NR Multi UE
This tutorial is to show how to simulate multiple UEs with a single UEsim. For the simplicity, You can simulate maximum of 500 or 1000 UEs with single Amari UEsim and single Amarisoft Callbox. Since Amarisoft Callbox support multiple UE in simultaneous connection, it can have diverse use case as follows. Amarisoft Callbox would be the only solution in test and measurement area that support Use Case 2.
Use Case 1 : LTE/NR network with single UE (single DUT) for protocol, function and performance testing in a lab
Use Case 2 : Single LTE/NR network shared by multiple UE (multiple DUT) for protocol, function in a lab
Use Case 3 : LTE/NR network with external RRH. With this setup, you can use Amarosft callbox as a deployed live network or test live network in UE development.
Following table shows the list of UE Simbox product line and major features supported by each model.
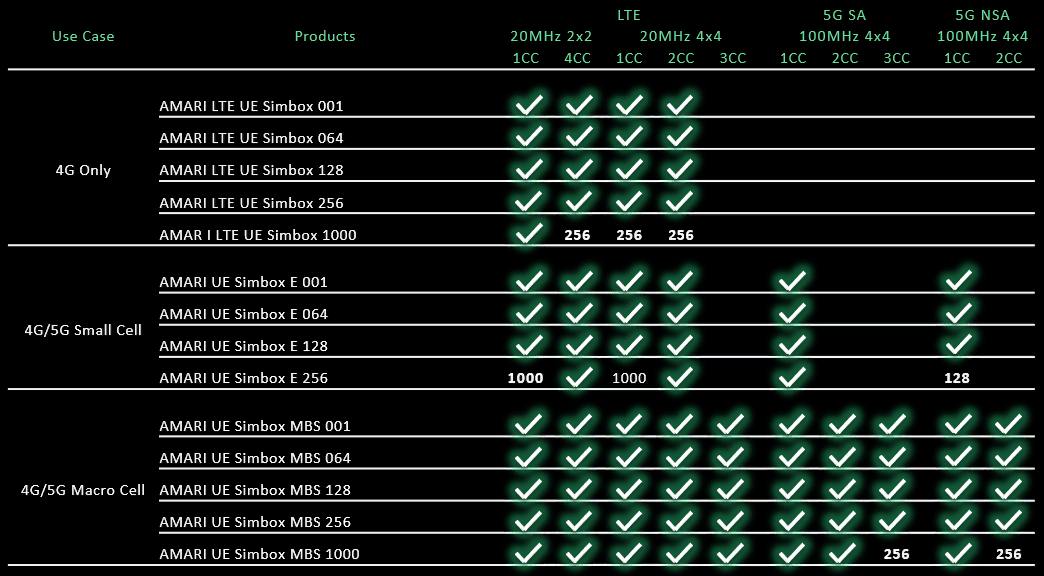
Table of Contents
Introduction
Amarisoft Callbox, coupled with UEsim, represents a highly flexible and scalable solution for simulating user equipment (UE) in LTE and 5G NR (New Radio) network environments. This integrated system enables the emulation of hundreds or even thousands of UEs using a single UEsim instance, seamlessly interacting with a single Amarisoft Callbox. Designed to address the growing complexity of mobile broadband and IoT scenarios, the platform empowers network engineers, protocol developers, and device manufacturers to perform comprehensive protocol, functional, and performance testing under realistic and controlled laboratory conditions. Architecturally, Amarisoft Callbox acts as a fully virtualized base station or core network emulator, supporting both standalone (SA) and non-standalone (NSA) network configurations. UEsim, in turn, generates virtual UEs that can attach, authenticate, and perform data transactions with the simulated network, mimicking the behavior of real devices. This approach is particularly significant in validating network performance, optimizing resource scheduling, and ensuring compliance with 3GPP standards without the logistical overhead of managing physical devices. The ability to simulate multiple UEs in parallel not only enhances test coverage but also enables use cases such as massive connectivity, handover scenarios, and stress testing of network infrastructure. Within the broader telecom ecosystem, Amarisoft solutions occupy a pivotal role in accelerating R&D, facilitating operator acceptance tests, and supporting continuous integration pipelines for evolving 4G/5G technologies.
-
Technology and Framework Context
- Amarisoft Callbox is a software-based radio access network (RAN) and core network emulator supporting LTE and 5G NR protocols.
