NR SA D2C (Direct To Cell)
This tutorial is to show you how to configure and test Direct to Cell in NR. Direct to Cell represents 'From Satellite directly to Cellular Phone'. The 'Cellular Phone' in this context is just an ordinary commercial mobile hone that you have and it does not need to support any special feature for satellite communication as long as it works with ordinary NR SA in terrestrial network.
Actually Direct To Cell is not the 3GPP based feature like NTN (NB NTN or NR NTN). So the UE is not expected to support any specific features to accommodate this type of connection. So all the functionality to handle such a long delay or doppler shift etc which are present for satellite communication should be implemented by gNB that is sitting on the Satellite. This gNB implementation is mostly up to gNB vendor since the functionality is not specified in 3GPP.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Direct to Cell in NR (New Radio) is an innovative approach that enables ordinary commercial cellular phones to connect directly to a satellite, extending mobile coverage to remote and underserved regions without requiring specialized hardware or modifications on the user equipment (UE). This technology leverages the existing NR Standalone (SA) capabilities of standard smartphones, facilitating satellite-to-cellular connectivity without relying on traditional terrestrial infrastructure. Unlike 3GPP-standardized features such as NB-IoT NTN (Narrowband Internet of Things Non-Terrestrial Networks) or NR NTN (New Radio Non-Terrestrial Networks), Direct to Cell is not governed by formal 3GPP specifications. As a result, the mobile device operates as it would on a conventional terrestrial network, while all satellite-specific adaptations—such as compensating for extended signal propagation delay and managing Doppler shifts—are handled entirely by the gNB (next-generation NodeB) located onboard the satellite. The architectural distinction places significant responsibility on the satellite-based gNB, which must emulate terrestrial network behavior and ensure seamless interoperability for the UE. This paradigm allows mobile network operators and satellite providers to bridge connectivity gaps, offering ubiquitous coverage and supporting new use cases without imposing changes on end-user devices. The implementation details and optimizations for Direct to Cell are predominantly determined by the gNB vendor, given the absence of standardized protocols or message structures for this deployment model. As such, understanding the architectural requirements, technical considerations, and practical steps for configuring and testing Direct to Cell in NR is crucial for engineers and practitioners seeking to deploy or evaluate this emerging technology within the broader mobile ecosystem.
-
Context and Background
- Direct to Cell extends NR connectivity by allowing unmodified commercial handsets to connect directly to satellites, bypassing the need for terrestrial cell towers.
- Unlike standardized NTN solutions, Direct to Cell is implemented outside the 3GPP-defined feature set, placing customization responsibilities on satellite gNB vendors.
- The technology addresses coverage challenges in remote, rural, or disaster-affected areas where terrestrial infrastructure is unavailable or impractical.
-
Relevance and Importance
- Direct to Cell represents a significant advancement in bridging the digital divide, enabling global connectivity for standard mobile devices.
- It offers a cost-effective alternative to deploying terrestrial infrastructure, with potential applications in emergency communications, IoT, and expanding rural access.
- Understanding the configuration and testing process is essential for engineers, operators, and vendors aiming to leverage this technology in commercial deployments.
-
Tutorial Outcomes
- Learners will gain insight into the architectural and operational principles of Direct to Cell in NR.
- The tutorial will guide users through practical configuration steps and testing methodologies relevant to satellite-based NR deployments.
- Participants will develop a foundational understanding of the technical distinctions between Direct to Cell and standardized NTN solutions.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge
- Familiarity with 5G NR architecture and core concepts, including the roles of UE and gNB.
- Basic understanding of satellite communication challenges, such as signal delay and Doppler effects.
- Experience with NR SA (Standalone) network configurations and testing tools is beneficial.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial details the setup and execution of low-layer Direct to Cell (D2C) testing using Amarisoft eNB and UEsim, focused on Simulated LEO satellite scenarios. The document emphasizes configuration, execution, and validation steps for D2C operation under NTN (Non-Terrestrial Networks) test profiles.
-
Test Setup Overview
- Uses a SIM card provided with the system; configuration changes are optional and referenced in a separate Configuration Guide.
- Test setup involves Amarisoft eNB (gNB) and UEsim, with focus on low-layer connectivity and not requiring complex IP configurations.
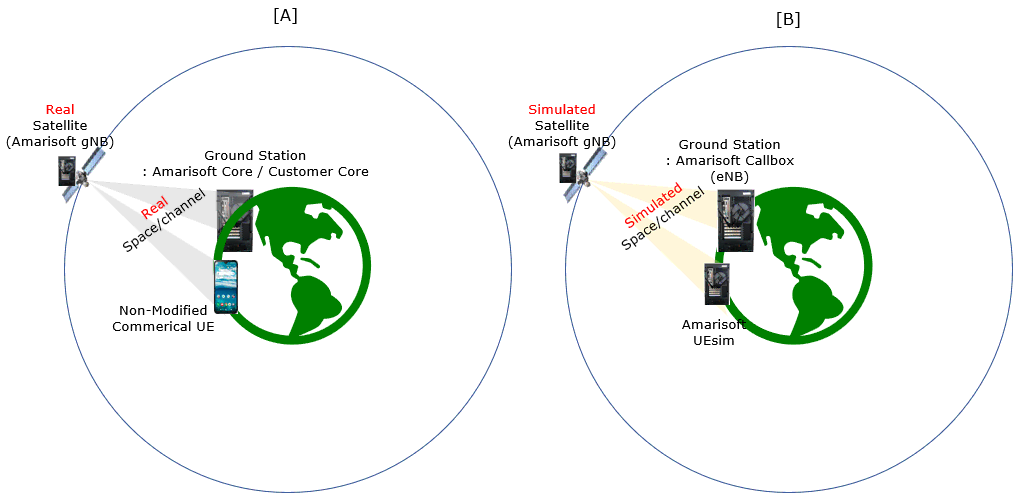
- Two possible hardware setups are referenced; the tutorial is based on the configuration indicated as [B] in the overview diagram.
