Remote API - Constellation
The purpose of this tutorial is to show to how to collect PHY constellation data using RemoteAPI and how to post process it. The end goal is similar to what you already have in WebGUI (see NOTE) . But the advantage in this method is that you can extract the data for resource element of received channels and signals (e.g, pusch, srs) from a binary file only. You don't need to carry both binary and text log. In addition, this way is much easier to extract the data from binary comparing to the existing method mentioned here WebGUI (see NOTE)
- The data mentioned in IQ_Capture , IQ_Plot and IQ_Decode are raw binary data, which includes all the captured I/Q data. These data is before/without any kind of Physical layer processing (e.g, equalization, OFDM demodulation, handling precoding etc)
- The data explained in this tutorial is the I/Q value on OFDM Resource Grid. It means the I/Q value captured in this tutorial is the captured after equalization, OFDM demodulation, handling precoding etc
Table of Contents
Introduction
Collecting and analyzing PHY (Physical Layer) constellation data is a vital process in modern wireless communications, enabling engineers to visualize and assess the quality of received signals in the resource elements of key physical channels such as PUSCH (Physical Uplink Shared Channel), SRS (Sounding Reference Signal), and their variants. Leveraging RemoteAPI for constellation data extraction provides a streamlined, efficient method for obtaining processed I/Q (In-Phase and Quadrature) values directly from binary files, post-equalization and demodulation, as opposed to capturing raw, unprocessed I/Q samples. This approach not only reduces the need for managing multiple log formats but also simplifies post-processing workflows, offering a direct pathway to high-fidelity constellation visualization and further analysis. The methodology aligns closely with the display capabilities of integrated WebGUIs but extends flexibility and accessibility for offline or automated analysis. Importantly, the nature of the data retrieved through RemoteAPI is distinct from conventional IQ captures—where data is acquired before physical layer procedures—and is specifically tailored for in-depth, post-processed examination of received signals. This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to collecting, extracting, and post-processing PHY constellation data using RemoteAPI, clarifying its scope and highlighting its integration into the broader wireless signal analysis and test automation ecosystem.
-
Context and Background
- PHY constellation data represents the processed I/Q values mapped onto the OFDM resource grid after physical layer operations such as equalization, demodulation, and precoding, differentiating it from raw IQ captures.
- RemoteAPI is a specialized interface designed to facilitate the remote extraction of PHY-level data from test equipment or base station emulators, supporting advanced offline analysis.
- This methodology is applicable to specific received channels (e.g., PUSCH, NPUSCH, PUSCH-DMRS, SRS on Callbox) and is supported from the release of the week of February 5th, 2024.
-
Relevance and Importance
- The ability to extract and post-process constellation data from binary files simplifies the workflow, eliminating the need for both binary and text logs, and enhances analysis efficiency compared to existing WebGUI methods.
- Processed I/Q data offers clearer insights into signal integrity and performance, being directly relevant for troubleshooting, performance evaluation, and research in wireless communications.
- The approach aligns with automated test environments and enables integration into continuous validation systems for wireless devices.
-
Learning Outcomes
- Gain an understanding of how to collect PHY constellation data using RemoteAPI and interpret its structure.
- Acquire practical skills in post-processing binary constellation data for visualization and in-depth signal analysis.
- Differentiate between raw IQ data and processed constellation data, and understand when to apply each method.
- Learn to overcome limitations of traditional capture and analysis workflows, optimizing data extraction for received channels.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge and Skills
- Familiarity with wireless communications fundamentals, particularly OFDM, resource grids, and physical channel concepts.
- Basic understanding of I/Q data, signal processing, and PHY layer procedures such as equalization and demodulation.
- Experience with binary data handling and post-processing tools (e.g., Python, MATLAB) for signal analysis.
- Access to compatible test equipment (e.g., Callbox or similar) that supports RemoteAPI-based PHY constellation data extraction.
-
Tutorial Scope and Alignment
- Focuses on the collection and post-processing of PHY constellation data for supported received channels only.
- Does not encompass complete RRC/NAS message analysis, message structure decoding, or the handling of transmitted channels.
- Provides technical guidance for engineers and researchers seeking efficient, reliable methods for constellation analysis in wireless test environments.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial describes the procedure for testing LTE PUSCH (Physical Uplink Shared Channel) resource element data capture using the Amarisoft Callbox environment.
