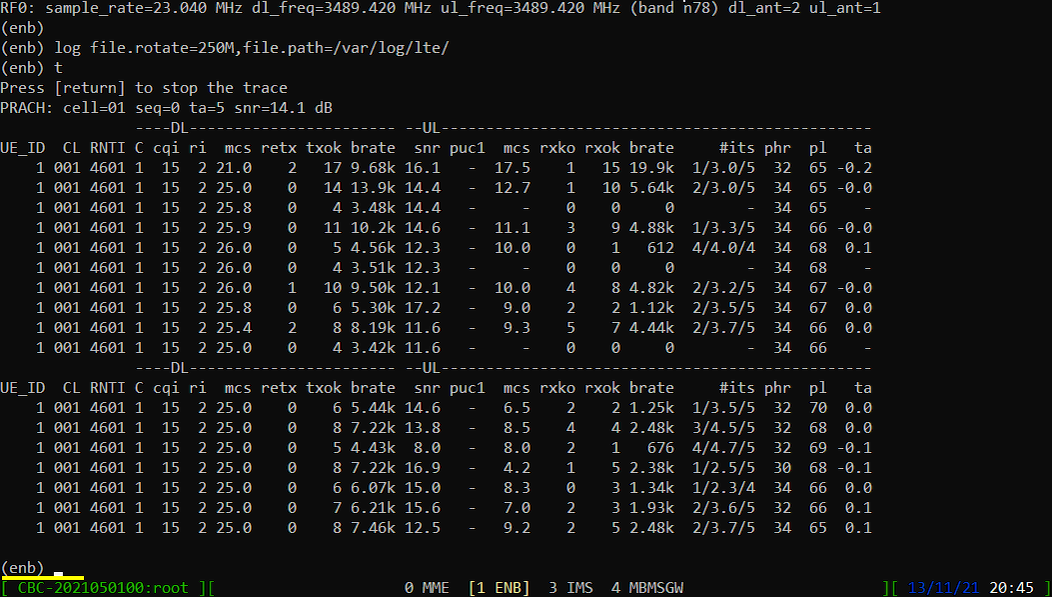
When you switches to [ENB] there are some important information provided without running any specific command. It provides RF information showing the sample_rate, dl_freq, ul_freq, band, dl_ant, ul_ant that gives you very fundamental RF information. Check out the details of these info and see if the RF is configured as you intended.
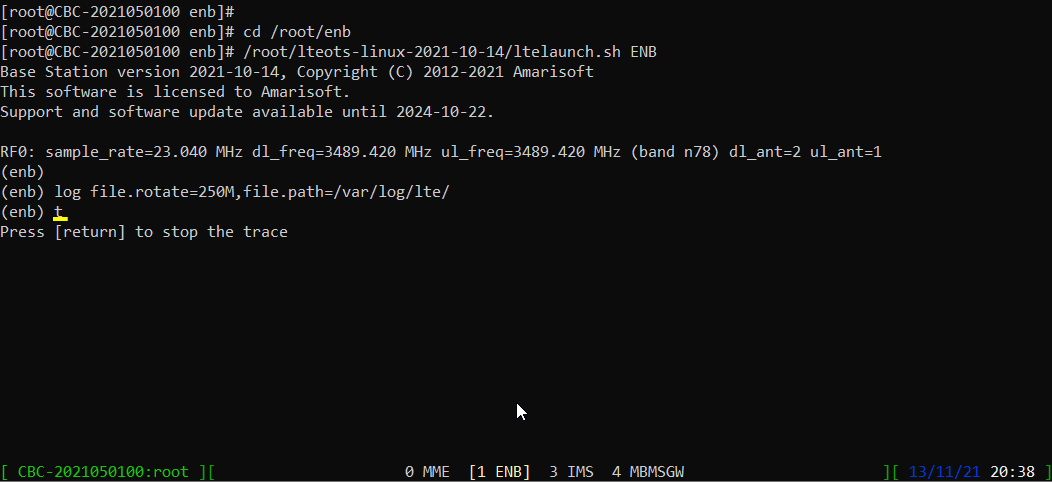
Start trace logging by 't' command as shown below.
You can run this command any time during the test, but it is always good idea to run this command before you power on UE to get the log from very beginning of initial attach.
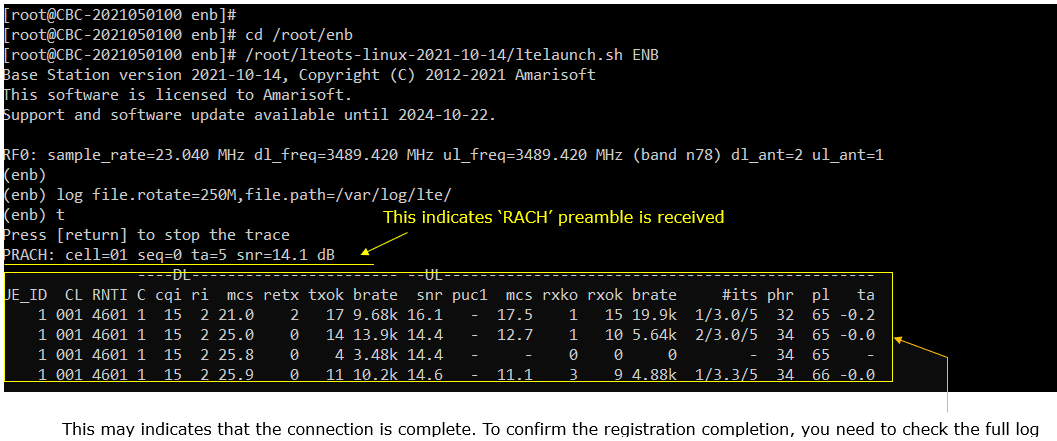
Power On UE and let it complete the attach and SA establishment. You would get trace as shown below.
If you started 't' command before you powe on UE, you will get the traces for PRACH attempt. The presence of PRACH trace can be a good troubleshooting indicator for initial attach problem. If PRACH is properly received and the entire RACH process is completed, it is highly likely that the initial attach gets completed and start getting traffic log. Regarding the details on the meaning of each column of this log and how to use the information for troubleshoot, refer tothis tutorial.