-
Key Configuration Parameters
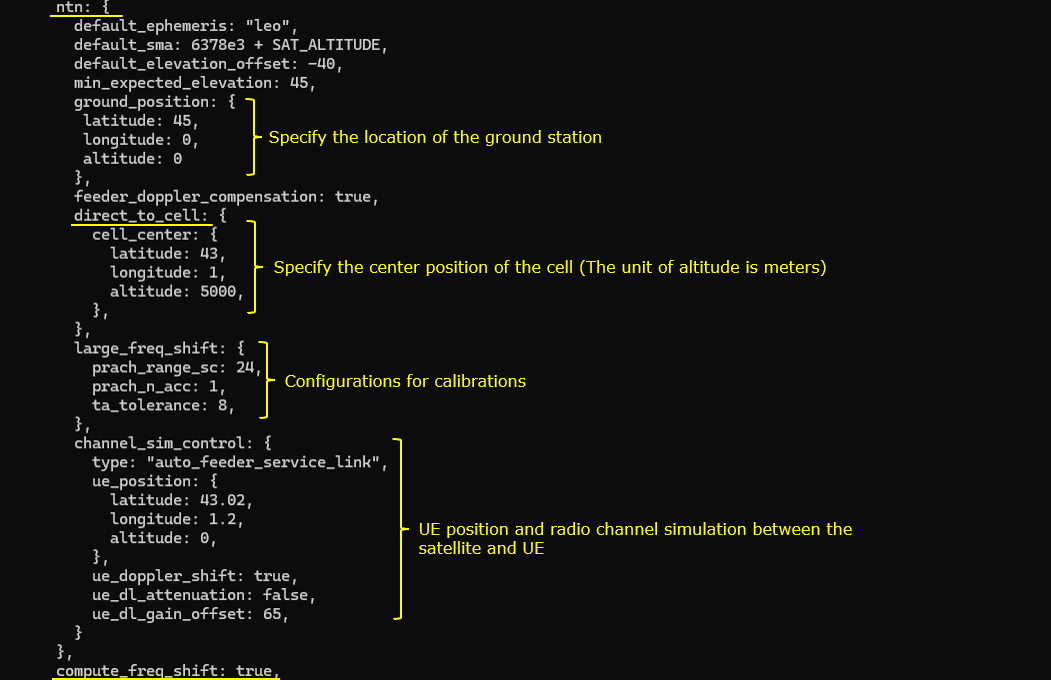
- The tutorial highlights the importance of a set of NTN-related configuration parameters in the Amarisoft system. These include satellite state vectors, ephemeris (orbital elements), ground station and UE positions, synchronization, frequency settings, direct_to_cell flag, and channel simulation controls, among others.
- Parameters such as ntn, default_ephemeris, ground_position, direct_to_cell, and channel_sim_control play a central role in modeling the satellite scenario.
-
Test 1: Direct to Cell with Simulated LEO and UEsim
- Objective: Configure and validate D2C operation with Amarisoft UEsim as the DUT (Device Under Test) under simulated LEO satellite conditions.
-
Configuration Steps:
-
Use gnb-sa-direct-to-cell.cfg for gNB configuration.
- Specify satellite orbit via NTN_MODE (choosing GEO for the test, even though LEO is referenced in the objective).
- Enable and configure CHANNEL_SIM (awgn profile for link simulation).
- Configure NR FDD band, set ssb_period to a low value for improved UE timing estimation, and adjust parameters such as force_full_bsr and force_dl_schedule for test visualization.
- Adjust prach_config_index as needed for long-distance links.
- MAC/RRC timers (e.g., retx_bsr_timer, sr_prohibit_timer, t300, t310, t_PollRetransmit) are set based on satellite-ground RTT and orbit type.
- NTN-specific parameters configured for satellite ephemeris, ground station, UE positions, and set direct_to_cell to indicate D2C mode.
-
Use ue-nr-sa-fdd-10Mhz.cfg for UEsim configuration.
- This configuration is a copy of a default NR SA config, modified only for band and channel bandwidth to align with gNB frequency settings.
- No satellite-specific changes are required for UEsim, mirroring the D2C objective of supporting standard UEs.
-
Use gnb-sa-direct-to-cell.cfg for gNB configuration.
-
Test Execution Procedure:
- Start LTE service on callbox, verify cell configuration via cell phy and cell commands.
- Optionally, enable BCCH logging for SIB message capture at test initiation.
- Start trace logging.
- Power on UE on UEsim (or commercial UE if available).
- Allow DUT to complete initial attach; additional troubleshooting may be required for commercial UEs or real satellites.
- Verify data plane by generating traffic (e.g., ping) to confirm data connectivity.
-
Log Analysis and Validation:
- Monitor real-time positions of eNB and UE using the WebGUI [ENB] and [NTN] tabs.
- Track satellite elevation, distance, and connectivity status; connection is lost if satellite elevation becomes negative.
- Observe signaling sequences, throughput, SNR, and DL CQI to assess link quality and system performance.
- Inspect satellite position (elevation, azimuth) and timing advance (TA) values for expected dynamic behavior as satellite moves.
- Filter logs for NTN-related status and metrics; log collection for NTN must be enabled during simulation runs.
In summary, the tutorial provides a detailed step-by-step methodology for configuring and validating Direct to Cell scenarios using simulated satellite links, with a focus on correct parameterization, test execution, and result analysis using Amarisoft systems. Critical configuration and procedural steps are highlighted to ensure repeatability and effective troubleshooting.
Test Setup
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below. This is just for low layer testing, you may not need any complicated IP layer setup.
- SIM Card used in this tutorial is the one delivered with the system as it is.
- If you want to change the configuration, The tutorial Configuration Guide would help
With Amarisoft eNB and UEsim, we can try with following two different setups.
Key Configuration Parameters
Followings are important configuration parameters for this tutorial. You may click on the items for the descriptions from Amarisoft documents.
- ntn : In this link, you can find the descriptions for all the parameters below.
- ephemeris
- use_state_vectors
- eci_reference
- ground_position
- n_ta_common
- n_ta_drift
- n_ta_drift_var
- n_ta_common_offset
- feeder_doppler_compensation
- feeder_dl_freq
- feeder_ul_freq
- large_freq_shift
- direct_to_cell
- channel_sim_control
- type
- ue_position
- ue_doppler_shift
- ue_dl_freq
- ue_ul_freq
- feeder_doppler_shift
- ue_dl_attenuation
- ue_dl_gain_offset
- ul_sync_validity
- k_offset
- k_mac
- dynamic_k_offset
- reference_location
- t_service
- neighbour_cells
- rat_type
- t318
Test 1 : D2C with Simulated LEO and UEsim
This is to configure and test Direct to Cell for Simulated LEO using Amarisoft UEsim as DUT.
