Out of the Box Test - UEsim NR SA
The purpose of this tutorial is to show you how to establish NR SA connection between a UEsim and Amari Callbox. It is assumed that you don't have any previous experience with Amari callbox. Basically this is same as the tutorial NR SA Attach. The only difference is that I uses UE Sim instead of a commercial UE.
UEsim stands for UE simulator and it is the product that can function as UE (User Equipment). It can simulates one or more UEs with a single box (single PC). It can simulator maximum over 1000 UEs in a single box. It supports full radio protocol stack from PHY to RRC/NAS and IP of UE, so that you can test eNB / gNB in full protocol stack from PHY to IP throughput.
UE sim support USIM parameters in purely software way meaning that you don't need any USIM card and you can configure USIM parameters for each and every UEs just by setting USIM parameters in configuration file. Regarding Authentication Algorithm, it support both 3GPP XOR algorithm and Milenage algorithm.
In terms of frequency and bands, Amarisoft UE sim support all the frequencies and bands defined in 3gpp. In terms of MIMO, it can support upto 4x4 MIMO. (
The purpose of this tutorial is to show how to operate UE sim for NR SA testing, not explain on the NR SA technology itself. If you are interested in NR SA technology itself with a commercial device, refer to this tutorial.
Table of Contents
Introduction
New Radio Standalone (NR SA) technology represents a foundational evolution in the 5G wireless ecosystem, enabling ultra-high-speed, low-latency, and massive connectivity capabilities required for next-generation mobile networks. Unlike the Non-Standalone (NSA) mode, NR SA operates independently of legacy LTE infrastructure, utilizing a 5G core network to deliver end-to-end 5G services. The integration of a UE simulator (UEsim) with the Amari Callbox provides a highly flexible and scalable testing environment for 5G NR SA scenarios. UEsim is engineered to emulate multiple user equipment devices within a single hardware setup, supporting comprehensive radio protocol stack implementation from the physical layer (PHY) up through RRC (Radio Resource Control), NAS (Non-Access Stratum), and IP layers. This allows for robust evaluation of gNB (next-generation NodeB) performance, protocol compliance, and throughput capabilities without the need for commercial user devices. The Amari Callbox, a versatile 5G network emulator, acts as the test network for NR SA connection establishment, authentication, and data transfer procedures. UEsim's software-configurable USIM parameters and support for both major authentication algorithms (3GPP XOR and Milenage) offer unparalleled flexibility in simulating diverse deployment scenarios. The system's support for a wide range of 3GPP-defined frequencies and MIMO configurations (up to 4x4, depending on hardware) further enhances its applicability for R&D, QA, and conformance testing. This tutorial focuses on the operational aspects of using UEsim with the Amari Callbox to establish and test NR SA connectivity, equipping users with the essential knowledge to perform effective 5G standalone tests in a laboratory setting.
-
Technology Context
- 5G NR SA Overview: NR SA enables direct communication with a 5G core network, providing enhanced features such as network slicing, ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), and massive machine-type communication (mMTC).
- Role of UEsim: UEsim functions as a virtualized user equipment, supporting full protocol stack operations required for 5G testing and eliminating the need for multiple physical devices.
- Amari Callbox Integration: The Amari Callbox acts as a network emulator, facilitating controlled NR SA environment testing for gNB and UE interaction.
-
Tutorial Relevance and Importance
- Provides step-by-step guidance on setting up NR SA connections using UEsim and Amari Callbox, a critical process for validating 5G deployments.
- Enables users to simulate large-scale UE scenarios, supporting over 1000 virtual UEs in a single test environment.
- Demonstrates flexibility in USIM parameter configuration and support for major authentication algorithms, allowing for diverse testing scenarios.
-
Learning Outcomes
- Understand how to configure and operate UEsim for NR SA testing.
- Gain experience establishing and monitoring 5G NR SA connections using Amari Callbox.
- Learn to perform authentication and data throughput testing in a simulated 5G environment.
- Acquire skills to adapt test scenarios for different frequency bands, MIMO configurations, and user profiles.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge
- Basic familiarity with 5G NR concepts and terminology (e.g., gNB, UE, 5G Core).
- Understanding of radio protocol stack layers (PHY, MAC, RLC, PDCP, RRC, NAS).
- Experience with network configuration, Linux command line, and basic IP networking is helpful but not mandatory.
- No previous experience with Amari Callbox or UEsim is required; the tutorial is suitable for beginners.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to setting up and testing a UE simulator (UEsim) with a network environment (using Amarisoft Callbox as an example). The procedures focus on configuration, service validation, operation in screen mode, UE attach process, log analysis, and specific configuration tips.
-
Test Setup:
- The test environment consists of a UEsim connected to a network provided by Amarisoft Callbox. The same procedures are applicable if using a live network or another test eNB/gNB.
-
Configuration Steps:
-
Key configuration parameters such as
cell_groups(includinggroup_type,multi_ue,cellssettings), andue_list(with parameters likesim_algo,imsi,opc,K, etc.) must be carefully set to match between UE sim and network. -
The tutorial references using default configurations (
ue-nr-sa.cfg,gnb-sa.cfg) without modification for Amarisoft; for other networks, matching configurations is required. -
SIM information (such as
imsiandK) must match on both UE and network side for successful authentication. - Duplex type, channel bandwidth, antenna configuration, frequency, and other radio parameters are highlighted as critical for NR cell setup and must be consistent between UEsim and network configuration.
-
Key configuration parameters such as
-
Service Validation:
-
Ensure the LTE service on the Callbox is running using
service lte status. -
If service is not running or issues are encountered, restart with
service lte restart.
-
Ensure the LTE service on the Callbox is running using
-
Screen Mode Operation:
-
Enter screen mode with
screen -rto monitor and interact with the UEsim and Callbox components. - RF information and current configuration details are displayed upon entering screen mode; verify that these match expected test setup.
- Switch between network components (e.g., MME, ENB, IMS) using Ctrl+A followed by the relevant number assigned on the screen.
-
Enter screen mode with
-
UE Attach Procedure:
- Begin by starting trace logging on the Callbox.
- Power on the UE in UEsim; observe detection of the cell and decoding of SIBs.
- Monitor PRACH and attach traces on the Callbox for successful initial attach process.
-
After attach completes, use commands like
cellsanduein Callbox screens to verify the UE’s registration and connection status. - If no UE information appears, troubleshoot for registration or IP allocation issues.
-
Log Analysis:
-
Analyze UE logs (e.g.,
/tmp/ue0.logon UEsim) to confirm each step of the registration process. -
Key steps to confirm in the log:
- Proper SIB decoding (mandatory SIB1 in NR).
- Trigger and completion of registration request and RRC connection procedures.
- Authentication and security procedures, including NAS and RRC security completion.
- UE capability enquiry and response (optional but typical in live networks).
- RRC connection reconfiguration and registration acceptance.
- Establishment and acceptance of PDU session with confirmation of assigned IP address.
- Log analysis helps pinpoint registration failures or configuration mismatches, especially authentication failures due to SIM parameter mismatches.
- For advanced or lower-layer troubleshooting, use the WebGUI as recommended.
-
Analyze UE logs (e.g.,
-
Tips:
-
SSB Frequency Configuration: Unlike commercial UEs, UEsim requires explicit configuration of the SSB frequency. This can be determined using the
cell phycommand on Callbox or by obtaining the information from the gNB provider.