Press [Enter] key to stop the trace logging. When you want to use another command, you need to stop 't' command by pressing the enter key and get back to prompt as shown below.
Log Analysis
In this section, you will see how to confirm if UE registration is complete from trace log. You can use the same method to find any issues (e.g, registration failure) for troubleshooting. When UE registration fails, you may use this tutorial to figure out the point of the failure and troubleshoot.
In this section, I will not go through each and every lines of the signaling message. Instead I will check out only some important messages that is required to be aquired for successful NR SA attach.
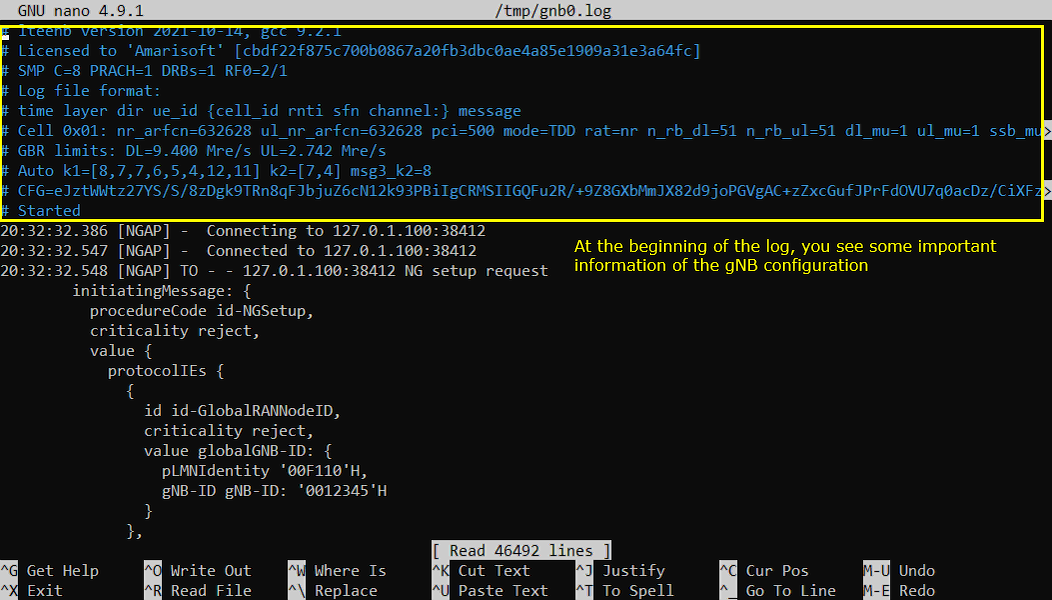
Open /tmp/gnb0.log using any text editor. I am using nano in this tutorial. you will see various high level information (meta data) at the beginning of the file. This is useful high level information. Check out this tutorial to the details on this meta data.
At the very beginning of the file, the gNB prints a compact “meta data” header that summarizes the running build and the active configuration, so you can validate the setup before you dig into detailed protocol messages. In this header you typically see the software version/build information and the license line, then high-level capability/configuration indicators such as SMP settings, PRACH configuration, number of DRBs, and the RF configuration. Right after that, the log declares the log record format so you know how to interpret each line (time, layer, direction, UE identifiers, and the message text). The most important part is the cell summary line, where you can quickly confirm core radio parameters such as nr_arfcn and ul_nr_arfcn (DL/UL frequency placement), pci (cell identity), mode=TDD, n_rb_dl/n_rb_ul (bandwidth in RB), and dl_mu/ul_mu (numerology). You may also see scheduling-related hints like automatic k1/k2 selections and Msg3 timing parameters, plus transport limits such as GBR limits that indicate configured throughput caps. After the “Started” marker, the log transitions into runtime events, for example NGAP connectivity to the core (Connecting/Connected to an IP:port) and the initial NG setup request, where identifiers like PLMNIdentity and gNB-ID appear and let you verify that the gNB is presenting the expected network identity to the AMF.
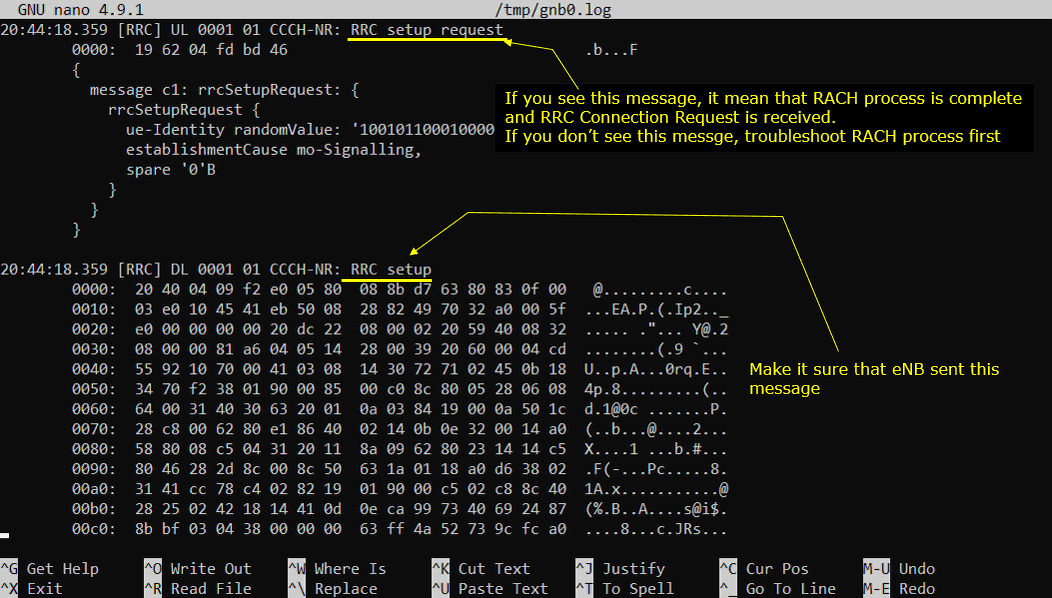
Now let's look into signaling message part of the log. The first thing you may want to check is 'RRC setupRequest' and 'RRC Setup'. If you get these message, it indicates that cell search and PRACH process is properly done on UE side and UE initiates RRC Setup.
