LTE D2C (Direct To Cell)
This tutorial is to show you how to configure and test Direct to Cell in LTE. Direct to Cell represents 'From Satellite directly to Cellular Phone'. The 'Cellular Phone' in this context is just an ordinary commercial mobile hone that you have and it does not need to support any special feature for satellite communication as long as it works with ordinary NR SA in terrestrial network.
Actually Direct To Cell is not the 3GPP based feature like NTN (NB NTN or NR NTN). So the UE is not expected to support any specific features to accommodate this type of connection. So all the functionality to handle such a long delay or doppler shift etc which are present for satellite communication should be implemented by gNB that is sitting on the Satellite. This gNB implementation is mostly up to gNB vendor since the functionality is not specified in 3GPP.
Table of Contents
- LTE D2C (Direct To Cell)
Test Setup
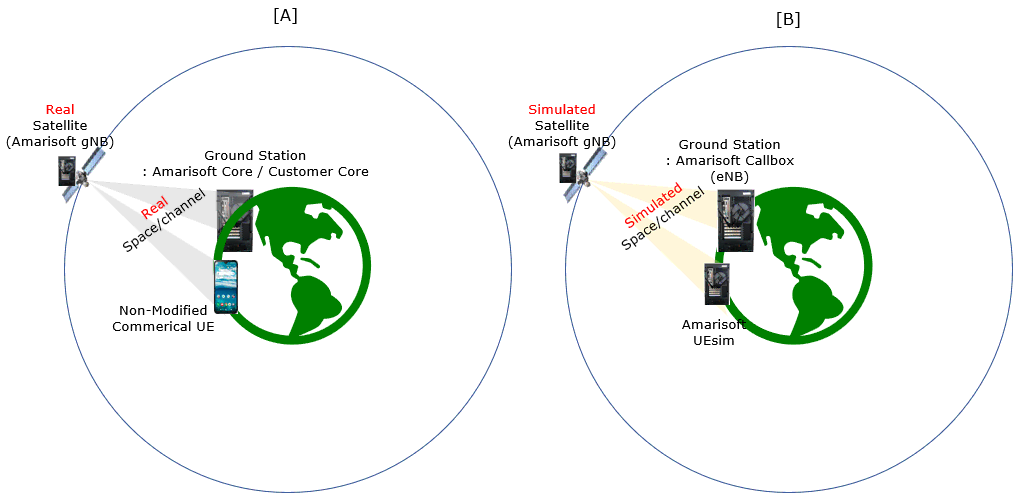
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below. This is just for low layer testing, you may not need any complicated IP layer setup.
- SIM Card used in this tutorial is the one delivered with the system as it is.
- If you want to change the configuration, The tutorial Configuration Guide would help
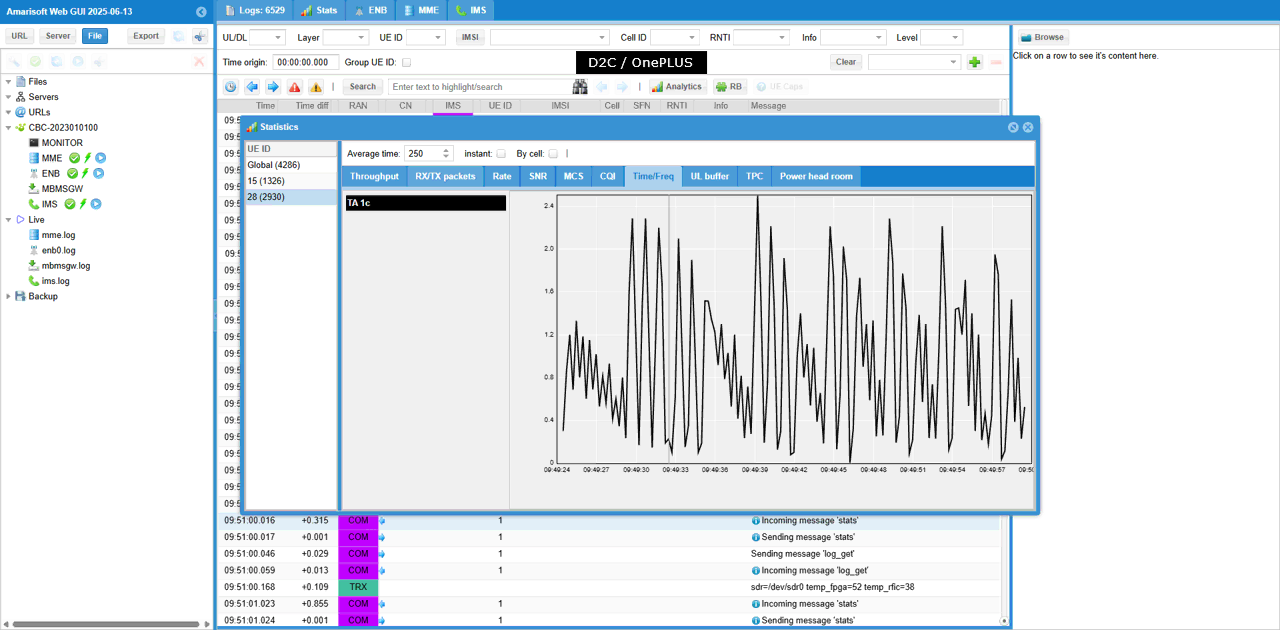
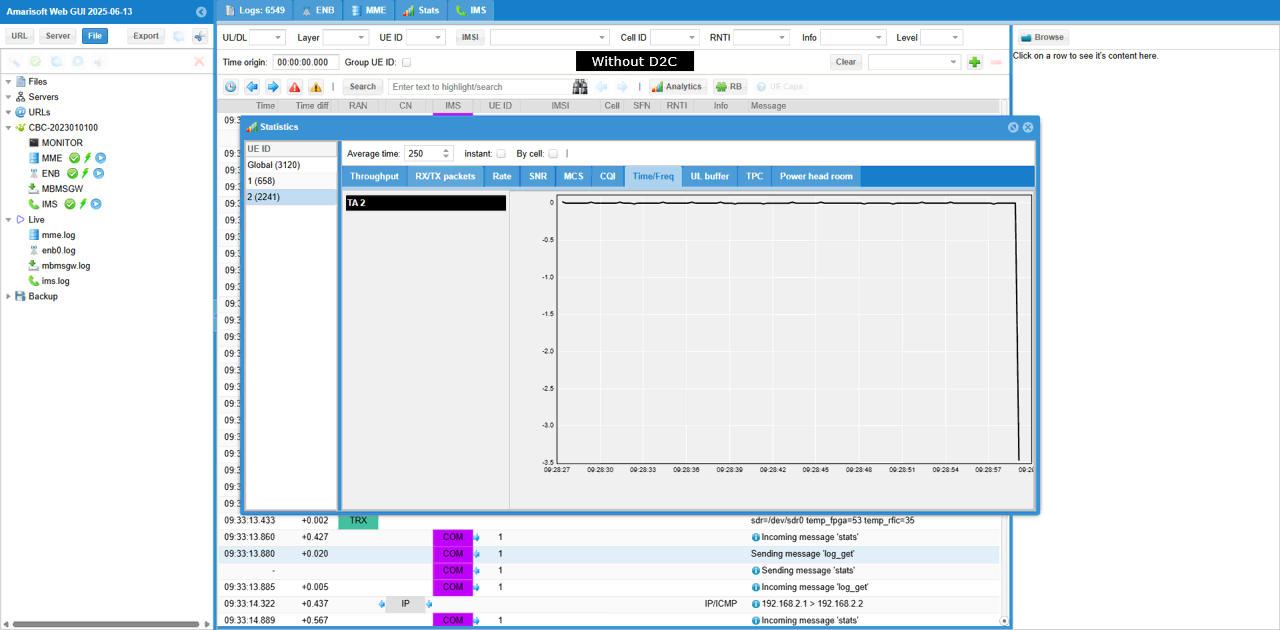
With Amarisoft eNB and UEsim, we can try with following two different setups.
Key Configuration Parameters
Followings are important configuration parameters for this tutorial. You may click on the items for the descriptions from Amarisoft documents.
- ntn : In this link, you can find the descriptions for all the parameters below.
- ephemeris
- use_state_vectors
- eci_reference
- ground_position
- n_ta_common
- n_ta_drift
- n_ta_drift_var
- n_ta_common_offset
- feeder_doppler_compensation
- feeder_dl_freq
- feeder_ul_freq
- large_freq_shift
- direct_to_cell
- channel_sim_control
- type
- ue_position
- ue_doppler_shift
- ue_dl_freq
- ue_ul_freq
- feeder_doppler_shift
- ue_dl_attenuation
- ue_dl_gain_offset
- ul_sync_validity
- k_offset
- k_mac
- dynamic_k_offset
- reference_location
- t_service
- neighbour_cells
- rat_type
- t318
Test 1 : D2C with Simulated LEO and UEsim
This is to configure and test Direct to Cell for Simulated LEO using Amarisoft UEsim as DUT.