-
SSB Frequency Configuration: Unlike commercial UEs, UEsim requires explicit configuration of the SSB frequency. This can be determined using the
The tutorial emphasizes the importance of configuration matching, step-by-step verification, and log analysis to ensure successful registration and operation of UEsim in a test network environment.
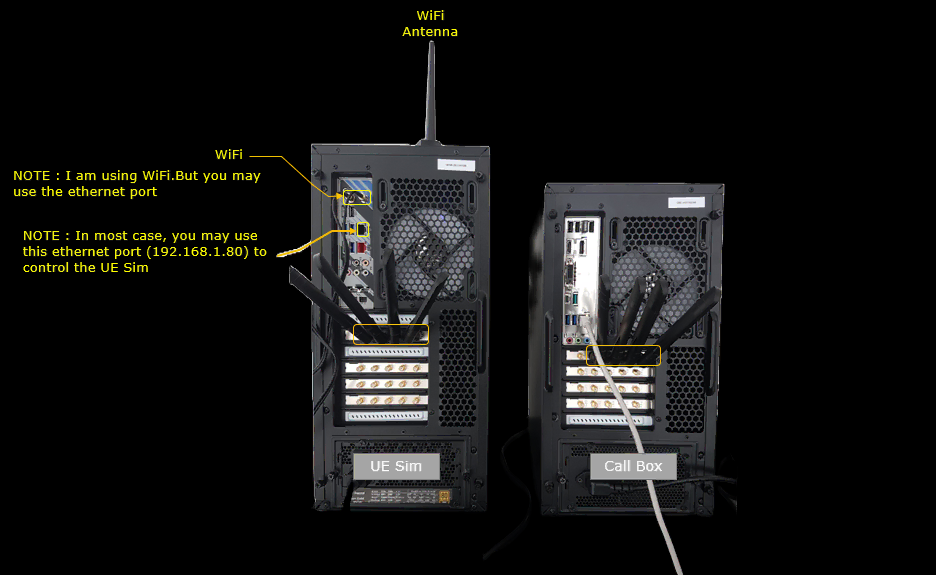
Test Setup
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below. In this setup, I used Amarisoft Callbox as the network for the UEsim to get connected. But for most UEsim users live network or their own test eNB/gNB would be used for the network.

Key Configuration Parameters
Followings are important configuration parameters for this tutorial. You may click on the items for the descriptions from Amarisoft documents.
- cell_groups
- group_type
- multi_ue
- cells
- ue_list : In this link, you will get the descriptions for all the items listed below
- sim_algo
- imsi
- opc
- amf
- sqn
- K
- as_release
- ue_category
- tun_setup_script
Configuration
An important thing in using UE sim is to do proper matching between UE sim configuration and Call box configuration In this tutorial, I used the ue-nr-sa.cfg and gnb-sa.cfg without any change
If you use other Network (e.g, other network simulator or real network), you have to make it sure to configure UE sim according to the settings on network side
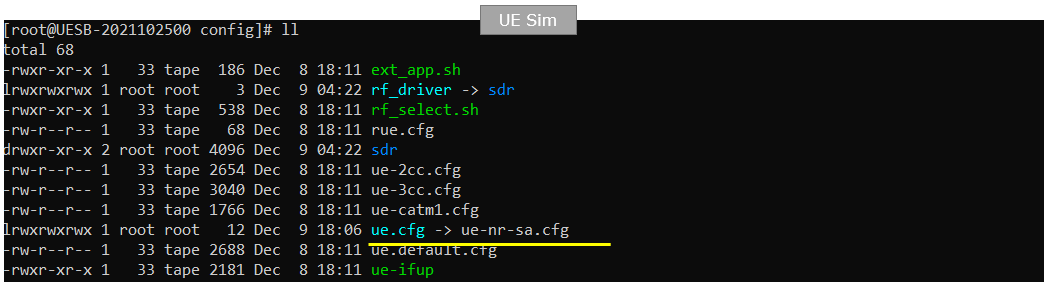
