Channel Simulator - UEsim
This tutorial is about how to configure channel simulator for UEsim and verify it using Amarisoft Callbox. Applying channel simulation to UEsim mean Uplink channel simulation. The channel model you can apply for UEsim is listed as follows
- 3GPP defined Fading Profile for LTE and NR (
NOTE : Amarisoft support TDL model only, does not support CDL) - UE distance simulation (Near / Far Simulation)
- Loss Model simulation (Modeling A + B * log10(d) )
The most common channel simulation we do is Near / Far modeling as illustrated below. In this scenario, UEsim simulator a UE moving toward a certain direction at a constant speed and observe UL channel power (e.g, PUSCH, PUCCH power) and throughput from gNB.
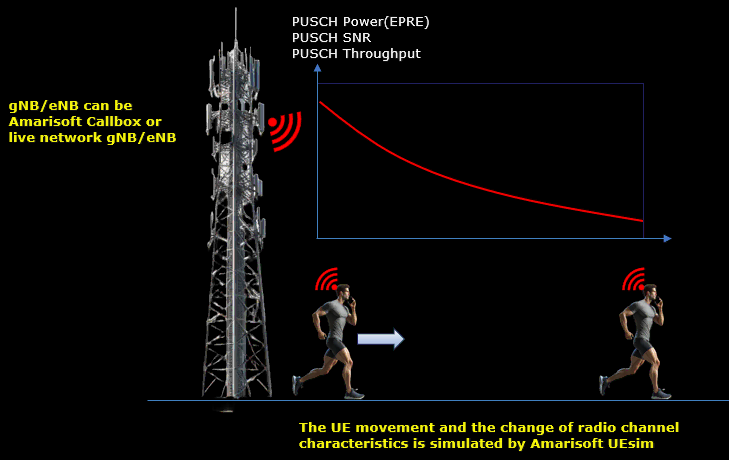
Table of Contents
- Channel Simulator - UEsim
Introduction
Channel simulation is a fundamental aspect in evaluating and validating the performance of User Equipment simulators (UEsim) within wireless communication test environments, such as those provided by Amarisoft Callbox. Accurate channel simulation allows engineers and researchers to mimic real-world radio propagation phenomena—such as fading, path loss, and distance-dependent signal attenuation—thereby enabling comprehensive testing of uplink (UL) channel conditions. In the context of LTE and 5G NR technologies, channel models such as the 3GPP-defined Fading Profiles (specifically, the Tapped Delay Line or TDL models) are used to replicate multipath fading effects according to standardized scenarios. Amarisoft Callbox supports the implementation of these TDL channel models, but not Cluster Delay Line (CDL) models. Additionally, channel simulation encompasses UE distance modeling (Near/Far simulation) and path loss modeling, where signal attenuation is mathematically represented as a function of distance (e.g., using the model: Loss = A + B * log10(d)). The most prevalent use case involves simulating a UE's movement along a trajectory at constant speed, observing the resulting variations in UL channel power (such as PUSCH and PUCCH) and throughput as measured by the gNB. This provides critical insights into system behavior under controlled, repeatable conditions, and directly supports development, troubleshooting, and optimization of wireless systems.
-
Context and Scope
- Channel simulation in UEsim is crucial for reproducing realistic radio environments and uplink propagation effects in laboratory settings.
- Amarisoft Callbox serves as a comprehensive test platform, supporting the configuration and verification of channel models for LTE and NR.
- Focus is placed on uplink channel simulation, specifically utilizing 3GPP-defined TDL fading profiles, UE distance simulation, and loss models.
-
Relevance and Importance
- Enables robust testing of UEs under a wide range of real-world channel conditions without the need for field trials.
- Supports rapid validation, regression testing, and performance optimization for both device and network-side algorithms.
- Provides a controlled, repeatable environment for observing uplink power and throughput metrics as a function of user mobility and distance.
-
Tutorial Outcomes
- Learn how to configure uplink channel simulation in UEsim using Amarisoft Callbox.
- Apply TDL-based fading profiles and distance-based loss models to emulate realistic propagation scenarios.
- Verify and analyze UL channel power and throughput variations as the simulated UE moves within the virtual test environment.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge and Skills
- Basic understanding of LTE and 5G NR radio access technologies, including uplink and downlink transmission principles.
- Familiarity with 3GPP channel models (especially TDL fading profiles) and path loss concepts.
- Operational knowledge of Amarisoft Callbox and UEsim configuration workflows.
- Ability to interpret radio performance metrics such as PUSCH/PUCCH power and throughput statistics.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial outlines four distinct low-layer wireless channel simulation and mobility tests using Amarisoft’s test environment, focusing on both single and multiple UE scenarios. Each test involves specific configurations and procedures to assess channel characteristics, link adaptation, and handover mechanisms under various simulated radio conditions.
-
Test 1: Basic AWGN Channel
- Objective: Simulate a UE moving away from a cell at constant speed under an Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) radio channel.
- Configuration Steps:
- Use modified configuration files (gnb-sa-channel-sim.cfg for gNB, ue-nr-sa-chan-sim.cfg for UE).
- Set NR_BANDWIDTH to 40 for gNB.
- Enable channel_sim and delay_sim in the cell group.
- Specify UE initial position, antenna type ("isotropic"), and reference signal power (from SIB1).
- Configure ul_power_attenuation and noise floor.
- Set channel type to awgn in UE configuration.
- Test Procedure:
- Verify cell configuration via 'cell phy' command.
- Start LTE service on both gNB and UEsim, ensuring UE attaches successfully.
- Move UE at 10 km/h away from cell using Remote API: ../ws.js ue '{"message" : "ue_move", "ue_id" : 1, "speed" : 10, "direction" : 0}'.
- Monitor physical layer measurements (UL SNR, MCS, bitrate, PHR, pathloss) in gNB logs as UE moves.
- Analyze downlink effects (SINR, RSRP) and perform log analysis on Callbox or UEsim logs.
-
Test 2: 3GPP Profile - EPA Channel
- Objective: Simulate UE movement under the 3GPP Extended Pedestrian A (EPA) fading channel model.
- Configuration Steps:
- Use gnb-sa-channel-sim.cfg (gNB) and ue-nr-sa-chan-sim-epa.cfg (UE).
- Set NR_BANDWIDTH to 40 for gNB.
- Enable channel simulation and set UE position and antenna characteristics.
- Configure UE channel type as epa with freq_doppler: 50 and mimo_correlation: "low".
- Test Procedure:
- Check cell configuration and start LTE service.
- Move UE at 10 km/h away from the cell using Remote API.
- Observe and record changes in physical layer measurements (UL SNR, MCS, bitrate, PHR, pathloss) and downlink parameters (SINR, RSRP).
-
Test 3: Triggering PingPong Handover by Channel Simulator - LTE/Single UE
- Objective: Simulate a single UE moving back and forth between two cells, triggering repeated “ping-pong” handovers using a 3GPP EVA channel model.
- Configuration Steps:
- Use enb-pingpong-ho.cfg (eNB) and ue-pingpong-ho.cfg (UE).
- Set N_CELL to 2 and enable TDD.
- Assign different frequencies to each cell for inter-frequency handover.
- Configure neighbor cell lists for both cells.
- Set up measurement-based handover conditions (event A3, measurement gaps) in cell_default block.
- Enable CHANNEL_SIM and set initial UE position at midpoint between cells.
- Configure UE to move at 5 km/h, “bounce” at max/min distances, and use eva channel model.
- Test Procedure:
- Start callbox and UEsim, power on UE.
- Allow UE to move automatically between the two cells, observing handover events.
- Monitor RSRP, SNR, CQI, Rank, Timing Advance, TPC command, and Power Headroom plots for discontinuities at handover points.
- Analyze protocol sequence in logs: measurement report triggering (A2, A3 events), measurement gap activation, handover command and reconfiguration, and confirmation of handover execution.
-
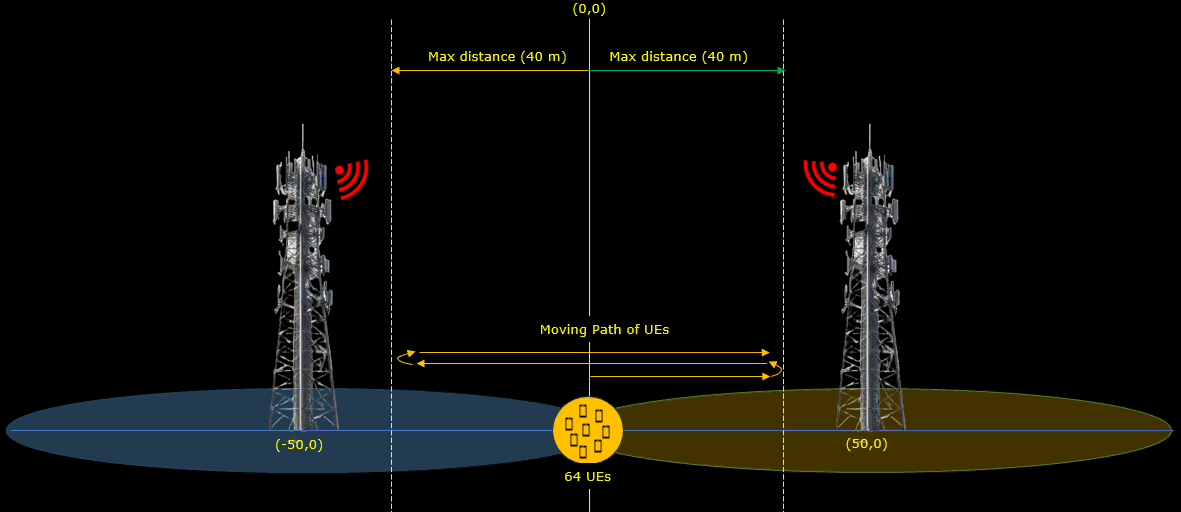
Test 4: Triggering PingPong Handover by Channel Simulator - LTE/64 UE
- Objective: Evaluate the gNB’s ability to handle mass handovers by repeating the Test 3 scenario with 64 UEs.
- Configuration Steps:
- Use gnb-sa-pingpong-ho-64ue.cfg (gNB), mme-ims-64.cfg (includes ue_db_64-UE.cfg for USIM info), and ue-nr-sa-pingpong-ho-64ue.cfg (UEs).
- Set cell bandwidth to 100 MHz (adjustable for hardware capability).
- Configure inter-frequency handover between two cells as in Test 3.
- Include USIM data for 64 UEs in UE configuration.
- Set UE movement and channel simulation parameters (direction, bounce, speed: 5 km/h, channel: epa).
- Test Procedure:
- Start the scenario using UEsim WebGUI, auto-generating USIM parameters.
- Monitor registration and handover events for all 64 UEs.
- Analyze high-level KPIs (throughput, error rates, SNR), and track the number of UEs per cell over time to evaluate handover performance.
- Review detailed log analysis for registration, measurement reporting, handover triggering, and completion for each UE.
Each test requires precise configuration of the channel simulator, UE movement parameters, and handover conditions. Measurements focus on both uplink and downlink physical parameters, as well as protocol-level behavior, to thoroughly evaluate system performance under controlled mobility and fading scenarios.
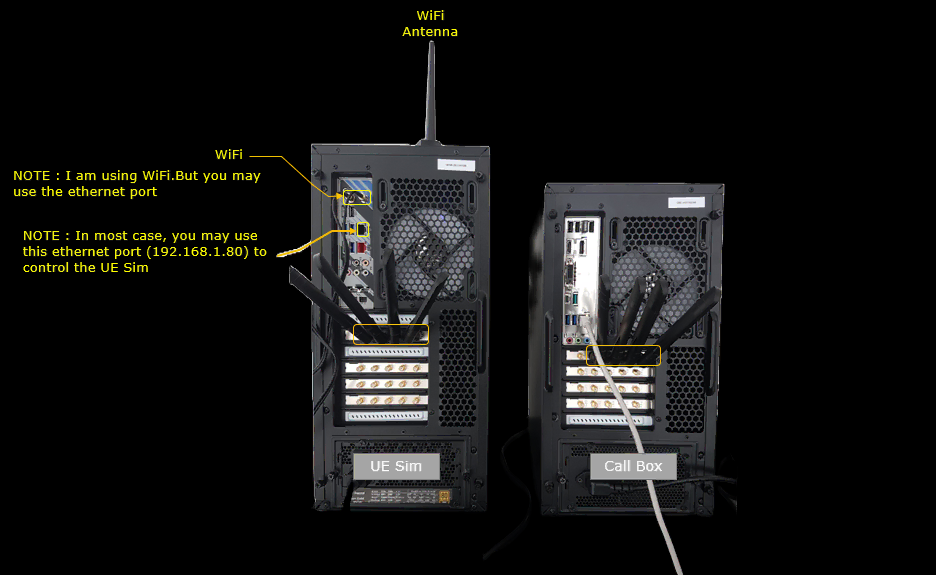
Test Setup
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below. This is just for low layer testing, you may not need any complicated IP layer setup.
- SIM Card used in this tutorial is the one delivered with the system as it is.
- If you want to change the configuration, The tutorial Configuration Guide would help

Key Configuration Parameters
Followings are important configuration parameters for this tutorial. You may click on the items for the descriptions from Amarisoft documents.
- channel_sim
- delay_sim
- position
- initial_radius
- speed
- direction
- elevation
- noise_spd
- channel
- ul_power_attenuation
- ref_signal_power
- min_distance
- max_distance
- bounce
Test 1 : Basic AWGN channel
In this test, we simulate a situation where a UE is moving away from the cell at a constant speed under simple awgn radio channel
Configuration
I have used gnb-sa-channel-sim.cfg that is copied and modified from gnb-sa.cfg. I will use the same file for all the test in this tutorial and just modify the parameters in the file without creating a new file.
I am using the default mme, ims config as shown below.
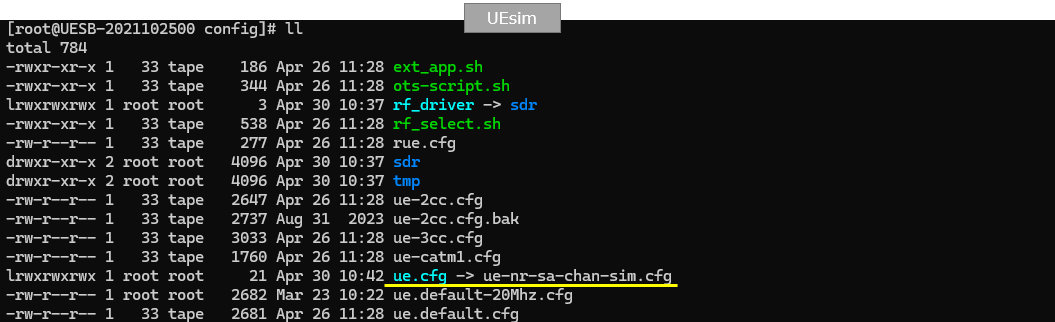
I used ue-nr-sa-chan-sim.cfg which is copied and modifed from ue-nr-sa.cfg on UEsim.
Following is the configuration on gNB. On gNB side, the configuration is almost identical to gnb-sa.cfg. The only difference is NR_BANDWIDTH which is changed to 40 (20 is the default value)

Following is the basic configuration in ue-nr-sa-chan-sim.cfg . The configuration here should match the configuration of Callbox(gNB). The only thing to be set independantly are tx_gain and rx_gain that should be adjusted depending on test setup.

Enable channel_sim and delay_sim in cell_groups and specify the position, antenna radiation type (antenna: {type :"isotropic"}, cell reference power(ref_signal_power) broadcast in SIB1. (

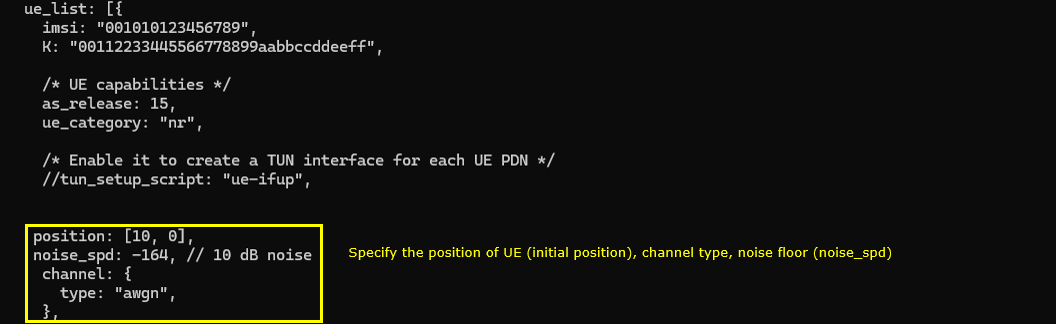
Then specify UE position (position), noise floor(noise_spd) and channel type( channel:{ type:"awgn"} in ue_list:[{ }]. The position specified here is the initial position, you can move this position while running with RemoteAPI.
This part is mainly for automation of the test process. But this is not mandatory, you can perform all of these operation manually. Just for this specific test, power_on, running LteSimServer and power_off is done automatically without human intervention.

Perform the Test
I will follow the same procedure as shown here for all the test in this tutorial.
Check if the cell is configured as intended by checking the output of 'cell phy'