Configuration
The configuration shown here is common configuration for all the subtests belonging to Test 1
I have used enb-dtc.cfg for eNB. In this configuration, specicialy configured SIB message sib23_rb25_dtc.asn is used.
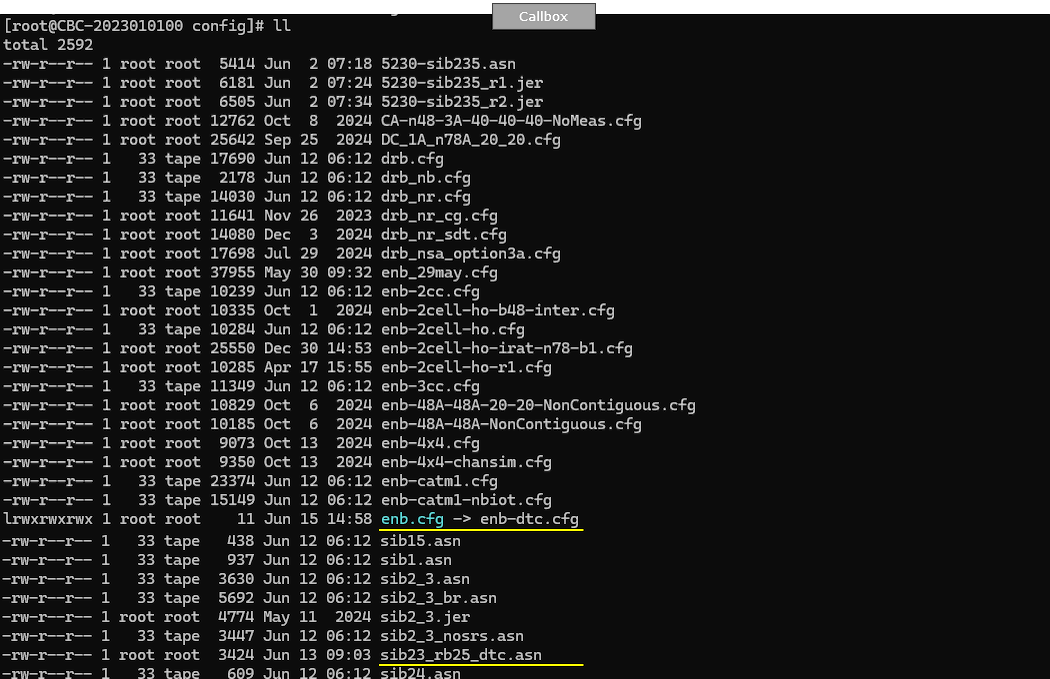
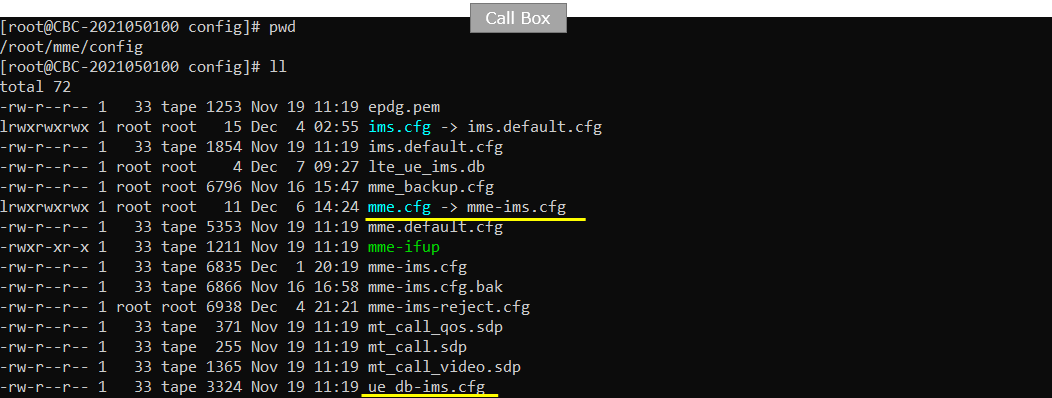
I am using mme-ims.cfg and ue_db-ims.cfg as they are.
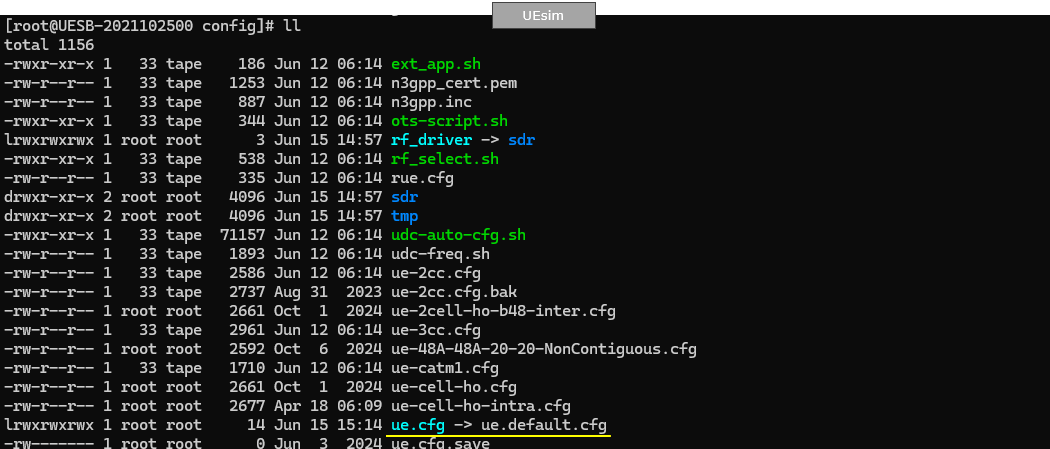
On UEsim, I used ue.default.cfg as it is
enb-dtc.cfg is configured as follows.
eNB configruation is very similar to the default enb configuration. The important thing is to enable Channel Sim(CHANNEL_SIM = 1). You can set the altitude of the satellite by setting SAT_ALTITUDE.
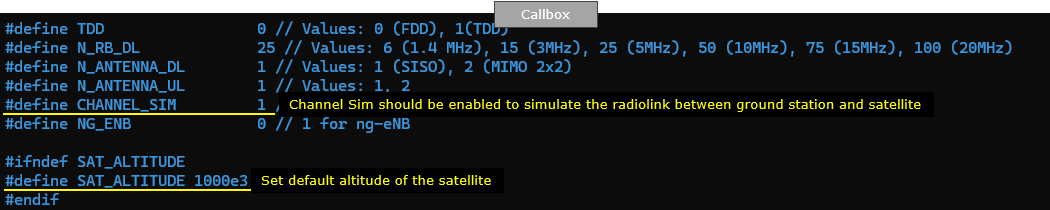
If CHANNEL_SIM is enabled, you can apply various channel profile to simulate the radio link between ground station and satellite. In this test, only constant delay is applied for simplicity.
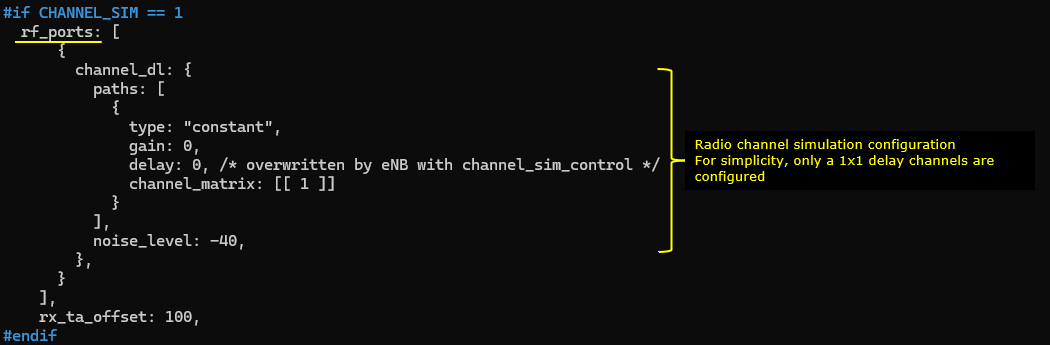
An LTE FDD band is configured for this tutorial. This is same as the default configuration for most of the sample config file.