-
Test Setup:
- Any test setup that allows the UE to attach to the callbox can be used.
-
Test 1: LTE PUSCH Data Capture Procedure
- The test demonstrates how to collect binary Resource Element (RE) data for LTE PUSCH transmission.
- Users should already be familiar with Amarisoft Callbox basic operations and eNB/gNB configuration. The example uses the default configuration (enb.default.cfg) without modifications.
-
Enable PHY Signal Capture:
- Activate physical layer signal capture before powering on the UE.
- This can be done via the WebGUI or by issuing the following command in the screen window:
(enb) log phy.signal=1
-
Run Remote API Command to Capture Data:
- Execute the command in the /root/enb directory to start binary data capture:
./ws.js enb --bin /tmp/lte_pusch.bin --bin-chan /tmp/lte_pusch_chan.bin --bin-re /tmp/lte_pusch_re.bin '{"message":"register","register":"pusch"}' -l
-
Note: The
-loption must be placed at the end of the command to prevent the websocket from closing immediately; otherwise, no data will be captured.
- Execute the command in the /root/enb directory to start binary data capture:
-
Binary Output Files:
-
--bin: Stores all data from the resource grid for the registered channel (both PUSCH user and DMRS data are saved).
-
The procedure focuses on enabling the appropriate logging and capture mechanisms prior to UE activation, and emphasizes the importance of correct command usage to ensure successful data collection.
Test Setup
You can use any kind of test setup that allow you to get UE attached to callbox.
Test 1 : LTE PUSCH
In this test, I will show you an example of collecting the binary data (RE data : Resource Element Data) for LTE PUSCH. In this tutorial, I will not explain the basic procedure like eNB/gNB configuration file, operation of lte service etc. It is assumed that the readers are already familiar with basic usage of Amarisoft Callbox.
Command
Before starting the capture (e.g, before powering on UE), you need to enable phy signal capture. You can enable it via WebGUI as shown here or you can enable it with command line command in screen window using log command as follows.
|
(enb) log phy.signal=1 |
Then Run the Remote API command ./ws.js enb --bin /tmp/lte_pusch.bin --bin-chan /tmp/lte_pusch_chan.bin --bin-re /tmp/lte_pusch_re.bin '{"message":"register","register":"pusch"}' -l at /root/enb directory. .
You would notice a few options for the binary files
-
--bin : the specified file store every data on the resource grid for the registerred channel. (for example, if you register pusch, the pusch data is composed of two different types of data, PUSCH user data and PUSCH DMRS data. in --bin option, the file saves both the user data and dmrs data)
-
--bin-re : the specified file store the user data only
-
--bin-chan : the specified file store the DMRS data only
Then you would get the initial print out as shown below and the remoteAPI will wait for the received signal
|
[root@CBC-2023010100 enb]# ./ws.js enb --bin /tmp/lte_pusch.bin --bin-chan /tmp/lte_pusch_chan.bin --bin-re /tmp/lte_pusch_re.bin '{"message":"register","register":"pusch"}' -l
WebSocket remote API tool version ##VERSION##, Copyright (C) 2012-2024 Amarisoft null [ '--bin', undefined, undefined, index: 0, input: '--bin', groups: undefined ] [ '--bin-chan', '-chan', 'chan', index: 0, input: '--bin-chan', groups: undefined ] [ '--bin-re', '-re', 're', index: 0, input: '--bin-re', groups: undefined ] null |
If the specified data(the data for the specified channel) is captured by gNB, you will get print as follows.