Start lte service on Callbox(gNB) and UEsim(UE) and make it sure that the UE is connected.
Once the initial attach is complete, go to /root/ue directory on UEsim and run the following remote API. This specific command is to move UE (ue_id 1) to move away from the cell at the speed of 10 km/h.
|
./ws.js ue '{"message" : "ue_move", "ue_id" : 1, "speed" : 10, "direction" : 0}' |
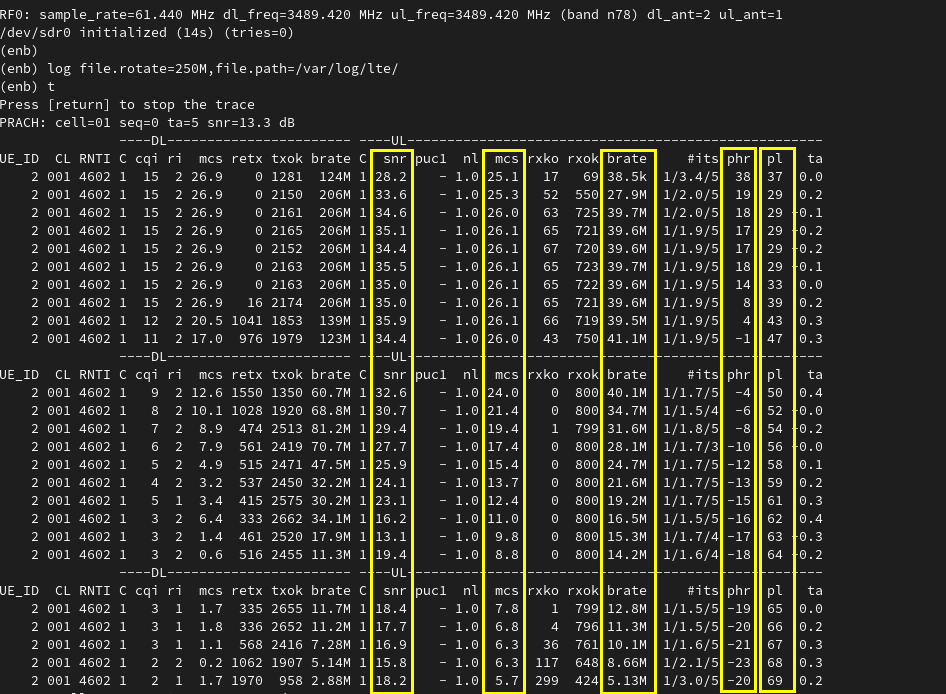
Then check how some of physical layer measurement changes in gNB trace log. Followings are some of the highlights you would notice :
- UL SNR is decreasing with time (as UE moves farther from gNB.
- UL MCS is decreasing with time (as UE moves farther from gNB (This is because gNB performs link adaptation).
- UL brate (Date Rate) is decreasing with time (as UE moves farther from gNB)
- UL phr (Power HeadRoom) is decreasing with time (as UE moves farther from gNB)
- Pathloss (pl) is increasing with time (as UE moves farther from gNB)
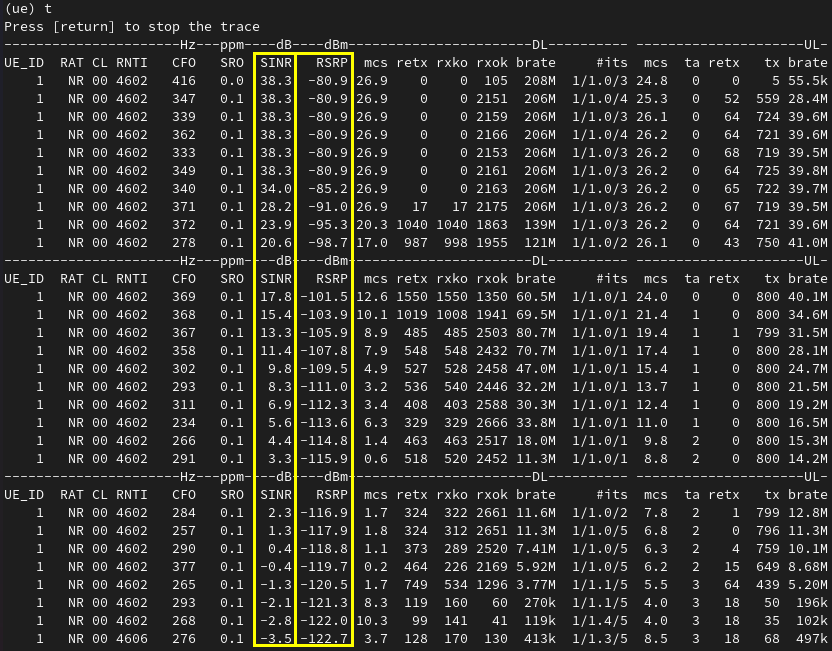
To check the effect of channel simulation on downlink, you can check out the 't' output on UEsim. You would notice that SINR and RSRP for DL decreases as UE moves farther away from the cell.
Log Analysis
You can analyze the channel characteristics with Callbox log or UEsim log, but I think Callbox log is better option since it is based on real measurement.
First let's check out SNR and Power(EPRE) for uplink data channel (PUSCH). As you see in the [SNR] tab, you see both SNR and EPRE for PUSCH(UL data) gradually decreseas as the mobile phone gets farther from gNB.
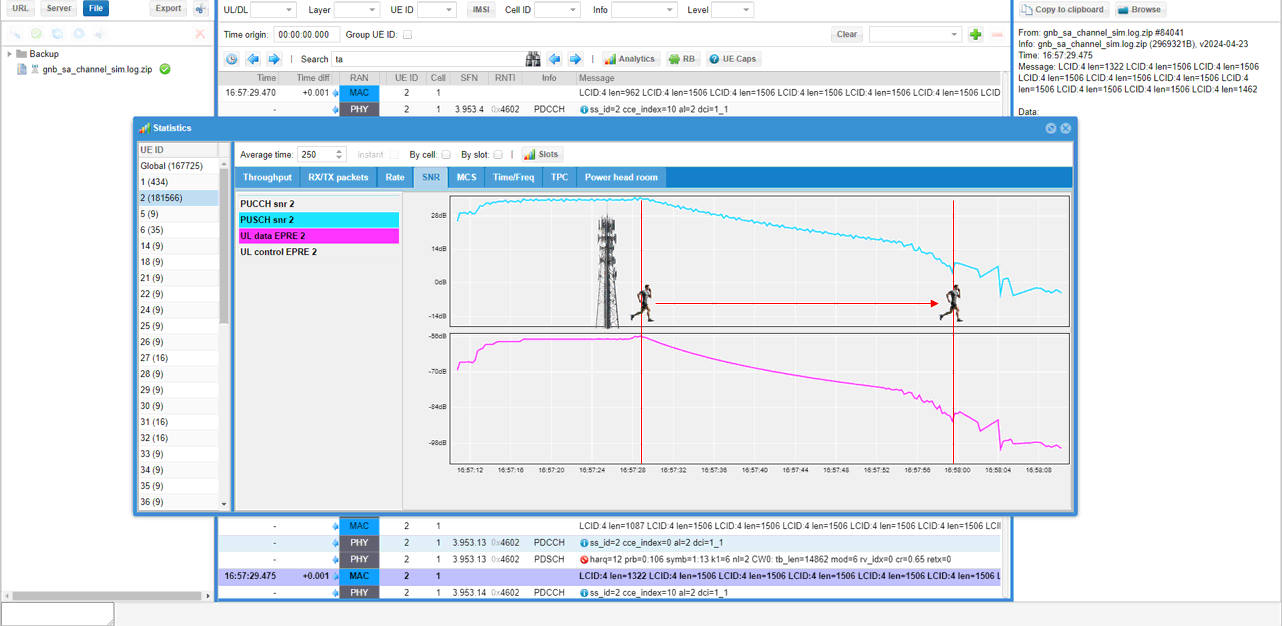
Now let's check out PHR(Power Headroom). As you see in the [Power head room] tab, you see the phr gradually decreseas as the mobile phone gets farther from gNB.
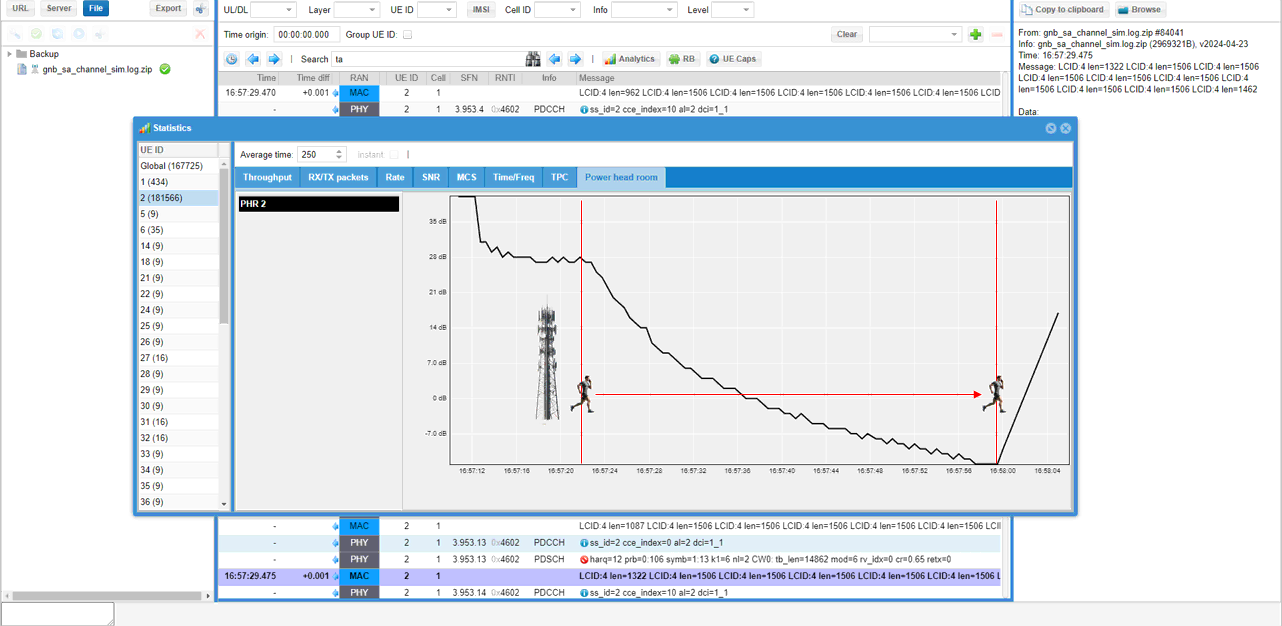
Then let's check out throughput. As you see in the [Throughput] tab, you see the throughput gradually decreseas as the mobile phone gets farther from gNB.

Now let's look into RX/TX packet status. I want to focus on RX Bad CRC. You may expect this to be increasing as UE get farther away from gNB, but in this result it stay same over most of the location except where the UE got very far away. The CRC Bad stays at very low becaues gNB is performing link adaption procedure (e.g, changing MCS to prevent CRC error)

You can confirm how link adaptation goes on in [MCS] tab. You see that gNB reduces MCS as UE gets farther away from the cell.
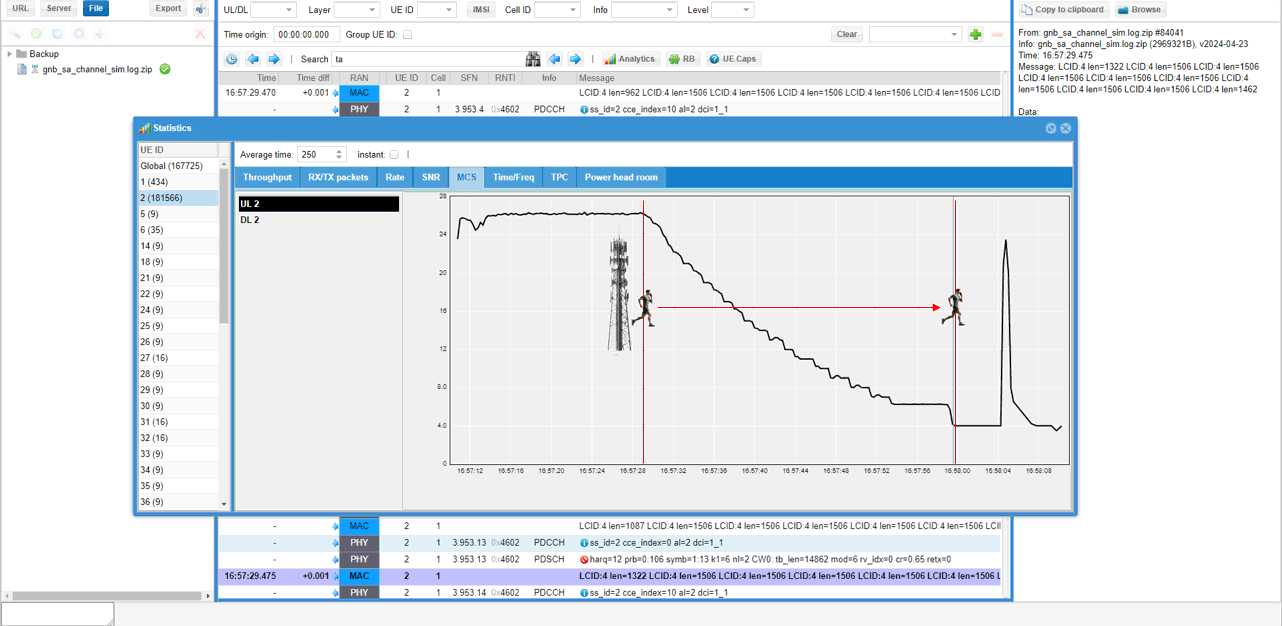
Since the UE is getting farther away, you may guess that there would be continuous adjustment of UL transmission timing with Timing Advance. This can be confirmed by the MAC CE with TA field. (
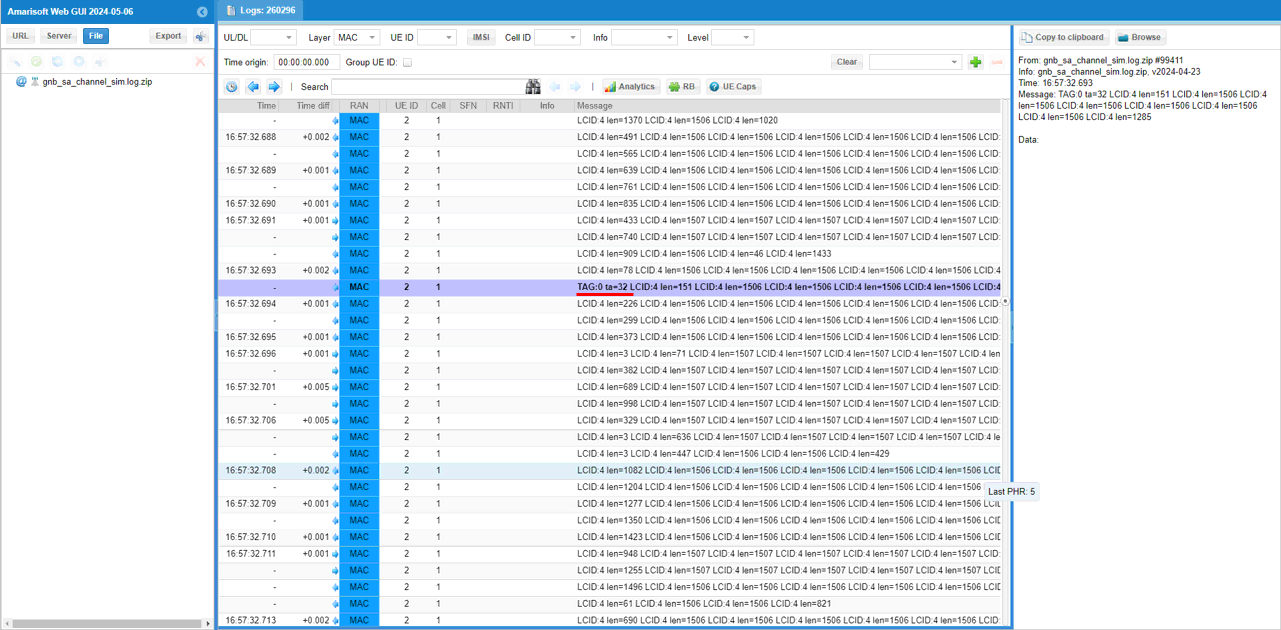
This is optional. You can do the same analysis shown above with UEsim log. An advantage of analyzing the log on UEsim would be that you can figure out exact point of the time that UE start moving from the log print ('move x=10 y=0 speed=10 dir=0 elevation=0' in this case). All other analysis is same as we checked with gNB log.

Test 2 : 3GPP Profile - EPA
In this test, we simulate a situation where a UE is moving away from the cell at a constant speed under one of 3GPP predefined channel model named "EPA"
Configuration
I have used gnb-sa-channel-sim.cfg that is copied and modified from gnb-sa.cfg. I will use the same file for all the test in this tutorial and just modify the parameters in the file without creating a new file.

I am using the default mme, ims config as shown below.

I used ue-nr-sa-chan-sim-epa.cfg which is copied and modifed from ue-nr-sa.cfg on UEsim.
Following is the configuration on gNB. On gNB side, the configuration is almost identical to gnb-sa.cfg. The only difference is NR_BANDWIDTH which is changed to 40 (20 is the default value)

Following is the basic configuration in ue-nr-sa-chan-sim.cfg . The configuration here should match the configuration of Callbox(gNB). The only thing to be set independantly are tx_gain and rx_gain that should be adjusted depending on test setup.

Enable channel_sim and delay_sim in cell_groups and specify the position, antenna radiation type (antenna: {type :"isotropic"}, cell reference power(ref_signal_power) broadcast in SIB1. (

Then specify UE position (position), noise floor(noise_spd) and channel type( channel:{ type:"epa", freq_doppler: 50, mimo_correlation: "low"} in ue_list:[{ }]. The position specified here is the initial position, you can move this position while running with RemoteAPI.

This part is mainly for automation of the test process. But this is not mandatory, you can perform all of these operation manually. Just for this specific test, power_on, running LteSimServer and power_off is done automatically without human intervention.

Perform the Test
I will follow the same procedure as shown here for all the test in this tutorial.
Check if the cell is configured as intended by checking the output of 'cell phy'

Start lte service on Callbox(gNB) and UEsim(UE) and make it sure that the UE is connected.
Once the initial attach is complete, go to /root/ue directory on UEsim and run the following remote API. This specific command is to move UE (ue_id 1) to move away from the cell at the speed of 10 km/h.
|
./ws.js ue '{"message" : "ue_move", "ue_id" : 1, "speed" : 10, "direction" : 0}' |
Then check how some of physical layer measurement changes in gNB trace log. Followings are some of the highlights you would notice :
- UL SNR is decreasing with time (as UE moves farther from gNB.
- UL MCS is decreasing with time (as UE moves farther from gNB (This is because gNB performs link adaptation).
- UL brate (Date Rate) is decreasing with time (as UE moves farther from gNB)
- UL phr (Power HeadRoom) is decreasing with time (as UE moves farther from gNB)
- Pathloss (pl) is increasing with time (as UE moves farther from gNB)
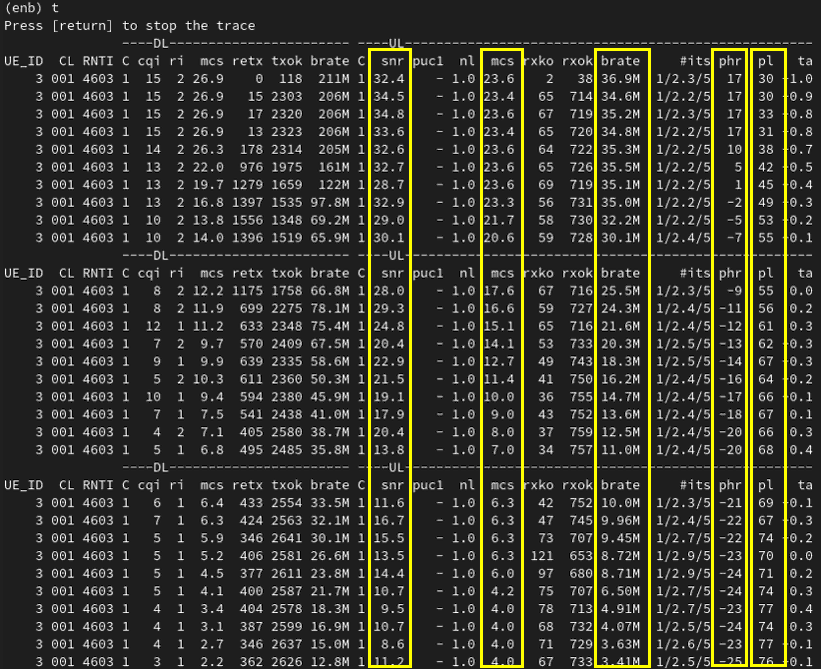
To check the effect of channel simulation on downlink, you can check out the 't' output on UEsim. You would notice that SINR and RSRP for DL decreases as UE moves farther away from the cell.

Test 3 : Triggering PingPong Handover by Channel Simulator - LTE/Single UE
In this test, we simulate a situation where a UE is moving away from the cell at a constant speed under simple pedesterial channel. It is similar to previous test cases, but the difference is that we move UE using internal configuration parameter instead of remote API. This method would be much handy than remote API in some scenario where you want to trigger Handover for multiple UEs and to trigger handover repeatedly (e.g, ping pong handover)
Configuration
I have used enb-pingpong-ho.cfg that is copied and modified from gnb-sa.cfg. I will use the same file for all the test in this tutorial and just modify the parameters in the file without creating a new file.
I am using the default mme, ims config as shown below.