When you see RRC setup request on the UL side, it means the UE already completed cell search and the PRACH/RACH procedure far enough to obtain the resources needed to send an initial RRC message. In the log line, the important fields are the direction and channel tag like UL ... CCCH-NR, which tells you this is the initial common control signaling, and the content inside rrcSetupRequest, especially ue-Identity (often a randomValue) and establishmentCause (why the UE is requesting access, such as mo-Signalling). Right after that, you should confirm the network response RRC setup on the DL side. The log line typically shows DL ... CCCH-NR: RRC setup, which indicates the gNB accepted the request and is sending the setup message back to the UE to create SRB1 and move the UE into the connected signaling phase. If you see the UL RRC setup request but do not see the DL RRC setup, the issue is usually on the network side response path or scheduling. If you do not see the UL RRC setup request at all, you troubleshoot the earlier access steps first, especially PRACH detection and RACH completion.
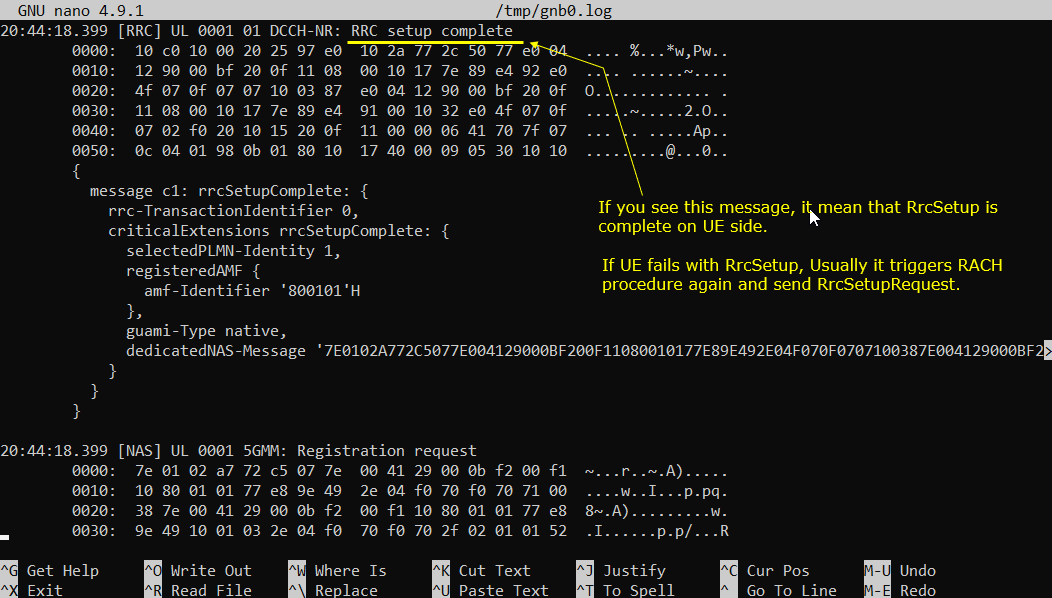
Next step you need to check is to see whether the eNB recieves RRC Setup Complete or not. If you see this message, it mean that RrcSetup is completed on UE side. If UE fails with RrcSetup, it usually triggers RACH procedure again and send Rrc Request.
In the log this appears as an UL message on DCCH-NR, which means the UE successfully decoded the RRC setup from the gNB, applied the configuration, created the initial signaling bearer, and is now acknowledging that the RRC setup procedure is finished on the UE side.In the decoded block, the key parameters are rrc-TransactionIdentifier (it should match the transaction used in the RRC setup), and the criticalExtensions that carry rrcSetupComplete. You often also see selectedPLMN-Identity, which tells you which PLMN the UE selected, and registeredAMF / amf-Identifier, which indicates the UE is tying the connection to a specific AMF identity in the core. Another important field is dedicatedNAS-Message. This is the NAS payload piggybacked inside RRC setup complete. In many traces, right after this you see a NAS line such as 5GMM: Registration request, which confirms the UE immediately moves from “RRC connected” into “NAS registration” over the newly established signaling path. If RRC setup complete does not show up, it usually means the UE failed to complete the setup on its side (decode failure, timing, RF issues, or configuration mismatch). In that case, the UE often retries access by running RACH again and sending a new RRC setup request.
Once RRC Setup Procedure is complete, eNB initiate the Authentication process. If the authentication is confirmed on UE side, UE send Authentication Response message. If you see the Authentication Failure instead of Authentication Response, it usually implies that there is SIM parameter mismatch between USIM and eNB SIM parameter setting. In most case, K value mismatch would be the culprit of the failure. Check ue_db.cfg or ue_db-ims.cfg and make it sure it has authentication parameter that matches DUT's USIM parameter.
In this log, UE answers with 5GMM: Authentication response if it was able to compute the correct response using its USIM credentials. In the log line, the important cues are NAS UL and 5GMM, because this tells you the message is coming from the UE as a NAS Mobility Management message. When you see Message type = 0x57 (Authentication response) and an Authentication response parameter field with a non-zero length, it is a strong sign that the authentication procedure succeeded on the UE side. If you see Authentication failure instead of Authentication response, it usually means the UE could not validate the network challenge or could not generate a valid response. In practice, the most common reason is a mismatch between the UE’s USIM parameters and the parameters configured in the eNB/gNB database, especially the shared secret K (and related auth settings). In that case you verify the subscriber entries in files such as ue_db.cfg or ue_db-ims.cfg and make sure the authentication fields match the DUT’s USIM configuration.