On gNB side, gnb-sa.cfg is used as eNB configuration (enb.cfg).
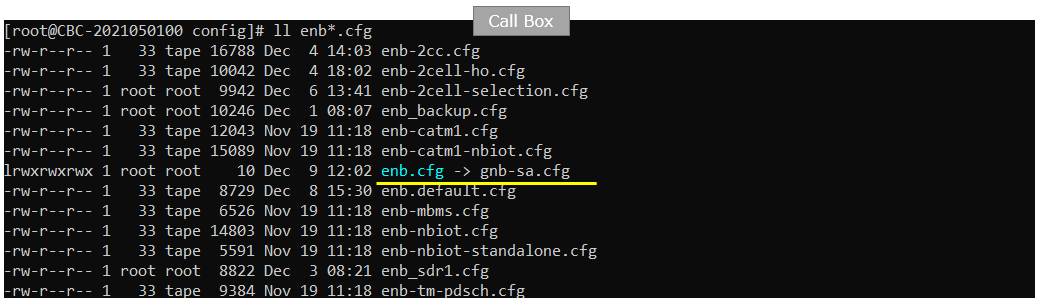
On eNB core network side, mme-ims.cfg is used for core network configuration (mme.cfg) and ims.default.cfg is used for ims configuration (ims.cfg). ue_db-ims.cfg is the file that carries UE database (subscriber information) on network side. This file is usually included within mme.cfg
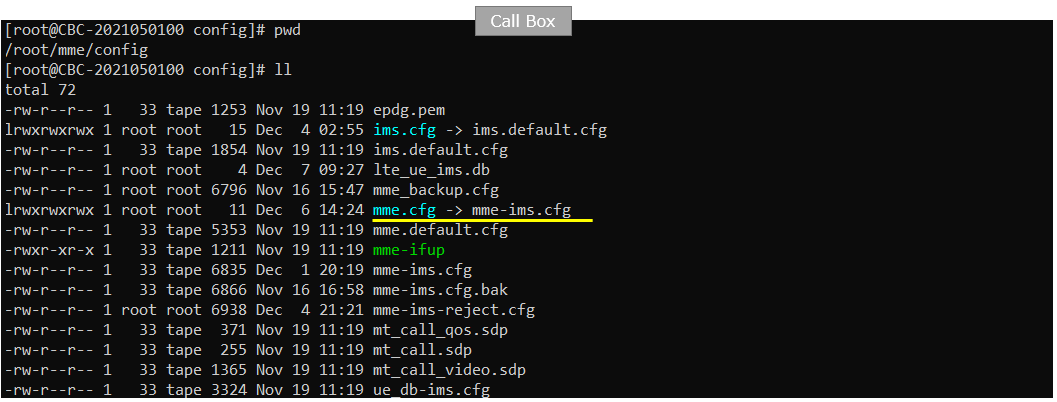
You would see following in /root/mme/config/ims-ims.cfg file on Callbox

In this tutorial, following SIM information will be used. Make it sure to configure the same parameters on UE side as well. (NOTE : this is the contents of ue_db-ims.cfg)
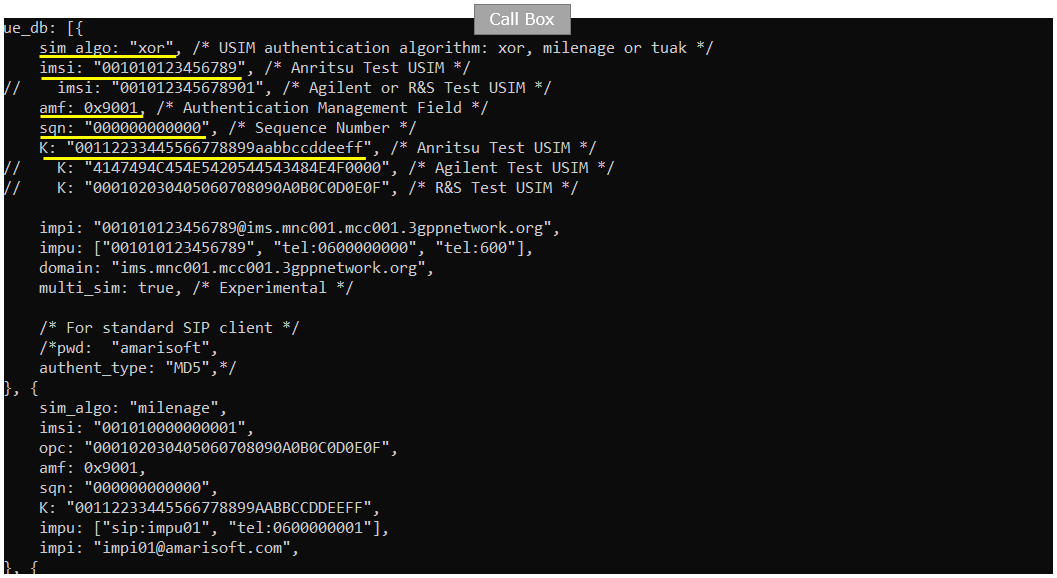
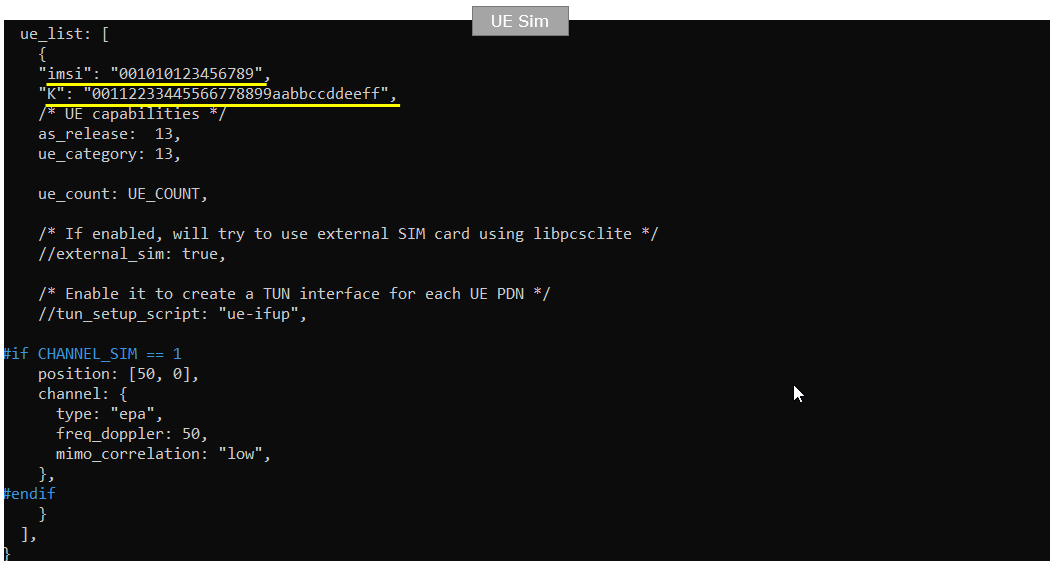
Make it sure that imsi and K value in this file matches the value on enb side shown in previous slide (NOTE : this is the contents of ue-nr-sa.cfg)
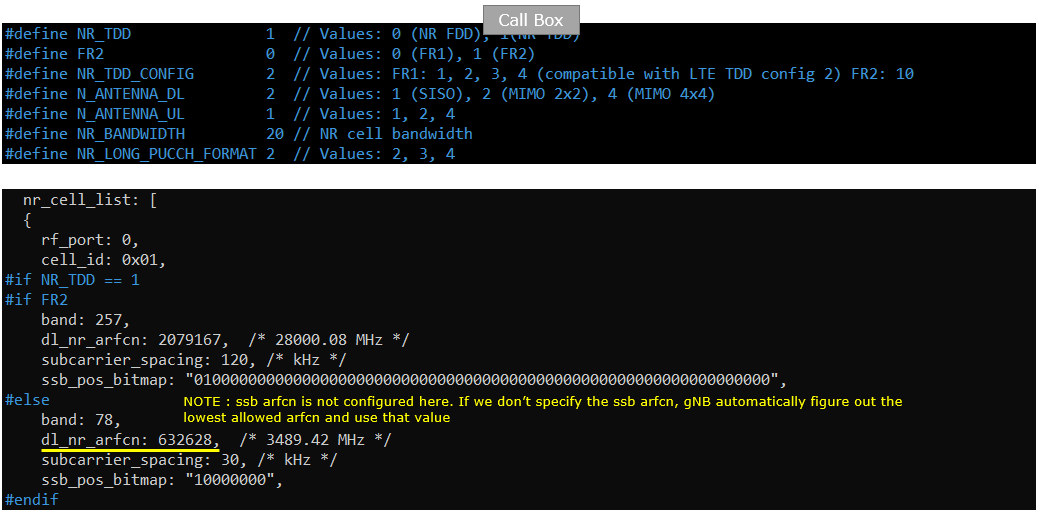
Following is the configuration on Callbox (gnb-sa.cfg). In this tutorial, Duplex type of NR SA is set to TDD (i.e, TDD 1) and the channel bandwidth ise set to 20 Mhz(i.e, N_RB_DL 25). And antenna configuration is set to be 2x2 MIMO(N_ANTENNA_DL 2). For the basic NR cell configurations, band is set to 78 (i.e, n78) and the frequency (dl_nr_arfcn) is set to 632628. When you configure NR cell, pay attention to subcarrier_spacing and ssb_pos_bitmap value because the allowed values for these parameters gets different depending FR and band.