I used ue-pingpong-ho.cfg which is copied and modifed from ue-nr-sa.cfg on UEsim.
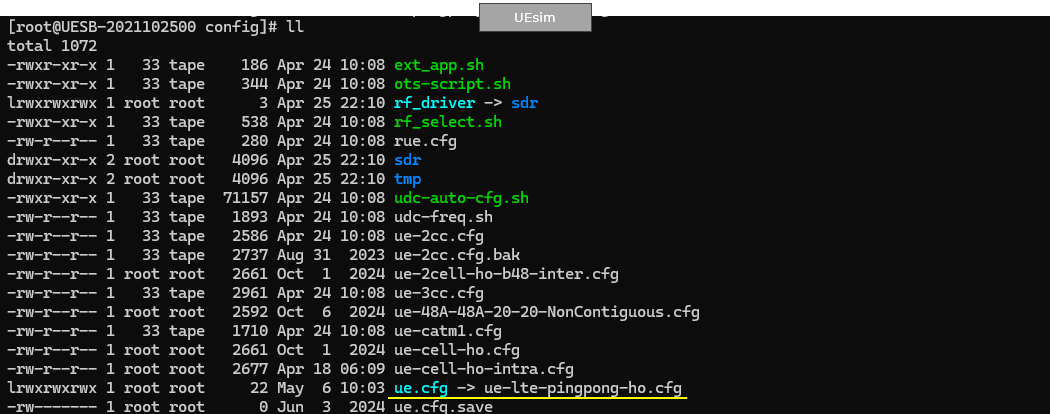
Following is the configuration on eNB. On eNB side, the configuration is almost identical to enb-2cell-ho.cfg.
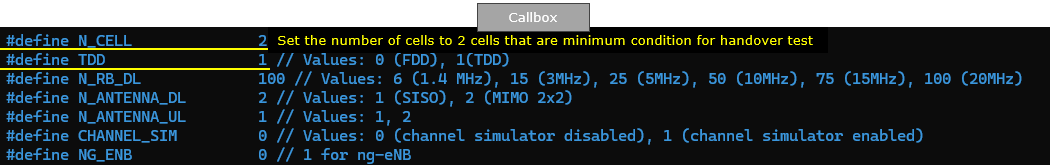
Obviously we set N_CELL to 2 because this is handover scenario between two cells. and I set TDD to 1 (i.e, TDD), but you can do the same thing for FDD as well.
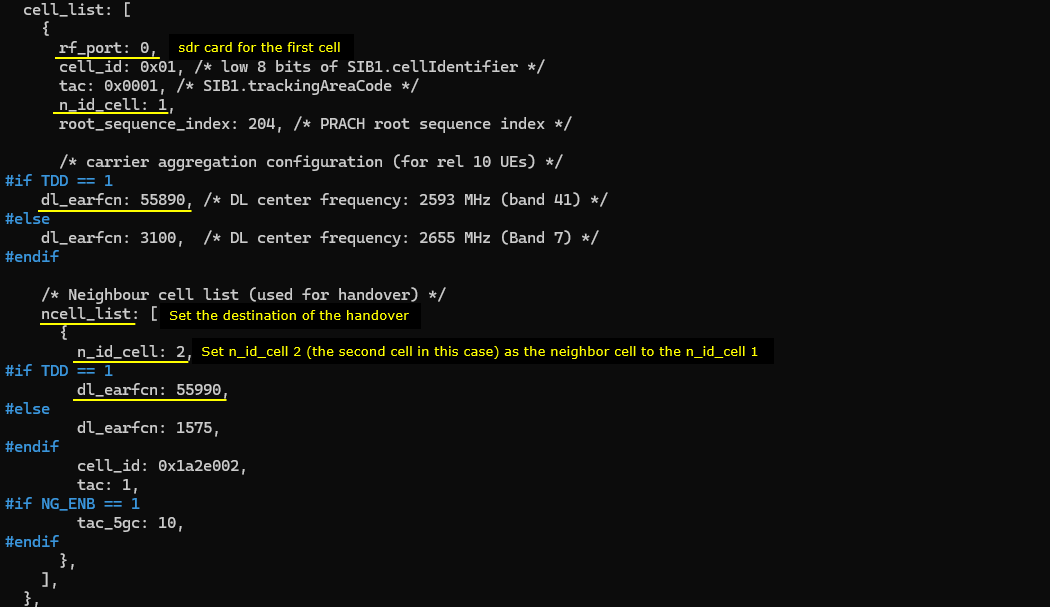
Now let's configure the two cells that will be involved in handover. Note that we configured the different frequency for the two cells. It means that we will perform inter frequency handover in this test.
This is the configuration for the first cell. Note that the second cell (n_id_cell 2) is configured as a neighbour cell (ncell_list) to the first cell
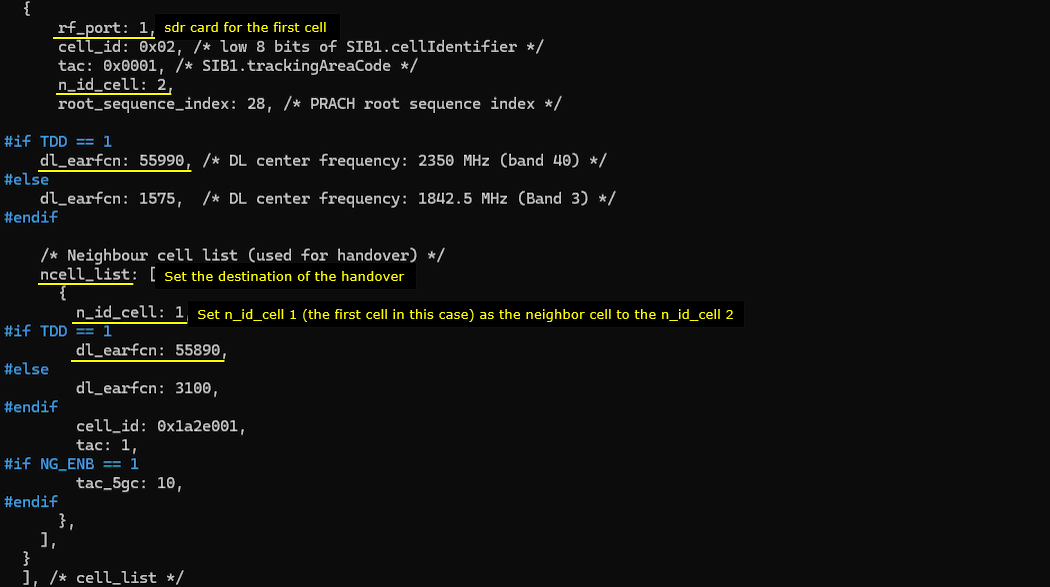
This is the configuration for the second cell. Note that the first cell (n_id_cell 1) is configured as a neighbour cell (ncell_list) to the second cell
With Amarisoft, you can do both blind handover and measurement based handover. In this test, we will do measurement based handover. In order to do measurement based handover, you need to configure appropriate measurement condition for the handover. We usually configure this in cell_default block.
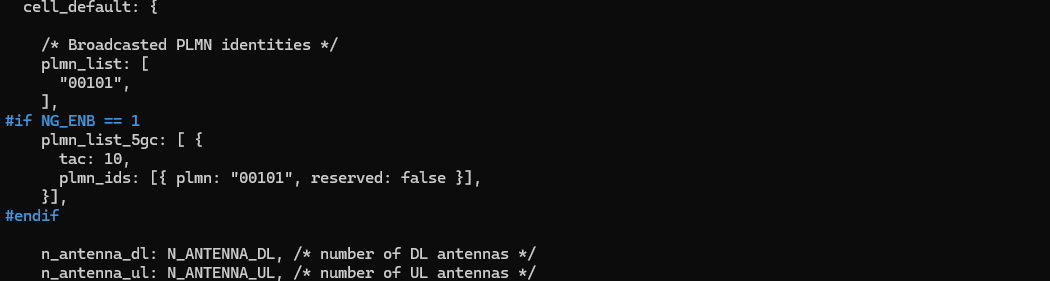
Configure measurement condition for source cell measurement and destination/handover measurement condition(a3 event in this case) as follows. In this test, we will do inter frequency handover, so we need to configure measurement gap (meas_gap_config) as well.
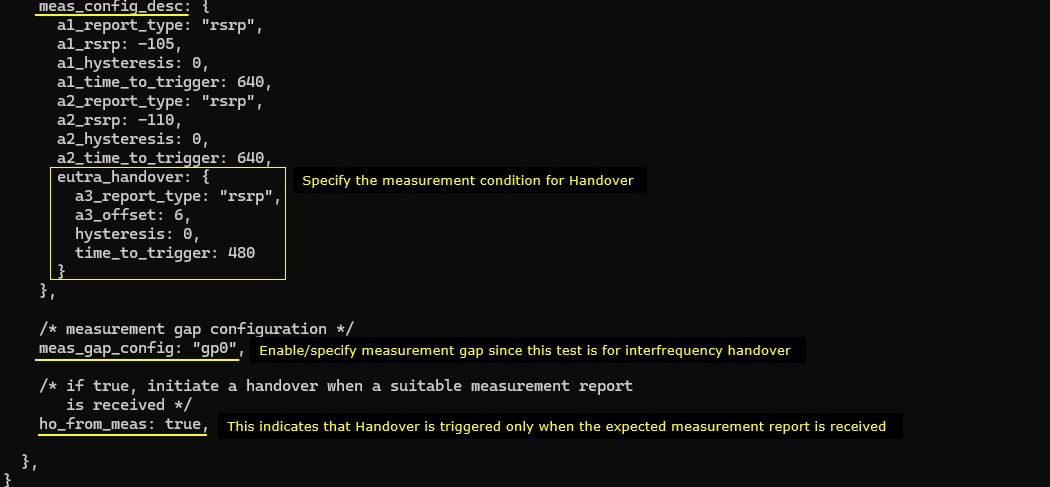
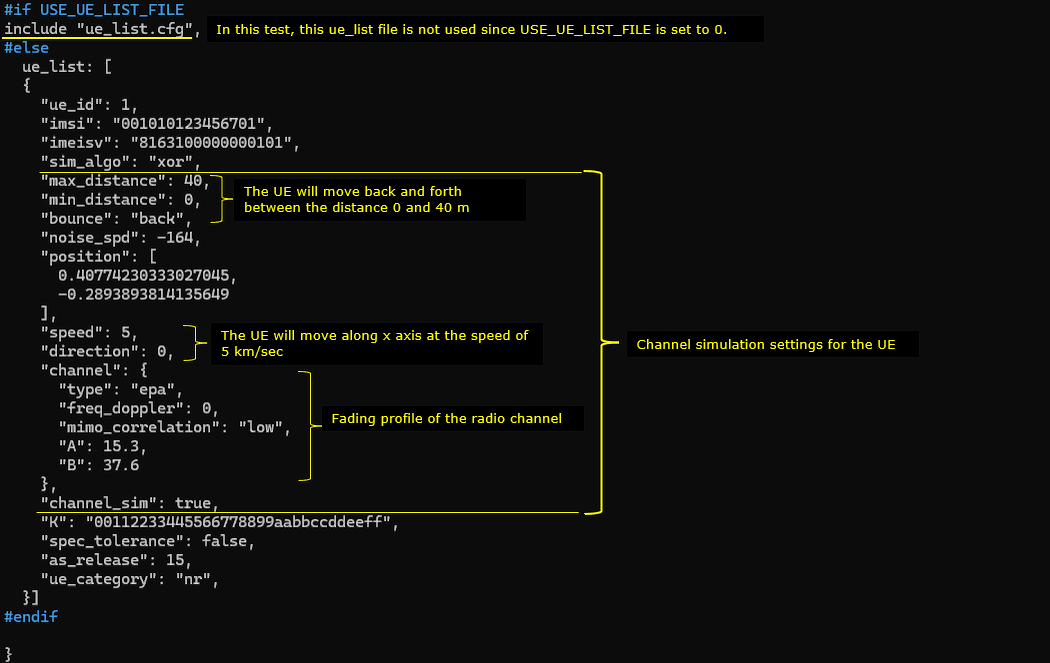
In ue-pingpong-ho.cfg , followings are configured. Since the main purpose of this test is to show how to simulate UE moving back and forth between two cells triggering pinpong handover. The UEsim configuration is the main part to be noted.
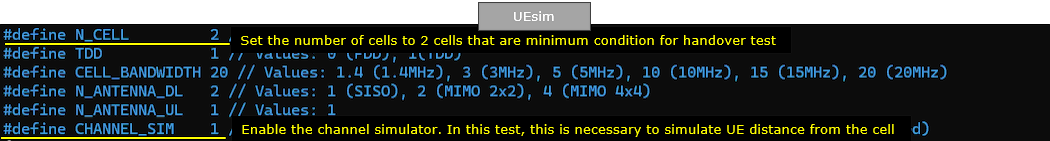
As in eNB case, N_CELL is set to 2 since this is the handover between the two cells. TDD is set to 1 (i.e, TDD) which is just to match the eNB configuration. Important to note is that CHANNEL_SIM is set to 1 which indicates the channel simulator will be used.
Now in cell_groups, channel_sim is set true which enables channel simulation functionality.
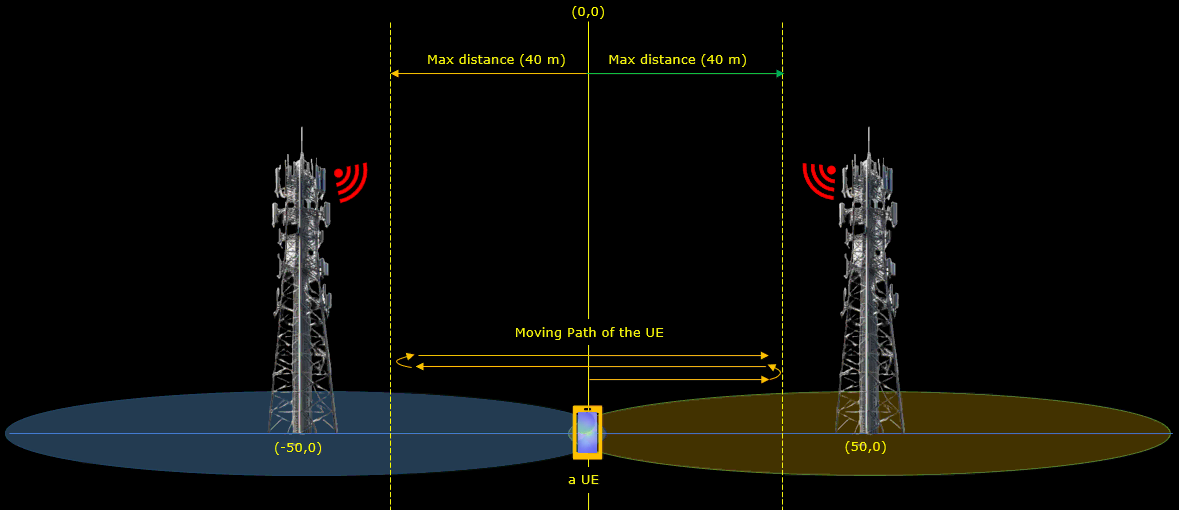
The position of the first cell is set to [50,0] and reference signal power(ref_signal_power), ul_power_attenuation and antenna type is configured for the simulated radio channel. In the same way, the simulated channel configuration for the second cell is set. The position of the cell is set to [-50,0] and all other configurations are same as the first cell.
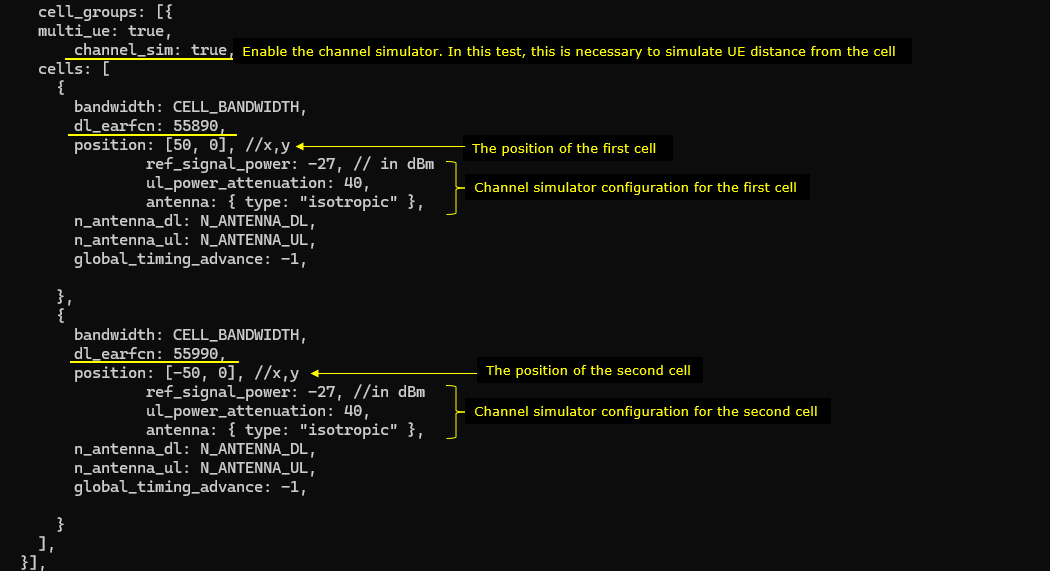
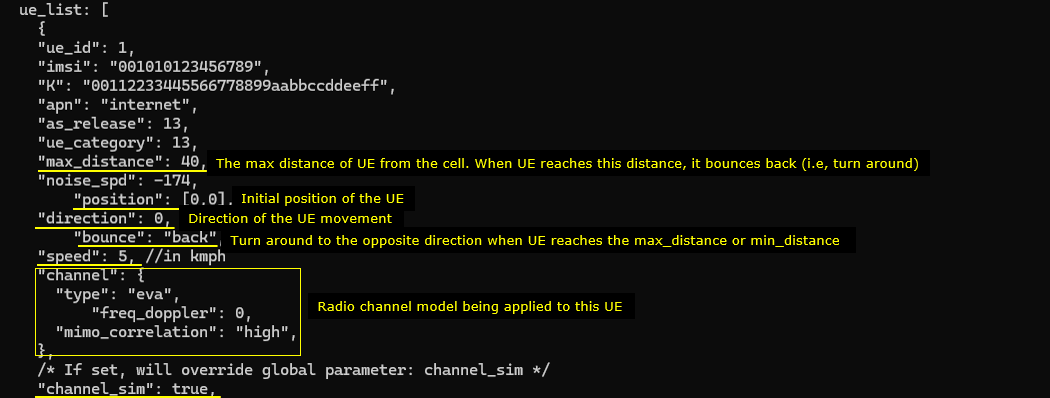
Following(ue_list) is the configuration that applies to a specific UE. Here you see the channel parameters that applies to the UE. First, UE is positioned at the [0,0] which is at the mid point between the two cells. It start moving towards the right cell (direction 0 meaning angle 0 degree). When it reaches the max_distance (in meters), it bounces back (turn 180 degree) and moves until it reaches min_distance (default 0). The moving speed is set to 5 km/h (speed: 5) in this test. The radio channel for this test is set to a 3GPP standard channel ("eva").
Following is optional configuration to automatically generate IP data stream. You can generate the IP data manually (e.g, ping)