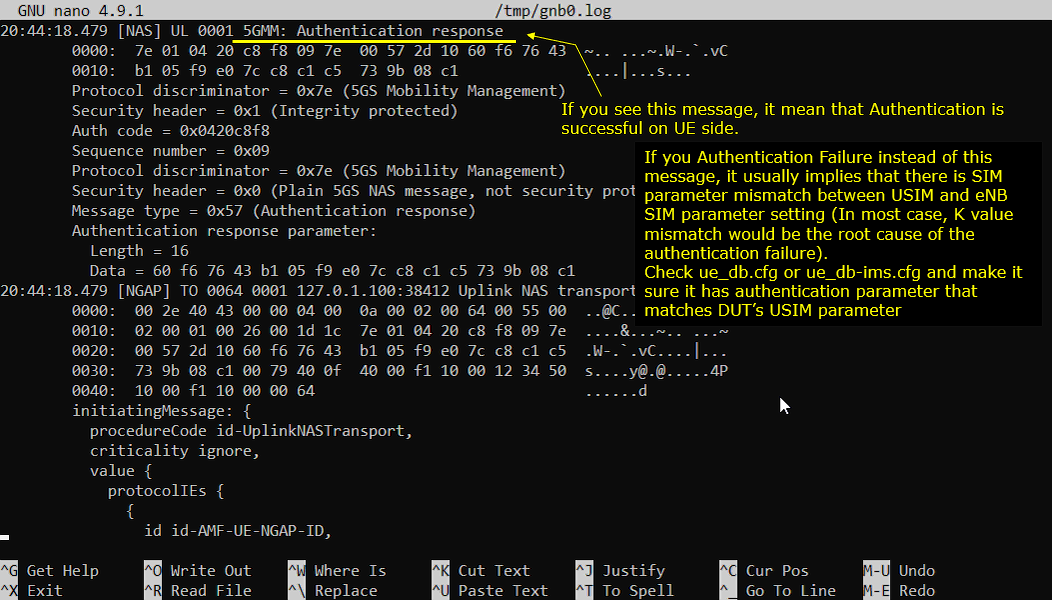
Once Authentication process is complete, gNB/5G Corestarts Security checkup. There are two different level of security checkup. The first one is NAS Security and the second one is RRC Security.
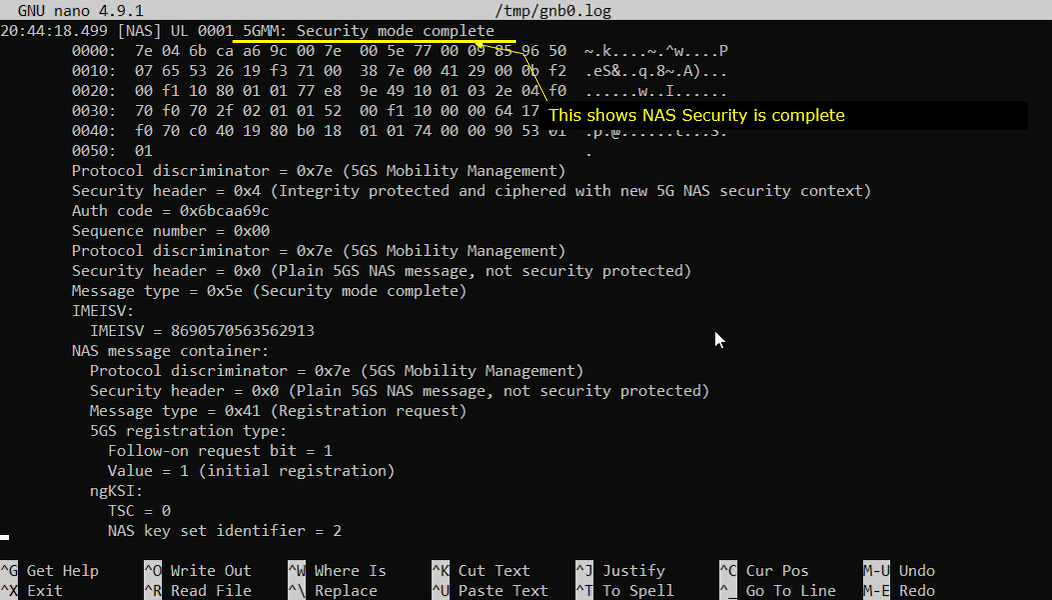
If you see GMM:Security mode complete message recieved, it indicates that NAS Security is complete. This message means the UE accepted the NAS security parameters selected by the network and confirmed that the new 5G NAS security context is now active, so subsequent NAS signaling is protected. In the decoded section, the most important parameters are the security header and the protection indicators. A value like Security header = 0x4 tells you the message is integrity protected and ciphered using the newly established NAS security context, and the presence of an auth code (MAC) and a sequence number confirms that integrity is actually being applied. You may also see identity information such as IMEISV, which is often carried after security is in place. Another useful detail is the NAS message container shown under the security mode complete. This indicates the UE is already continuing the registration procedure under the secured context, and you can verify items like Message type inside the container (for example Registration request), the 5GS registration type (initial registration), and the ngKSI / NAS key set identifier, which tells you which key set the UE is using. If this Security mode complete is missing, NAS security did not finish, so you typically backtrack to the preceding Security mode command and the key/agreement configuration.
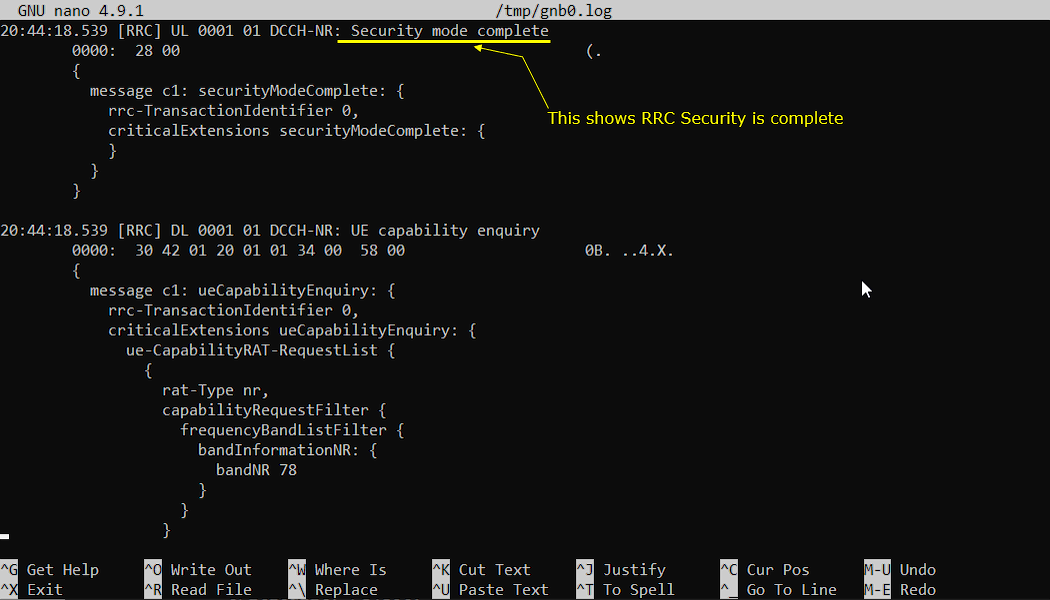
If you see DCCH-NR:Security mode complete message recieved, it indicates that RRCSecurity is complete. It means the UE accepted the radio bearer security configuration from the gNB and confirmed that RRC security is now active for the dedicated control channel. The important indicators are the channel and message type. DCCH-NR tells you this is dedicated control signaling after the UE is already in RRC connected state, and securityModeComplete is the explicit acknowledgement of the RRC Security Mode Command. Inside the decoded block, rrc-TransactionIdentifier is useful to correlate this completion to the earlier security mode transaction. Right after RRC security completes, the gNB typically proceeds with capability exchange. In the same time window you often see UE capability enquiry on DL, which is the network asking the UE to report its NR capability set. Parameters like rat-Type = nr and requested band information (for example bandNR 78) show what the network is trying to learn from the UE for later configuration decisions.