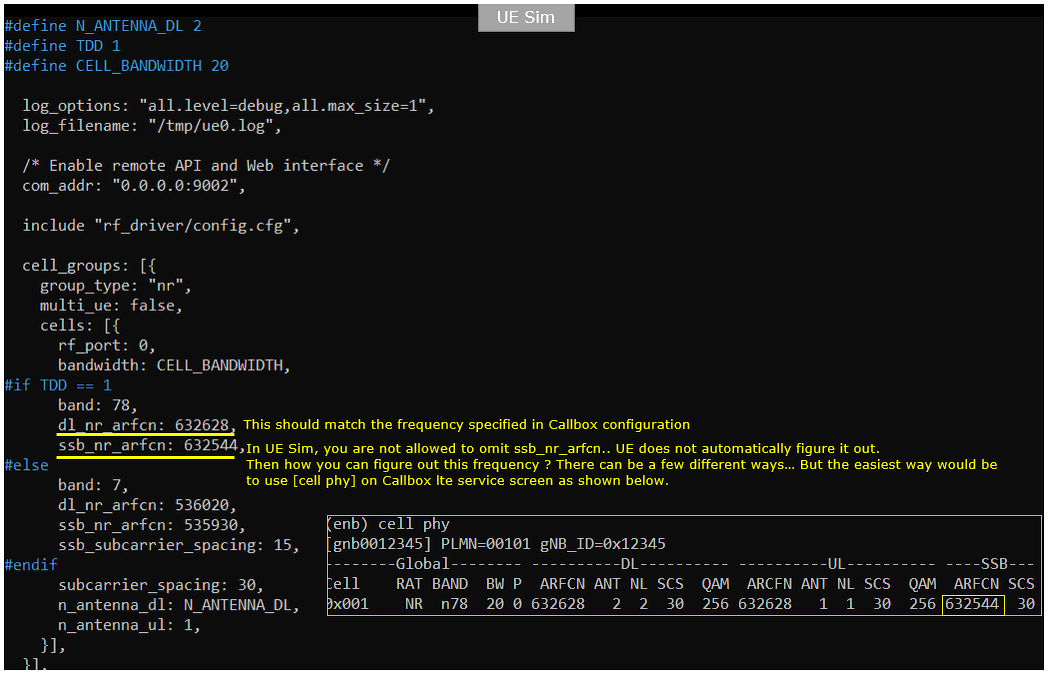
Following is the configuration on Callbox (ue-nr-sa.cfg). Duplex type of LTE on UEsim is set to TDD (i.e, TDD 1) and the channel bandwidth ise set to 20 Mhz(i.e, CELL_BANDWIDTH 5). And antenna configuration is set to be 2x2 MIMO(N_ANTENNA_DL 2). The important things to configure are band, dl_nr_arfcn, ssb_nr_arfcn which are n78, 632628 and 632544 respectively. These should exactly match the settings on gNB configuration.
Check if LTE service is Running
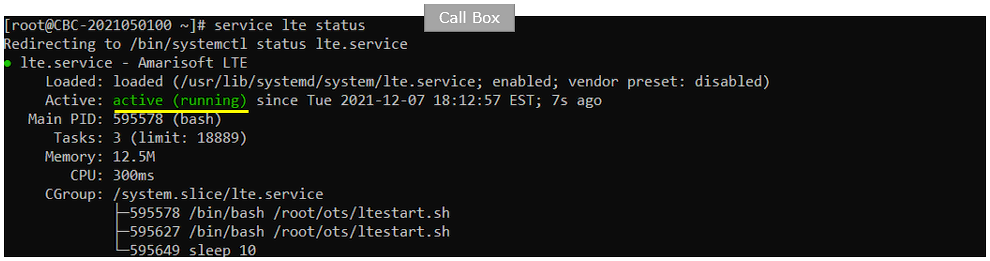
Whatever you want to test, the first thing you need to do is that call box program (LTE Service) is running. You can check on the execution status of the call box program by running following command and you should get the result as shown below
# service lte status
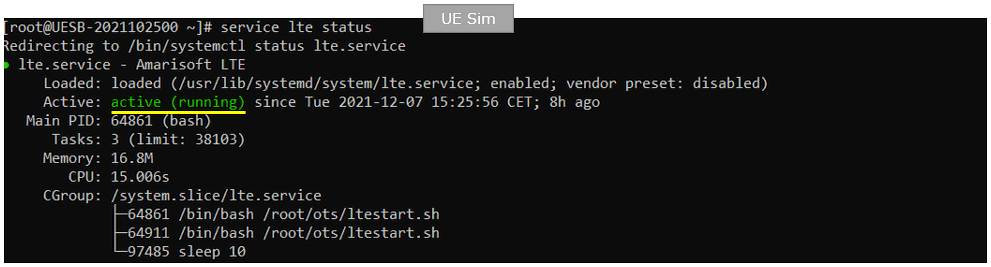
Same as in UEsim, make it sure that Active is indicated as acitive (running) on UEsim when you run "service lte status". If you don't get this status, try 'service lte restart' and then check the status again.
NOTE : Getting this result is pre-requisite for Call Box Operation, but this result itself does not guarantee the normal operation. If you see some unexpected issues. You may restart the call box with following command
# service lte restart
Getting into Screen Mode
If it is confirmed that the lte service is running, go to screen mode by running 'screen -r' and follow through the steps as shown below. The steps shown here is the procedure that you would use for almost every test and it is highly recommended to get familiar with these steps. For further commands you can use in this screen mode, refer to the tutorial : Command Line Command
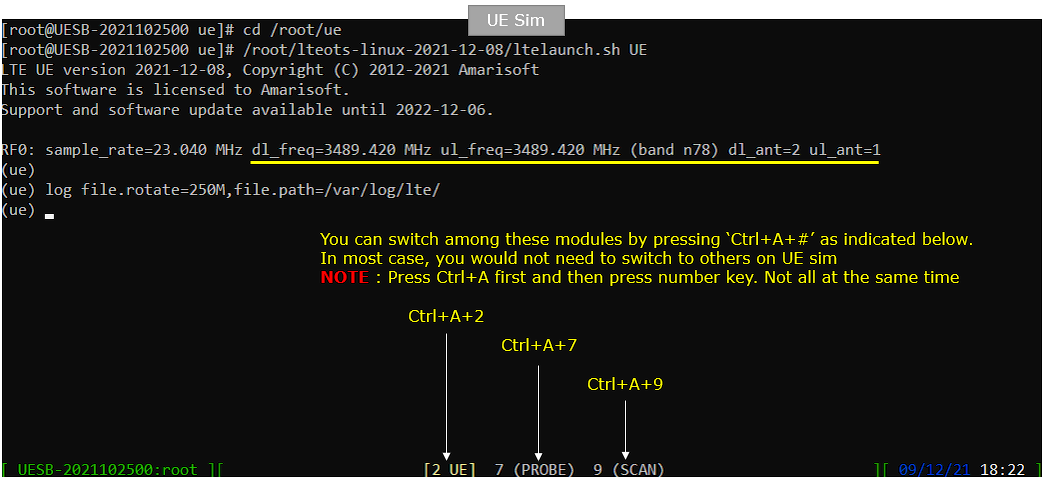
Run following command on UE sim

You will get the screen as shown below. there are some important information provided without running any specific command. It provides RF information showing the sample_rate, dl_freq, ul_freq, band, dl_ant, ul_ant that gives you very fundamental RF information. Check out the details of these info and see if the RF is configured as you intended.