Perform the Test
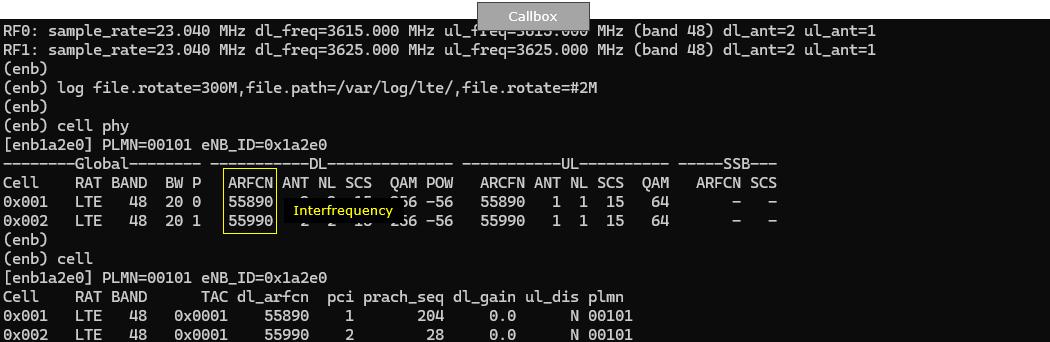
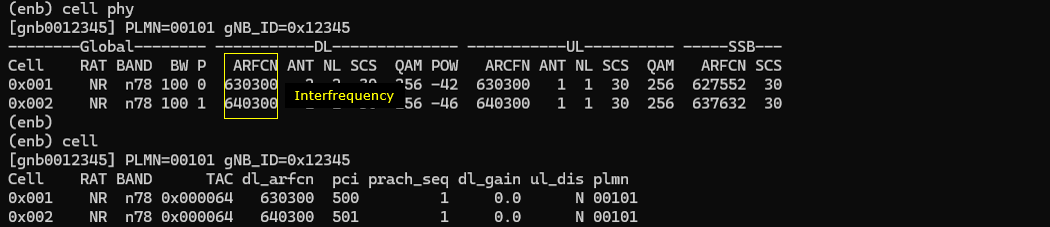
Now run the callbox and check out basic physical cell configuration. Note that two cells are configured for inter cellular frquency (
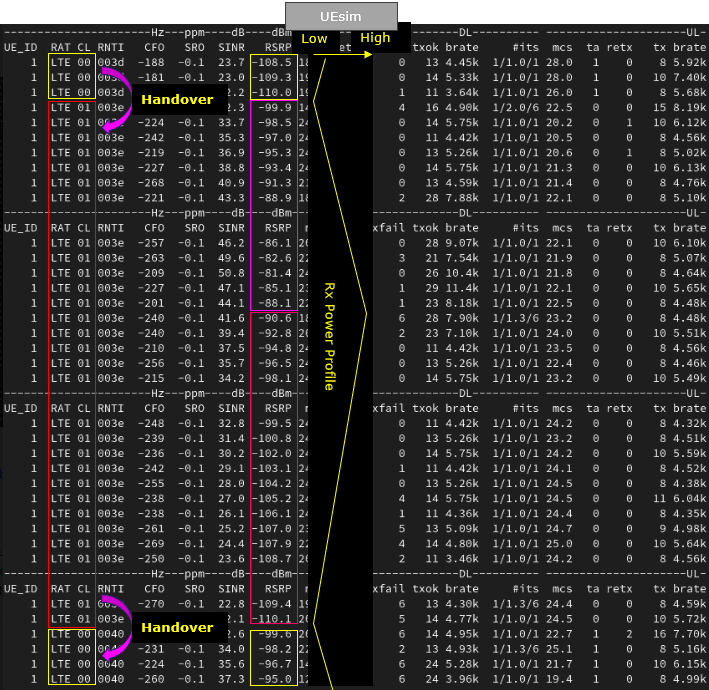
Then Start UEsim and power on UE and let it alone for some time. Then you will see the cell that the UE connected are switching back and forth between the two cells. Note that RSRP increases and descrease by itself implying that UE is getting closer and farther from the cell.
Log Analysis
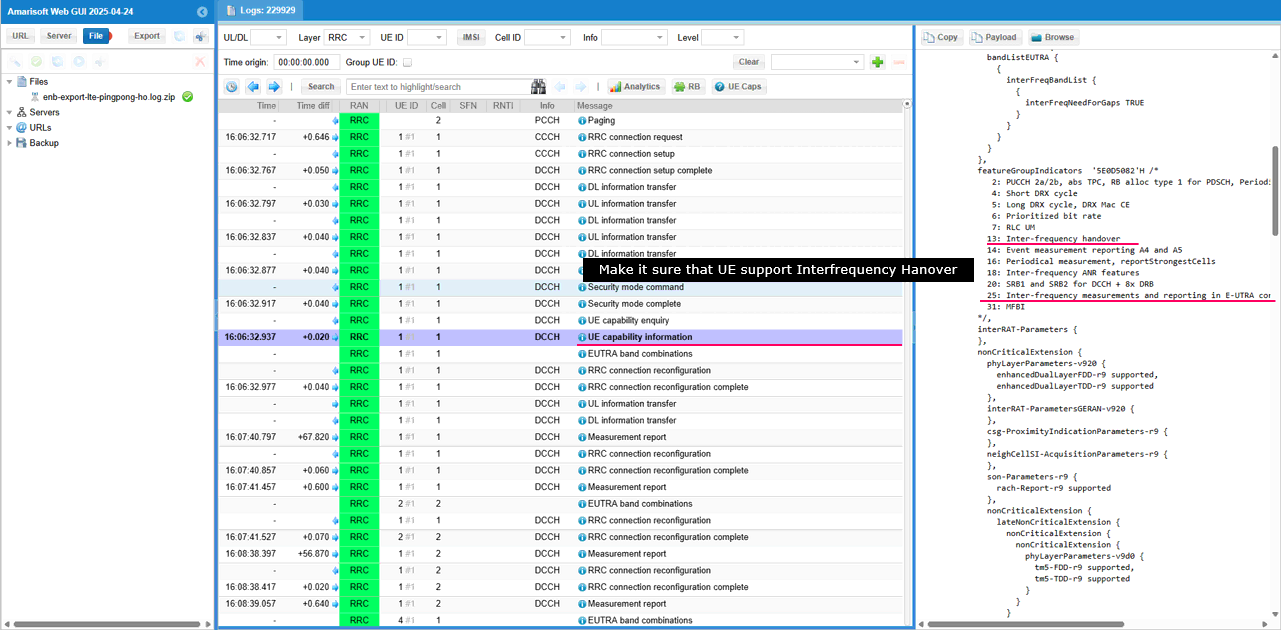
First it is always good to check with UE capability.
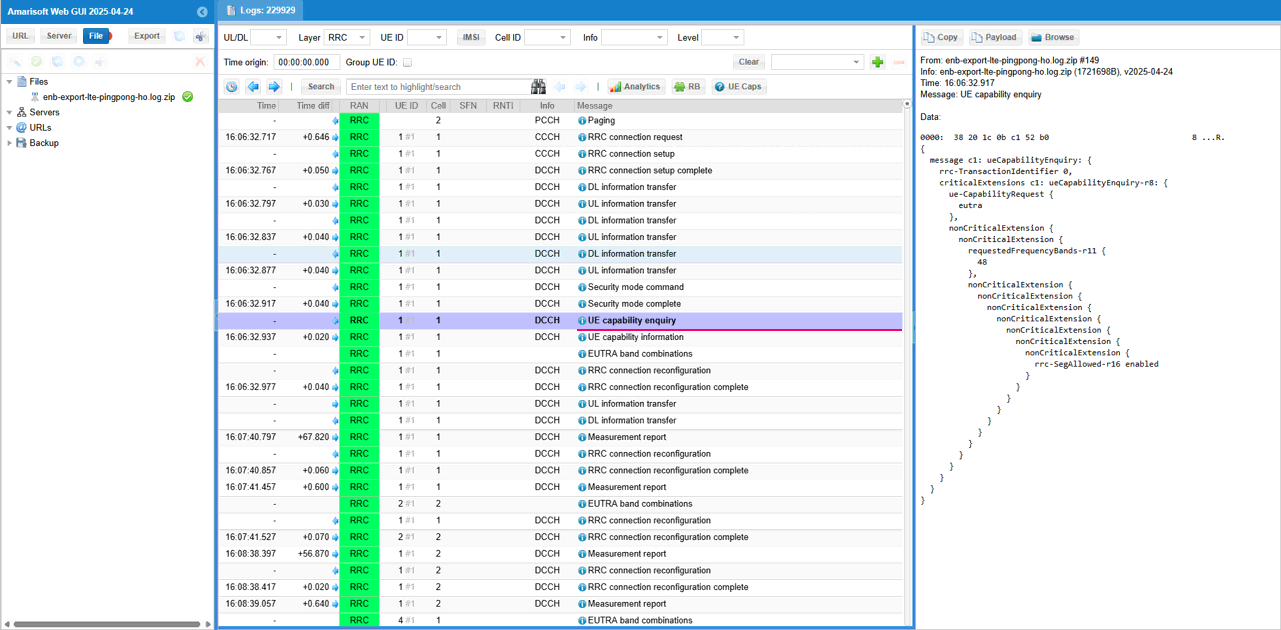
Since this test is configured for inter frequency handover, make it sure that UE capability support the related features (Interfrequency measurement report and interfrequency handover)
Now eNB sets up measurement configuration. First, defines measurement object that sets up the measurement frequency in measObjectToAddModList.
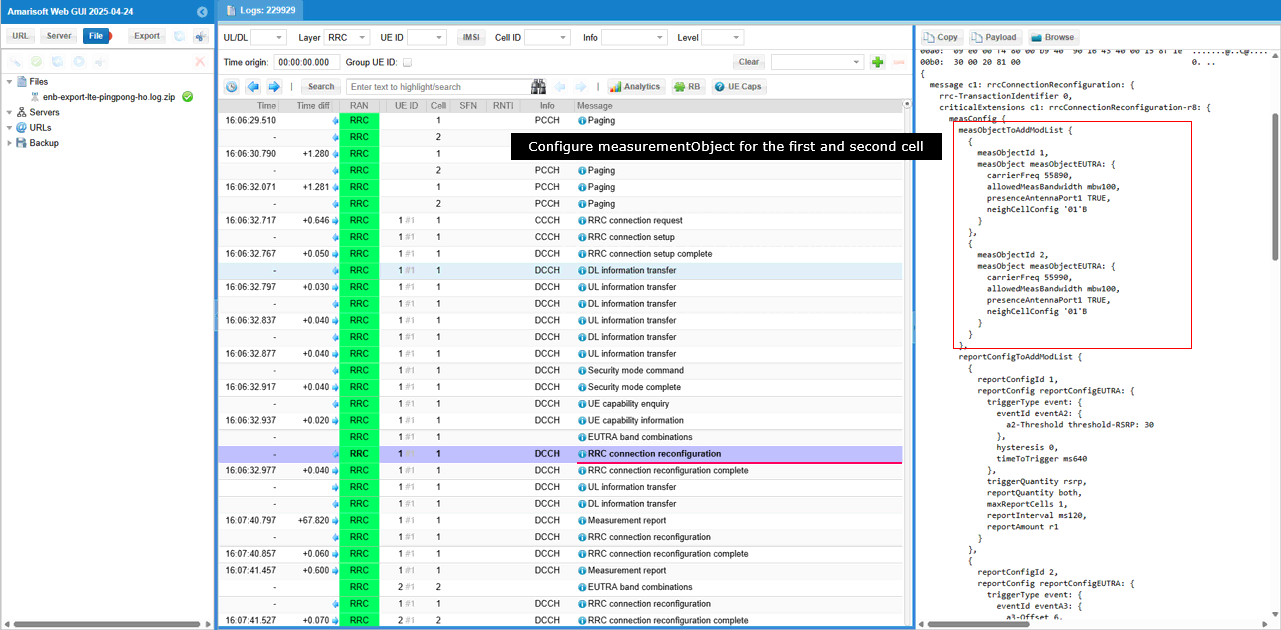
Then configures measurement events. In this case, two types of the events eventA2 and event A3 are defined in reportConfigToAddModList.
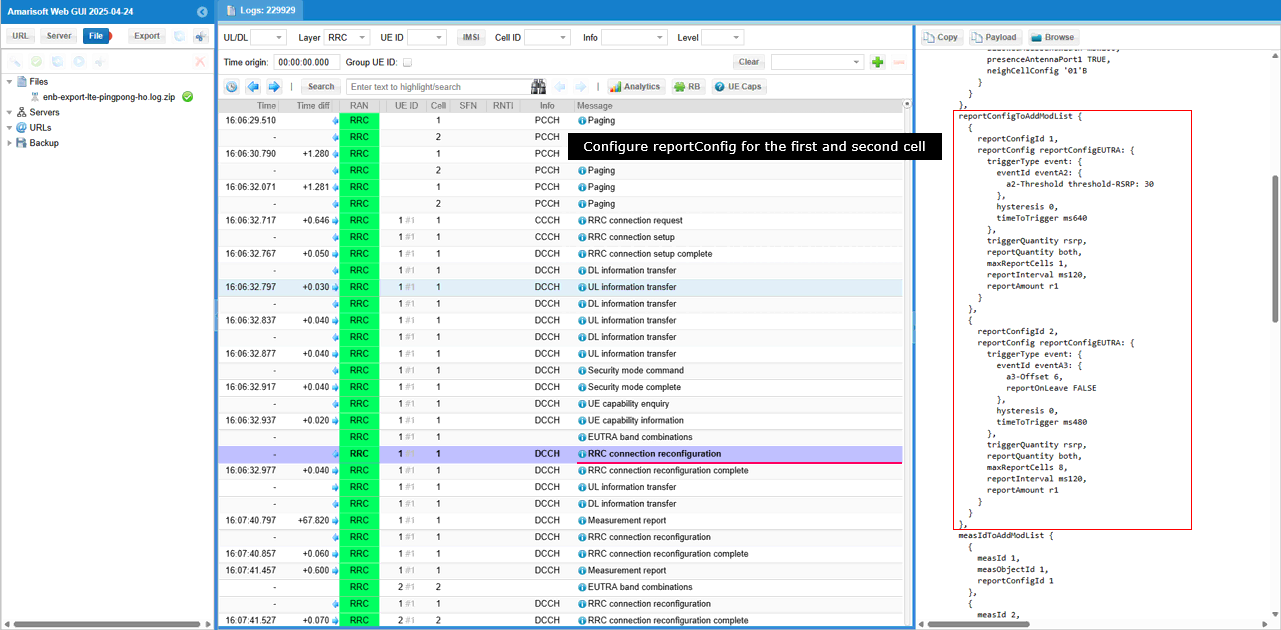
Combining the measurement object and report configuration, specific measurement configurations are defined in measIdToAddModList. In this case, two measurement configurations are defined. One with measObjectId 1 and reportConfigId 1 and the second one with measObjectId 2 and reportConfig 2. At this point, measurementGap is not configured yet.
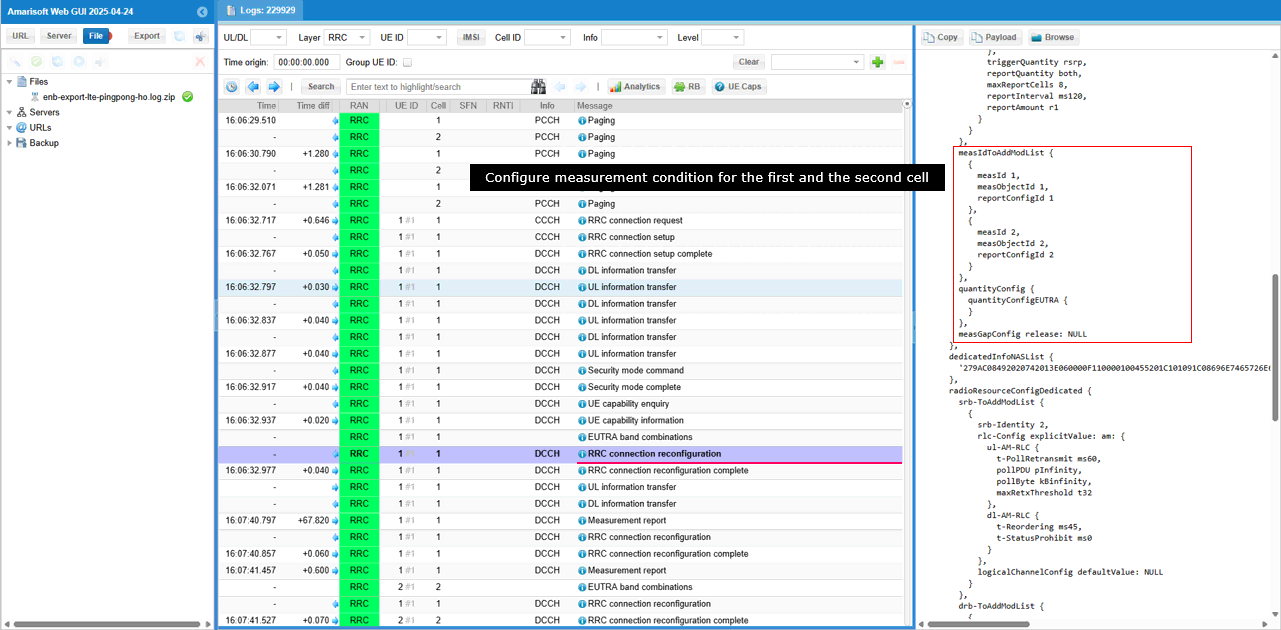
If the measurement requirement is met, UE send measurement Report for the PCell. By measId, you would notice that this is the report for event A2
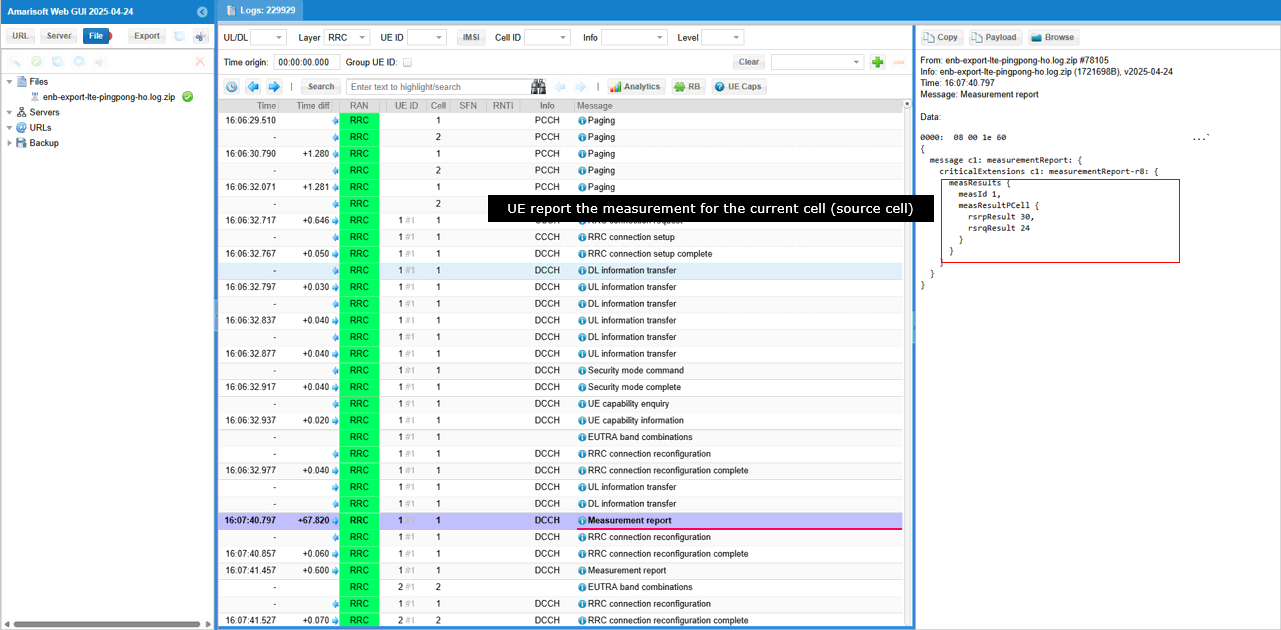
When the event A2 report is recieved, eNB activates measurement Gap. (
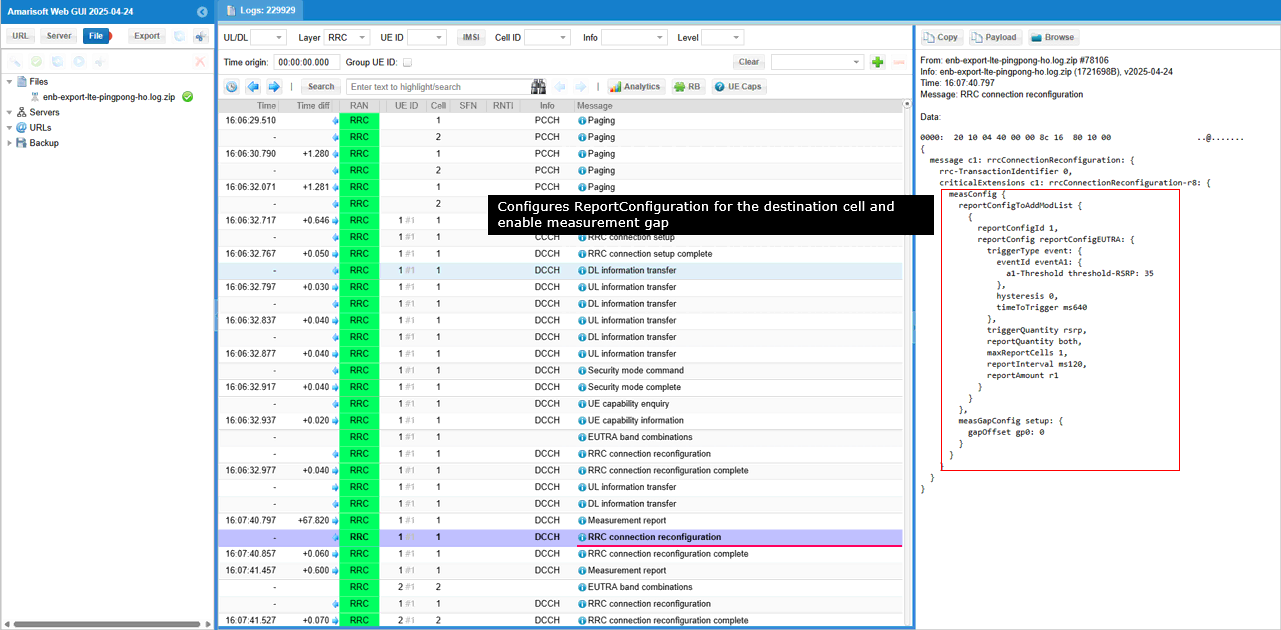
Now UE sends measurement report for both PCell and neighbor cell. By the measId and its definition shown above, you would notice this is the report for event A3.
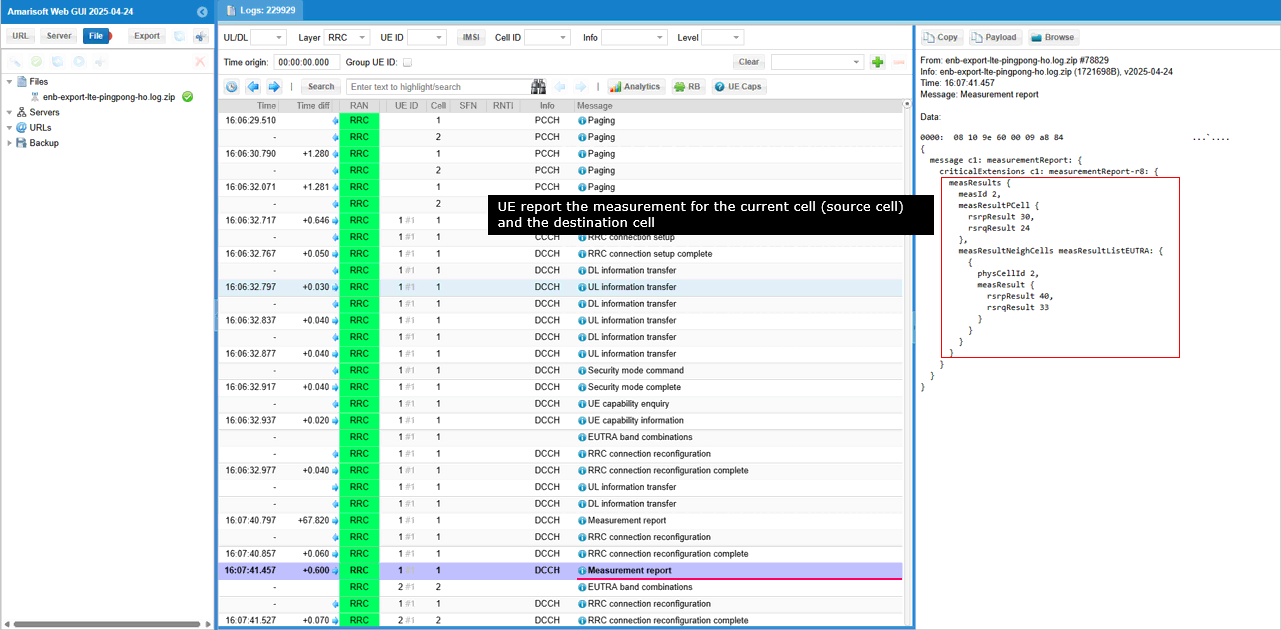
Now eNB sends RRC Connection Reconfiguration to UE for handover. In addition to handover configuration, various measurement reconfiguration are done in the same message as well.
First the unnecessary measurement configurations at this points are removed.
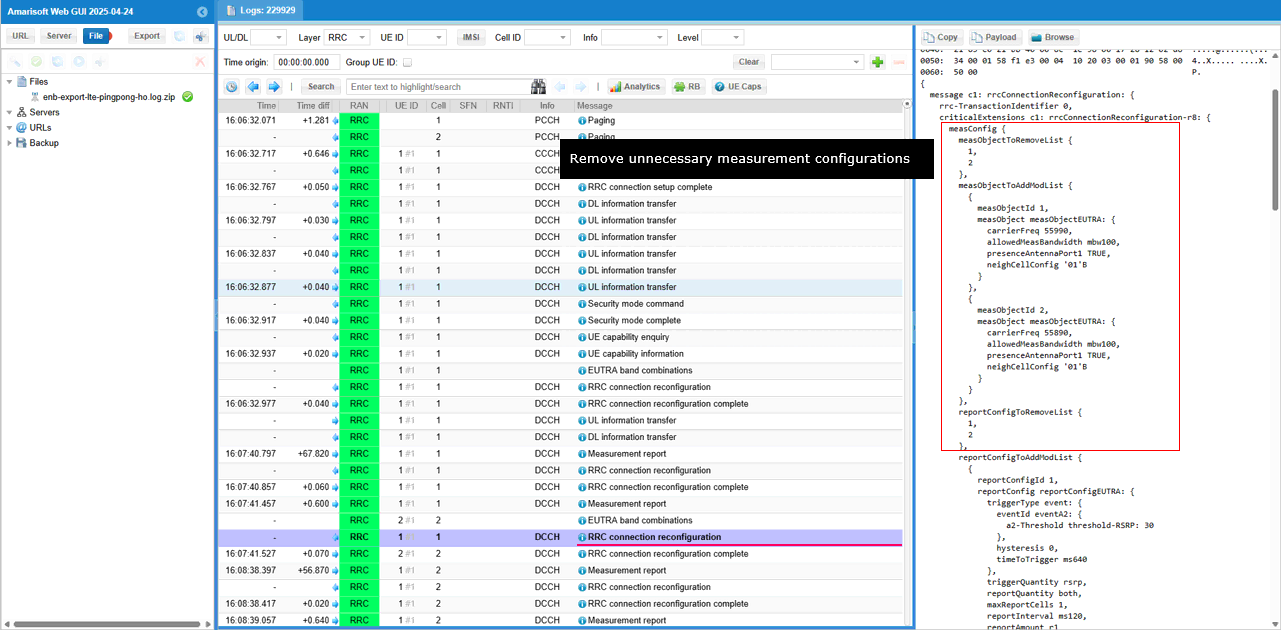
Then some ReportConfigurations are sets up again.
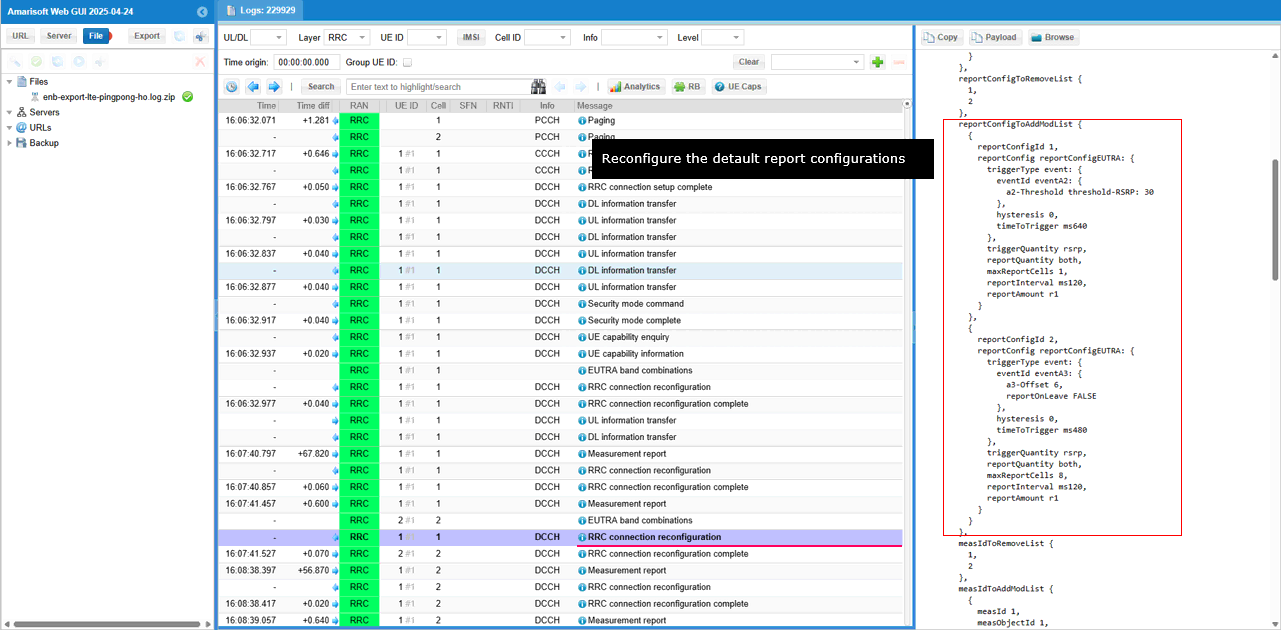
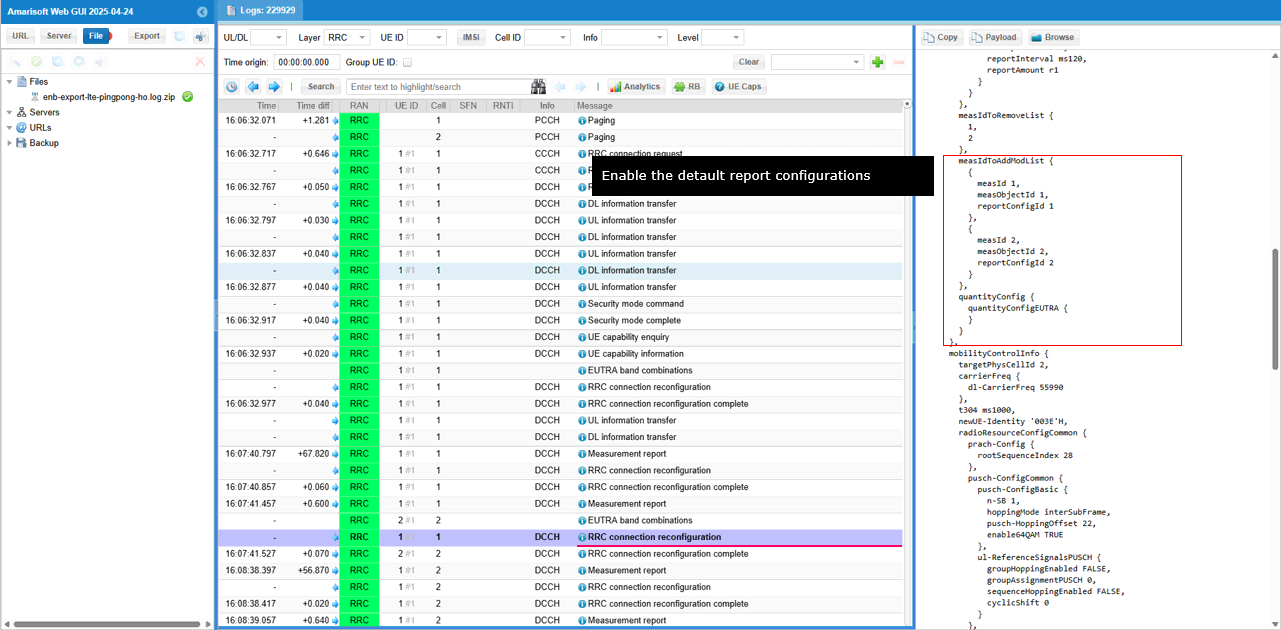
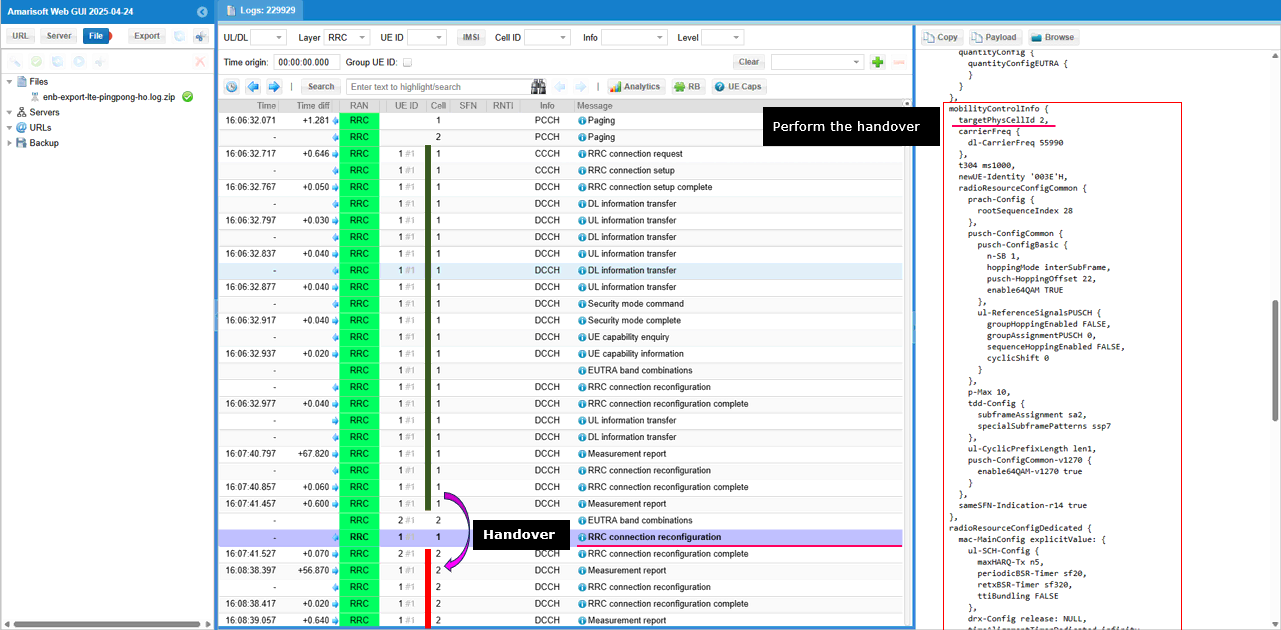
Finally Handover configuration is configured and handover is done in both UE and eNB.
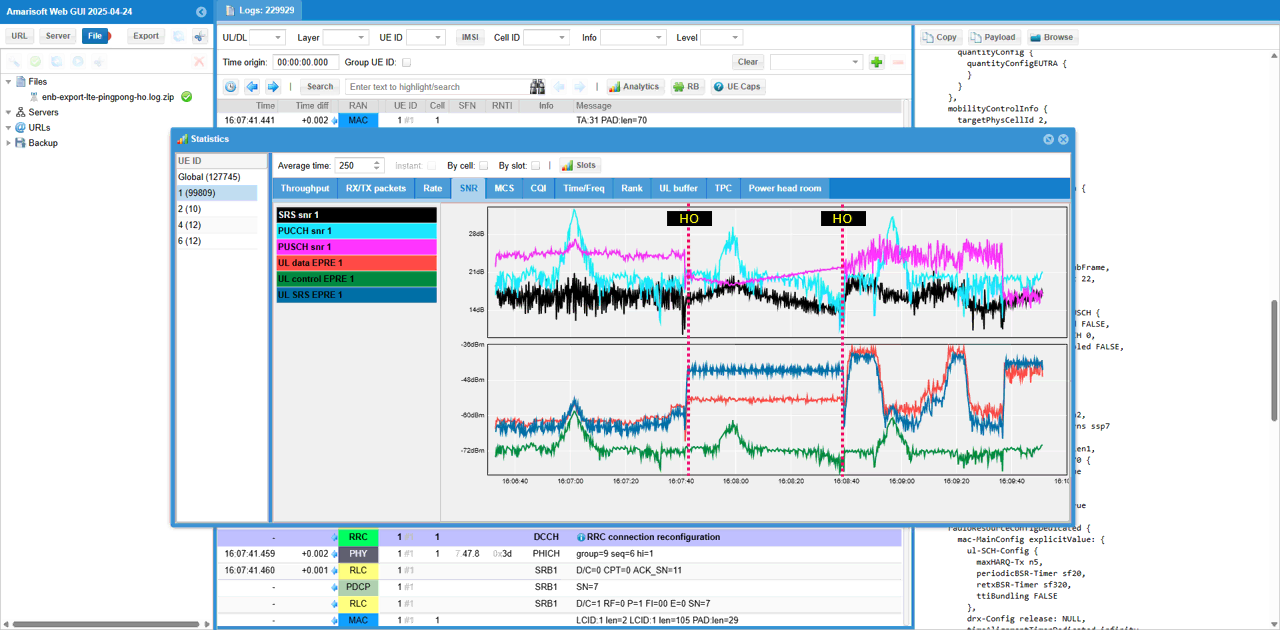