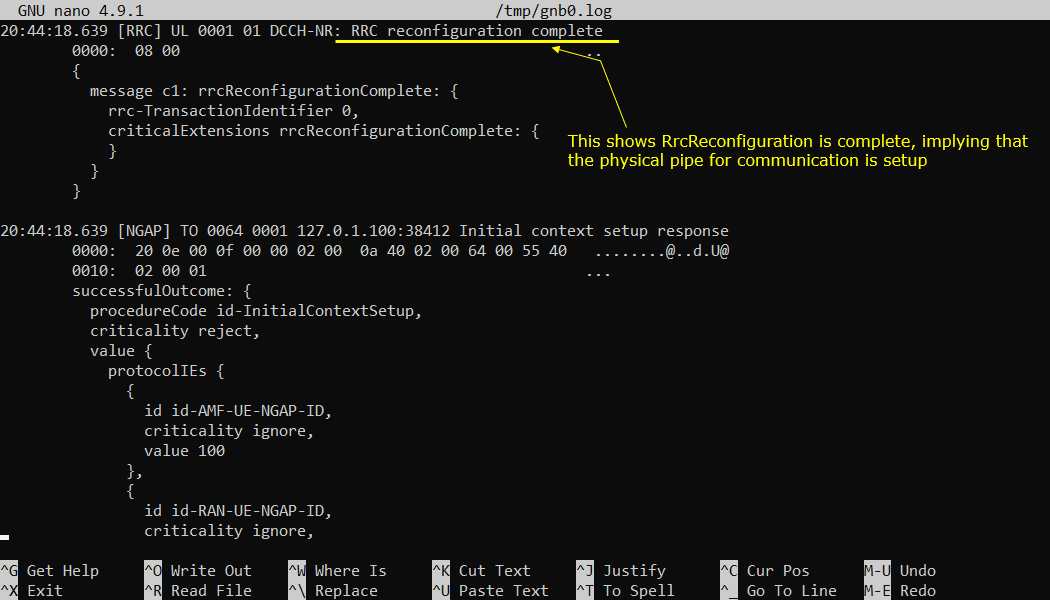
Once Authentication and Security checkup is done, eNB initiate RRC Reconfiguration. If the Rrc Reconfiguration is properly processed on UE side, UE send RRC Reconfiguration Complete. The key indicator is the presence of rrcReconfigurationComplete on the UL direction and DCCH-NR, because reconfiguration is dedicated control signaling after the UE is already connected and secured. The rrc-TransactionIdentifier is the parameter you use to correlate this completion to the corresponding reconfiguration command. When this completion appears, it usually implies that the main physical and logical communication “pipe” is now set up, such as SRB/DRB additions, security activation, and any initial measurement or capability-driven settings needed for service. In many traces you also see a related NGAP step around the same time, such as Initial context setup response, which indicates the access side and core side context are now aligned for that UE, using identifiers like AMF-UE-NGAP-ID and RAN-UE-NGAP-ID.
Once all the required RRC and NASProcedure for initial registration is complete, UE is supposed to send 5GMM:Registration completemessage. This message means the UE finished all required steps for initial attach/registration, including the necessary RRC procedures and NAS security procedures, and is now confirming to the network that the registration procedure is complete. In the decoded header, the important parameters are the security header, the auth code (MAC), and the sequence number. When you see Security header = 0x2 (Integrity protected and ciphered), it tells you this Registration complete is sent under NAS security, so integrity and ciphering are active as expected. Message type = 0x43 (Registration complete) is the explicit indicator of the procedure completion, and the increasing Sequence number shows this is part of a valid protected NAS signaling flow. Right below it you often see the NGAP wrapper Uplink NAS transport, which is how the NAS message is carried through the RAN to the AMF. If this Registration complete appears, you can treat it as the point where the initial attach process is successfully finished from the UE perspective.