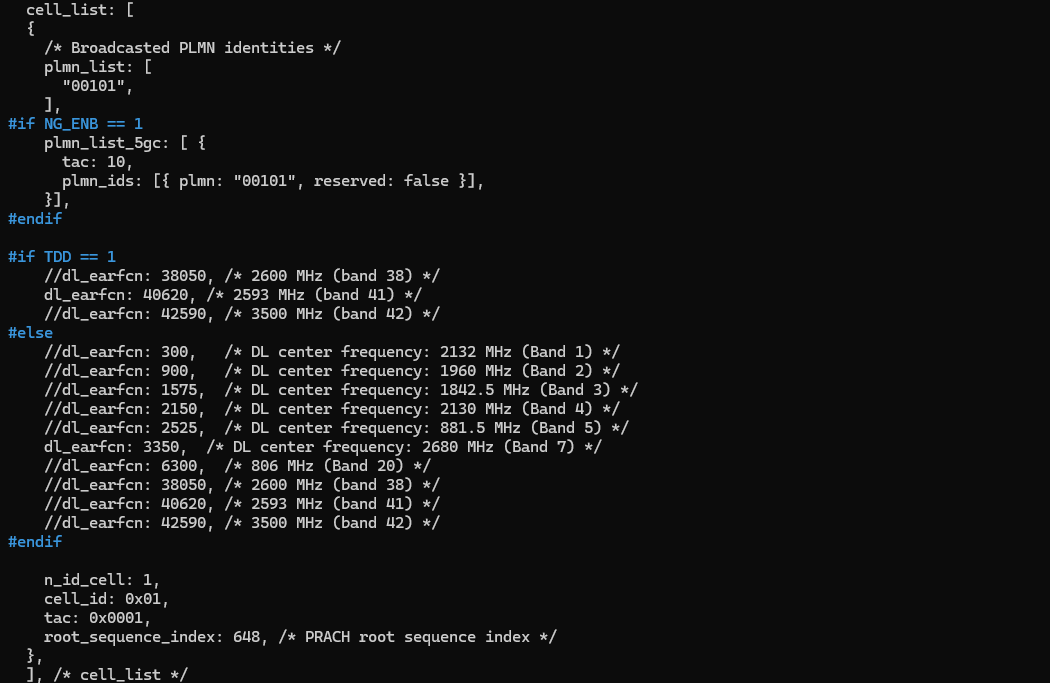
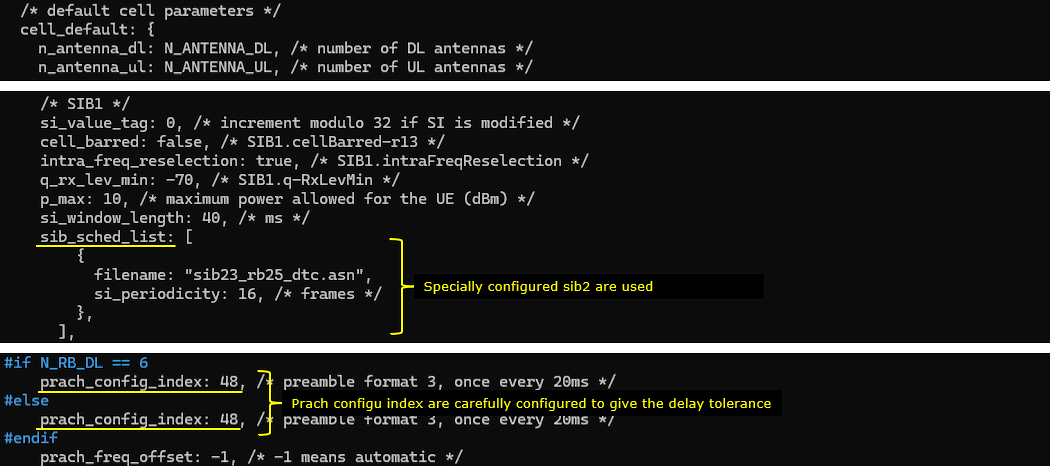
In this test, a specially configured SIB message is used (mainly for setting timer values to accommodate the long distance case). and you may need to tweak prach_config_index to accommodate the long distance situation.
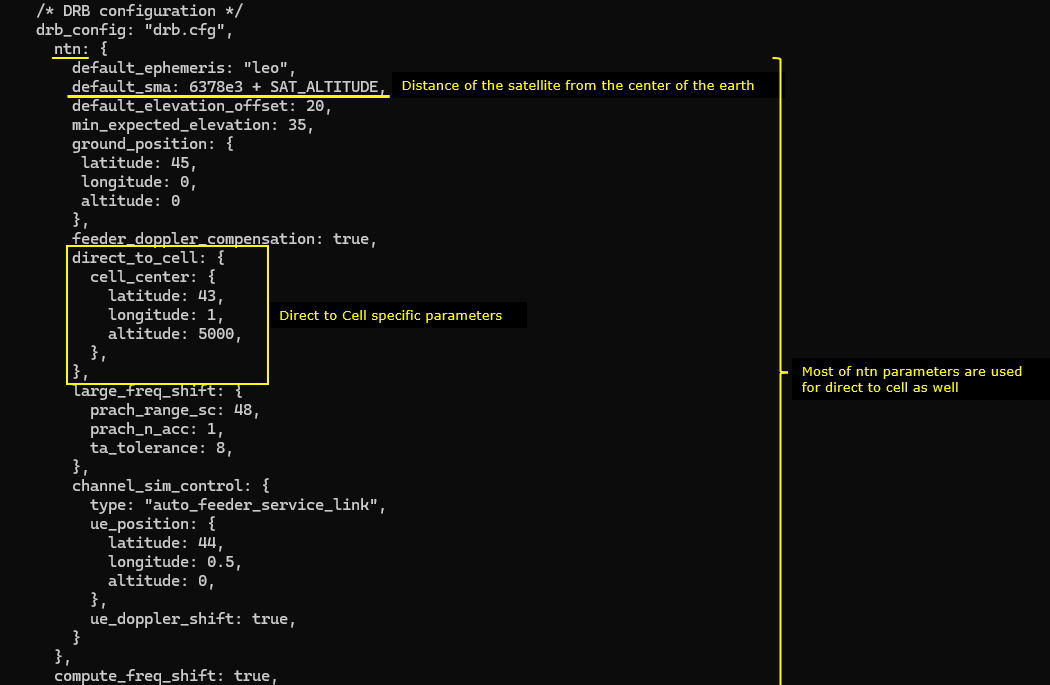
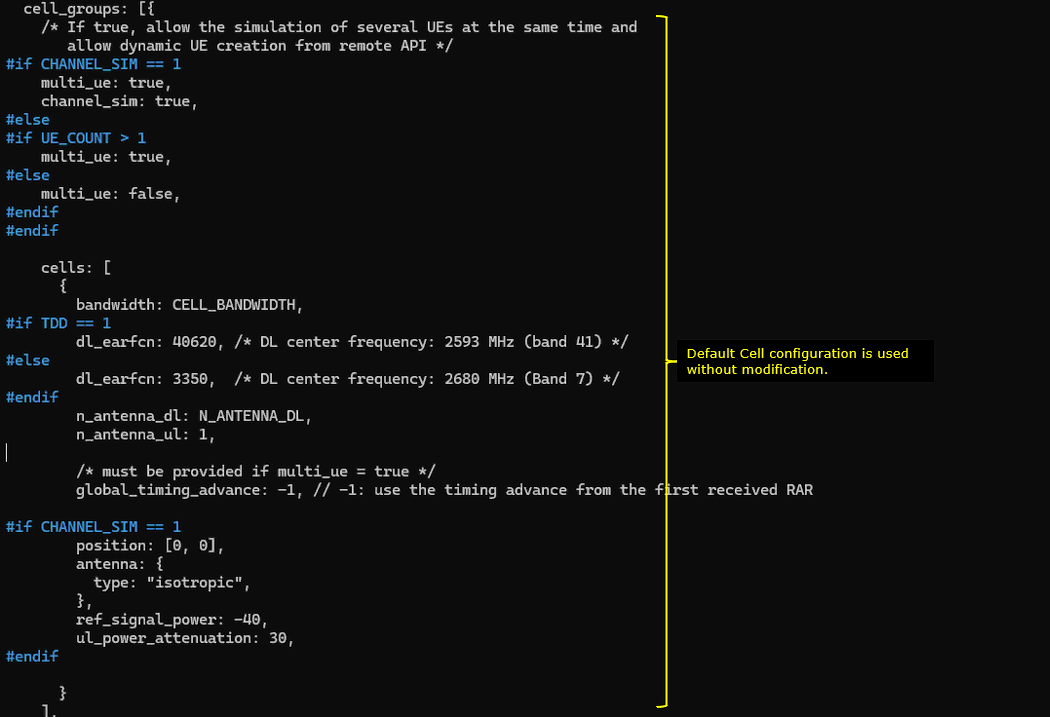
Now for the configurations specific for ntn. The configuration parameter name itself is ntn. In this parameter, you can specify the location of the satellite (i.e, the ephemeris), the location of ground station (i.e, the location of eNB) and ue location. The location of the ground station is specified by the parameter ground_position, the location of UE is specified by the parameter ue_position and the position of the satellite is specified by the parameter default_ephemeris. The parameter direct_to_cell indicates this is for Direct to Cell, not for NTN.
ue.default.cfg is configured as shown below. (
The key point here is that you don't need to configure any specific settings for satellite communication since Direct to Cell is designed to make Satellite communication possible with ordinary UE without any special modification. So in this tutorial, you will see all the configuration on UEsim remain same as in default configuration (ue.default.cfg)
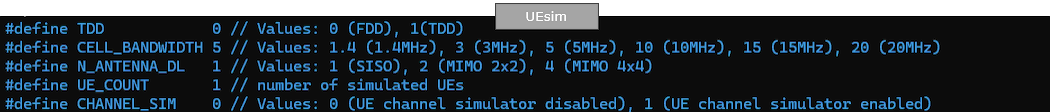
Only band and channel (dl_earfcn) is changed to match eNB frequency and band settings.