Configuration
The configuration shown here is common configuration for all the subtests belonging to Test 1
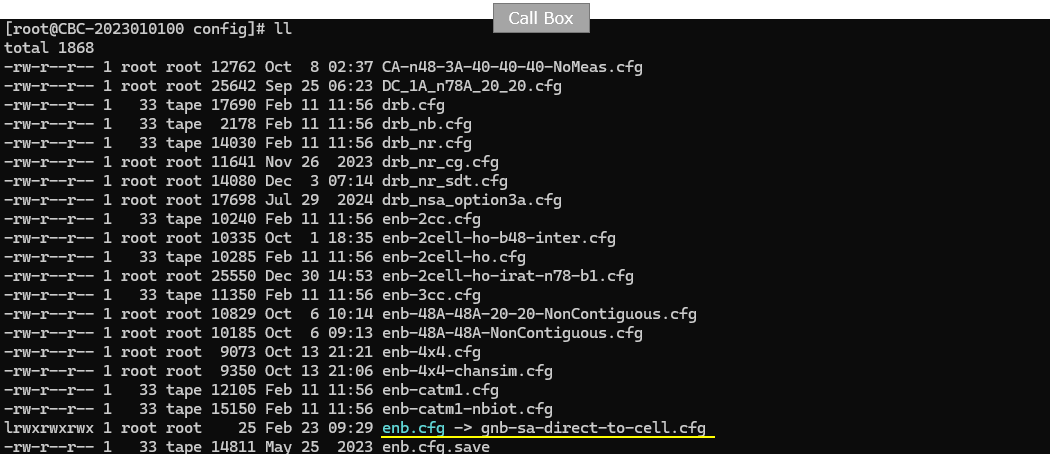
I have used gnb-sa-direct-to-cell.cfg for gNB.
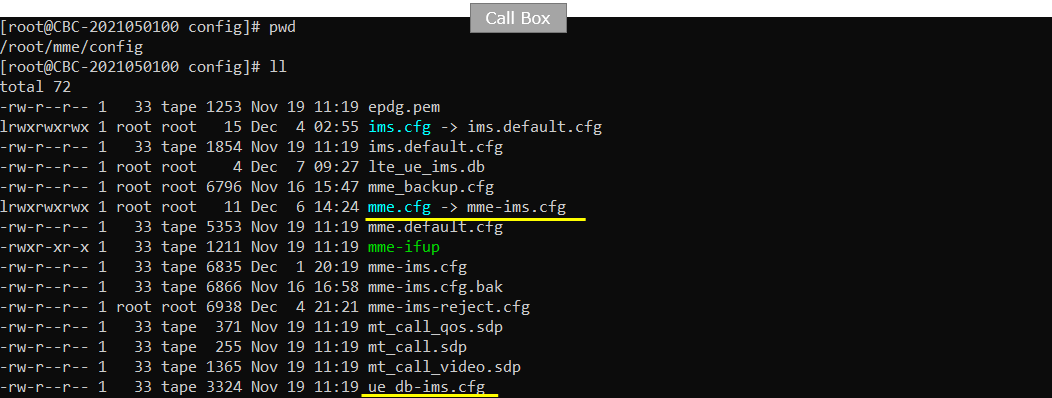
I am using mme-ims.cfg and ue_db-ims.cfg as they are.
On UEsim, I used ue-nr-sa-fdd-10Mhz.cfg which is copied and modified from ue-nr-sa.cfg
gnb-sa-direct-to-cell.cfg is configured as follows.
In gNB configruation, specify satellite orbit first with the test parameter NTN_MODE. You can select the type among GEO, MEO, LEO. In this test, GEO is selected. Once this parameter (NTN_MODE) is specified, various other test parameters are configured based on the selected NTN_MODE. (
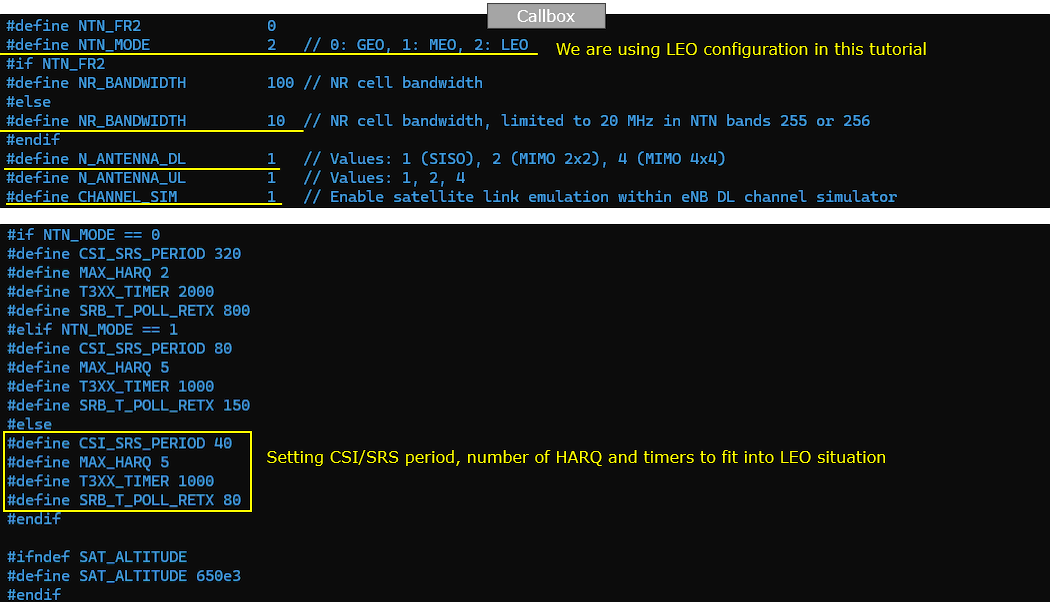
If CHANNEL_SIM is enabled, you can apply various channel profile to simulate the radio link between ground station and satellite. In this test, only awgn is applied.

An NR FDD band is configured for this tutorial. And note that ssb_period is set to very small number (short period) to help UE get better timing estimation. In addition, just to help visualization of the test result, I set force_full_bsr, force_dl_schedule to true.