|
[root@CBC-2023010100 enb]# ./ws.js enb --bin /tmp/lte_pusch.bin --bin-chan /tmp/lte_pusch_chan.bin --bin-re /tmp/lte_pusch_re.bin '{"message":"register","register":"pusch"}' -l
WebSocket remote API tool version ##VERSION##, Copyright (C) 2012-2024 Amarisoft null [ '--bin', undefined, undefined, index: 0, input: '--bin', groups: undefined ] [ '--bin-chan', '-chan', 'chan', index: 0, input: '--bin-chan', groups: undefined ] [ '--bin-re', '-re', 're', index: 0, input: '--bin-re', groups: undefined ] null [0.003] ### Connected to 127.0.0.1:9001 [0.003] ### Ready: name=ENB, type=ENB, version=2024-02-01 [0.023] <== Send message register id#1 [0.034] ==> Message received { "message": "register", "message_id": "id#1", "time": 210.709, "utc": 1706903997.95 } [12.640] Binary log received Label: re Log: harq=7 prb=19:4 symb=0:13 CW0: tb_len=11 mod=2 rv_idx=0 cr=0.11 retx=0 crc=OK snr=25.3 epre=-95.3 ta=-0.6 re_symb=48,48,48,0,48,48,48,48,48,48,0,48,48 n_ant=2 chan_symb=3,10 Size: 2120 Type: 1 Len: 528 [12.640] Binary log received Label: chan Log: harq=7 prb=19:4 symb=0:13 CW0: tb_len=11 mod=2 rv_idx=0 cr=0.11 retx=0 crc=OK snr=25.3 epre=-95.3 ta=-0.6 re_symb=48,48,48,0,48,48,48,48,48,48,0,48,48 n_ant=2 chan_symb=3,10 Size: 1544 Type: 0 Len: 192 [12.649] Binary log received Label: re Log: harq=0 prb=2:3 symb=0:14 CW0: tb_len=161 mod=4 rv_idx=0 cr=0.76 retx=0 crc=OK snr=24.9 epre=-95.3 ta=-0.5 re_symb=36,36,36,0,36,36,36,36,36,36,0,36,36,36 n_ant=2 chan_symb=3,10 Size: 1736 Type: 1 Len: 432 [12.650] Binary log received Label: chan Log: harq=0 prb=2:3 symb=0:14 CW0: tb_len=161 mod=4 rv_idx=0 cr=0.76 retx=0 crc=OK snr=24.9 epre=-95.3 ta=-0.5 re_symb=36,36,36,0,36,36,36,36,36,36,0,36,36,36 n_ant=2 chan_symb=3,10 Size: 1160 Type: 0 Len: 144 [12.760] Binary log received Label: re Log: harq=0 prb=20:3 symb=0:14 CW0: tb_len=161 mod=4 rv_idx=0 cr=0.76 retx=0 crc=OK snr=25.4 epre=-95.4 ta=-0.5 re_symb=36,36,36,0,36,36,36,36,36,36,0,36,36,36 n_ant=2 chan_symb=3,10 Size: 1736 Type: 1 Len: 432 |
Press Ctrl+C when you want to stop the data capture.
Collecting the saved file
Once the data capture is complete, you would get the files saved as shown below.
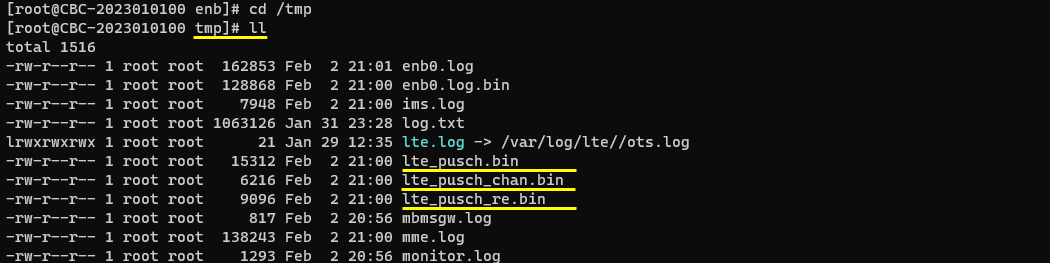
Post Processing
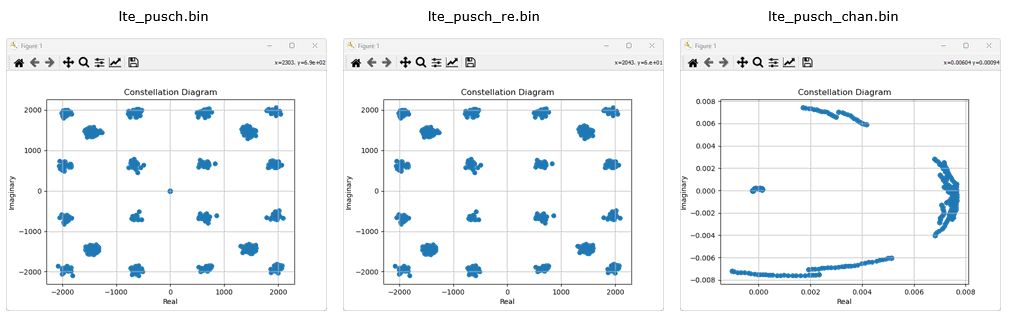
Once you capture the channel data that you wanted, you can write your own script to post process it as you desire. This is just a simple example of the post processing : plotting the captured data as a constellation.