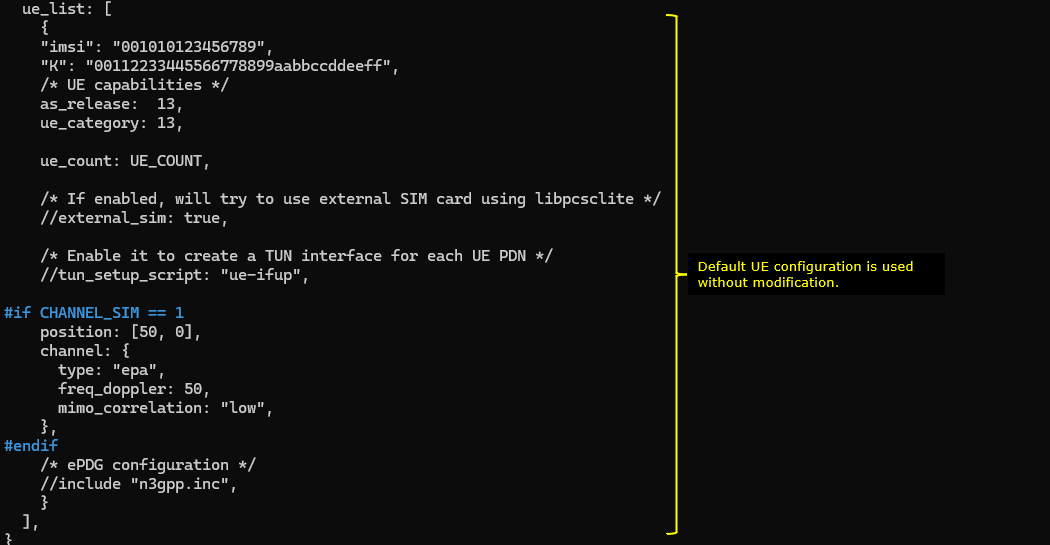
ue_list configuration is also set to be same as in default.
Perform the Test
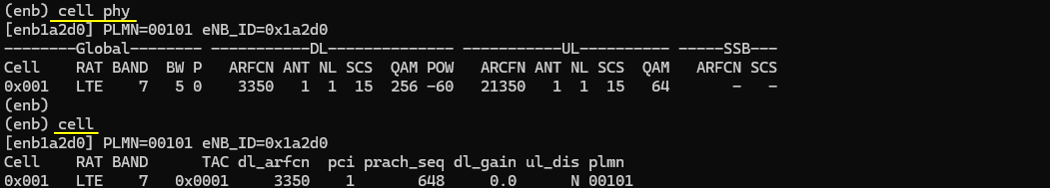
Run lte service on callbox and then check 'cell phy' and 'cell' command. Make it sure that cell is configured as you intended. In this test, band 7(FDD) is used
This is not the mandatory process.. but you may do this to collect SIB message in the log for a few seconds at the beginning. I did bcch=1 and after a few seconds did bcch=0.
![]()
Now start trace logging.
![]()
Power on UE on UEsim (If your DUT is a commercial phone, turn on the phone)
Wait until the DUT complete the initial attach. (
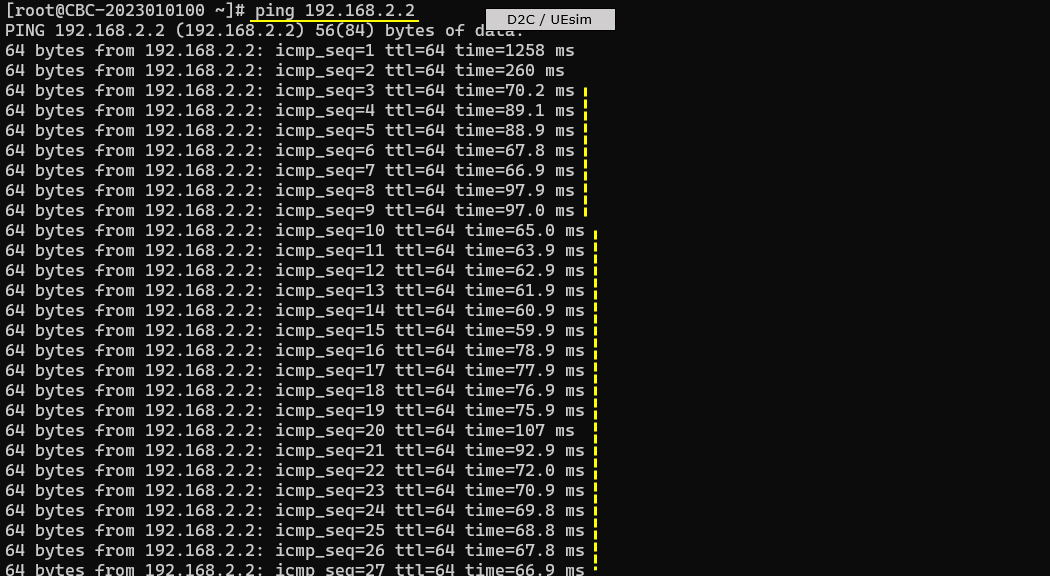
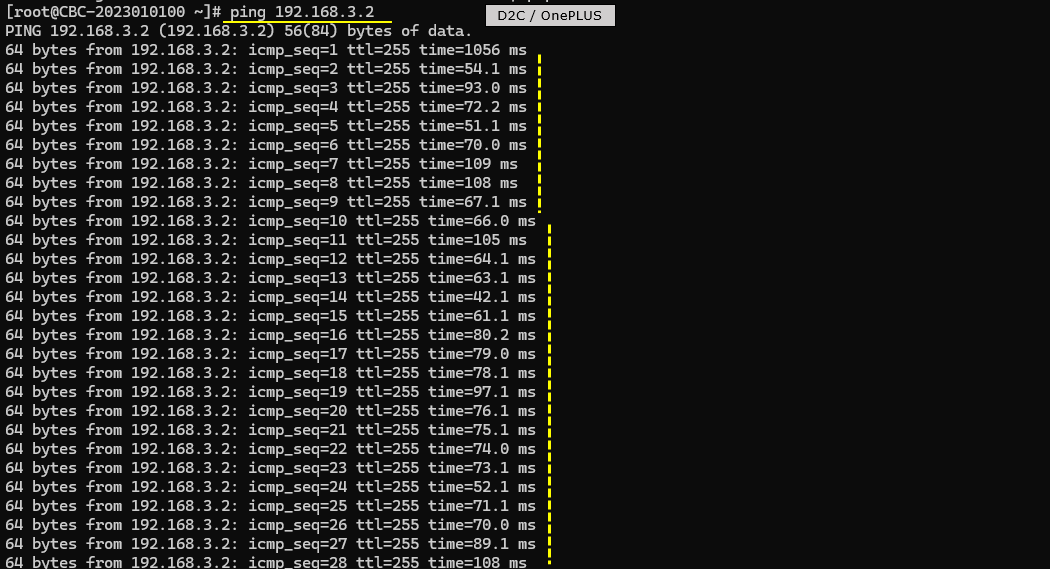
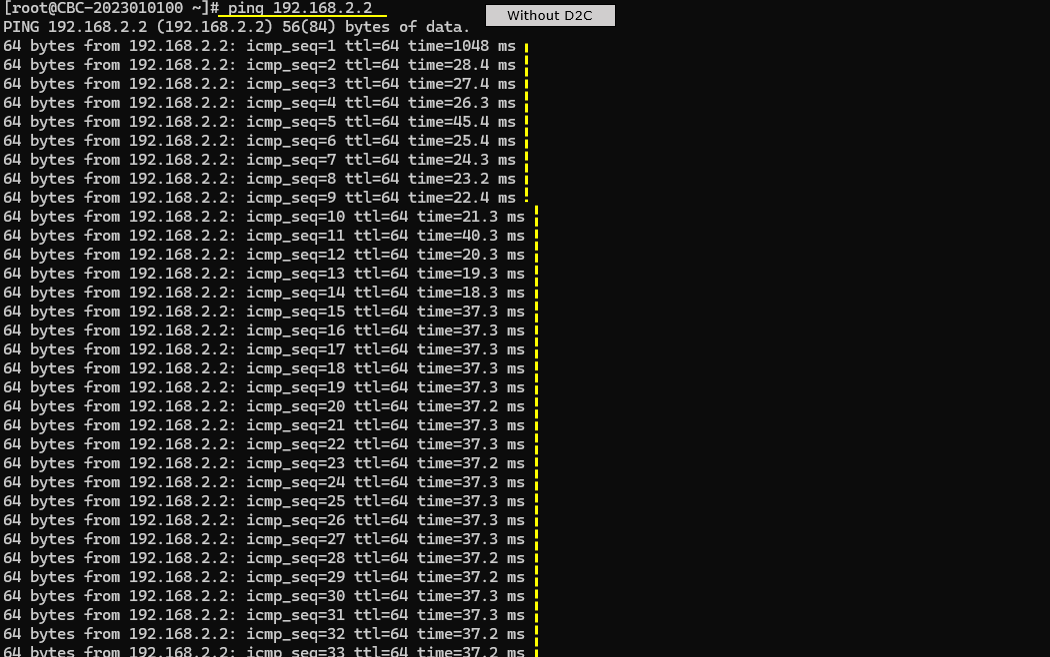
Try some data traffic (e.g, ping) to verify the data pipe setup. Check out the ttl time and see if it reflects the long propgation delay
Log Analysis
Following is the log snapshot that are involved in communication with NTN.