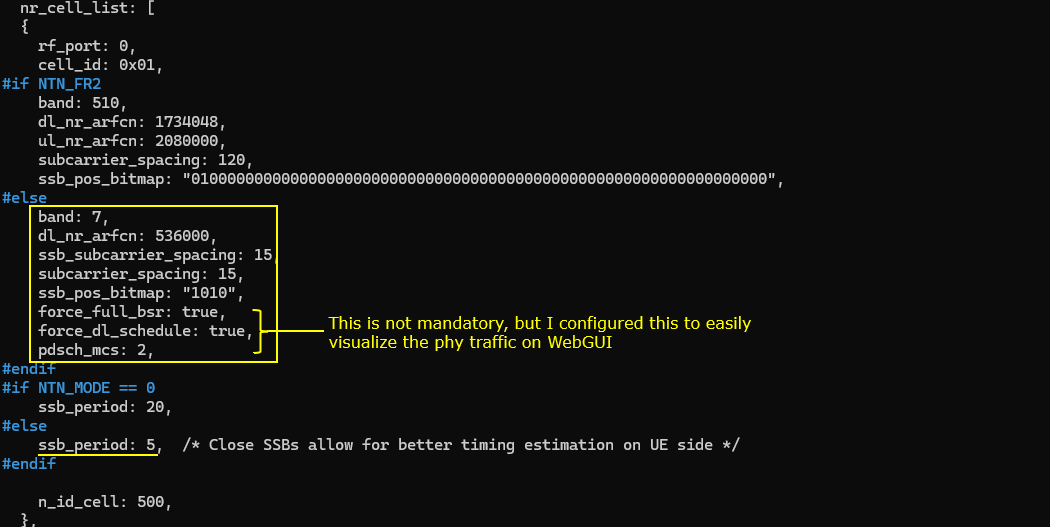
This may not be a mandatory but you may need to tweak prach_config_index to accommodate the long distance situation.
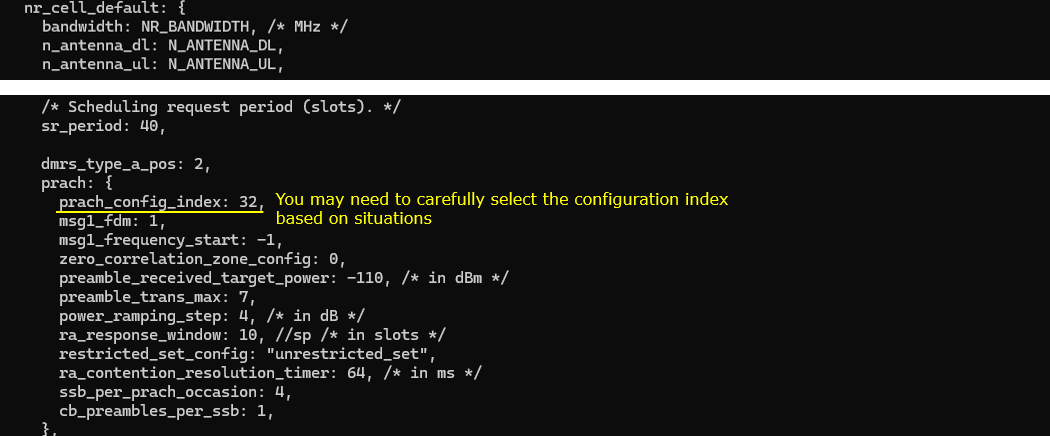
Now as MAC configuration, configure retx_bsr_timer, sr_prohibit_timer, prohibit_phr_timer, sr_trans_max differently based on the type of orbit. The basic idea is to configure these parameters differently based on RTT between the satellite and ground station.
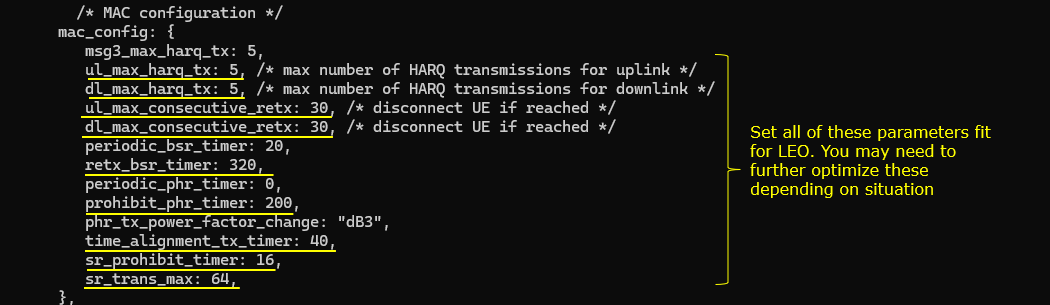
Then adjust RRC timers t300, t310 appropriately for each orbit type. And then adjust t_PollRetransmit based on the type of the orbit.

Now for the configurations specific for ntn. The configuration parameter name itself is ntn. In this parameter, you can specify the location of the satellite (i.e, the ephemeris), the location of ground station (i.e, the location of gNB) and ue location. The location of the ground station is specified by the parameter ground_position, the location of UE is specified by the parameter ue_position and the position of the satellite is specified by the parameter default_ephemeris. The parameter direct_to_cell indicates this is for Direct to Cell, not for NTN.
ue-nr-sa-fdd-10Mhz.cfg is configured as shown below. (
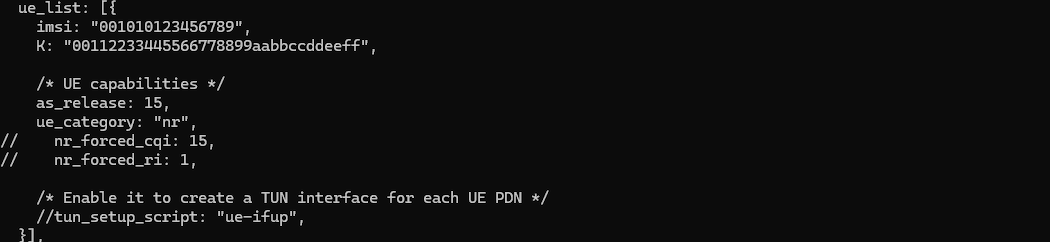
The key point here is that you don't need to configure any specific settings for satellite communication since Direct to Cell is designed to make Satellite communication possible with ordinary UE without any special modification. So in this tutorial, you will see all the configuration on UEsim remain same as in default configuration (ue-nr-sa.cfg) except band and channel bandwidth just to make it match gNB frequency settings.