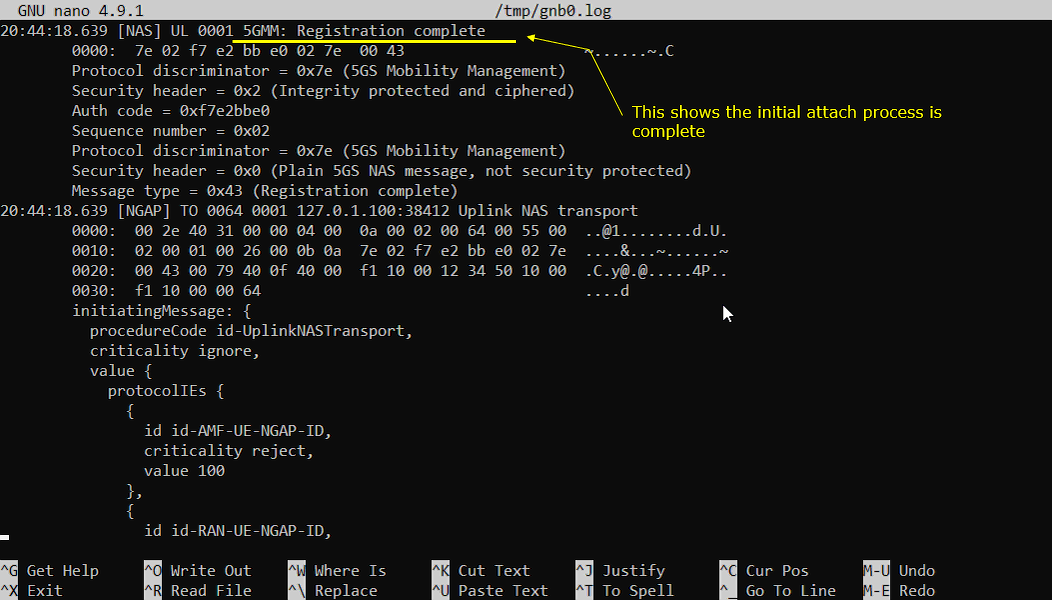
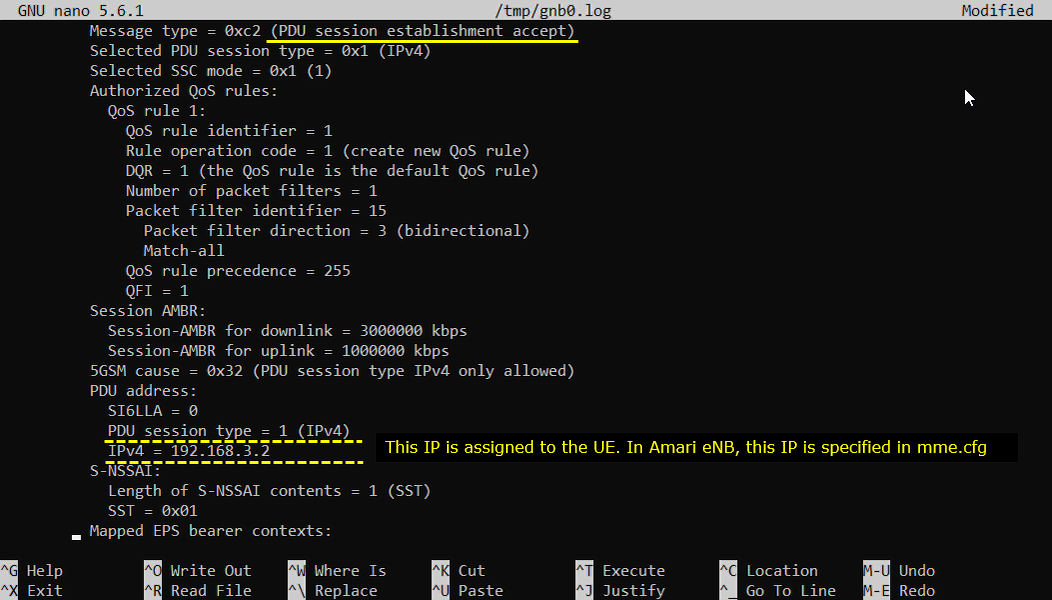
Once all the initial registration is complete, UE is supposed toinitiate PDU Sesttion Establishment. Network is supposed to send PDU Session establishment accept message when the request from UE is acceptable. One of the important information you would check in this message is IP address. This IP address is the one assigned to the UE.
In this accept message, the most important item to check is the PDU address, because this is the IP address assigned to the UE. In the example, the session type is IPv4, and the PDU address section shows an IPv4 value such as 192.168.3.2. This is the address the UE will use for data traffic, and in Amarisoft setups it typically comes from the core-side configuration (for example the IP pool defined in mme.cfg). The same message also tells you how the session will be handled. Selected PDU session type confirms whether it is IPv4/IPv6/IPv4v6. Selected SSC mode indicates the session continuity behavior. The Authorized QoS rules section shows the default rule creation, the packet filter direction (often bidirectional), and the resulting QoS flow identity such as QFI. Session AMBR provides the allowed aggregate bit rate for downlink and uplink, which is a quick way to confirm the data-rate limits applied to this UE.
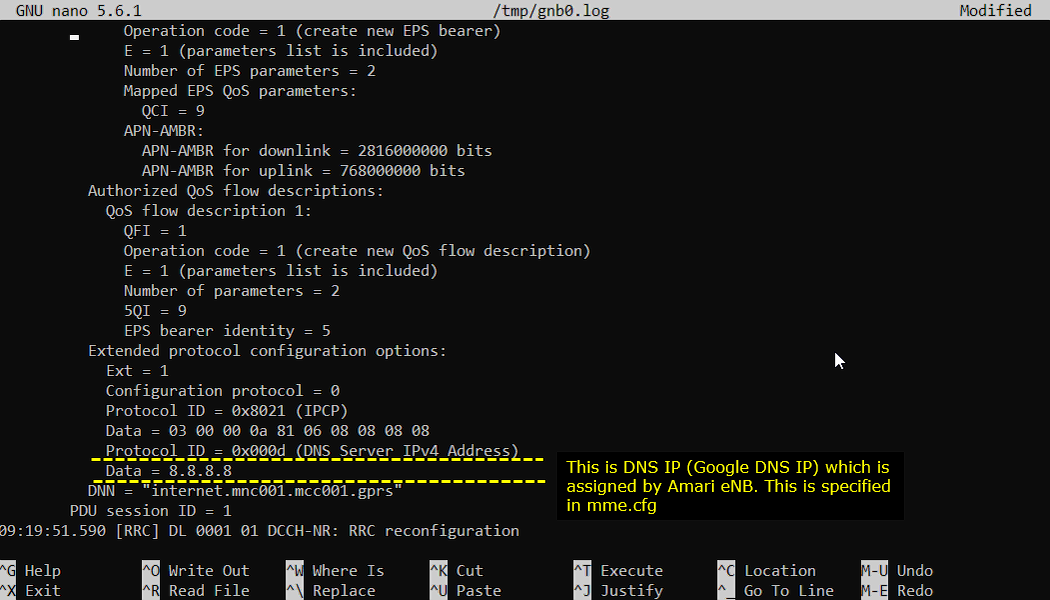
In the PDU session establishment accept, another practical item to verify is the DNS server address delivered to the UE. This is typically carried inside the Extended Protocol Configuration Options (EPCO) / protocol configuration container, where the log shows a protocol identifier for DNS (for example DNS Server IPv4 Address) and the corresponding Data field. In the example, the DNS value is shown as 8.8.8.8, which is a public DNS server address, and it tells you what resolver the UE will use for name resolution once the data session is up. In Amarisoft setups, this DNS value is usually configured on the core side (commonly in mme.cfg), so if the UE gets the wrong DNS or cannot resolve names, this is one of the first fields you cross-check against your configured DNS settings.