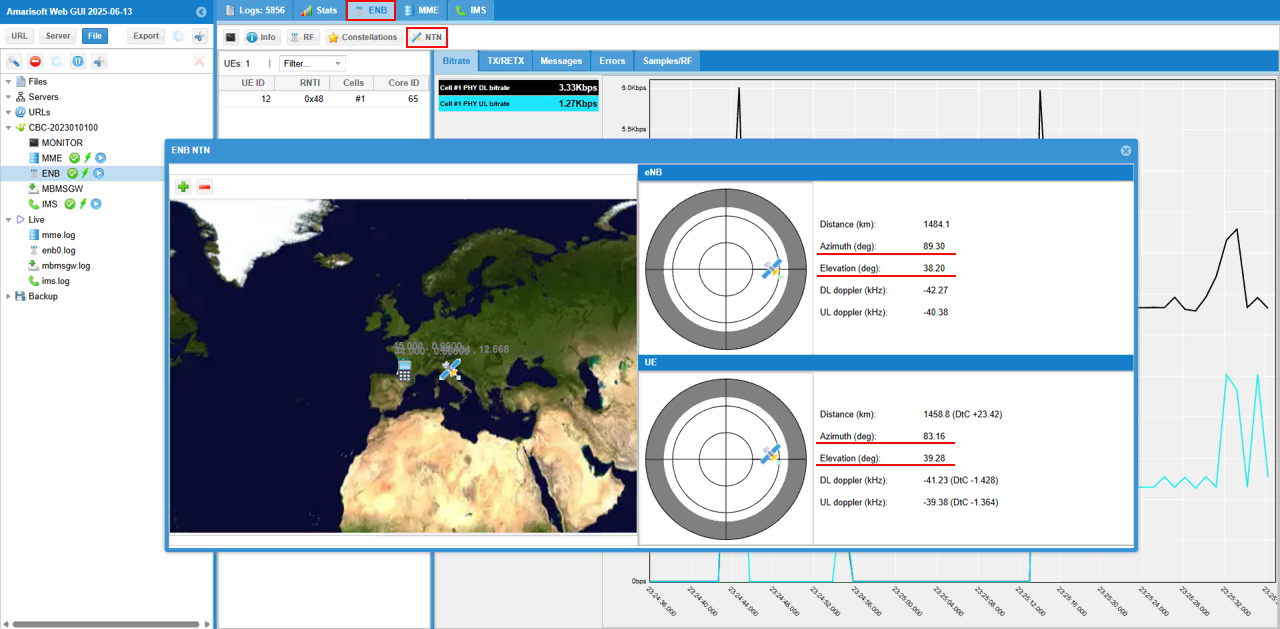
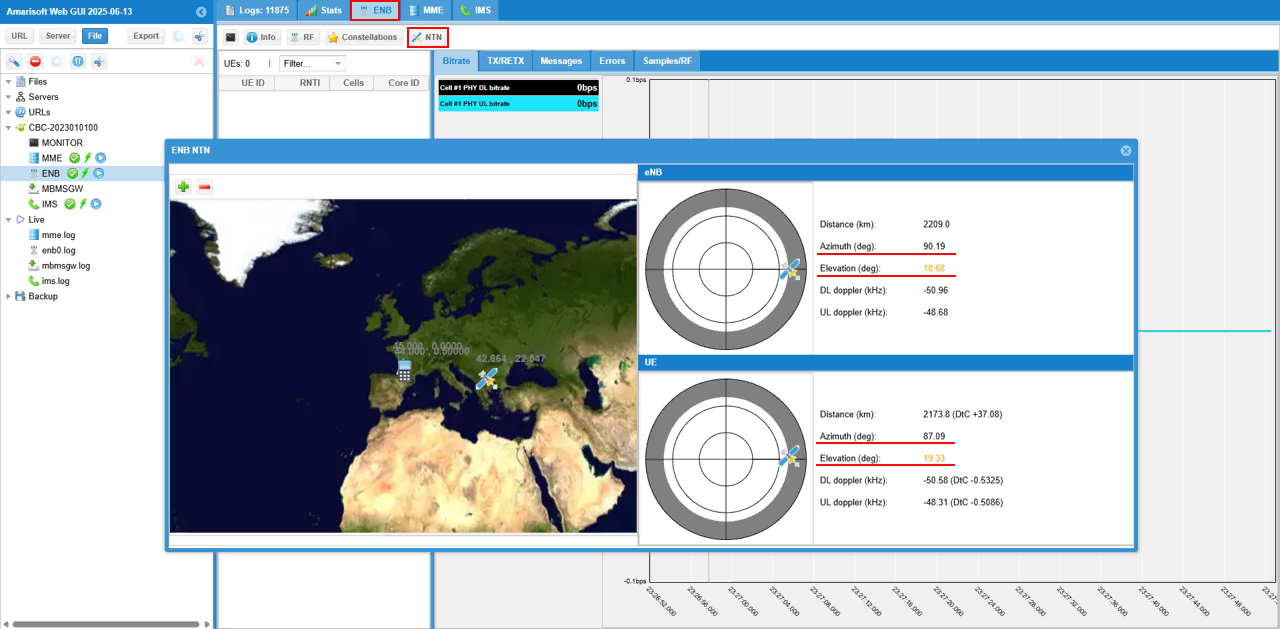
While the test is running, you can check out the position of eNB and UE in real time with WebGUI. While running, select [ENB] tab and hit [NTN] button and you see the view as shown below.
[eNB] pannel shows the sky view of eNB (sky view from eNB) and [UE] pannel shows the sky view of UE (sky view from UE). When the following value goes negative, satellite link gets disconnected since the satellite is not obserbable from UE.
- Elevation
- DtC value in Distance on UE pannel
You may check out overall signaling sequence and details, in Direct to Cell there is almost no differences in signaling side from what you see regular communication (i.e, terrestrial communication). But there would be some tweakings of SIB parameters related to RACH configuration and timers to handle the long propation delay between the UE and Satellite.