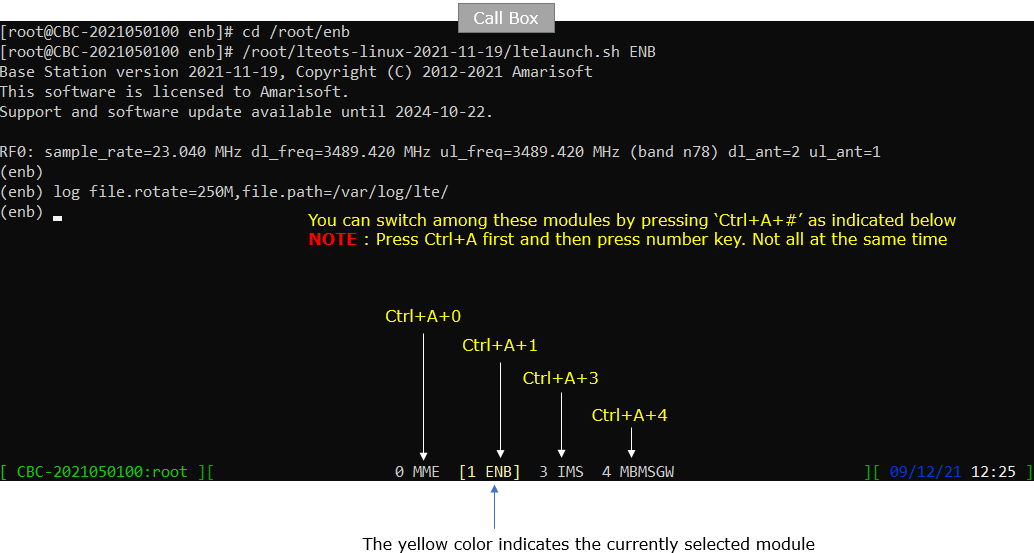
Run following command on Callbox

You will get the screen as shown below. This screen shows all the network components installed in the callbox. In this tutorial, it indicates MME, ENB, IMS, MBMSGW are installed in the callbox.
You would see a number before each component name. With Ctrl+A and the number before the component name, you can switch to command line window for the specific component. For example, if you press Ctrl+A+1, the command line window switches to ENB and if you press Ctrl+A+0, the command line window switches to MME and so on.
Attach UE
Now perform UE attach procedure. This would be a little bit busy process since you need to switch back and forth between Callbox screen and UEsim screen.
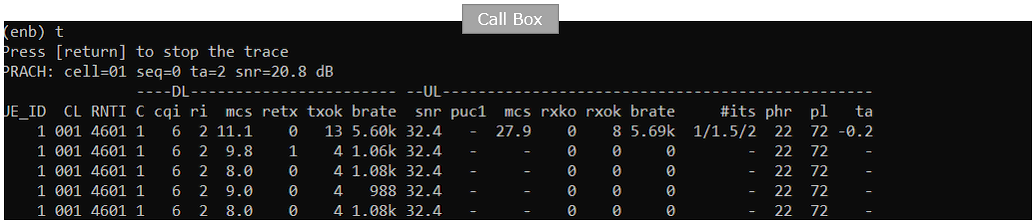
Start tracing on Callbox

power_on UE on UE sim.

You will see following message once UE detect the cell and decoded SIBs.

Once UE completed SIB decoding and perform initial attach, you will see following trace on Callbox screen. If you started 't' command before you powe on UE, you will get the traces for PRACH attempt. The presence of PRACH trace can be a good troubleshooting indicator for initial attach problem. If PRACH is properly received and the entire RACH process is completed, it is highly likely that the initial attach gets completed and start getting traffic log. Regarding the details on the meaning of each column of this log and how to use the information for troubleshoot, refer to this tutorial.
When the initial attach completed, you can check on the cell information to which the UE sim is registered to with 'cells' command.

You can get the ue information that is in connection with gNB on Callbox with 'ue' command in (enb) screen.

You can get the ue information that is in connection with gNB on Callbox with 'ue' command in (mme) screen.

Log Analysis
In this section, you will see how to confirm if UE registration is complete from trace log. You can use the same method to find any issues (e.g, registration failure) for troubleshooting. When UE registration fails, you may use this tutorial to figure out the point of the failure and troubleshoot
Open /tmp/ue0.log on UEsim using any text editor. I am using nano in this tutorial. (
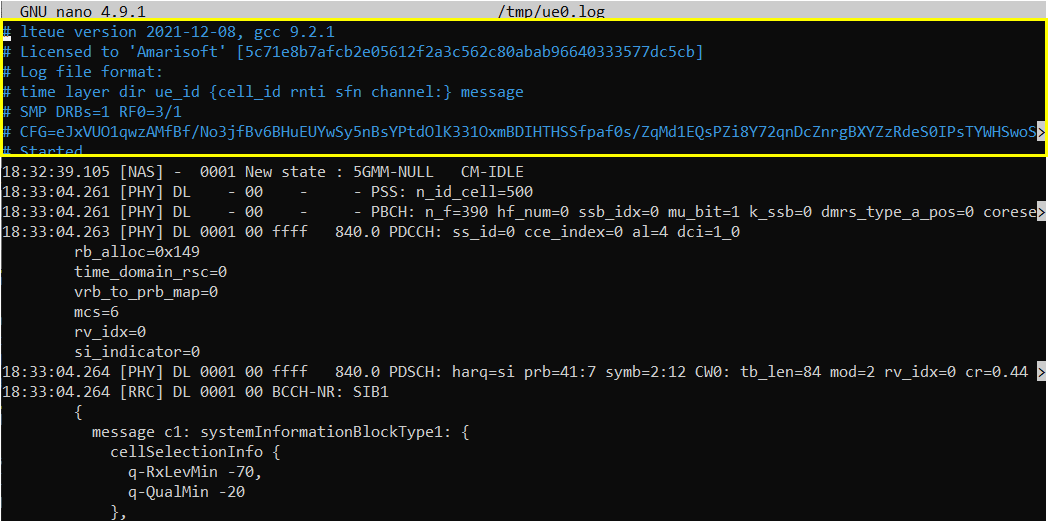
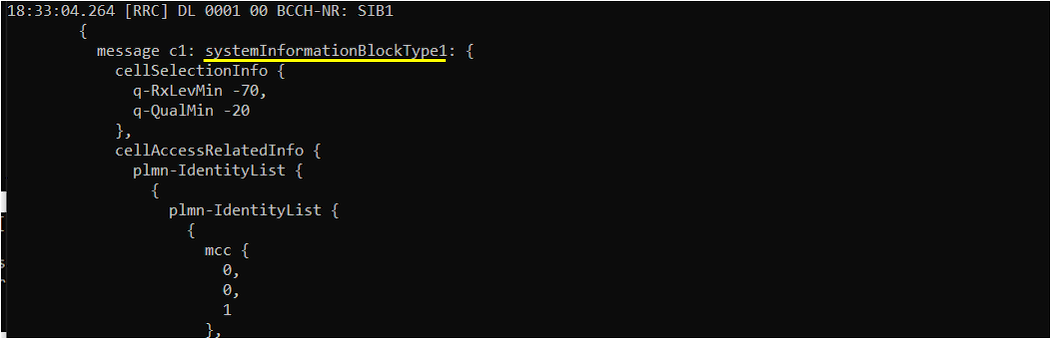
Since this is UE side log, it would be good to check if SIBs are received and decoded properly. In NR, only SIB1 are mandatory to be received otherwise UE would not try attach.