Once the full registration flow is finished, the UE has everything needed to start real data traffic. 5GMM: Registration complete confirms the control-plane attach is done. PDU session establishment accept confirms the UE has a user-plane session. The PDU address field provides the UE’s assigned IP address, and the DNS server field provides the resolver IP. With IP and DNS delivered and security already established, the UE is now ready for end-to-end data communication.
RRC / NAS Signaling
: This section is to show you the overall structure of important Rrc messages and Information IE (IE) that are related to this tutorial. It is not intended to describe the details on every RRC/NAS Information elements. With the overall structure and key IEs shown here, it hope it would be easier / clearer to go through the sample log provided in this tutorial or any logs that you captured from your own test setup or live network.
SIB1
: This is the SIB1message sent by gNB to configure NR SA. (
{
"message": {
"c1": {
"systemInformationBlockType1": {
"cellSelectionInfo": {
"...": "..."
},
"cellAccessRelatedInfo": {
"plmn-IdentityList": [
"..."
]
},
"connEstFailureControl": {
"...": "..."
},
"servingCellConfigCommon": {
"downlinkConfigCommon": {
"frequencyInfoDL": {
"frequencyBandList": [
{
"freqBandIndicatorNR": 78
}
],
"offsetToPointA": 24,
"scs-SpecificCarrierList": [
{
"offsetToCarrier": 0,
"subcarrierSpacing": "kHz30",
"carrierBandwidth": 51
}
]
},
"initialDownlinkBWP": {
"genericParameters": {
"locationAndBandwidth": 13750,
"subcarrierSpacing": "kHz30"
},
"pdcch-ConfigCommon": {
"setup": {
"...": "..."
}
},
"pdsch-ConfigCommon": {
"setup": {
"...": "..."
}
},
"bcch-Config": {
"...": "..."
},
"pcch-Config": {
"...": "..."
}
}
},
"uplinkConfigCommon": {
"frequencyInfoUL": {
"scs-SpecificCarrierList": [
{
"offsetToCarrier": 0,
"subcarrierSpacing": "kHz30",
"carrierBandwidth": 51
}
],
"p-Max": 10
},
"initialUplinkBWP": {
"genericParameters": {
"locationAndBandwidth": 13750,
"subcarrierSpacing": "kHz30"
},
"rach-ConfigCommon": {
"setup": {
"...": "..."
}
},
"pusch-ConfigCommon": {
"setup": {
"...": "..."
}
},
"pucch-ConfigCommon": {
"setup": {
"...": "..."
}
}
},
"timeAlignmentTimerCommon": "infinity"
},
"ssb-PositionsInBurst": {
"inOneGroup": "0x80"
},
"ssb-PeriodicityServingCell": "ms20",
"tdd-UL-DL-ConfigurationCommon": {
"...": "..."
},
"ss-PBCH-BlockPower": -28
},
"ue-TimersAndConstants": {
"...": "..."
}
}
}
}
}
RrcSetup
: This is the RrcSetupmessage sent by gNB to configure NR SA. (
{
"message": {
"c1": {
"rrcSetup": {
"rrc-TransactionIdentifier": 0,
"criticalExtensions": {
"rrcSetup": {
"radioBearerConfig": {
"...": "..."
},
"masterCellGroup": {
"cellGroupId": 0,
"rlc-BearerToAddModList": [
"..."
],
"mac-CellGroupConfig": {
"...": "..."
},
"physicalCellGroupConfig": {
"...": "..."
},
"spCellConfig": {
"spCellConfigDedicated": {
"initialDownlinkBWP": {
"pdcch-Config": {
"setup": {
"...": "..."
}
},
"pdsch-Config": {
"setup": {
"...": "..."
}
}
},
"firstActiveDownlinkBWP-Id": 0,
"uplinkConfig": {
"initialUplinkBWP": {
"pucch-Config": {
"setup": {
"...": "..."
}
},
"pusch-Config": {
"setup": {
"...": "..."
}
},
"srs-Config": {
"setup": {
"...": "..."
}
}
},
"firstActiveUplinkBWP-Id": 0,
"pusch-ServingCellConfig": {
"setup": {}
}
},
"pdcch-ServingCellConfig": {
"setup": {}
},
"pdsch-ServingCellConfig": {
"setup": {
"nrofHARQ-ProcessesForPDSCH": "n16"
}
},
"csi-MeasConfig": {
"setup": {
"...": "..."
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
Registration Request
: Following is an example of registration request message from UE (
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x1 (Integrity protected)
Auth code = 0x4295c610
Sequence number = 0x2e
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x0 (Plain 5GS NAS message, not security protected)
Message type = 0x41 (Registration request)
5GS registration type:
Follow-on request bit = 1
Value = 1 (initial registration)
ngKSI:
...
5GS mobile identity:
5G-GUTI
...
UE security capability:
...
NAS message container:
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x0 (Plain 5GS NAS message, not security protected)
Message type = 0x41 (Registration request)
5GS registration type:
Follow-on request bit = 1
Value = 1 (initial registration)
ngKSI:
..
5GS mobile identity:
5G-GUTI
...
5GMM capability:
...
UE security capability:
...
Requested NSSAI:
...
Last visited registered TAI:
...
S1 UE network capability:
...
UE's usage setting = 0x01 (Data centric)
LADN indication:
...