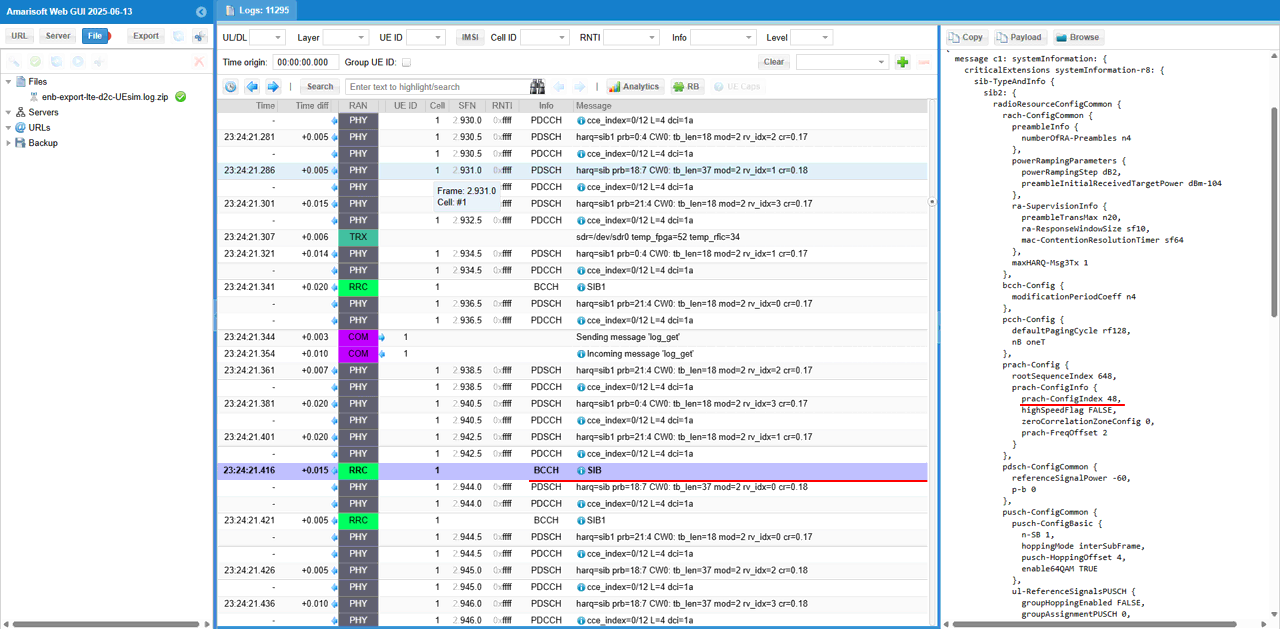
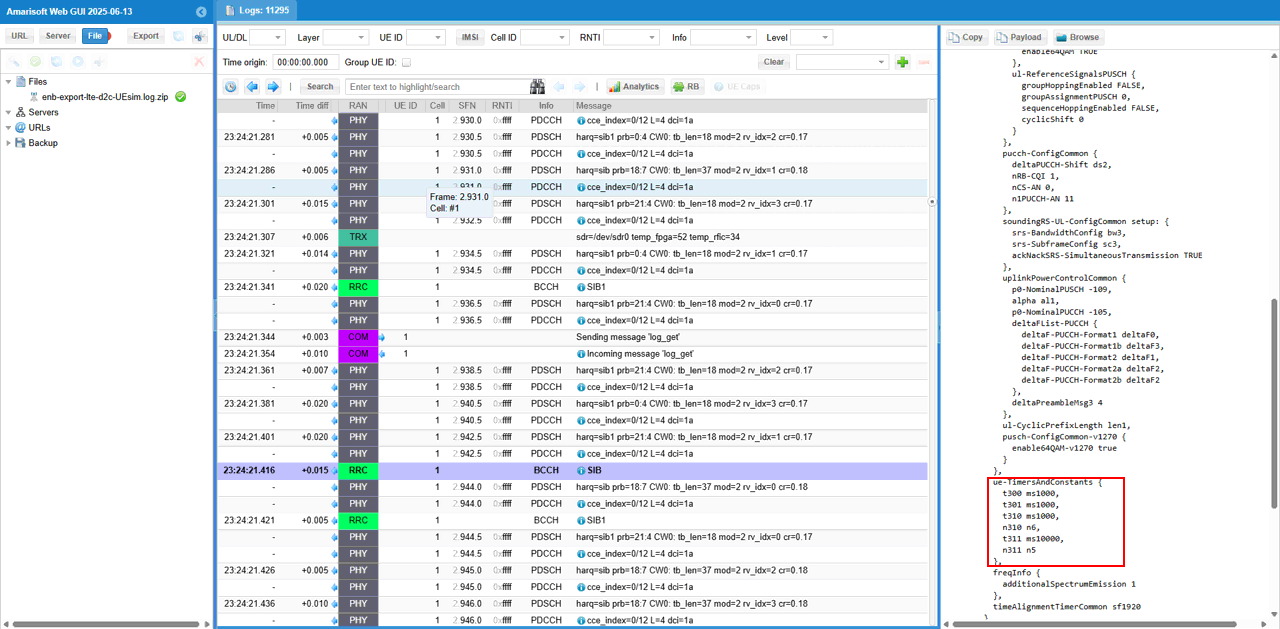
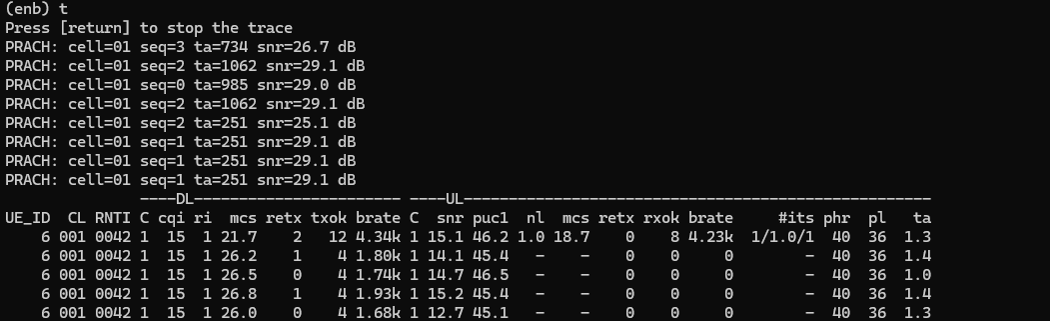
Then it would be good idea to check out the details on RACH. You would see 4 consetive RACH procedure going on here. This is a special modification on eNB to handle the large propagation delay during the RACH process. It is a kind of modification on the PRACH to be able to send the RAR to a future PRACH request : In LTE you cannot have less than 4 CBRA preamble so for one PRACH I send 4 RAR messages for each preamble