Here I want to share various plots showing different states / quality of the radio channel. Since fading is being applied during the test, the plots may not always obvious in terms of triggering handover, but I just want to let you know that you can use these plots for more intuitive analysis. If you apply more simple channel model (e.g, with constant awgn channel rather than fading channel), you may have a little bit clearer correlation between these plots and the UE movement(position change)
At this moment, I am not much interested in throughput related plots. I like to check plots more related to radio channel quality.
Check out SNR plots and see how each of the physical channel characterstics varies.
Check out CQI plot and see how it varies
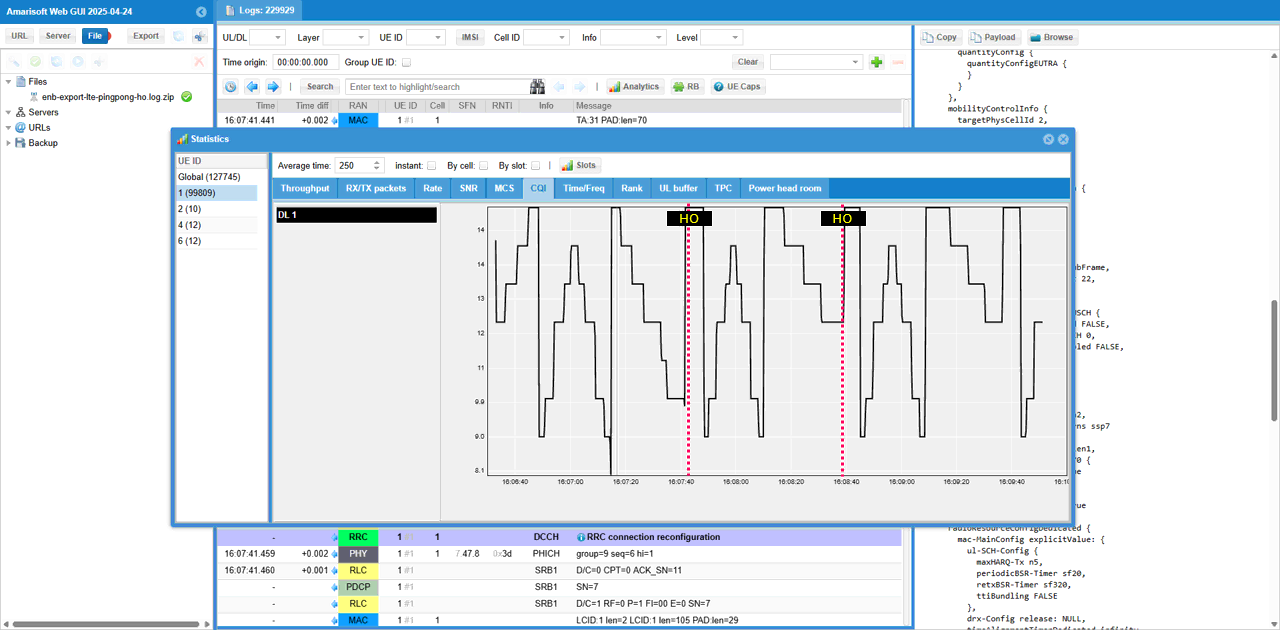
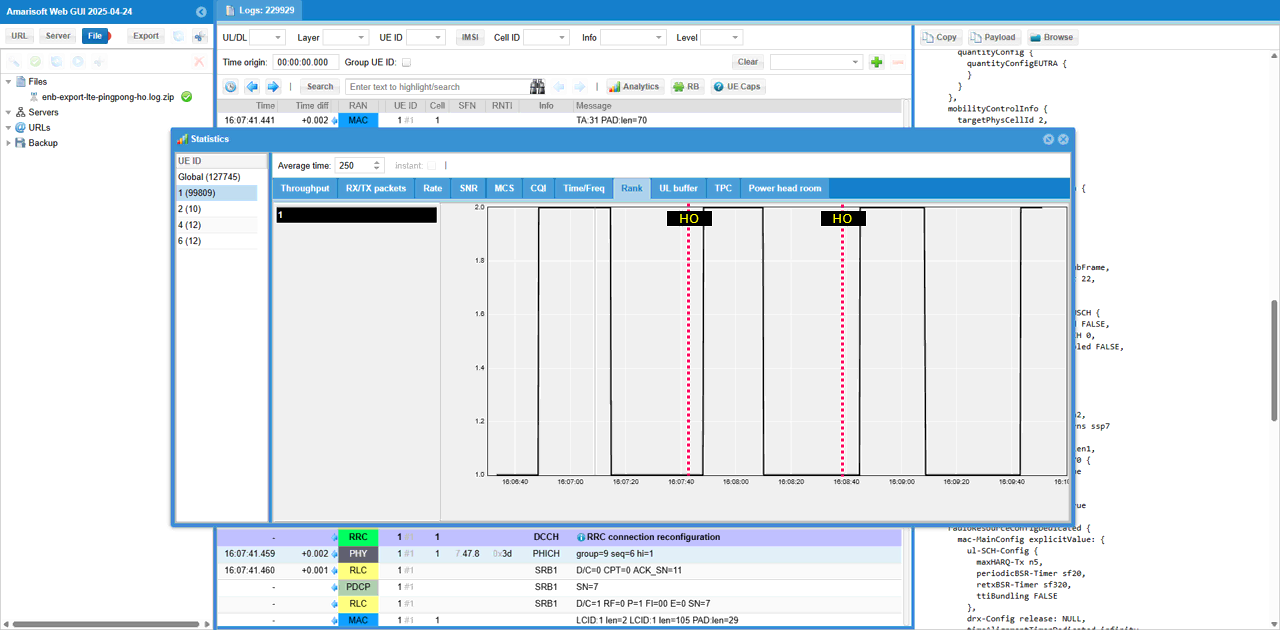
Check out Rank plot and see how it changes
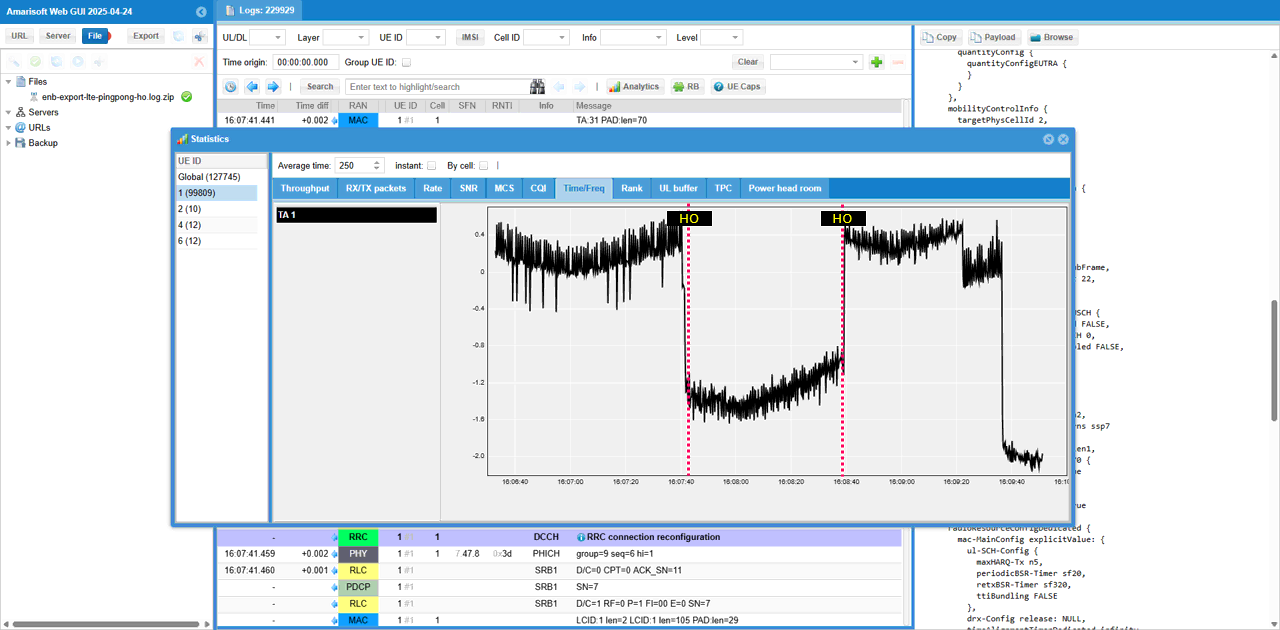
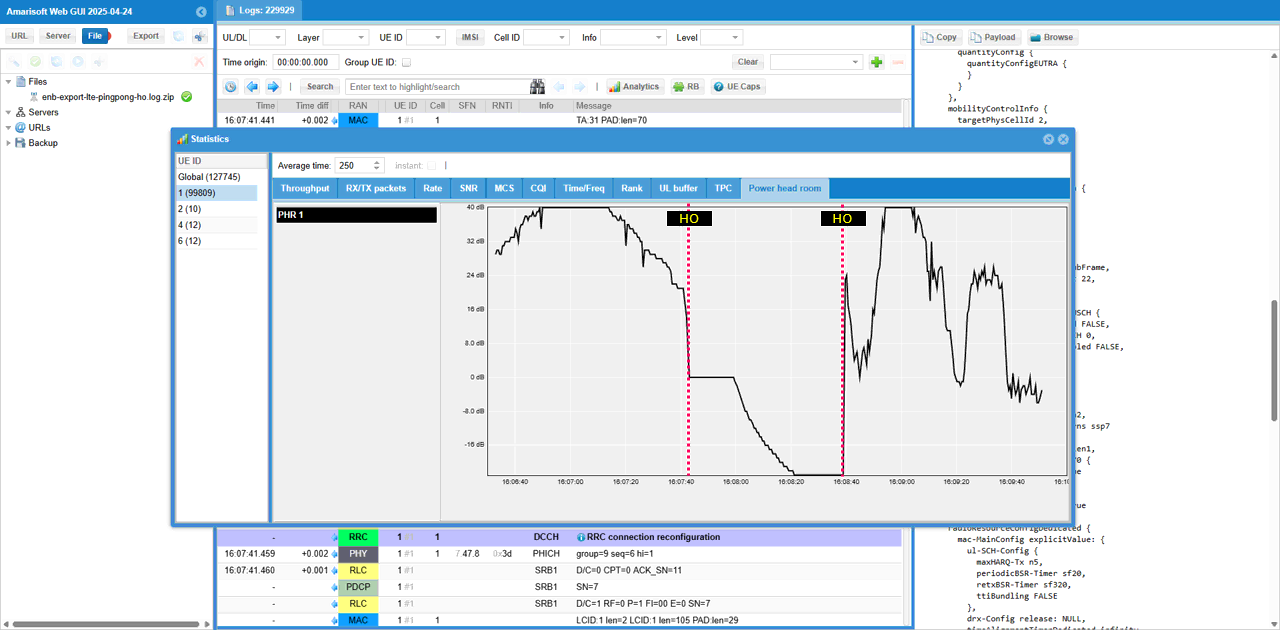
Check out Timing Advance. You see the drastic discontinuity at the point of handover.
Check out TPC command plot. You see the drastic discontinuity at the point of handover.
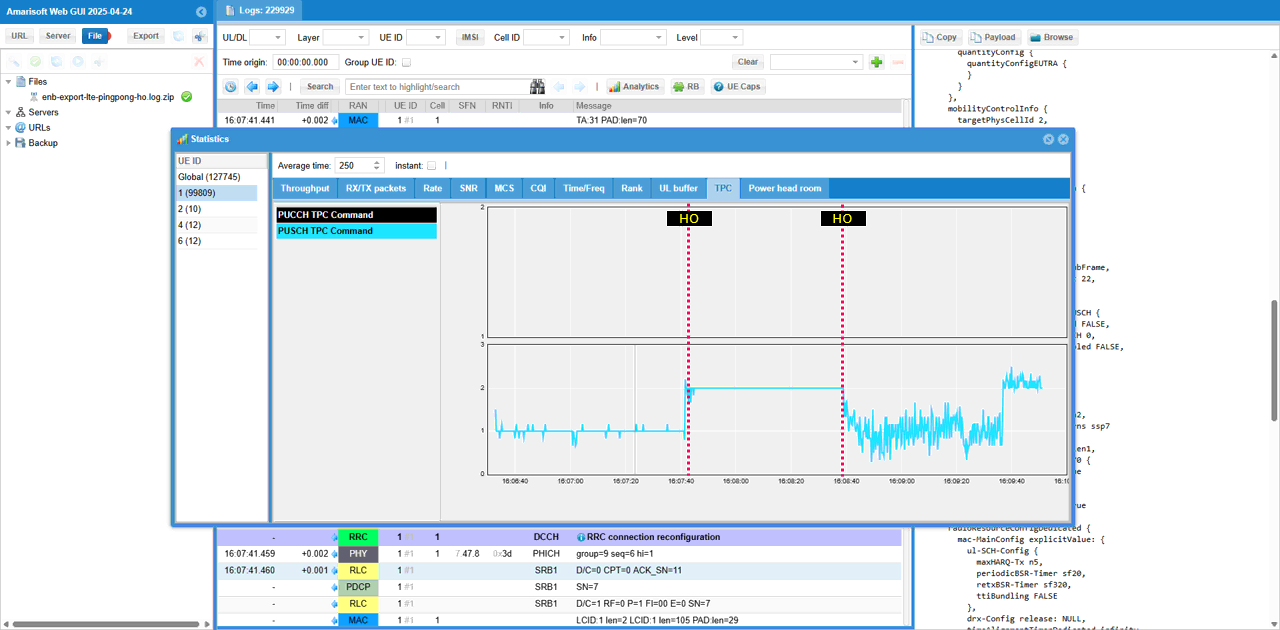
Check out Power headroom plot. You see the drastic discontinuity at the point of handover.
Test 4 : Triggering PingPong Handover by Channel Simulator - LTE/64 UE
In this test, we simulate a situation where a UE is moving away from the cell at a constant speed under simple pedesterial channel. In terms of protocol sequence and mechanism, this test is almost same as the previous test (Test 3). The difference is that the previous test is with only one UE whereas this test is with multiple UEs (64 UEs). This test can be a good reference test to check how a gNB can handle the overloaded handover process (i.e, triggering and processing the handover for many UEs in short time span).
Configuration
I have used gnb-sa-pingpong-ho-64ue.cfg that is copied and modified from gnb-sa.cfg. I will use the same file for all the test in this tutorial and just modify the parameters in the file without creating a new file.
I am using the mme-ims-64.cfg as shown below. Within mme-ims-64.cfg, ue_db_64-UE.cfg is used (included)
I used ue-nr-sa-pingpong-ho-64ue.cfg which is copied and modifed from ue-nr-sa.cfg on UEsim.
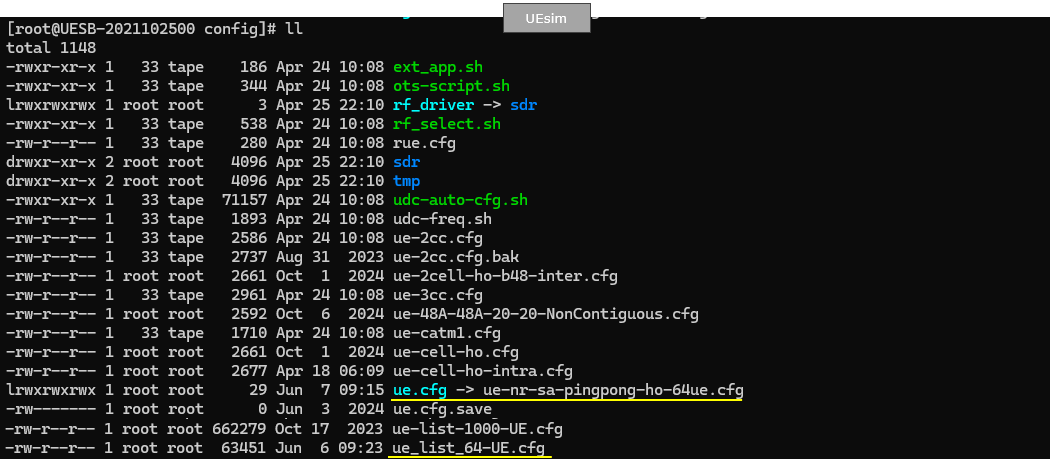
Following is the configuration on gNB.
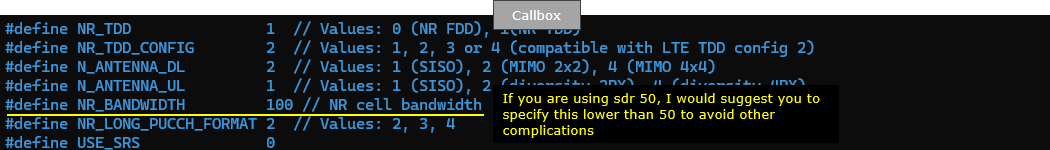
In this test, we set the bandwidth of both cells to 100 Mhz. If you are using the callbox with sdr 50, I would suggest you to set narrower bandwidth (e.g, 20 or 40 Mhz) to avoid other complications (e.g, configuring rf_driver).
Now let's configure the two cells that will be involved in handover. Note that we configured the different frequency for the two cells. It means that we will perform inter frequency handover in this test.
As shown here, the second cell (cell_id 2) is set as the neighbour cell (ncell_list) of the first cell and the first cell (cell_id 1) is set as the neighbour cell (ncell_list) of the second cell