- UEsim is a scalable virtual UE simulation platform, capable of generating hundreds or thousands of virtual UEs for laboratory testing.
- The architecture is designed for rapid deployment, ease of configuration, and interoperability with a range of test and measurement equipment.
- The system supports both standalone (SA) and non-standalone (NSA) modes, allowing for diverse deployment and testing scenarios.
-
Relevance and Importance of Multi-UE Simulation
- Simulating multiple UEs on a single platform reduces hardware requirements, operational costs, and complexity in laboratory environments.
- Enables testing of network scalability, resource management, and performance under high load or dense UE scenarios.
-
Supports a wide range of use cases:
- Use Case 1: Single UE protocol, function, and performance testing.
- Use Case 2: Multiple UEs sharing a single LTE/NR network for advanced protocol and function testing.
- Use Case 3: Integration with external RRH for live network emulation or device development.
- Unique in supporting simultaneous multi-UE connections with a single callbox, which is especially valuable for stress and interoperability testing.
-
Learning Outcomes
- Understanding how to configure and operate UEsim and Amarisoft Callbox for multi-UE simulation.
- Gaining insight into best practices for scalable UE emulation and network performance evaluation.
- Acquiring knowledge of test planning, execution, and result analysis in high-density UE environments.
- Familiarity with key product features, selection criteria, and licensing considerations for large-scale simulation.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge
- Basic understanding of LTE and 5G NR network architectures and protocols.
- Familiarity with RF concepts and test lab environments.
- Experience with network configuration, IP connectivity, and test automation frameworks is beneficial but not required.
- Awareness of product-specific limitations, such as maximum supported UEs depending on technology, product variant, and licensing.
-
Tutorial Scope
- The tutorial focuses on step-by-step procedures for simulating multiple UEs with a single UEsim and Amarisoft Callbox instance.
- Architectural overview, configuration guidelines, and practical tips for maximizing test coverage and efficiency are provided.
- Special considerations for scenarios exceeding standard UE limits, such as the use of Simbox-MBS for large-scale NR SA and NSA simulations, are discussed.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial demonstrates the procedure for testing up to 1000 UEs using Amarisoft UEsim and callbox (gNB), focusing on configuration-based multi-UE simulation. The test methodology, configuration steps, and analysis procedures are outlined below, with all original indentation, formatting, and structure preserved.
-
Test Setup Overview
- Case 1: Utilizes one callbox (gNB) and one UEsim, where the UEsim emulates multiple UEs (up to 1000 in this tutorial).
- Case 2: Involves multiple real mobile phones instead of UEsim. This configuration allows shared test equipment with many DUTs and supports various function tests (e.g., initial call setup, data connectivity, IMS). An external radio head can be added for increased coverage in a private network scenario.
-
Key Configuration Parameters
-
UEsim:
- multi_ue, ue_count, global_timing_advance, sim_events
-
Callbox:
- sr_period, n_rb_max, ue_count_max, short_pucch_an_rsc_count, cb_preambles_per_ssb, duration (pdcch->duration), sched_latency_for_prb_max
-
UEsim:
-
Test 1: Test with Configuration File Only
-
Configuration Procedure:
-
UEsim Configuration:
- Use the configuration file ue-nr-sa-1000.cfg, which includes the file ue-list-1000-UE.cfg.
- Each UE’s USIM information is predefined in ue-list-1000-UE.cfg (parameters such as imsi, K, amf, sqn, sim_algo).
- The sim_events section configures each UE’s behavior (e.g., when to power on, start IP traffic, and power off).
- The configuration covers the basic physical information for cell camping.
- The Scenario function in the WebGUI can automate file creation, though the tutorial uses a predefined file.
-
Callbox (gNB) Configuration:
- Use gnb-sa-1000-UE-bis.cfg, similar to gnb-sa.cfg.
- Set NR_TDD = 1 for NR TDD operation (can switch to FDD as needed).
- Configure NR band 78, subcarrier spacing 30kHz, and SSB bitmap (modifiable as per 3GPP compliance).
- Increase sr_period to 320 (from default 40) to prevent excessive SR requests from numerous UEs.
- Increase cb_preambles_per_ssb to provide sufficient PRACH resources for simultaneous RACH attempts by many UEs.
- Increase duration (pdcch->duration) to ensure enough PDCCH resources for control information transmission to multiple UEs.
- Adjust short_pucch_an_rsc_count to accommodate more simultaneous uplink Ack/Nack feedbacks.