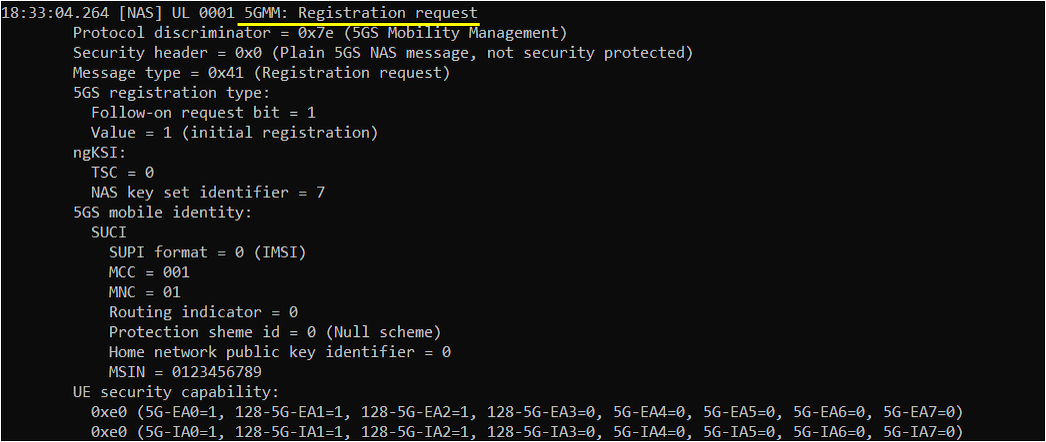
Once SIB is properly received and decoded, UE side attach is started first from NAS layer by triggering 5GMM:Registration request. If you look into gNB log, this message will be received after RRC setup, but in UE side log you would see this message before RRC process start.
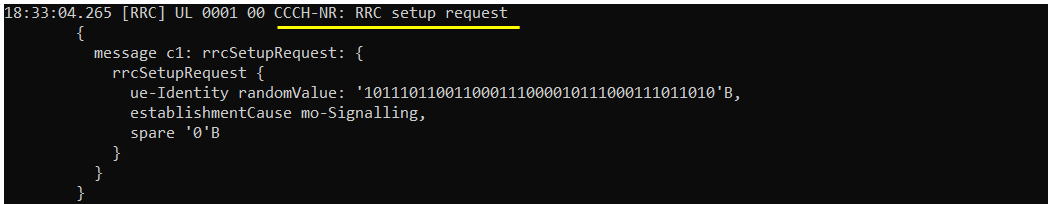
Once triggered by NAS layer, UE triggers RRC Connection Request and UE is supposed to send RRC setup request.
Then make it sure that UE received RRC Setup.
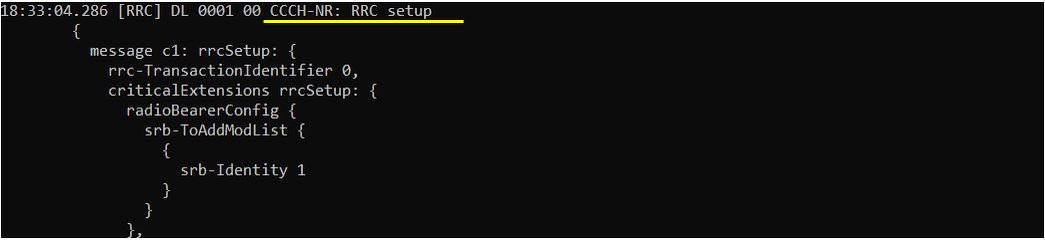
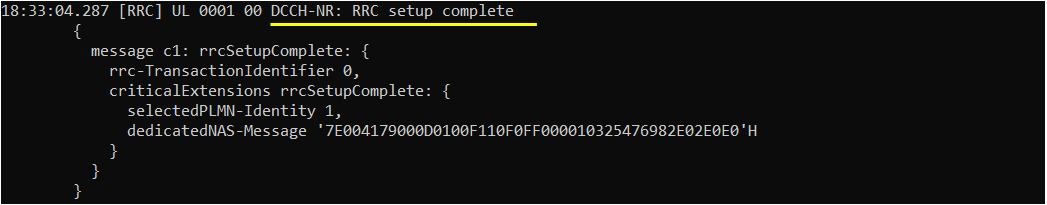
Next step you need to check is to see whether the UE send RRC Connection Setup Complete or not. If you see this message, it mean that RrcSetup is completed on UE side. If UE fails with RrcSetup, it usually triggers RACH procedure again and send RrcConnectionRequest.
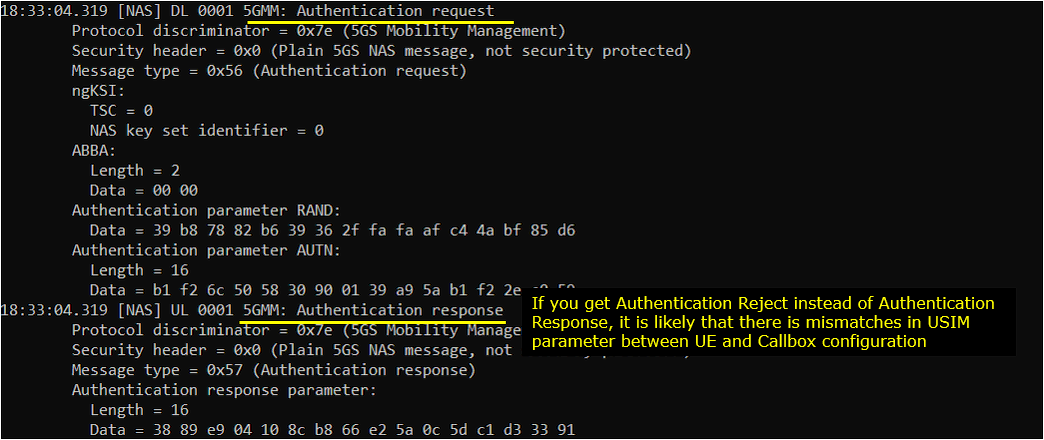
Once RRC Setup Procedure is complete, eNB initiate the Authentication process. If the authentication is confirmed on UE side, UE send Authentication Response message. If you see the Authentication Failure instead of Authentication Response, it usually implies that there is SIM parameter mismatch between USIM and eNB SIM parameter setting. In most case, K value mismatch would be the culprit of the failure. Check ue_db.cfg or ue_db-ims.cfg and make it sure it has authentication parameter that matches DUT's USIM parameter.
Once Authentication process is complete, gNB/5G Core starts Security checkup. There are two different level of security checkup. The first one is NAS Security and the second one is RRC Security.
If you see 5GMM:Security mode complete message recieved, it indicates that NAS Security is complete.
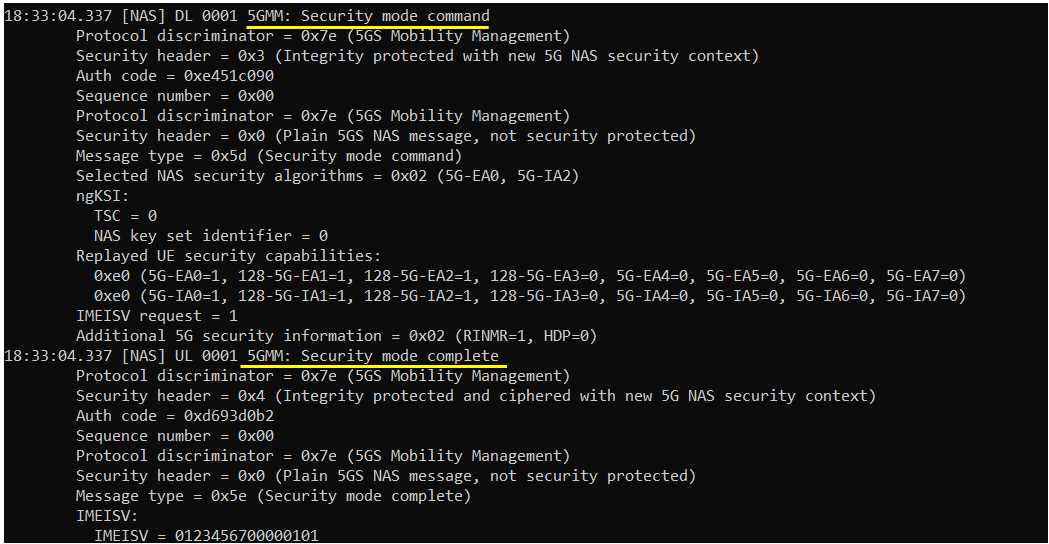
If you see DCCH:Security mode complete message recieved, it indicates that RRC Security is complete.