Network slicing indication = 0x00 (DCNI=0, NSSCI=0)
5GS update type = 0x01 (EPS-PNB-CIoT=no additional information, 5GS-PNB-CIoT=no additional information, NG-RAN-RCU=0, SMS requested=1)
Registration Accept
: Following is an example of registration acceptmessage from UE (
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x2 (Integrity protected and ciphered)
Auth code = 0xc93c7d52
Sequence number = 0x02
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x0 (Plain 5GS NAS message, not security protected)
Message type = 0x42 (Registration accept)
5GS registration result = 0x09 (Emergency registered=0, NSSAA to be performed=0, SMS allowed=1, 3GPP access)
5G-GUTI:
...
TAI list:
...
Allowed NSSAI:
...
5GS network feature support:
...
T3512 value:
...
Emergency number list:
...
PDU Session Establishment Request
: Following is an example of PDU session establishment requestmessage from UE (
Protocol discriminator = 0x2e (5GS Session Management)
PDU session identity = 1
Procedure transaction identity = 85
Message type = 0xc1 (PDU session establishment request)
Integrity protection maximum data data:
...
PDU session type = 0x3 (IPv4v6)
5GSM capability:
...
Extended protocol configuration options:
Ext = 1
Configuration protocol = 0
Protocol ID = 0xc223 (CHAP)
Data = 01 00 00 16 10 8c bb 1d 1d 8c bb 1d 1d 8c bb 1d 1d 8c bb 1d 1d 2a
Protocol ID = 0xc223 (CHAP)
Data = 02 00 00 16 10 c6 00 c0 d1 3b de b9 d7 0b 68 d9 33 26 ec fe fb 2a
Protocol ID = 0x8021 (IPCP)
Data = 01 00 00 10 81 06 00 00 00 00 83 06 00 00 00 00
Protocol ID = 0x000d (DNS Server IPv4 Address Request)
Data =
Protocol ID = 0x0003 (DNS Server IPv6 Address Request)
Data =
Protocol ID = 0x000a (IP address allocation via NAS signalling)
Data =
Protocol ID = 0x0005 (MS Support of Network Requested Bearer Control indicator)
Data =
Protocol ID = 0x0010 (IPv4 Link MTU Request)
Data =
Protocol ID = 0x0011 (MS support of Local address in TFT indicator)
Data =
Protocol ID = 0x0023 (QoS rules with the length of two octets support indicator)
Data =
Protocol ID = 0x0024 (QoS flow descriptions with the length of two octets support indicator)
Data =
PDU Session Establishment Accept
: Following is an example of PDU session establishment requestmessage from UE (
Protocol discriminator = 0x2e (5GS Session Management)
PDU session identity = 1
Procedure transaction identity = 85
Message type = 0xc2 (PDU session establishment accept)
Selected PDU session type = 0x1 (IPv4)
Selected SSC mode = 0x1 (1)
Authorized QoS rules:
...
Session AMBR:
...
5GSM cause = 0x32 (PDU session type IPv4 only allowed)
PDU address:
SI6LLA = 0
PDU session type = 1 (IPv4)
IPv4 = 192.168.3.2
S-NSSAI:
Length of S-NSSAI contents = 1 (SST)
SST = 0x01
Mapped EPS bearer contexts:
...
Authorized QoS flow descriptions:
...
Extended protocol configuration options:
Ext = 1
Configuration protocol = 0
Protocol ID = 0x8021 (IPCP)
Data = 03 00 00 0a 81 06 08 08 08 08
Protocol ID = 0x000d (DNS Server IPv4 Address)
Data = 8.8.8.8
DNN = "internet.mnc001.mcc001.gprs"
Troubleshoot
: SA capable device is not as common as NSA capable device. Even when you get a device (UE) that claims to support SA. You may see many cases that would not work (would not camp on) to callbox. Check out the items below to figure out the root cause of the failure.
SA Camp On Failure
: If your UE does not camp on to SA (meaning that UE does not even trigger PRACH to SA Cell), you may check on followings.
Check Point 1 : Try with NSA
: Try first with NSA. If it does not work even with NSA, it is highly likely that your UE does not support NR at all. (
Check Point 2: Check out UE capability information
: Collect UE capability Information from LTE log or NSA log and check if NR SA capability is supported. You may check with IE N1mode and irat-ParametersNR
UE network capability:
0xf0 (EEA0=1, 128-EEA1=1, 128-EEA2=1, 128-EEA3=1, EEA4=0, EEA5=0, EEA6=0, EEA7=0)
0x70 (EIA0=0, 128-EIA1=1, 128-EIA2=1, 128-EIA3=1, EIA4=0, EIA5=0, EIA6=0, EIA7=0)
0xc0 (UEA0=1, UEA1=1, UEA2=0, UEA3=0, UEA4=0, UEA5=0, UEA6=0, UEA7=0)
0x40 (UCS2=0, UIA1=1, UIA2=0, UIA3=0, UIA4=0, UIA5=0, UIA6=0, UIA7=0)
0x19 (ProSe-dd=0, ProSe=0, H.245-ASH=0, ACC-CSFB=1, LPP=1, LCS=0, 1xSRVCC=0, NF=1)
0x80 (ePCO=1, HC-CP CIoT=0, ERw/oPDN=0, S1-U data=0, UP CIoT=0, CP CIoT=0, ProSe-relay=0, ProSe-dc=0)
0xb0 (15 bearers=1, SGC=0,
irat-ParametersNR-v1540 {
eutra-EPC-HO-ToNR-TDD-FR1-r15 supported,
sa-NR-r15 supported,
{
bandNR-r15 41
},
{
bandNR-r15 78
}
}
Check Point 3: the bandwidth and SCS
: Check out the bandwidth and SCS(Subcarrier Spacing) that are supported by the UE and see if you configured them accordingly in your configuration file. Following is an example.
channelBWs-DL-v1530 fr1: {
scs-15kHz '0000000000'B,
scs-30kHz '0000001111'B, => support 40,50,60,80 and 100 (max BW)
scs-60kHz '0000000000'B
},
channelBWs-UL-v1530 fr1: {
scs-15kHz '0000000000'B,
scs-30kHz '0000001111'B, => support 40,50,60,80 and 100 (max BW)
scs-60kHz '0000000000'B
}
Check Point 4: check if Any Well Known UE Issue
: Based on our experience, some wellknown commercial UEs disable NR SA when it is with Test USIM (Not the Network Operator UE). I would suggest you to check about this possibility before you purchase the UE if it is only for testing.