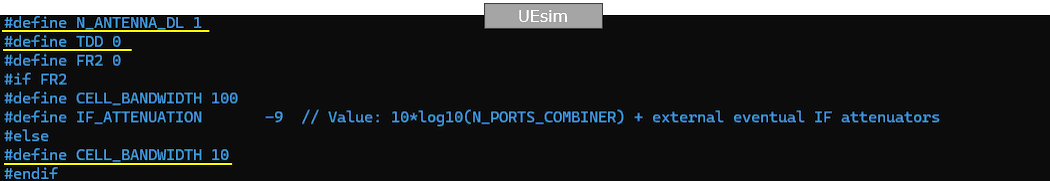
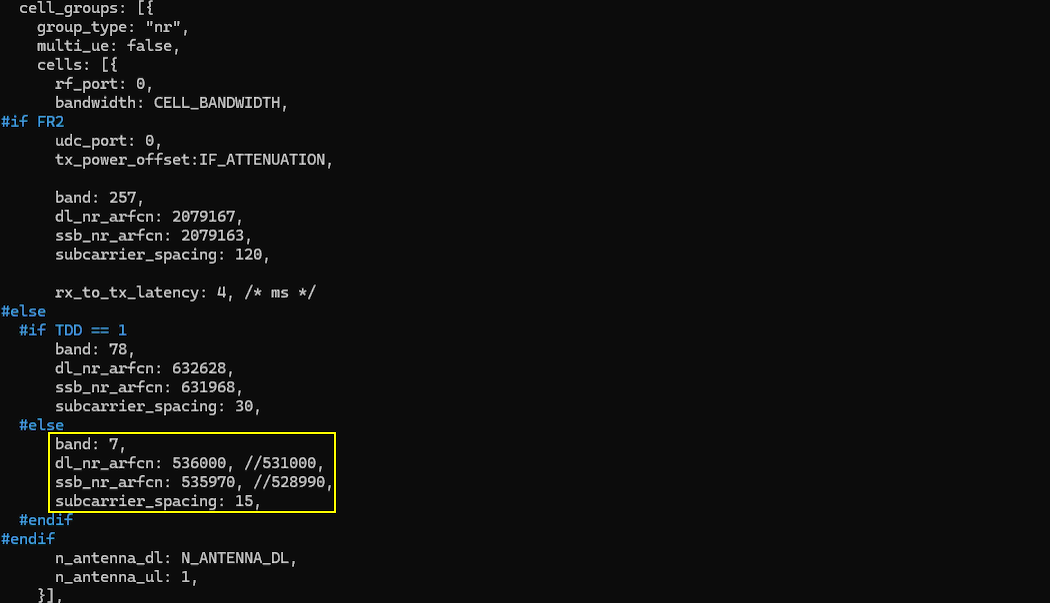
Only band and channel (dl_nr_arfcn, ssb_nr_arfcn) is changed to match gNB frequency and band settings.
ue_list configuration is also set to be same as in default.
Perform the Test
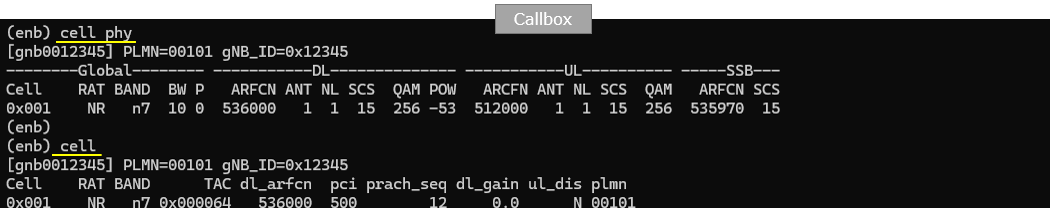
Run lte service on callbox and then check 'cell phy' and 'cell' command. Make it sure that cell is configured as you intended. In this test, n7(FDD) is used
This is not the mandatory process.. but you may do this to collect SIB message in the log for a few seconds at the beginning. I did bcch=1 and after a few seconds did bcch=0.
![]()
Now start trace logging.
![]()
Power on UE on UEsim (If your DUT is a commercial phone, turn on the phone)
Wait until the DUT complete the initial attach. (
Try some data traffic (e.g, ping) to verify the data pipe setup.
Log Analysis
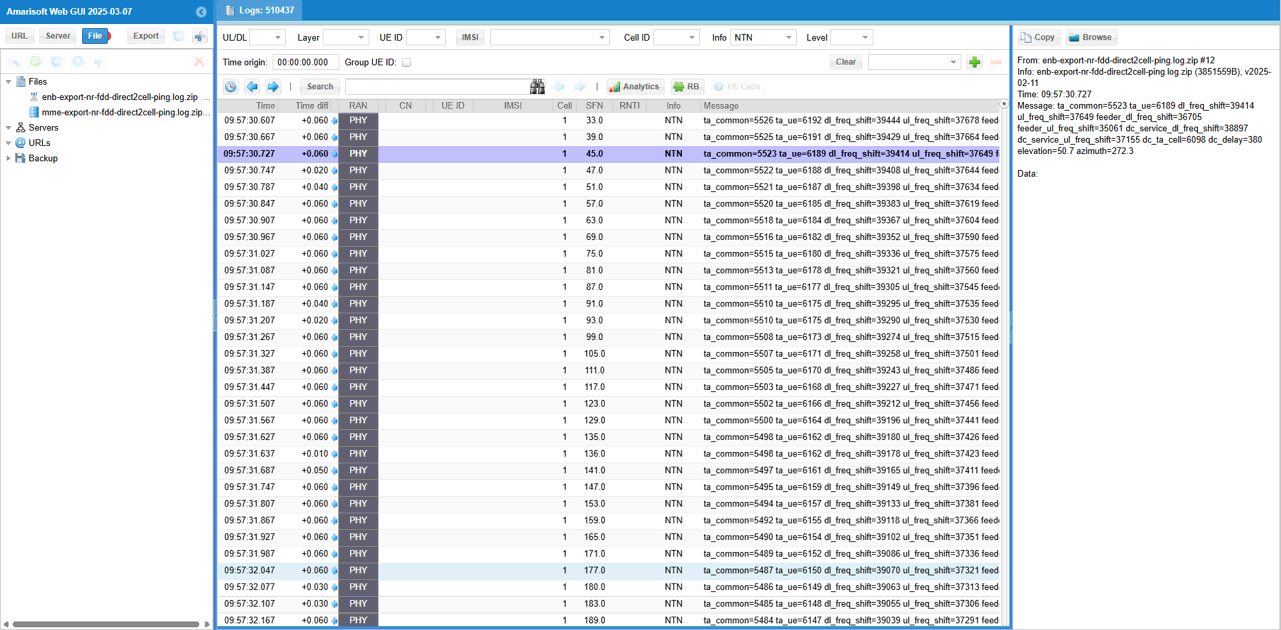
Following is the log snapshot that are involved in communication with NTN.