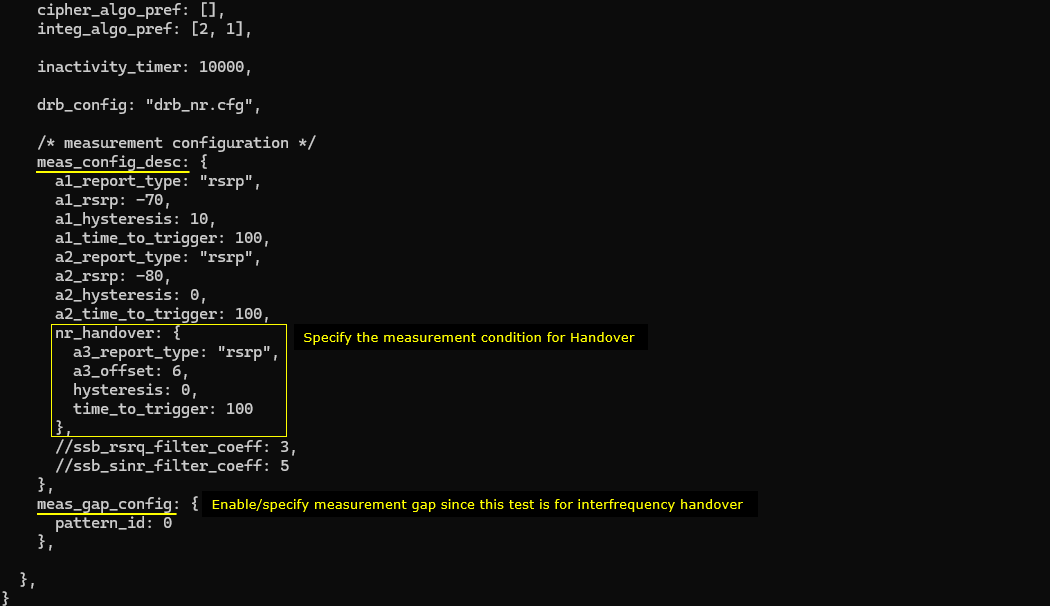
With Amarisoft, you can do both blind handover and measurement based handover. In this test, we will do measurement based handover. In order to do measurement based handover, you need to configure appropriate measurement condition for the handover. We usually configure this in cell_default block.