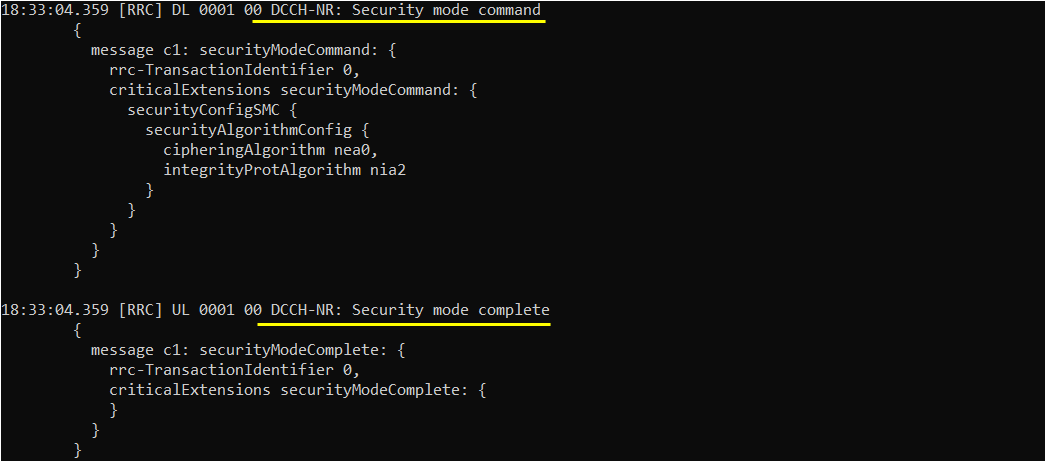
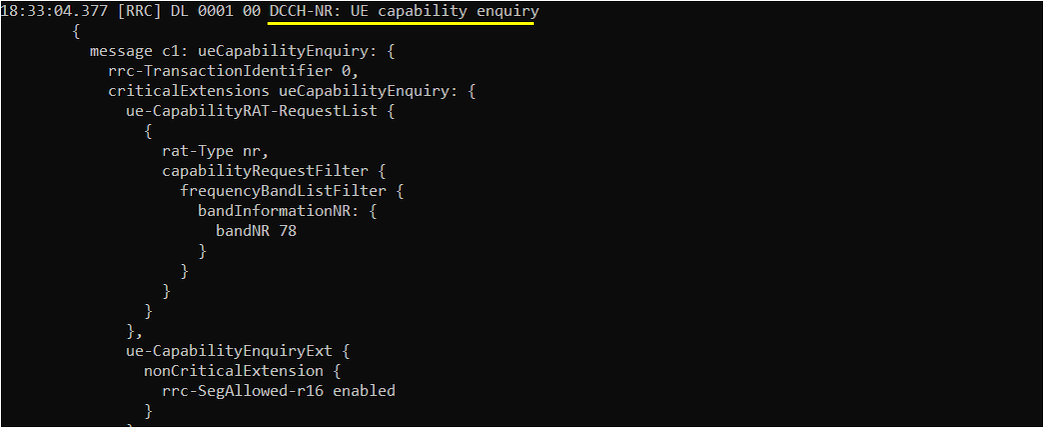
Then Network (eNB) send UE capability enquiry message to check on various features supported by the UE. This is an optional step, but every live network would go through this procedure.
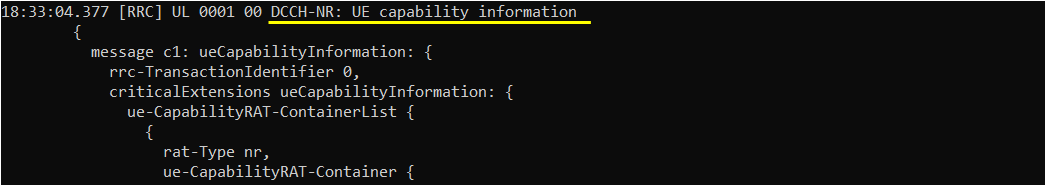
Once UE recieves UE capability information, it is supposed to notify about the featurs it supports via UE capability information message.
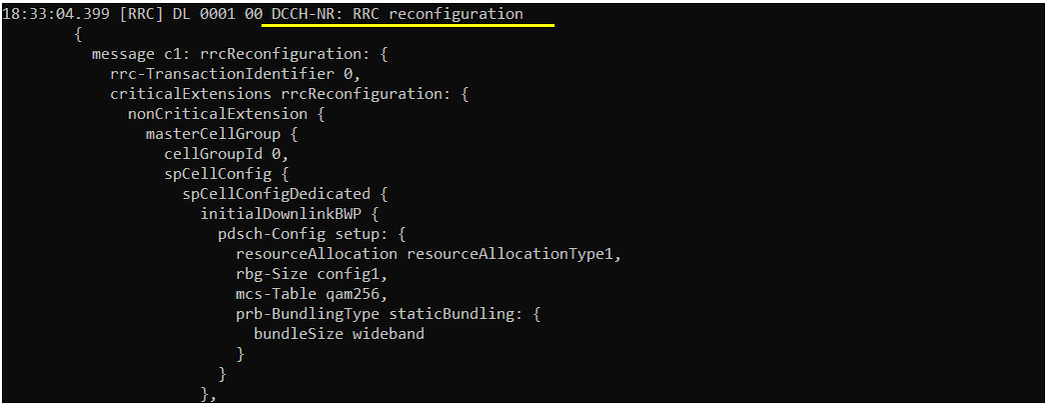
Once Authentication and Security checkup is done, eNB initiate RRC Connection Reconfiguration.
If the Rrc Connection Reconfiguration is properly processed on UE side, UE send RRC Connection Reconfiguration Complete.
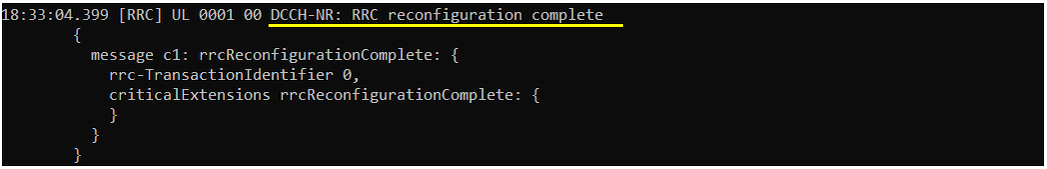
Once all the authentication and security check is done, Network sends 5GMM: Registration accept.