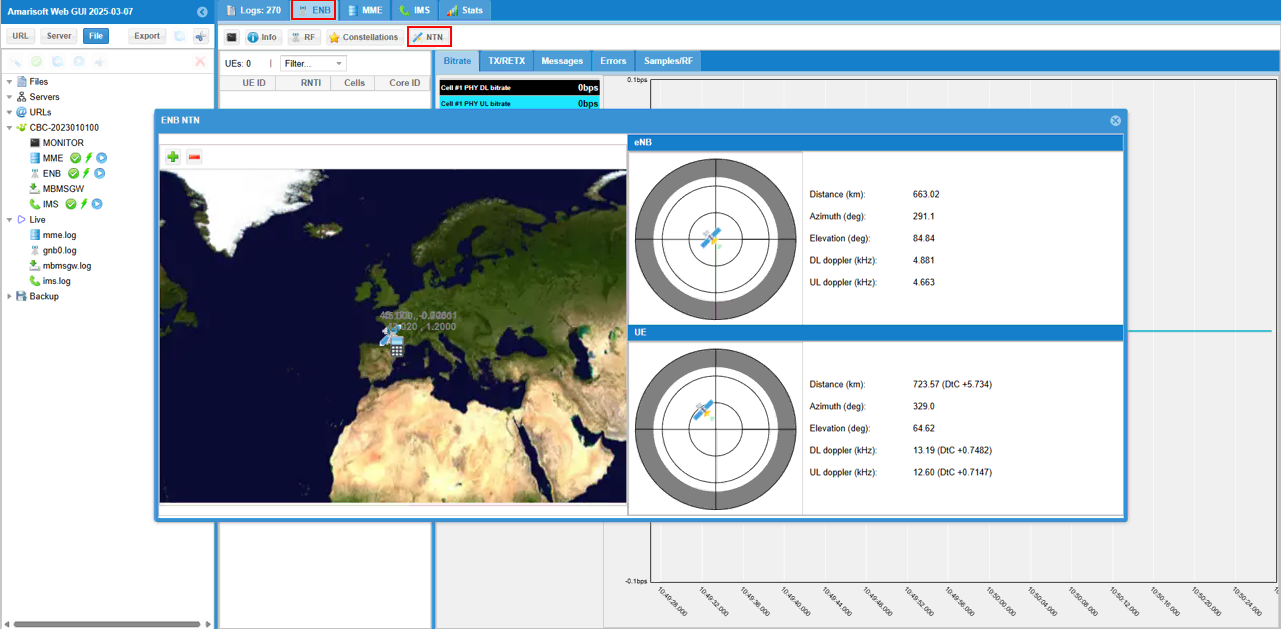
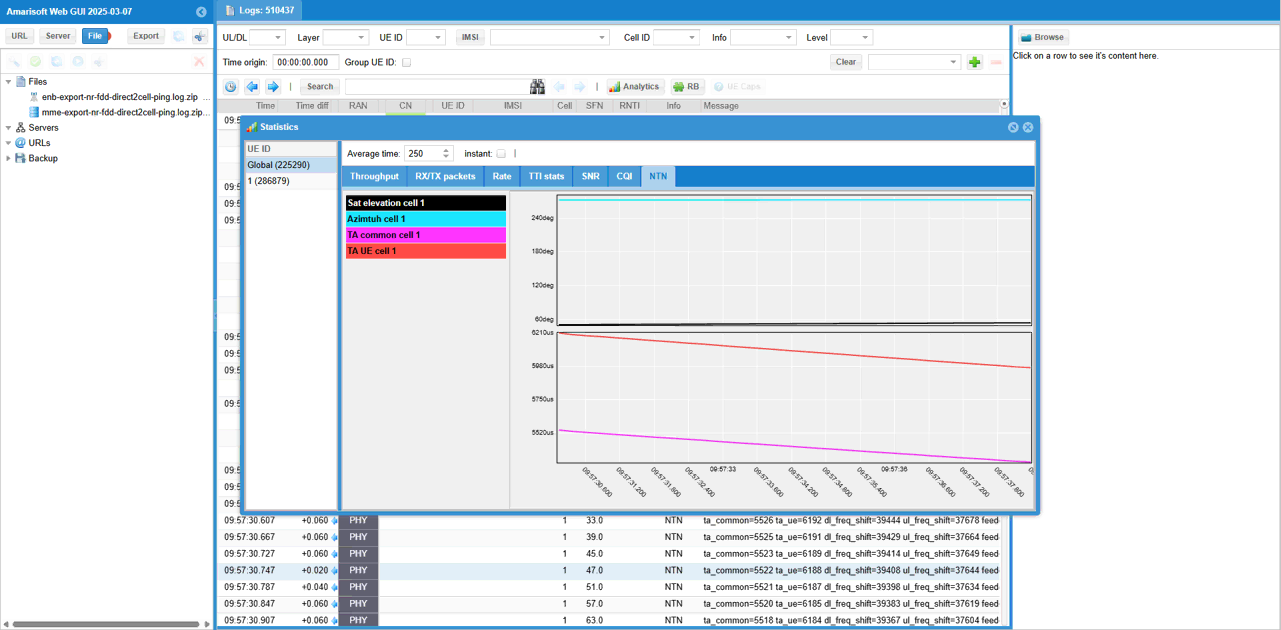
While the test is running, you can check out the position of eNB and UE in real time with WebGUI. While running, select [ENB] tab and hit [NTN] button and you see the view as shown below.
[eNB] pannel shows the sky view of eNB (sky view from eNB) and [UE] pannel shows the sky view of UE (sky view from UE). When the following value goes negative, satellite link gets disconnected since the satellite is not obserbable from UE.