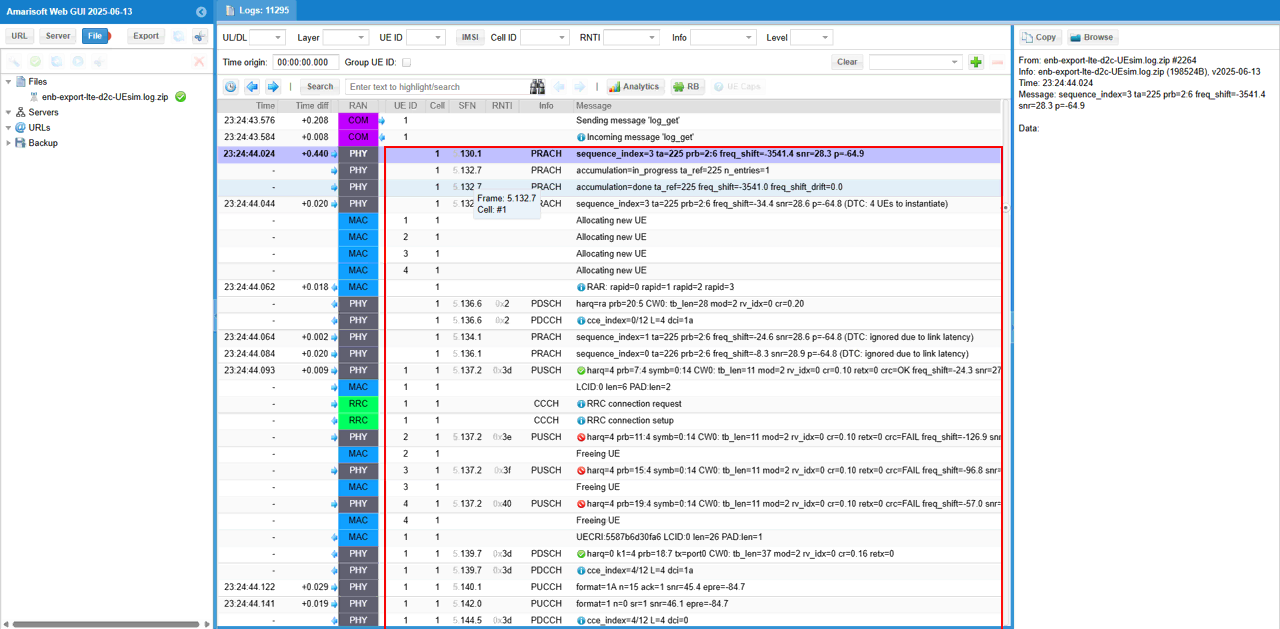
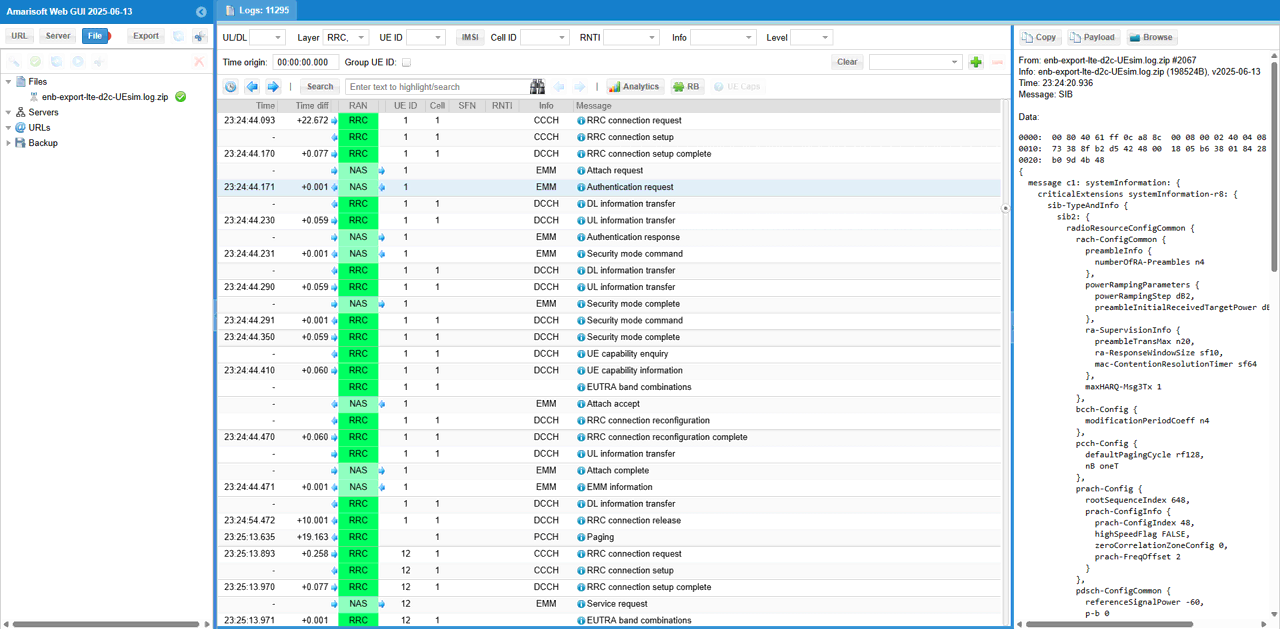
Now confirm that entire attach process gets completed
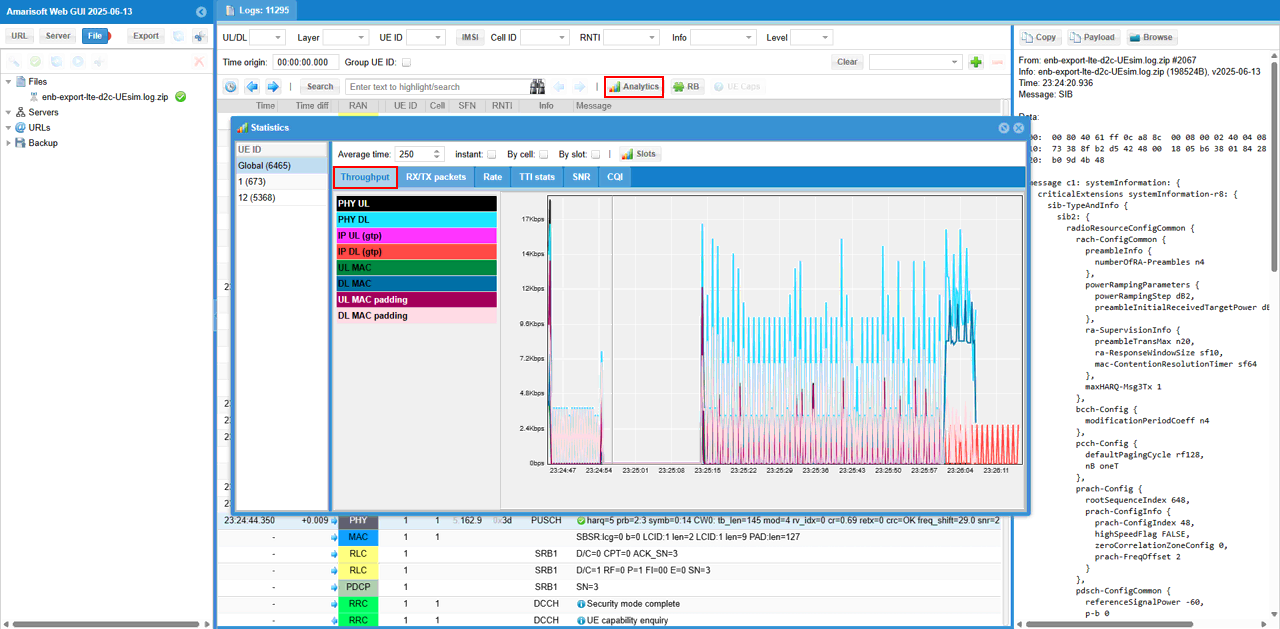
Check out throughput and see if you are getting expected throughput. In this test, I did continous ping to check if end to end data pipe is working OK.
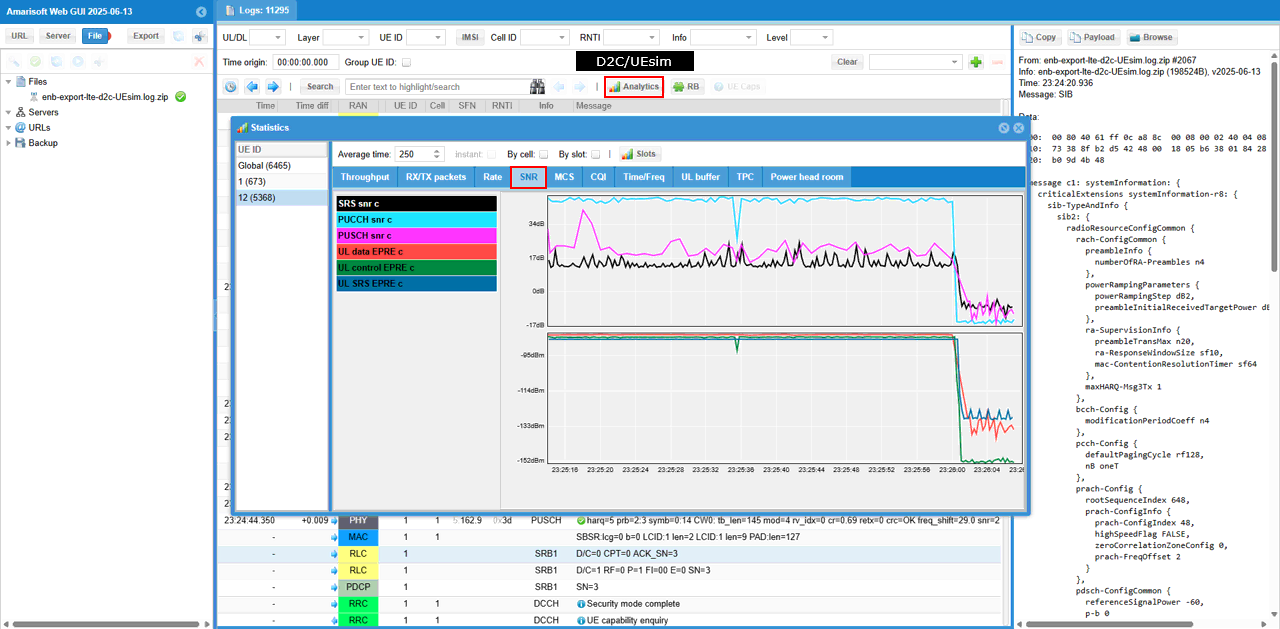
Then check SNR to check the radio link quality over the course of the test. (NOTE : Connection between eNB and UEsim is via RF cable (i.e, conductive connection))
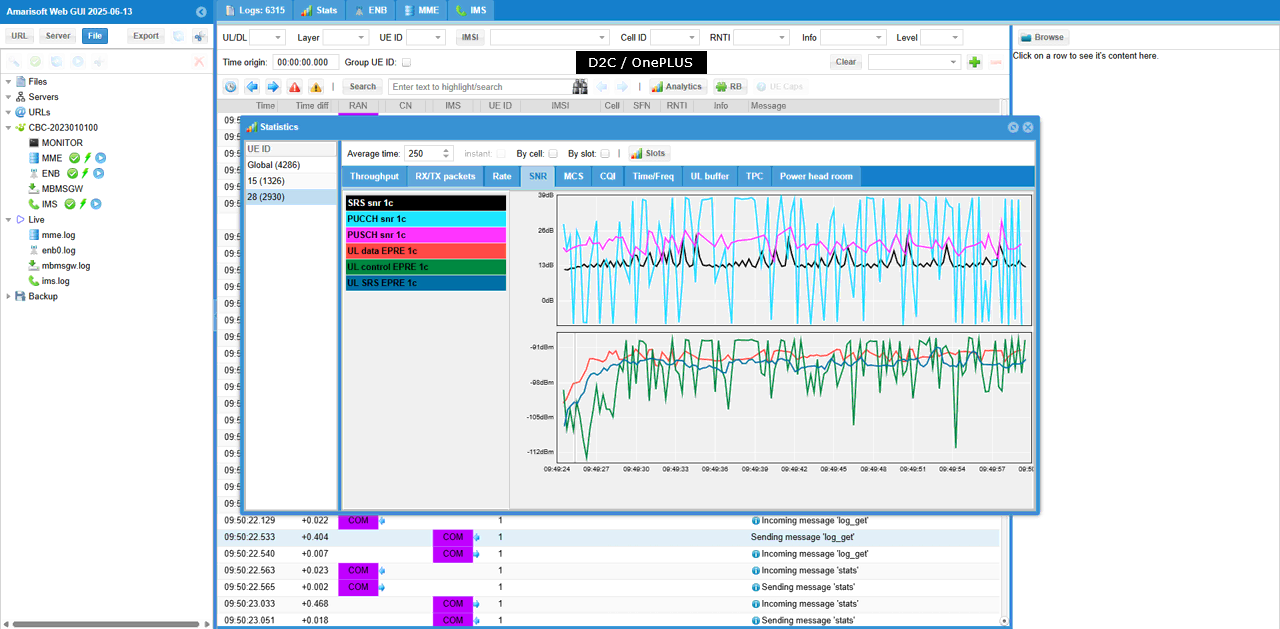
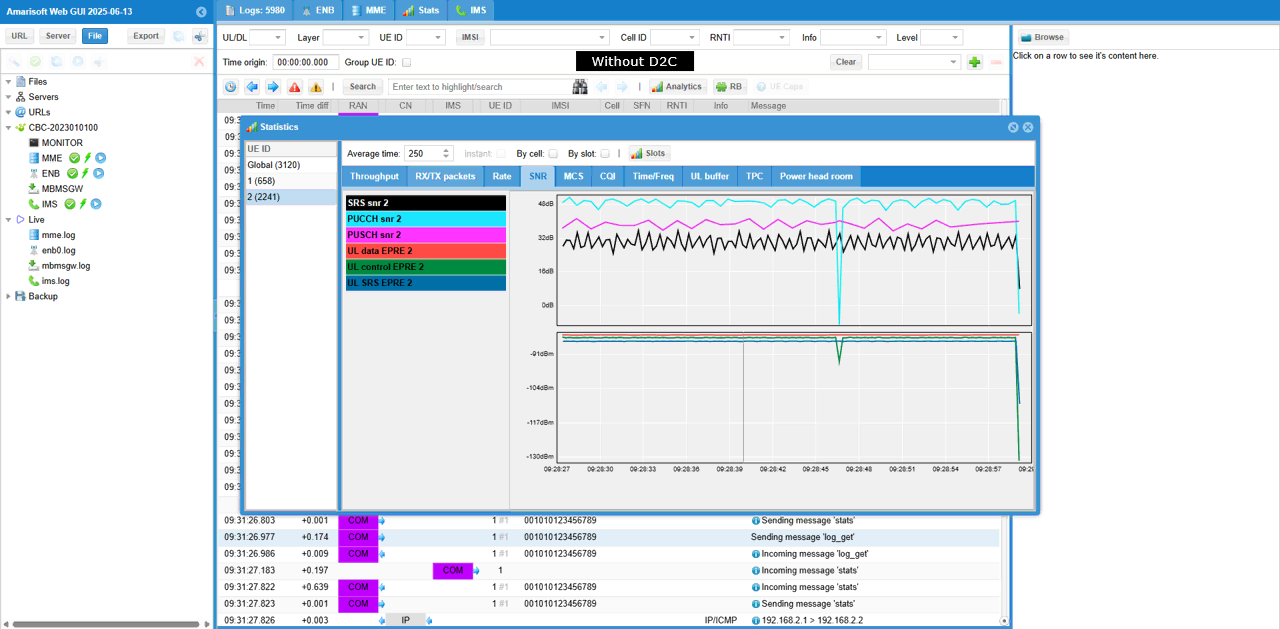
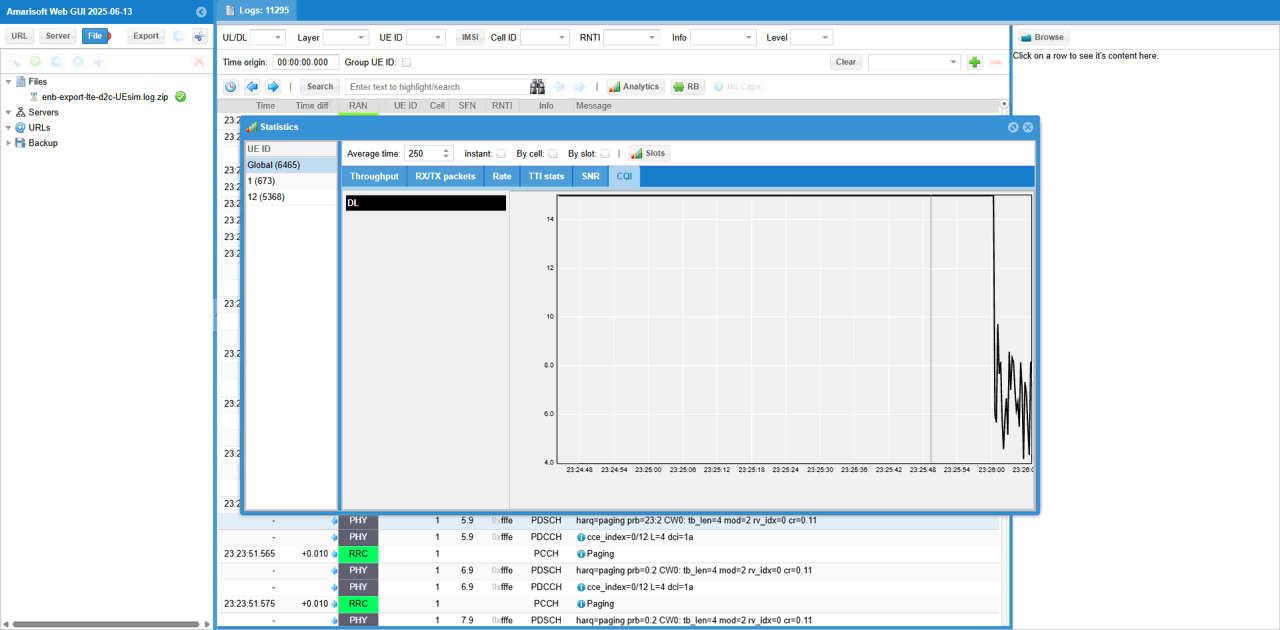
You can check out the signal quality percieved by UE from DL CQI plot
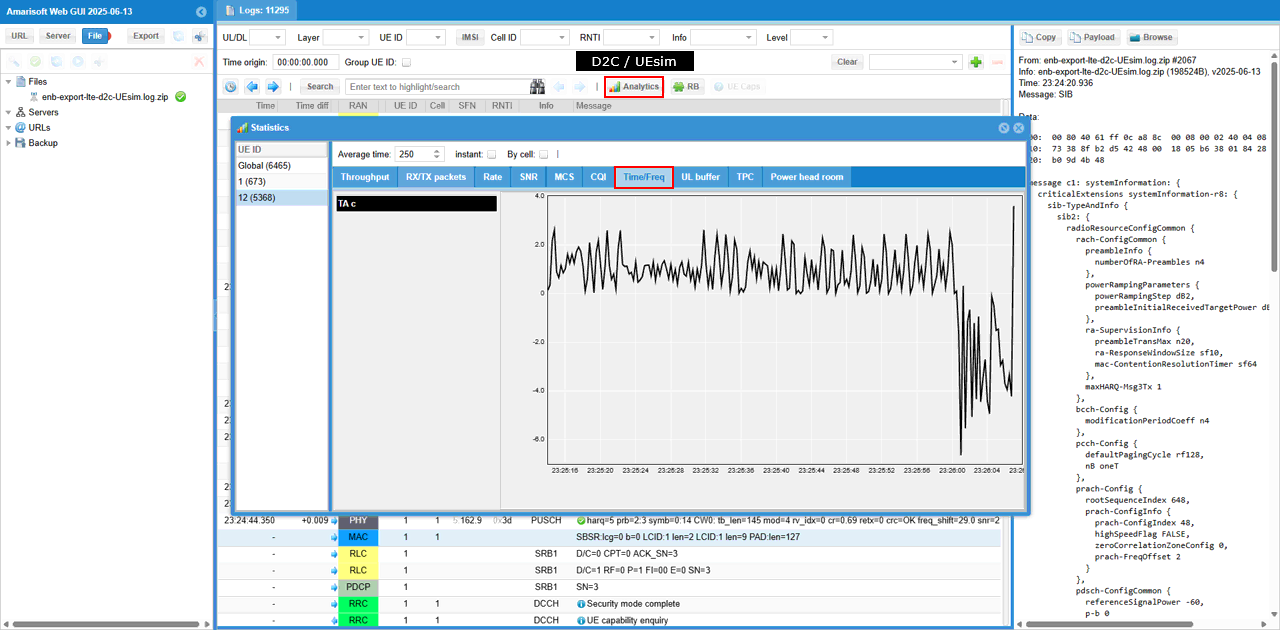
If you magnify TA command value in [Time/Freq] tab, you would see a pattern as shown below. ((NOTE : Connection between eNB and UEsim is via RF cable (i.e, conductive connection))