Test 2 : LTE SRS
In this test, I will show you an example of collecting the binary data (RE data : Resource Element Data) for LTE SRS. In this tutorial, I will not explain the basic procedure like eNB/gNB configuration file, operation of lte service etc. It is assumed that the readers are already familiar with basic usage of Amarisoft Callbox.
Command
Before starting the capture (e.g, before powering on UE), you need to enable phy signal capture. You can enable it via WebGUI as shown here or you can enable it with command line command in screen window using log command as follows.
|
(enb) log phy.signal=1 |
Then Run the Remote API command ./ws_new.js enb --bin /tmp/lte_srs.bin '{"message":"register","register":"srs"}' -l at /root/enb directory. .
You would notice a few options for the binary files
-
--bin : the specified file store every data on the resource grid for the registerred signal. (NOTE : In case of SRS, you don't need to specify --bin-re, --bin-chan since SRS is made up of only one type of data)
Then you would get the initial print out as shown below and the remoteAPI will wait for the received signal
|
[root@CBC-2023010100 enb]# ./ws.js enb --bin /tmp/lte_srs.bin '{"message":"register","register":"srs"}' -l
WebSocket remote API tool version ##VERSION##, Copyright (C) 2012-2024 Amarisoft null [ '--bin', undefined, undefined, index: 0, input: '--bin', groups: undefined ] null |
Then you would get the initial print out as shown below and the remoteAPI will wait for the received signal
|
[root@CBC-2023010100 enb]# ./ws_new.js enb --bin /tmp/lte_srs.bin '{"message":"register","register":"srs"}' -l
WebSocket remote API tool version ##VERSION##, Copyright (C) 2012-2024 Amarisoft null [ '--bin', undefined, undefined, index: 0, input: '--bin', groups: undefined ] null [0.004] ### Connected to 127.0.0.1:9001 [0.004] ### Ready: name=ENB, type=ENB, version=2024-02-01 [0.024] <== Send message register id#1 [0.035] ==> Message received { "message": "register", "message_id": "id#1", "time": 200.369, "utc": 1706902810.038 } [84.110] Binary log received Label: chan Log: snr=24.6 epre=-97.5 ta=0.0 prb=6:4 symb=13:1 n_ant=2 chan_interp=2 Size: 392 Type: 0 Len: 48 [84.111] Binary log received Label: chan Log: snr=26.5 epre=-97.6 ta=0.0 prb=14:4 symb=13:1 n_ant=2 chan_interp=2 Size: 392 Type: 0 Len: 48 [84.220] Binary log received Label: chan Log: snr=23.6 epre=-98.2 ta=0.0 prb=2:4 symb=13:1 n_ant=2 chan_interp=2 Size: 392 Type: 0 Len: 48 [84.220] Binary log received Label: chan Log: snr=18.6 epre=-96.7 ta=0.0 prb=10:4 symb=13:1 n_ant=2 chan_interp=2 Size: 392 Type: 0 Len: 48 |
Press Ctrl+C when you want to stop the data capture.
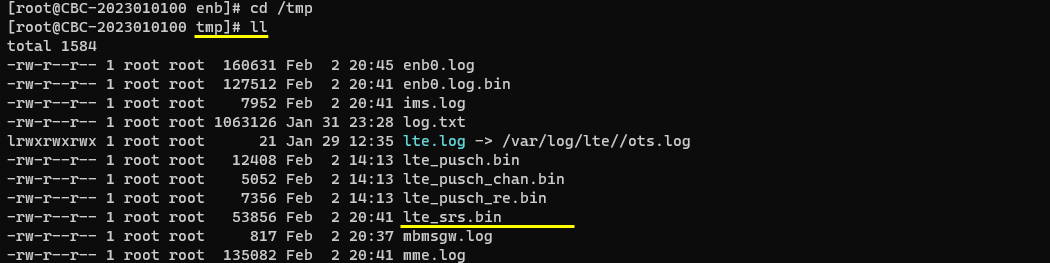
Collecting the saved file
Once the data capture is complete, you would get the files saved as shown below.