Configure measurement condition for source cell measurement and destination/handover measurement condition(a3 event in this case) as follows. In this test, we will do inter frequency handover, so we need to configure measurement gap (meas_gap_config) as well.
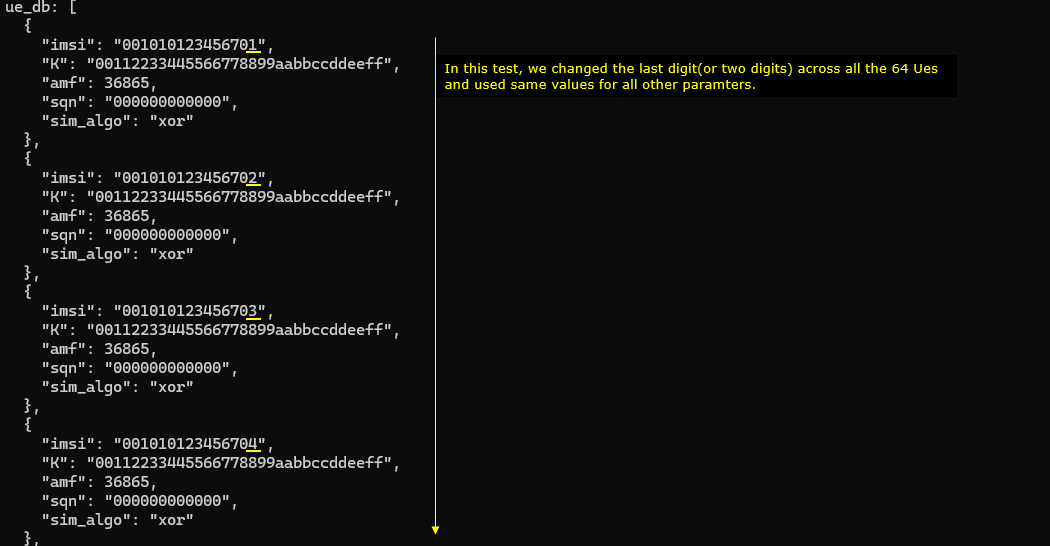
Since this test should handle multiple UE, you need to include ue data base carrying the USIM information of all the UEs (ue_db_64-UE.cfg)
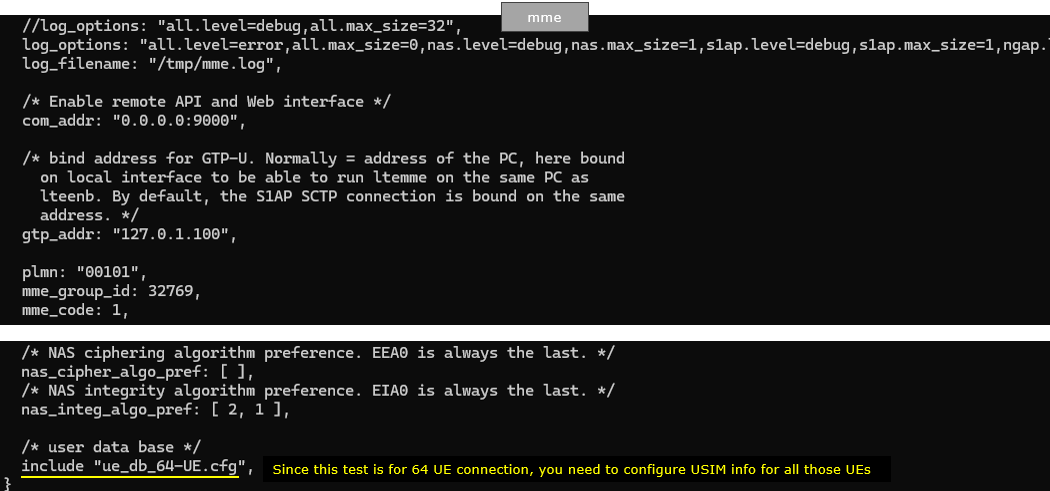
Within ue_db_64-UE.cfg , USIM information of all the UEs are defined as shown below (In this test, we will use the USIMs that differs only in terms of imsi and all other parameters are set to same value)
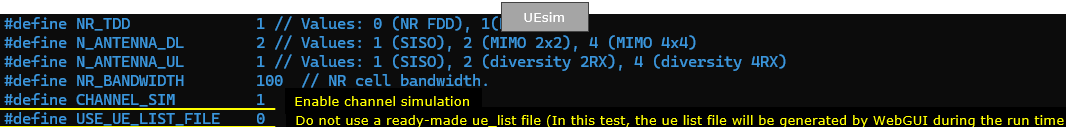
In ue-nr-sa-pingpong-ho-64ue.cfg , followings are configured. Since the main purpose of this test is to show how to simulate UE moving back and forth between two cells triggering pinpong handover. The UEsim configuration is the main part to be noted.
TDD is set to 1 (i.e, TDD) which is just to match the eNB configuration. Important to note is that CHANNEL_SIM is set to 1 which indicates the channel simulator will be used.
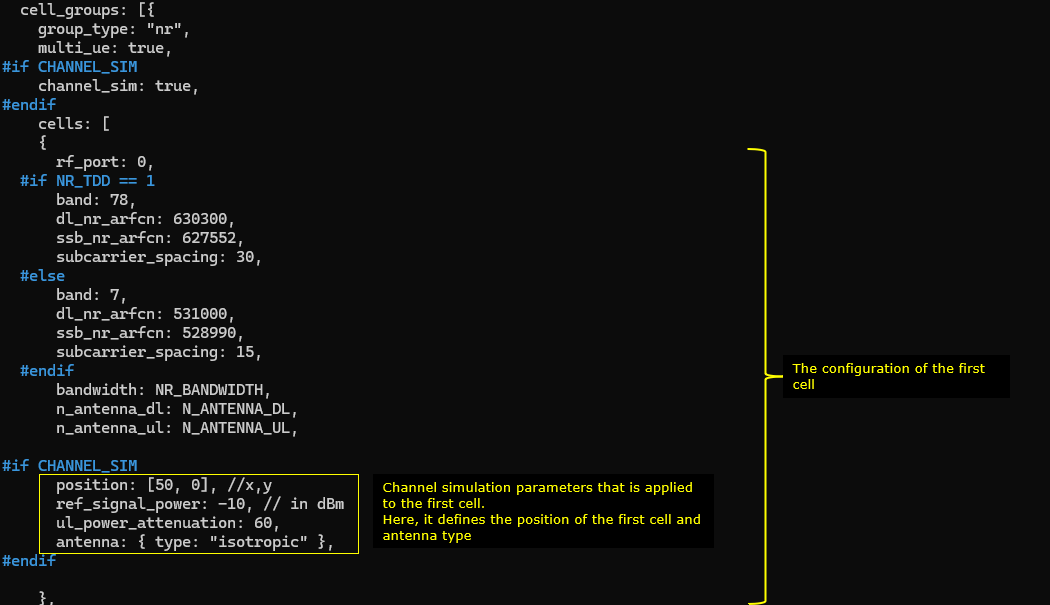
Now in cell_groups, channel_sim is set true which enables channel simulation functionality.
The position of the first cell is set to [50,0] and reference signal power(ref_signal_power), ul_power_attenuation and antenna type is configured for the simulated radio channel. In the same way, the simulated channel configuration for the second cell is set. The position of the cell is set to [-50,0] and all other configurations are same as the first cell.
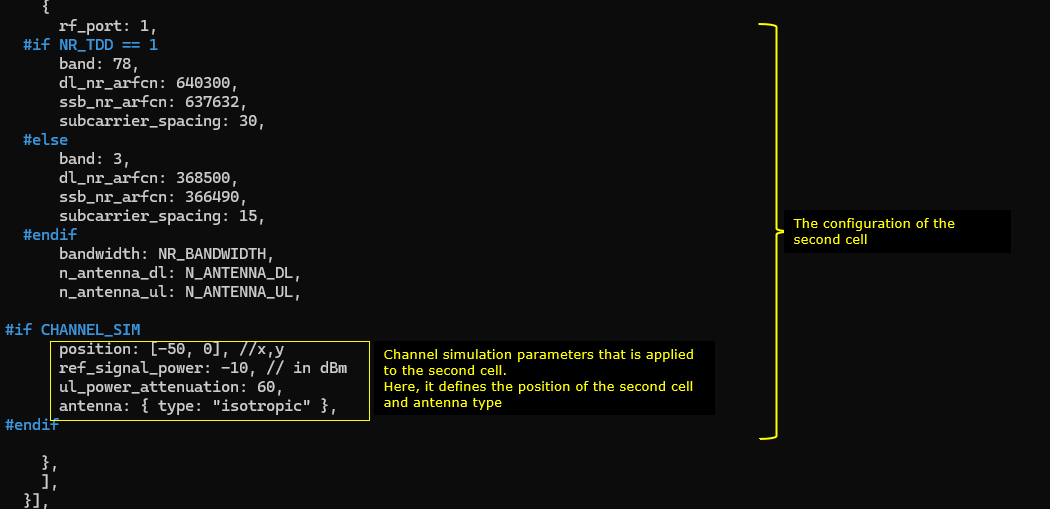
Following(ue_list) is the configuration that applies to a specific UE. Here you see the channel parameters that applies to the UE. First, UE is positioned at the [0,0] which is at the mid point between the two cells. It start moving towards the right cell (direction 0 meaning angle 0 degree). When it reaches the max_distance (in meters), it bounces back (turn 180 degree) and moves until it reaches min_distance (default 0). The moving speed is set to 5 km/h (speed: 5) in this test. The radio channel for this test is set to a 3GPP standard channel ("epa").
Perform the Test
Now run the callbox and check out basic physical cell configuration. Note that two cells are configured for inter cellular frquency (
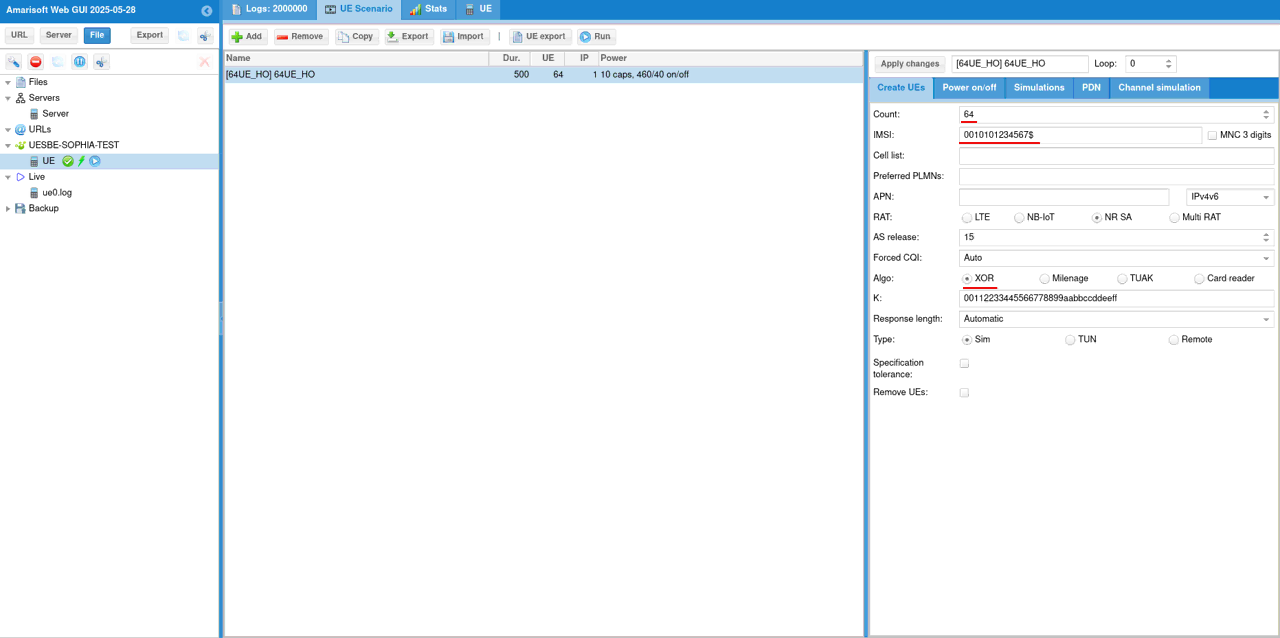
In this test, we used the UE scenarion function of UEsim WebGUI to generate USIM parameters automatically (
Then [Start] Scenario and you will see the registration process of all the UEs
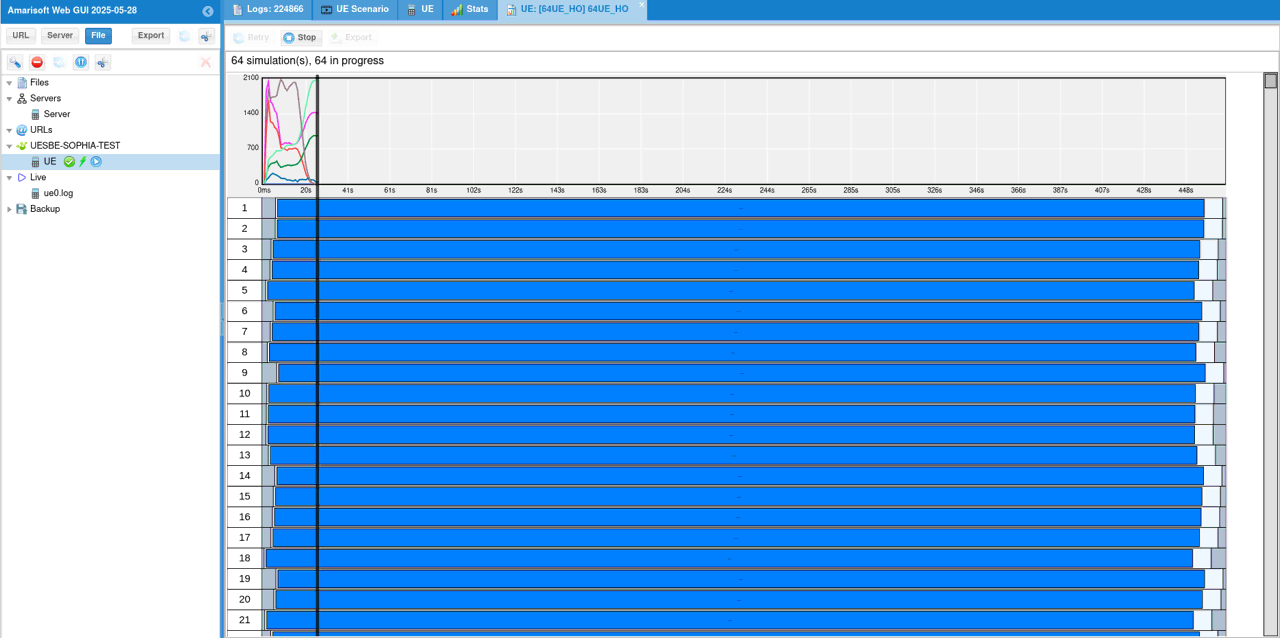
You can check some of high level KPIs (e.g, Bitrate, Packets, Signals etc)
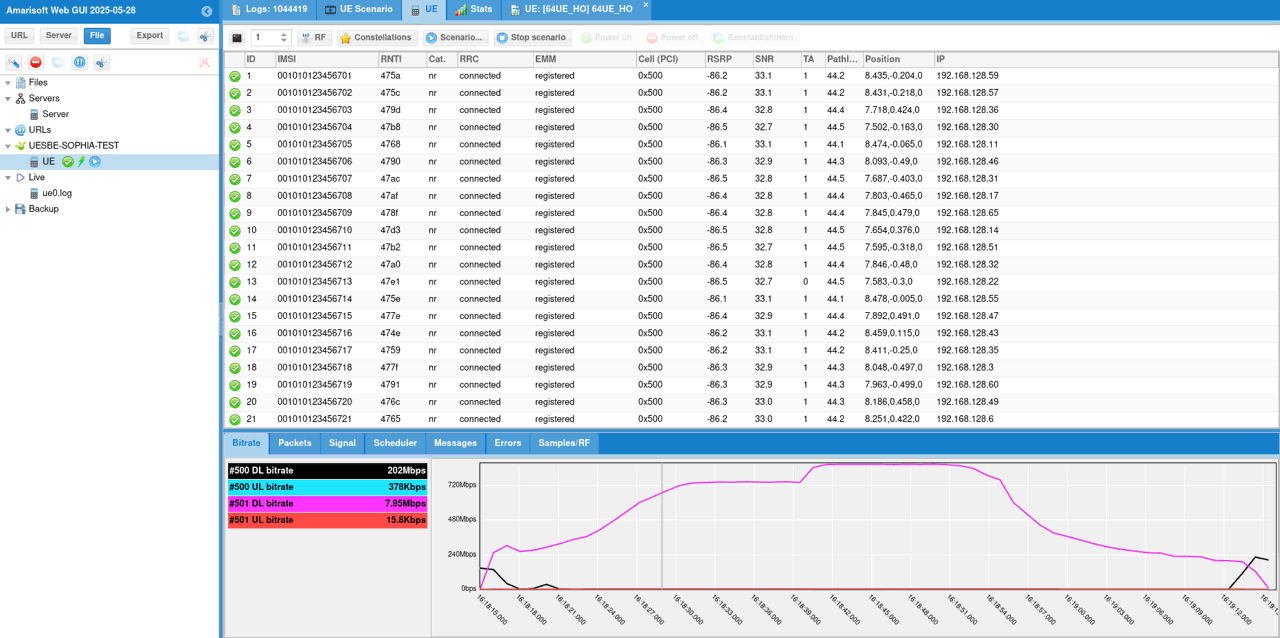
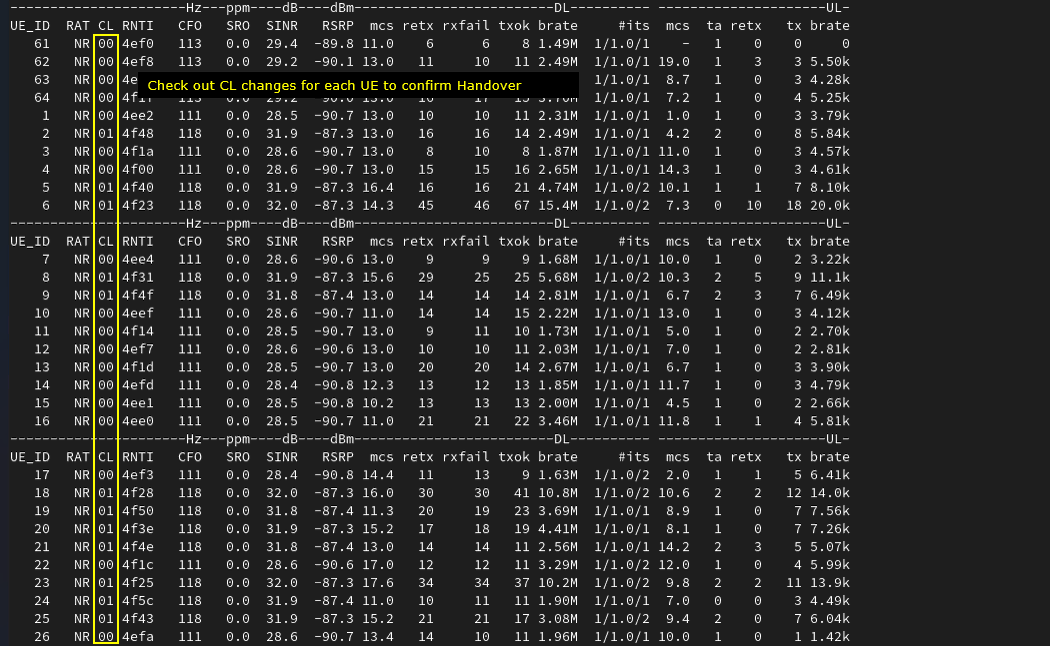
You can check out the high level status of each UEs with t command. Check out CL column value for each UE to check which cell a UE is connected to.