- Elevation
- DtC value in Distance on UE pannel
You may check out overall signaling sequence and details, in Direct to Cell there is no differences in signaling side from what you see regular communication (i.e, terrestrial communication)
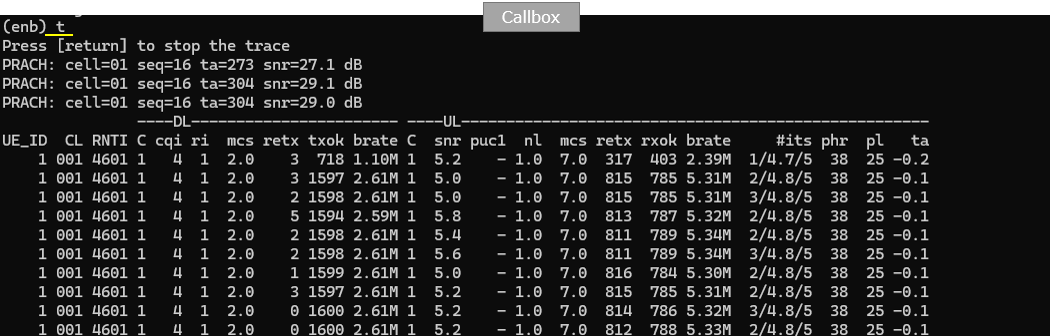
Check out throughput and see if you are getting expected throughput. In this test, I set force_full_bsr, force_dl_schedule to true. So you would get relatively high throughput at PHY,MAC.
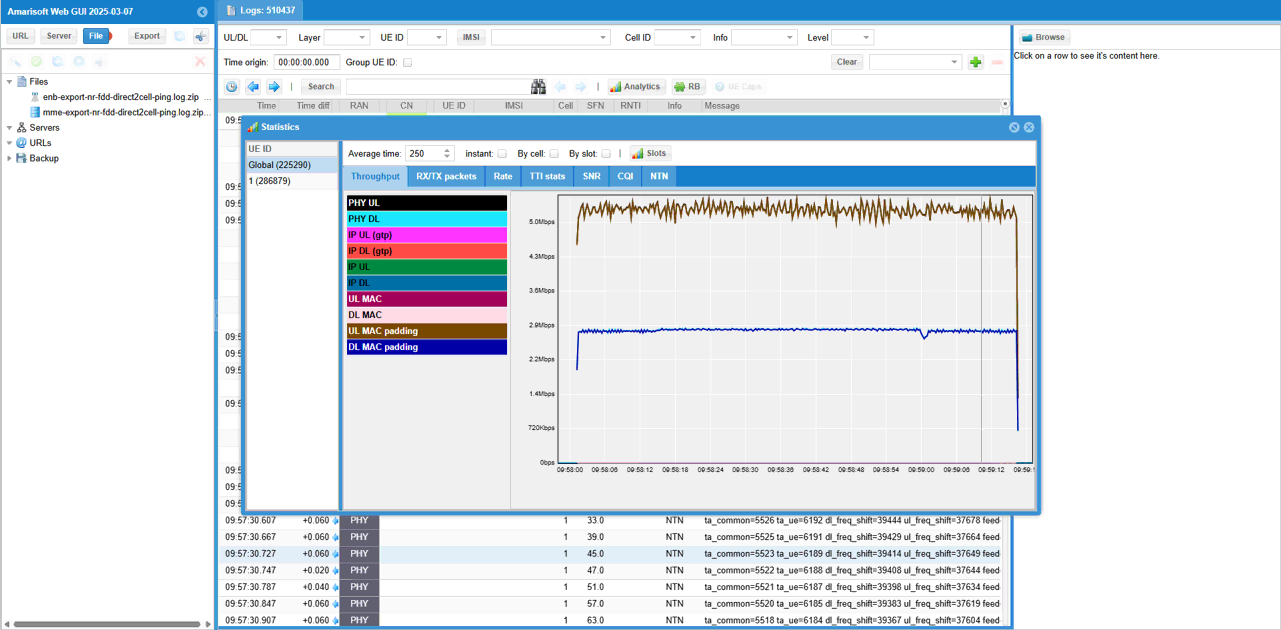
Then check SNR to check the radio link quality over the course of the test.