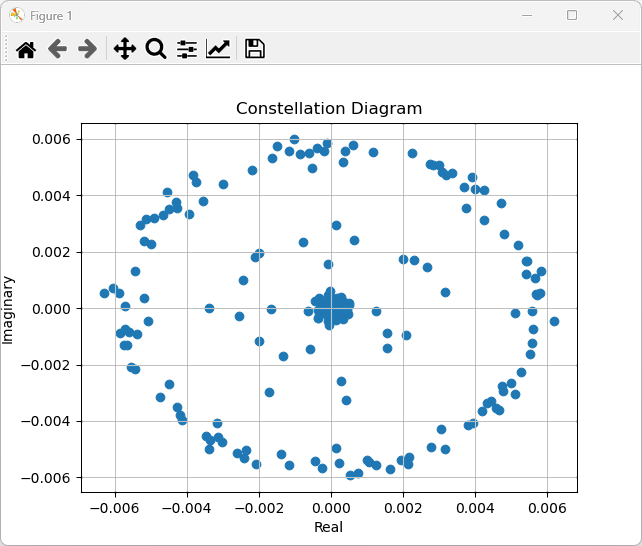
Post Processing
Once you capture the channel data that you wanted, you can write your own script to post process it as you desire. This is just a simple example of the post processing : plotting the captured data as a constellation.
Post Processing Script : Example
Following is an example of Python script that shows how to process the collected bin file. For simplicity, I tried to keep the script as simple as possible without doing any complicated processing or cosmetics. You may use this as a template and extend it as you like.
|
import struct import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import struct
def read_remoteAPI_bin(filename,nBlock=1,skipBlock=0): data = [] with open(filename, 'rb') as f: for iblock in range(nBlock): # read nBlock number of blocks. the 'block' mean the chunk of data recieved by one remoteAPI Event # for every set of captured channel/signal, 3 x 4 bytes(12 bytes) of header are added as follows. total_length = struct.unpack('I', f.read(4))[0] # read 4 bytes and convert to integer. data_type = struct.unpack('H', f.read(2))[0] # read 2 bytes and convert to integer data_label = struct.unpack('H', f.read(2))[0] # read 2 bytes and convert to integer block_length = struct.unpack('I', f.read(4))[0] # read 4 bytes and convert to integer
print(f'Size(Byte 0-3): {total_length}') print(f'Type(Byte 4-5): {data_type} - 0: 32 bits floats, 1: 16 bits integer, 2124: new data type') #print(f'Label(Byte 6-7): {data_label} - 1: chan, 2: re') print(f'Reserved(Byte 6-7): {data_label}') print(f'Len(Byte 8-11) Block Length = Number of complex number(I/Q Pair): {block_length}')
if data_type== 0: # 32 bits floats format_char = 'f' elif data_type == 1: # 16 bits integer format_char = 'h' elif data_type == 2124: # new data type format_char = 'f' # replace with correct format character else: raise ValueError('Invalid data type')
blockdata = [] for ire in range(block_length): re = struct.unpack(format_char, f.read(struct.calcsize(format_char)))[0] im = struct.unpack(format_char, f.read(struct.calcsize(format_char)))[0] blockdata.append(complex(re, im)) # create complex number
# do not return the read data if the block index is less than skipBlock. This is mainly for debugging purpose. skipBlock=0 means return all of the read data(blocks) if iblock >= skipBlock: data.append(blockdata) flat_data = [item for sublist in data for item in sublist] # flatten the list of lists. 'data' is 2D list. this is to make it 1D list
return flat_data
#bin_file = "bin\\remoteApi_bin\\lte_pusch_re.bin" bin_file = "bin\\remoteApi_bin\\lte_pusch_chan.bin" #bin_file = "bin\\remoteApi_bin\\lte_pusch.bin" #bin_file = "bin\\remoteApi_bin\\lte_srs.bin" RE_list = read_remoteAPI_bin(bin_file,nBlock=5 , skipBlock=0) print(f'total number of REs : {len(RE_list)}')
# Extract real and imaginary parts real = [x.real for x in RE_list] imag = [x.imag for x in RE_list]
# Create a scatter plot plt.scatter(real, imag) plt.xlabel('Real') plt.ylabel('Imaginary') plt.title('Constellation Diagram') plt.grid(True) plt.show() |