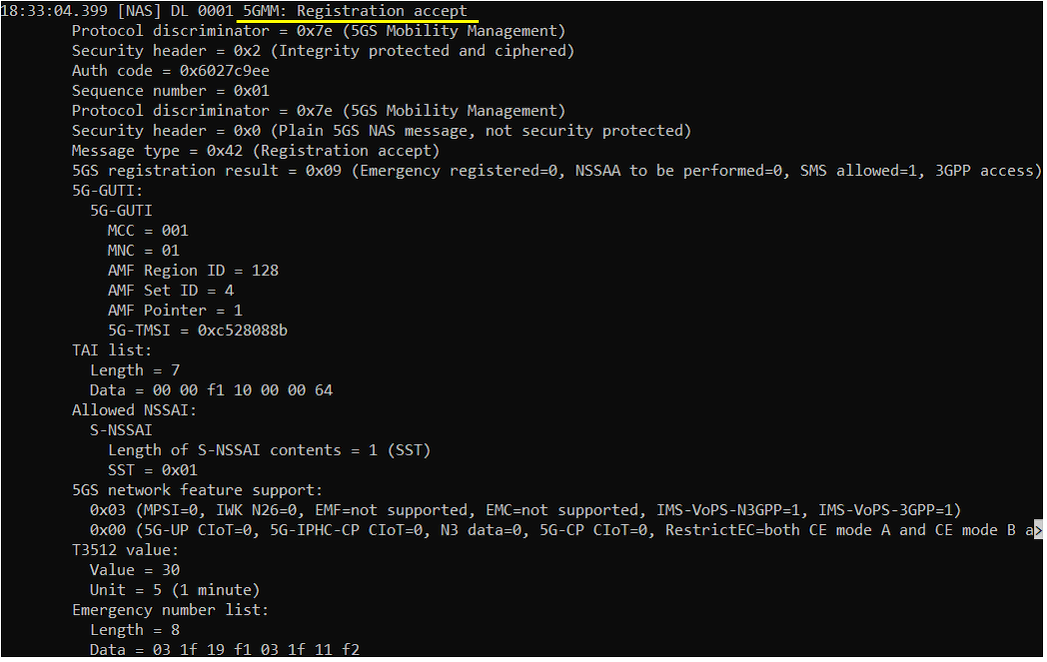
Once all the required RRC and NAS Procedure for initial registration is complete, UE is supposed to send 5GMM:Registration complete message.
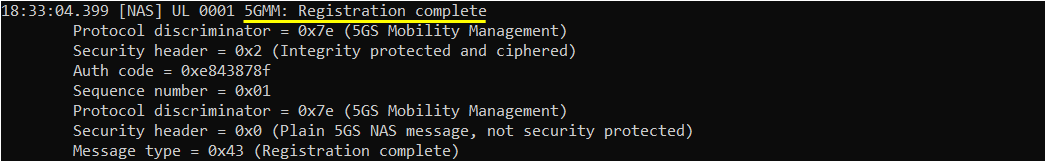
Once all the initial registration is complete, UE is supposed to initiate PDU Sesttion Establishment.
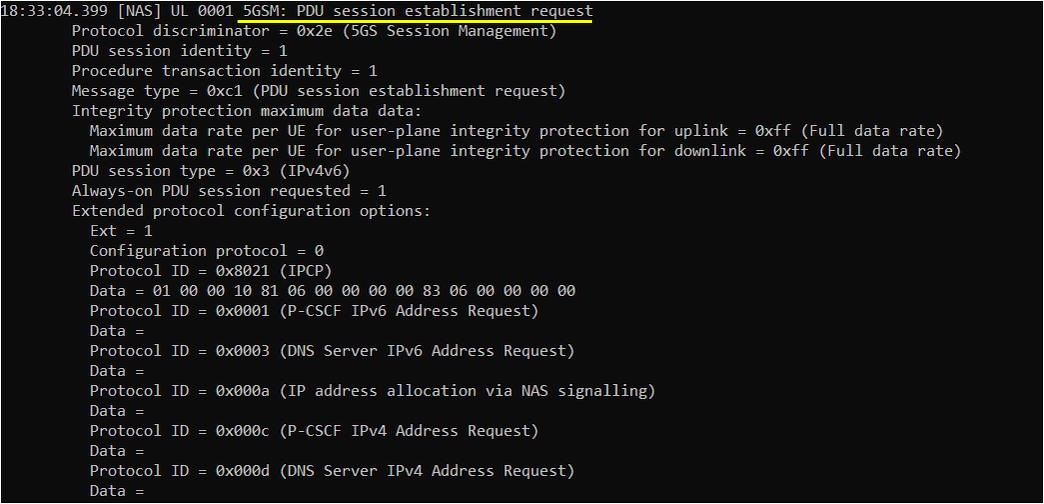
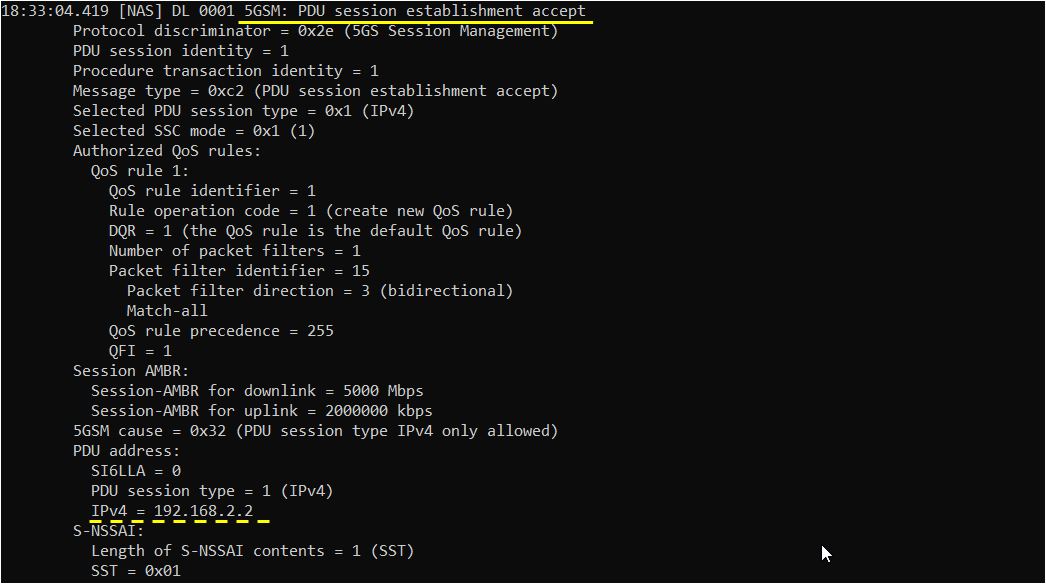
Network is supposed to send PDU Session establishment accept message when the request from UE is acceptable. One of the important information you would check in this message is IP address. This IP address is the one assigned to the UE.
Tips
Finding SSB Frequency for UEsim Configuration
For commercial UE (like mobile phone) you don't have to care much about finding the SSB frequency yourself because UE perform channel scan and cell search and finally figure out SSB frequency on its own, but UEsim does not perform this kind of procedure and you need to configure explicitely the SSB frequency in UEsim configuration file. The easiest way to figure out the SSB frequency would be to use 'cell phy' command in Callbox (end) screen as shown below. (If you are using other network (i.e, non-Amari Callbox), you need to figure it out from the party who supports the gNB).