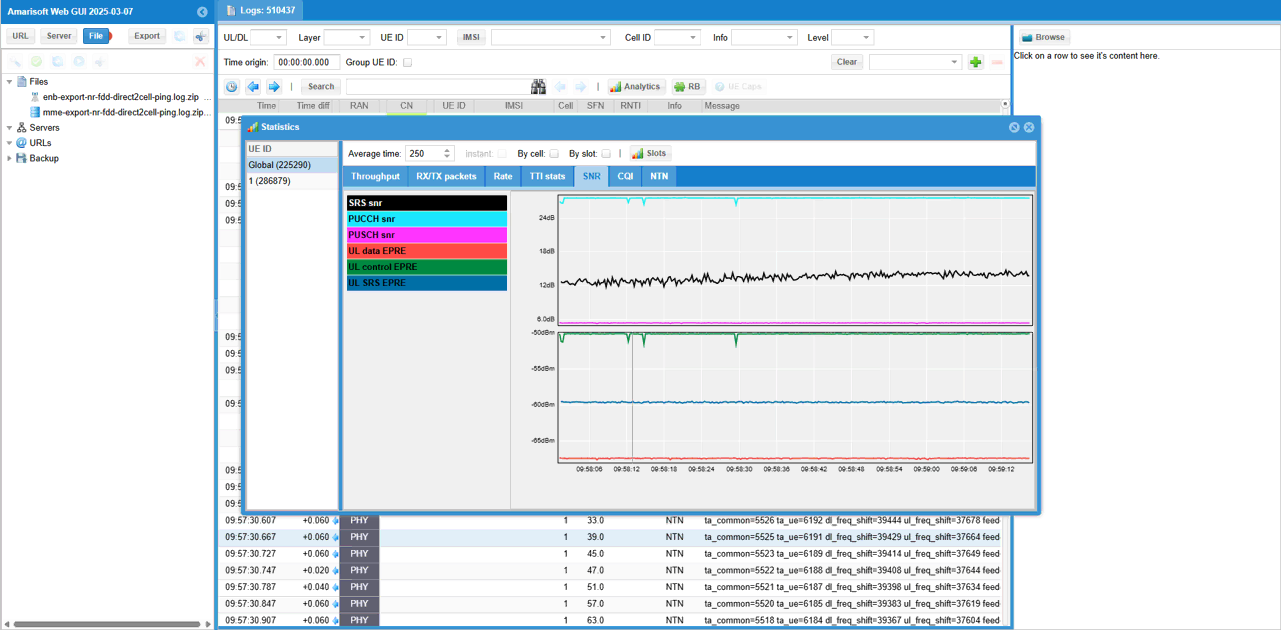
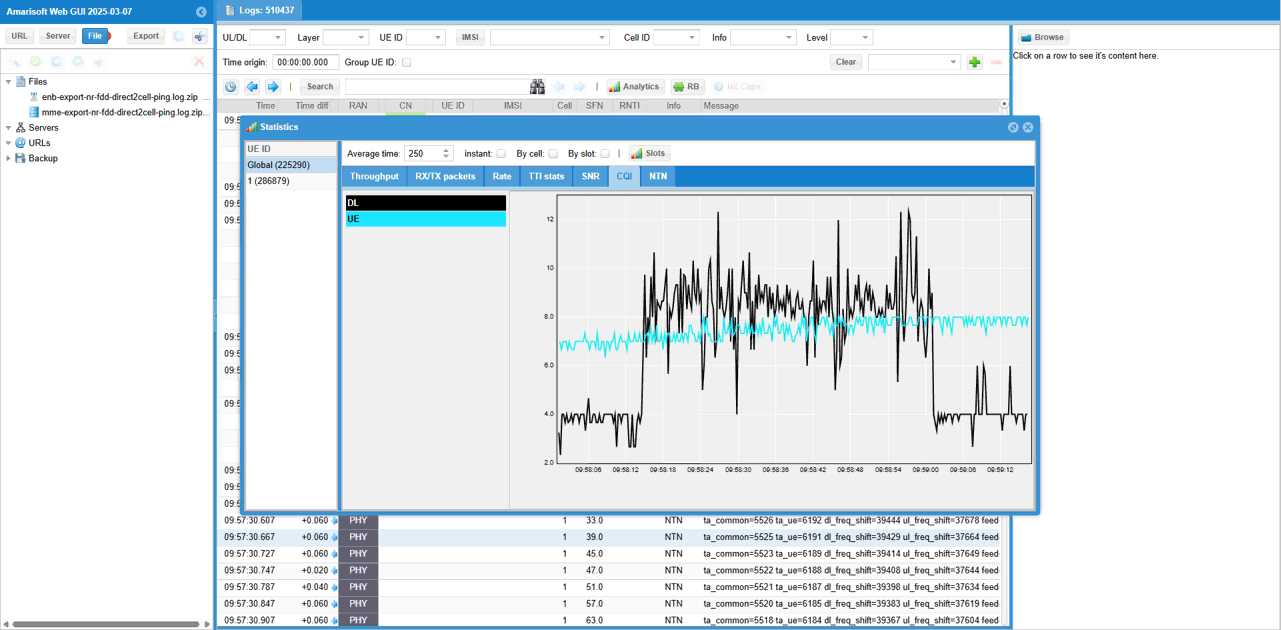
You can check out the signal quality percieved by UE from DL CQI plot
In [NTN] tab, you can check out Satellite position (Elevation and Azimuth) and Timing Advance command value.
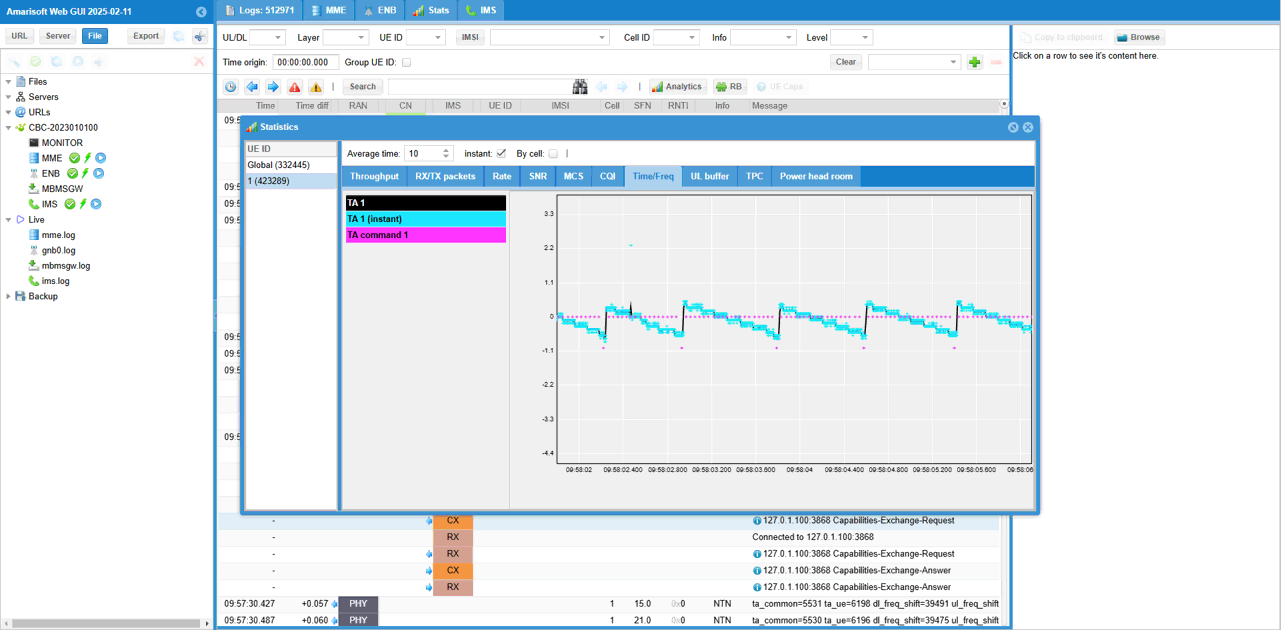
If you magnify TA command value in [Time/Freq] tab, you would see a pattern as shown below. When TA dropes below -0.5, we send a command to do TA +1 and it goes to +0.5 and then slowly decreases as the satellite moves
If you want the check all the NTN status in values, you may apply the filter 'NTN' in the info combo box. (