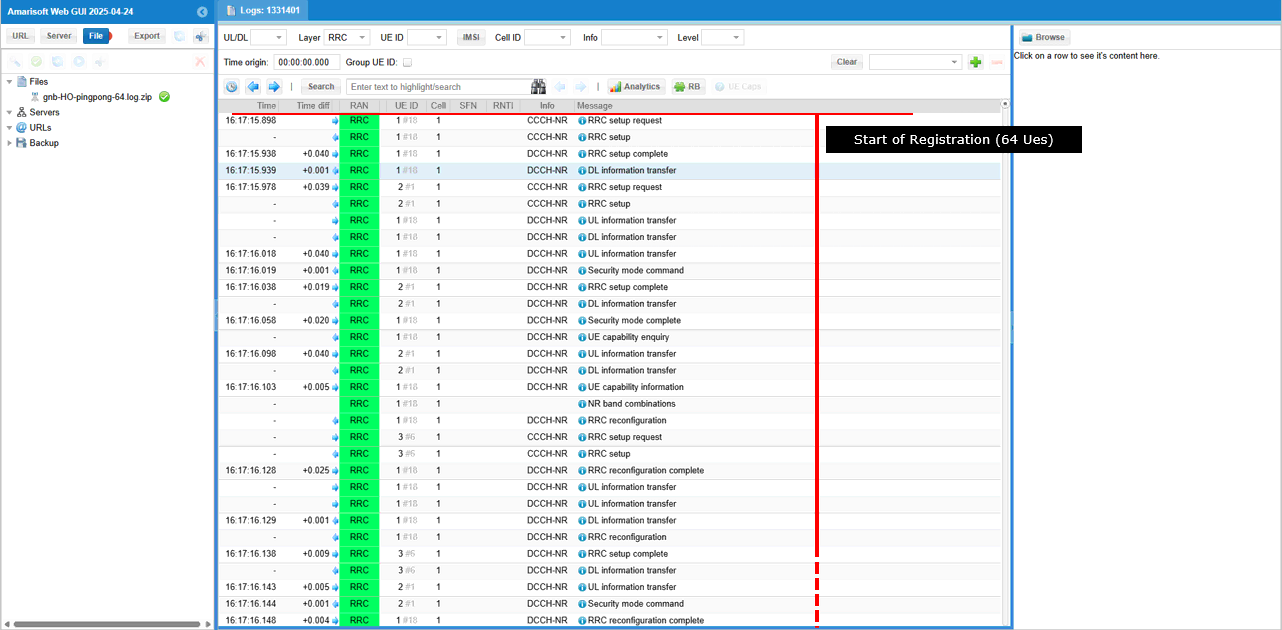
Log Analysis
You can check out if all the UEs completed registration. You may also the total amount of time for the registration completion of all 64 UEs.
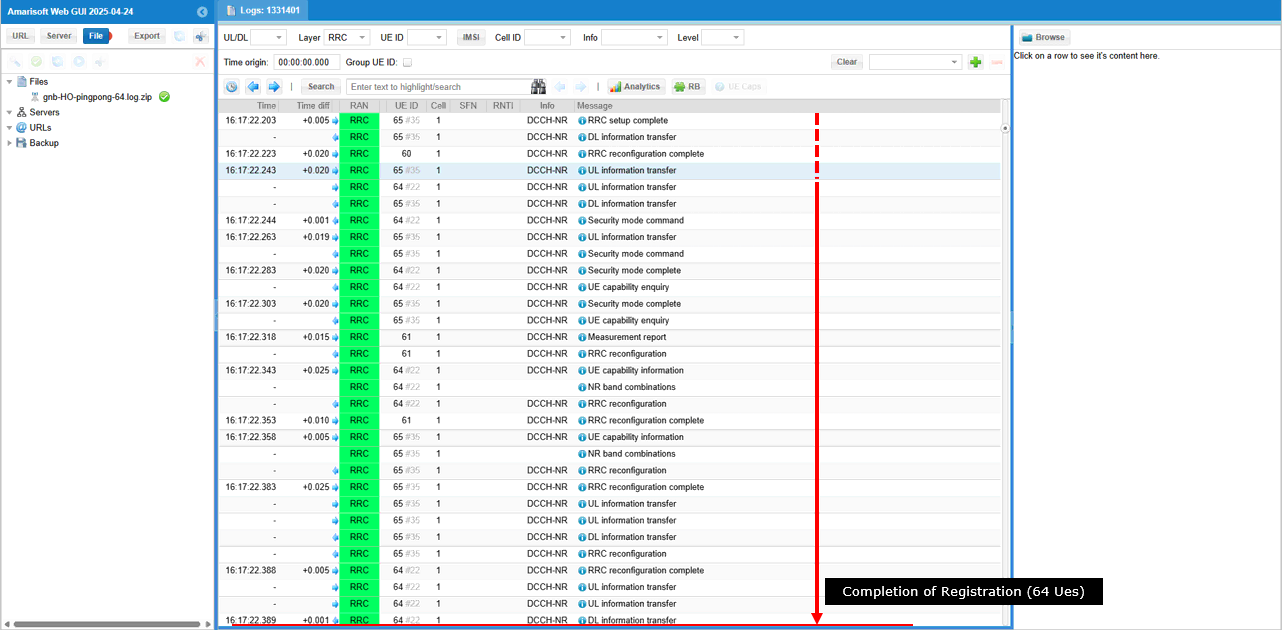
After the completion of the registration, gNB start the process of handover by sending measurement report configuration for each UEs.
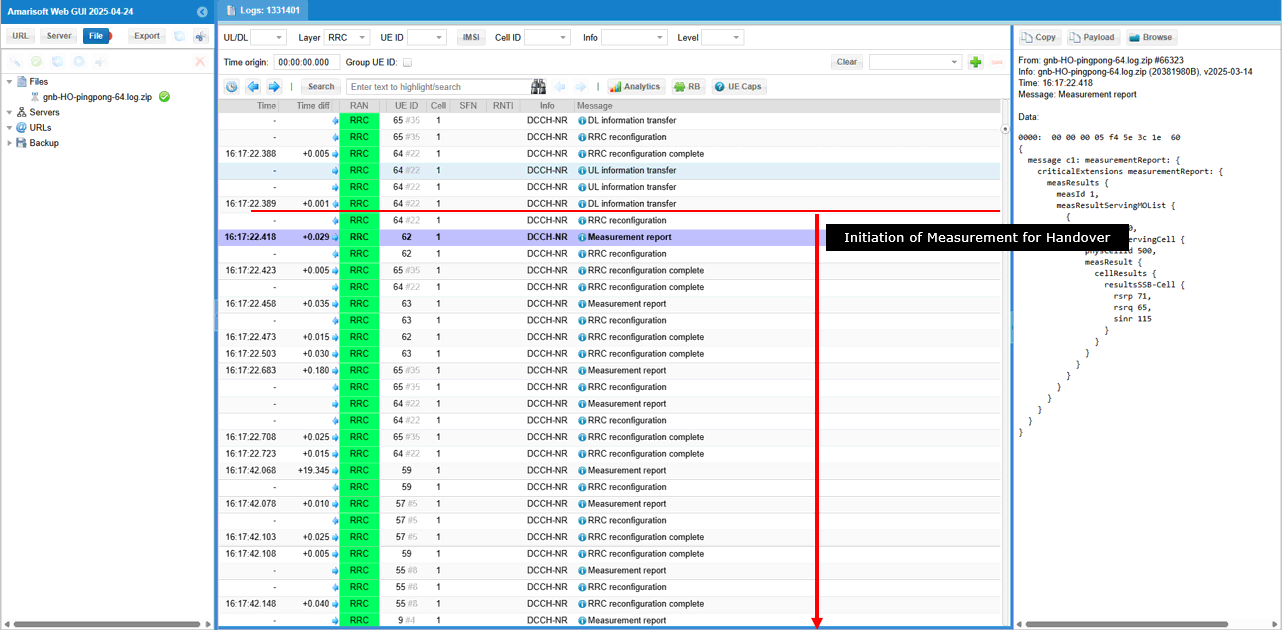
If a specific UE reaches a location where the channel condition(recieved cell power) mets the condition of the measurement configuration, it send measurement report required for the handover
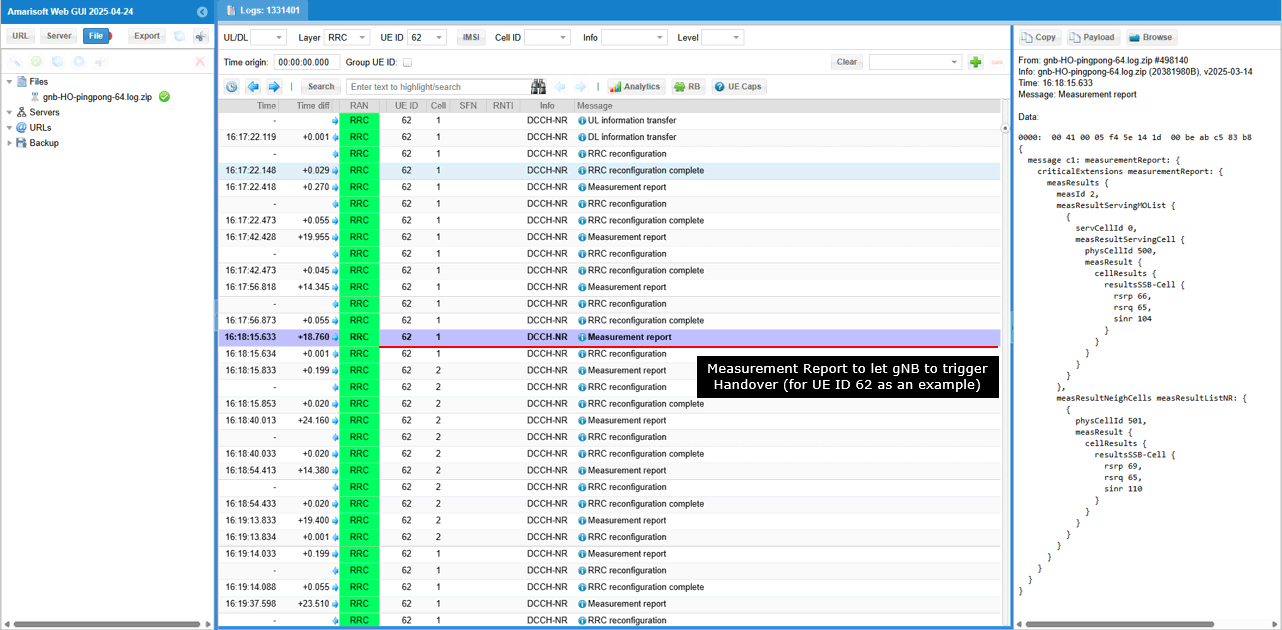
Once gNB recieves the measurement report that satisfy the handover condition, it triggers handover with RRC Reconfiguration carrying spCellConfig.reconfigrationwithSync.spCellConfigCommon.phyCellId <PCID of Destination Cell> (
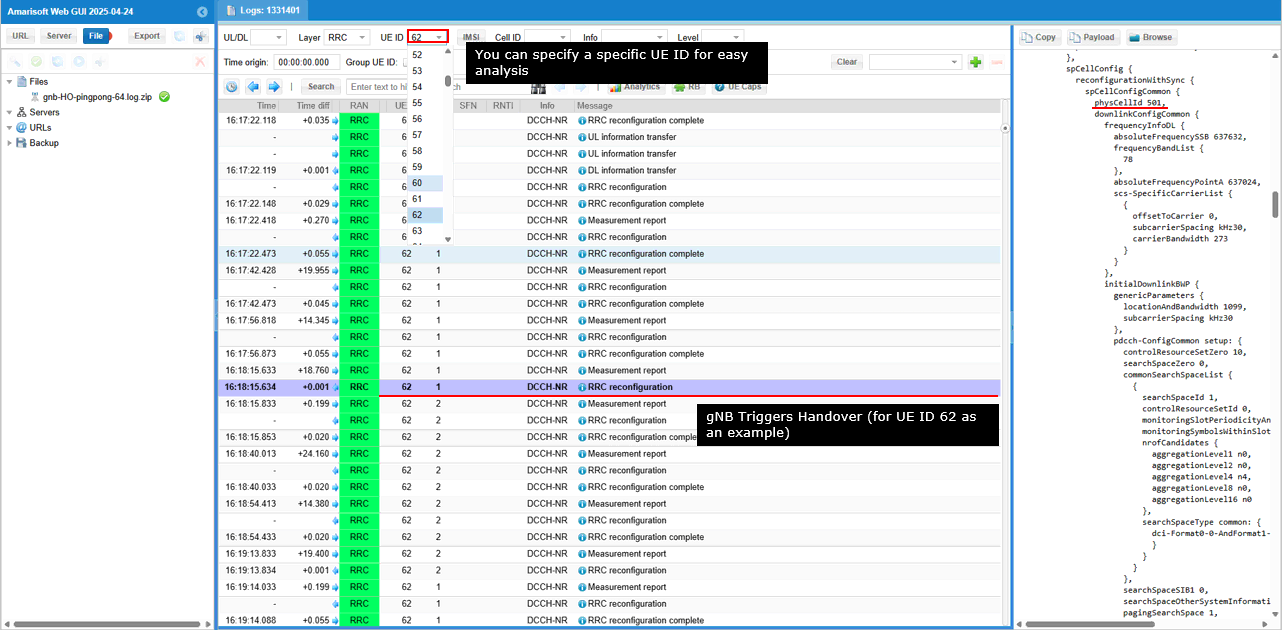
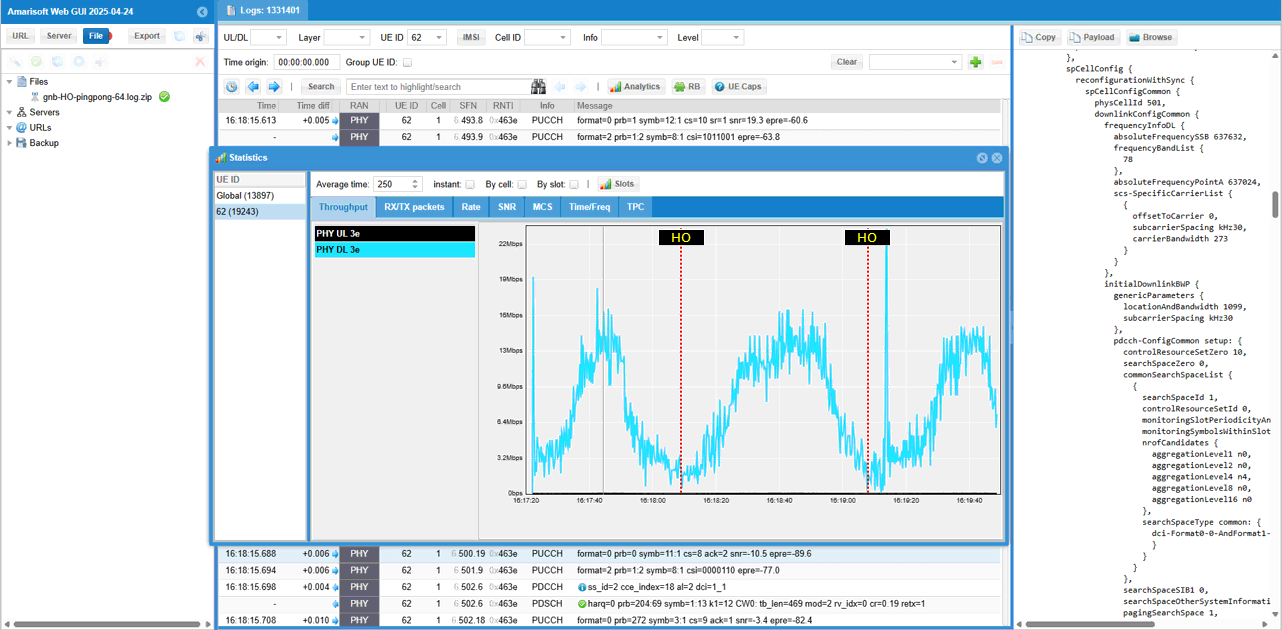
For more intuitive analysis, let check out how some of KPI(e.g, throughput) and lower layer measurement changes during the UE movement and handover.
You see throughput goes down as UE moves away from the serving cell and reach the location where it switches the cell (handover)
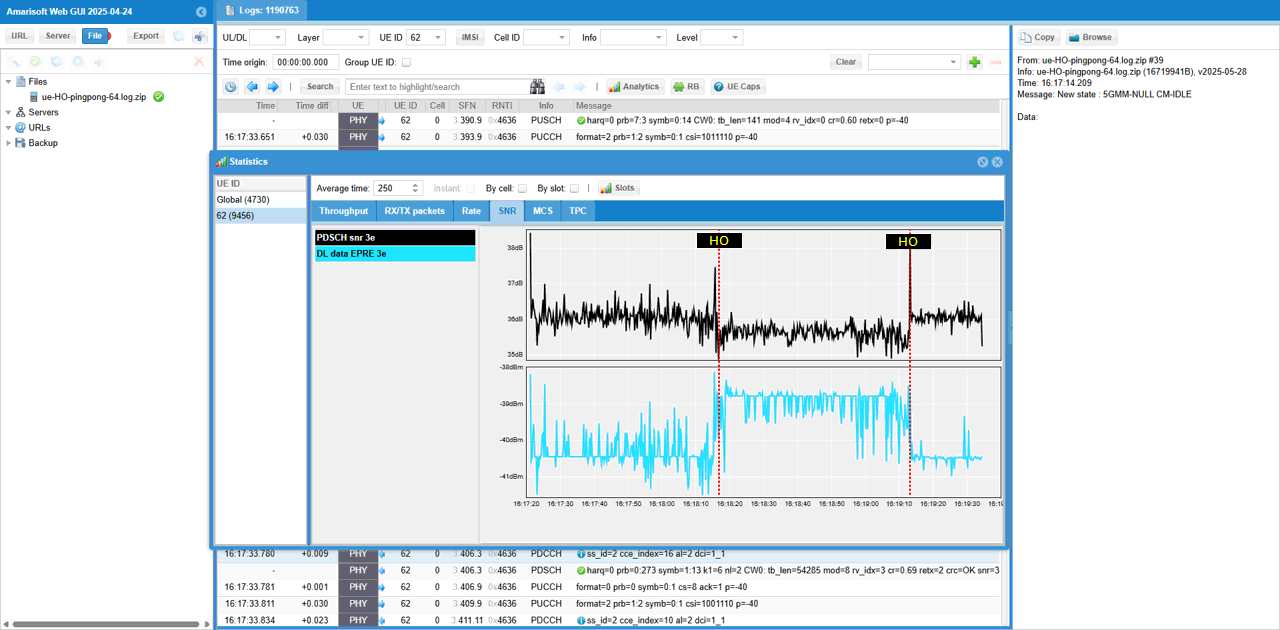
You see SNR goes down as UE moves away from the serving cell and reach the location where it switches the cell (handover). Depending on radio channel quality of each cells, you would see discontinuity of SNR between the cells.
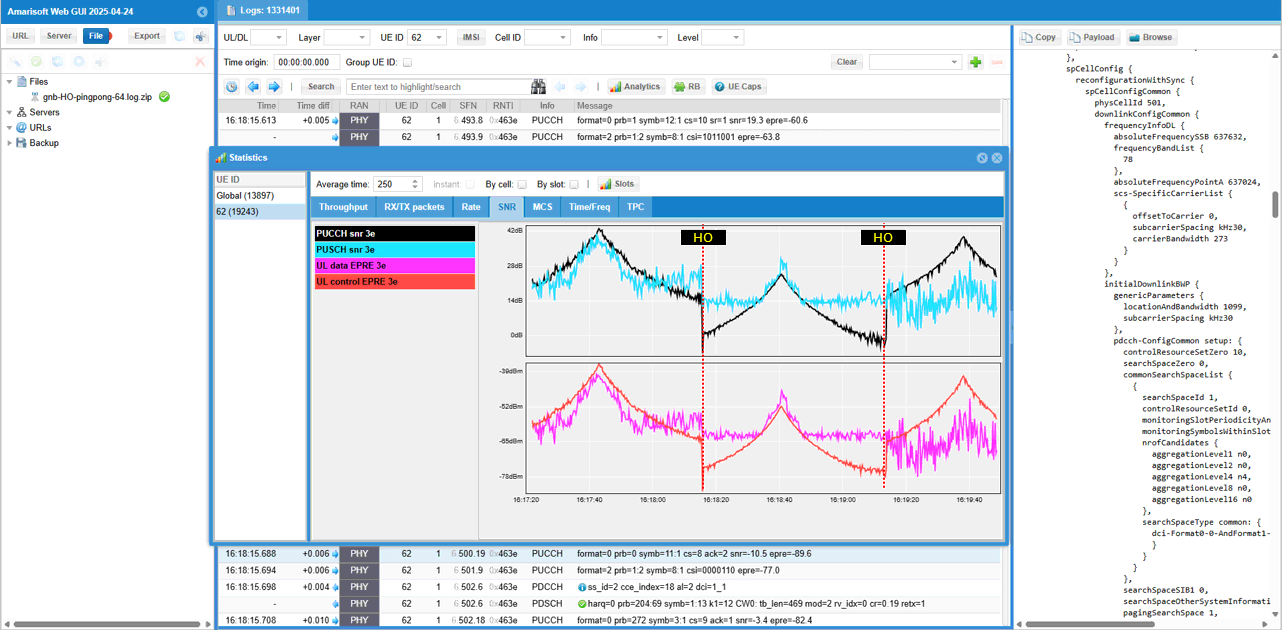
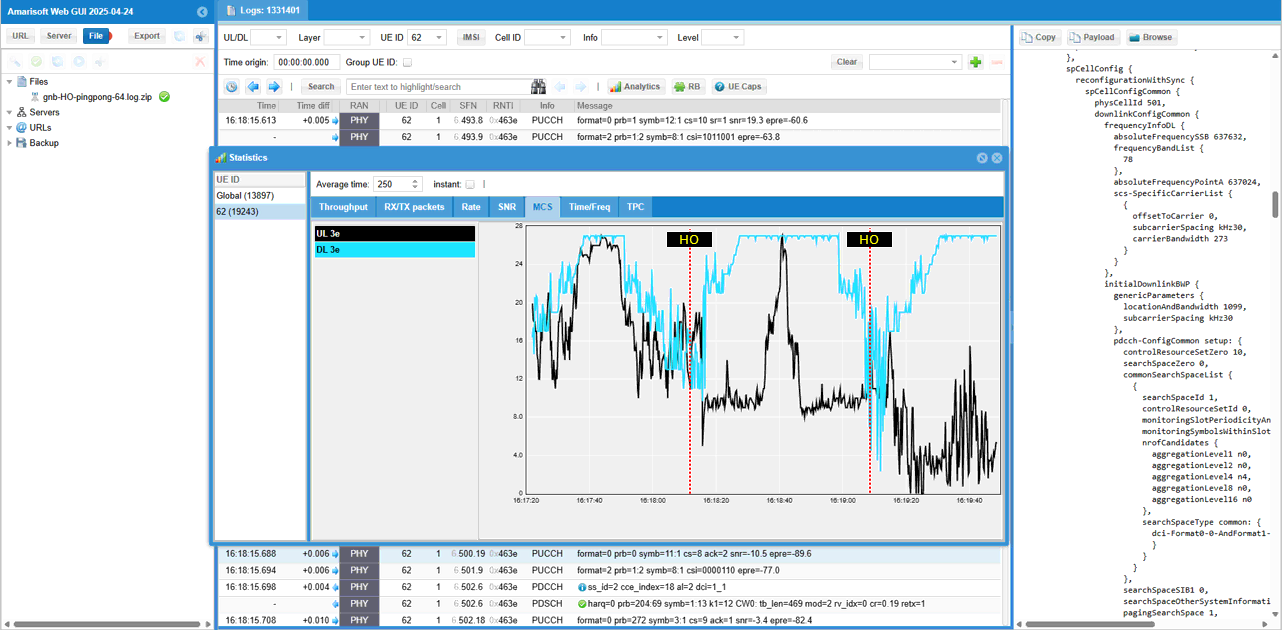
MCS change over the UE movement and handover is not that obvious, but still see some general tendency that MCS gets lower as UE move away from the cell and reach the cell boundary where handover happens
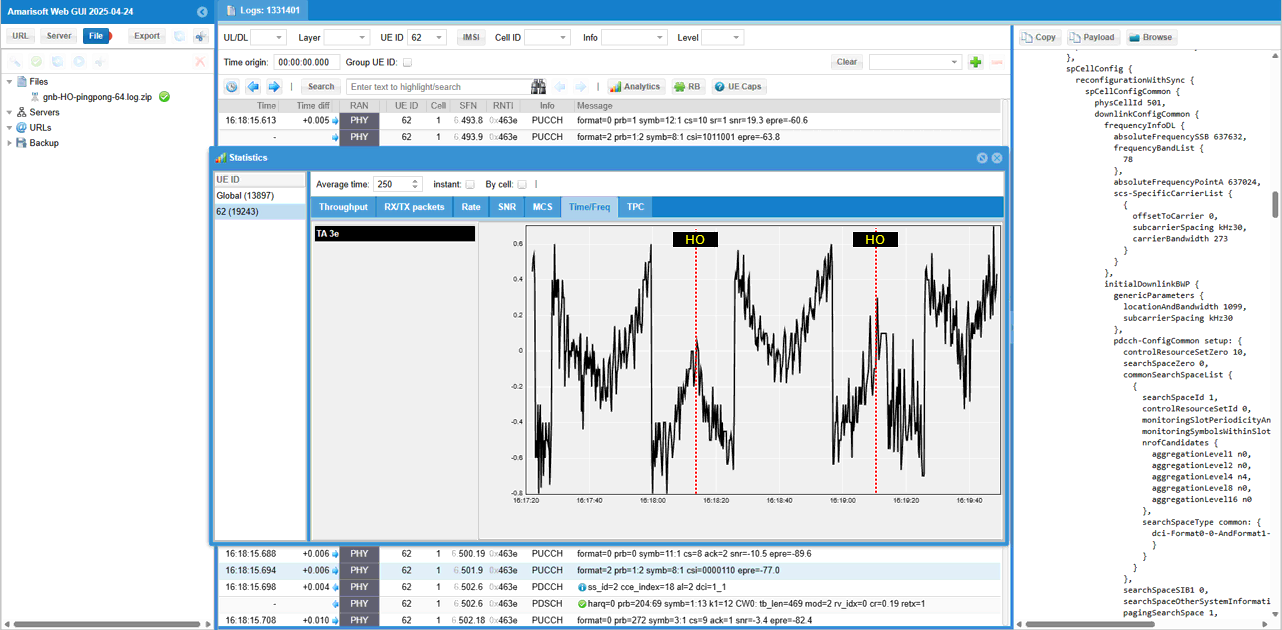
You can check out the TA (Timing Advance) changes while the UE moves back and forth between the two cells
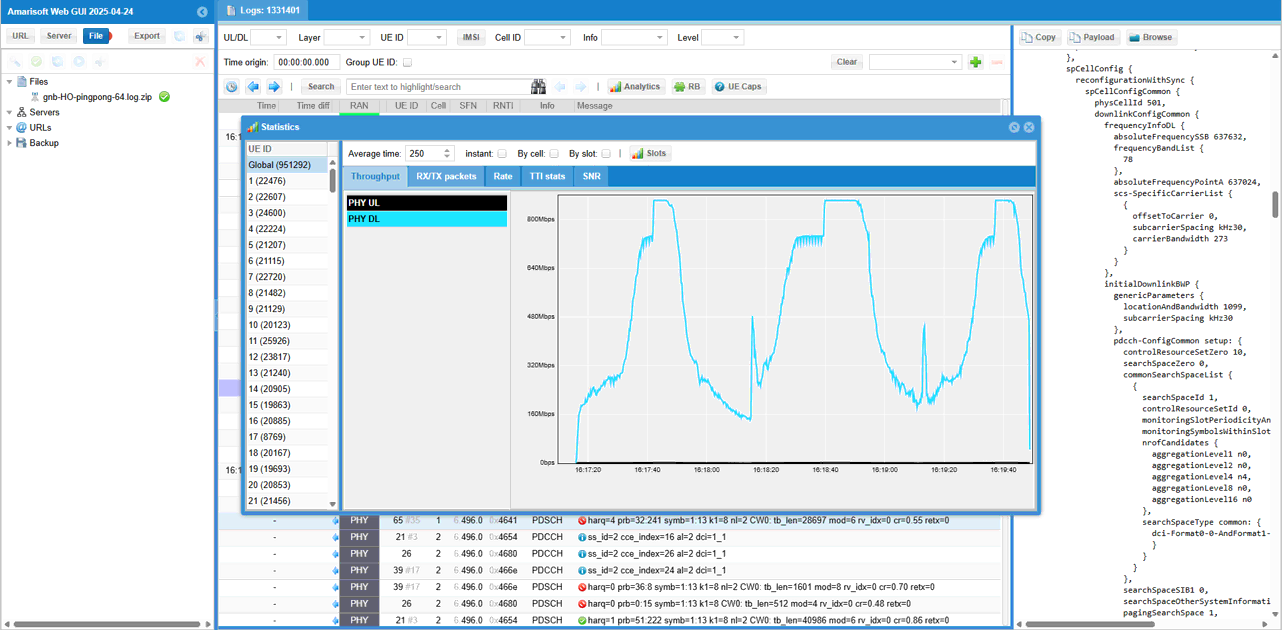
Now let's look into some aspects of KPI and other measurements for the consolidation of all 64 UEs.
First check out the Throughput profile as all the UEs moves back and forth between the two cells undergoing handover.
Then check out the Tx Error Rate (TX retransmission) and RX error. You see that both TX error and RX error reaches peak around handover point.
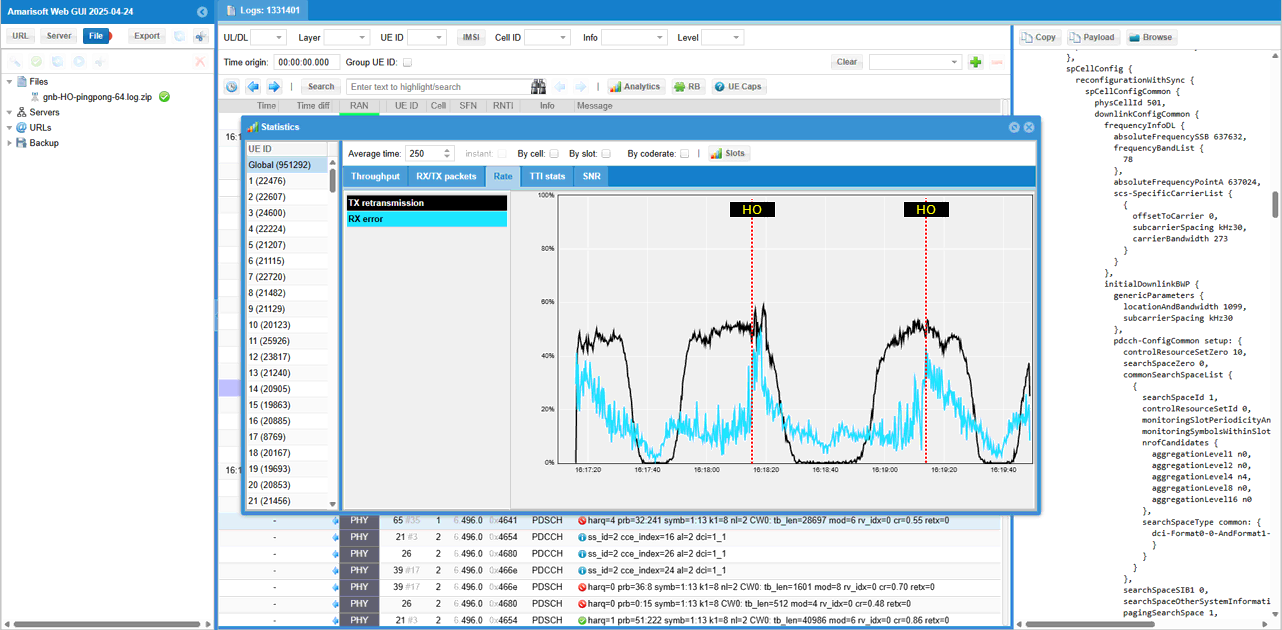
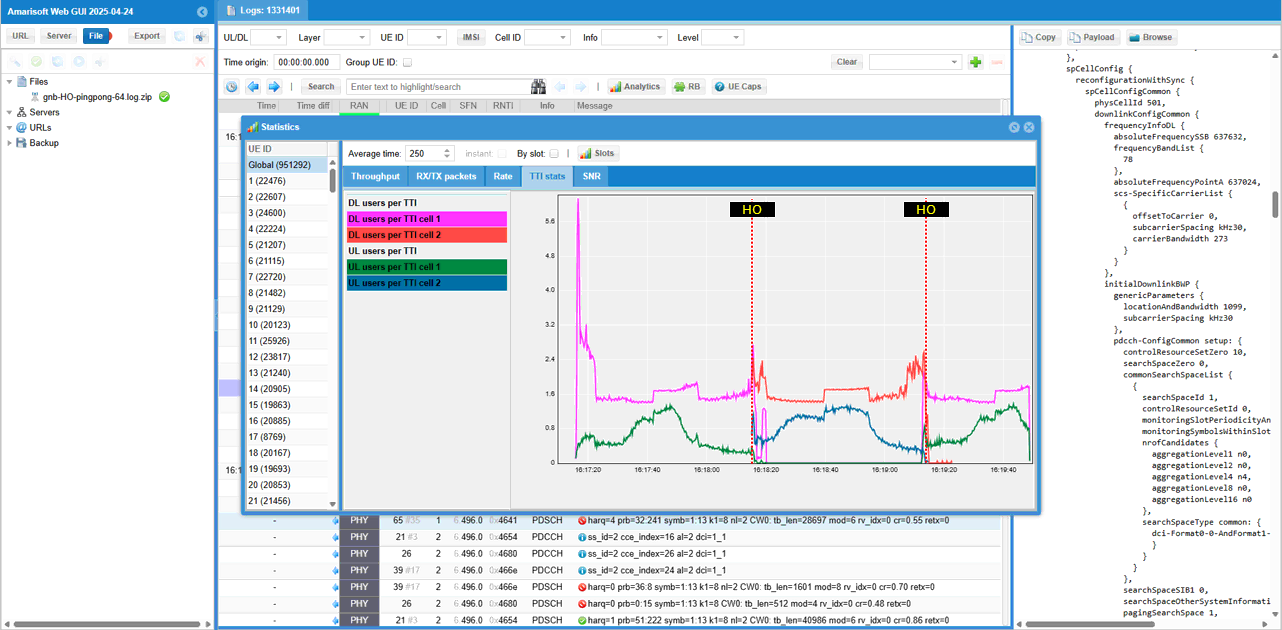
Now you can check out the number of UEs connected to each cell over time. This plot is a good indicator to verify on how well the handover of the multiple UEs went through.
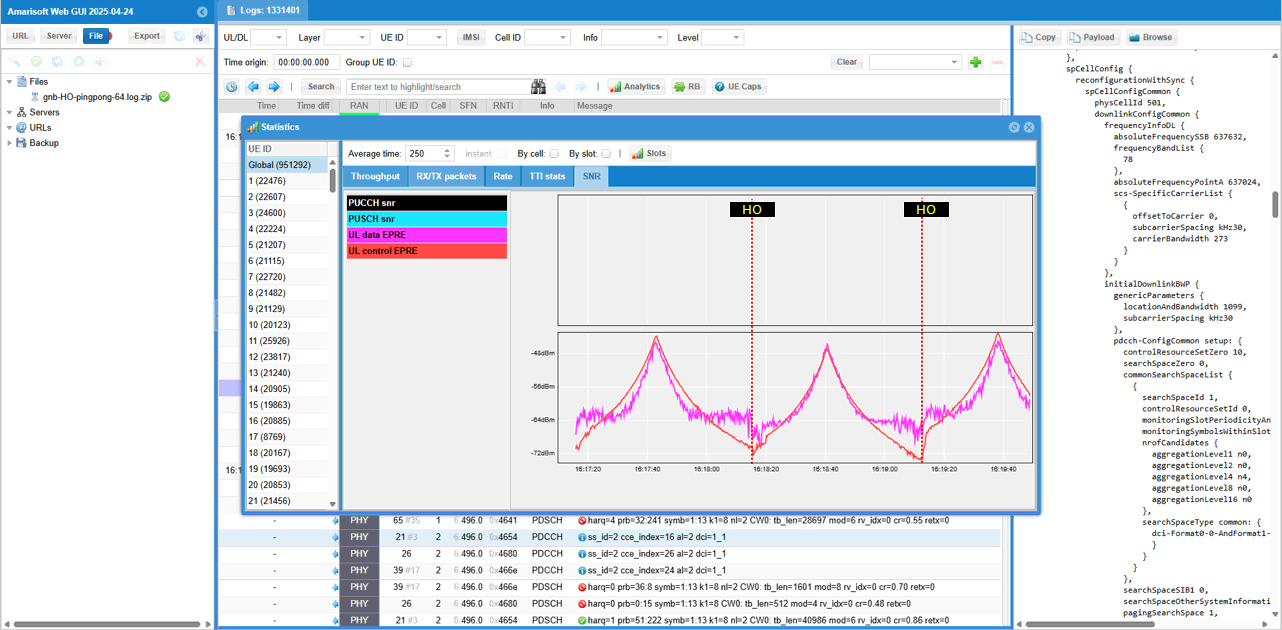
You can also check out SNR profile and notice the SNR shows distinctive pattern as UEs gets closer and farther away (to) from the connected cells.
You can do similar analysis from UEsim log as well (