- Set n_rb_max to prevent PUCCH from occupying all uplink bandwidth, preserving space for PUSCH.
-
Core Network Configuration:
- Use mme-ims-1000.cfg (modified from mme-ims.cfg) with included ue_db_1000-UE.cfg for large-scale UE support.
- Specify a wide enough IP address range using first_ip_addr and last_ip_addr to accommodate all UEs.
- Ensure the same SIM parameters are configured on both UE and core network sides.
-
UEsim Configuration:
-
Test Execution Steps:
- Verify the cell physical configuration to ensure intended settings.
- Start UEsim, execute the t command, and confirm all UEs (ID 1 to 1000) register successfully.
- Use the t command on the callbox if using commercial UEs to check registration.
- Retrieve global statistics with t g to observe UE states (idle, off, connected).
-
Test Analysis Methods:
-
While UEs are connected, analyze log files to:
- Observe PDCCH scheduling per slot, ensuring multiple DCI (DL/UL) are transmitted within a single slot.
- Verify PDSCH and PUSCH transmissions based on corresponding DCI scheduling.
- Check total and per-UE throughput statistics.
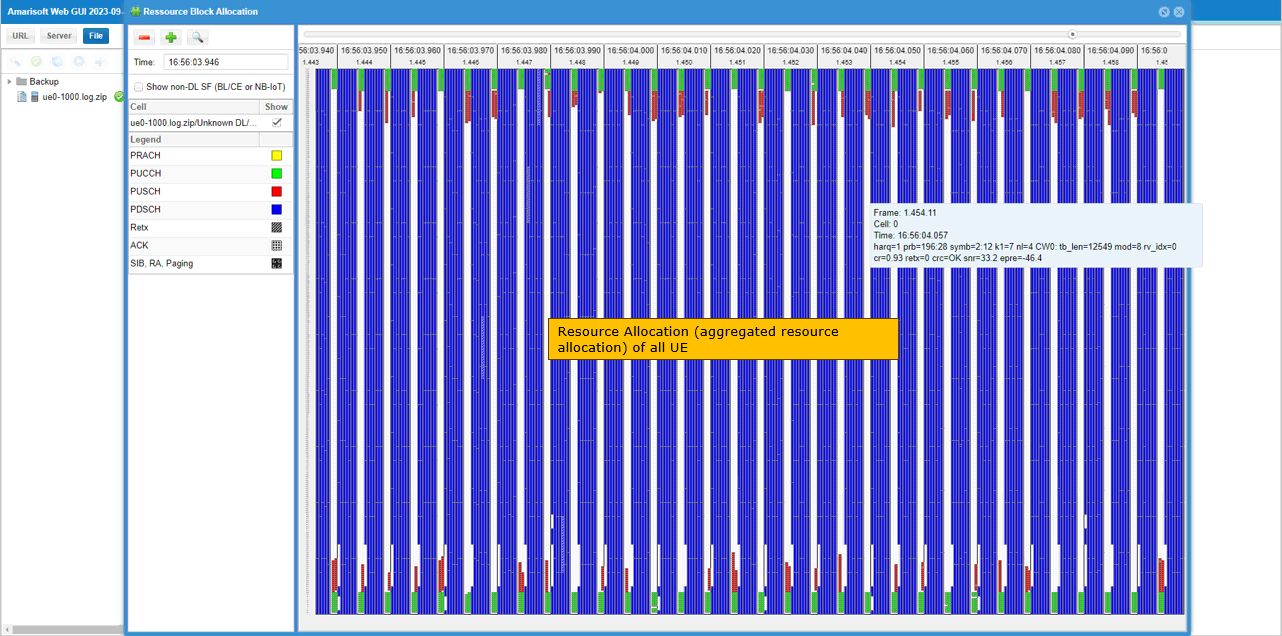
- Review aggregated physical resource allocation for all connected UEs.
-
While UEs are connected, analyze log files to:
-
Configuration Procedure:
Note: The tutorial emphasizes the importance of adequate configuration for large-scale UE simulation, including resource allocation, parameter adjustments, and log/statistical analysis to validate system behavior under high UE density scenarios.
Test Setup
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below. In this tutorial, < Case 1 > setup is used, but < Case 2 > setup is also possible. The fact that <Case 2> is possible indicates you can use Amarisoft callbox as a deployed network(live network) as well.
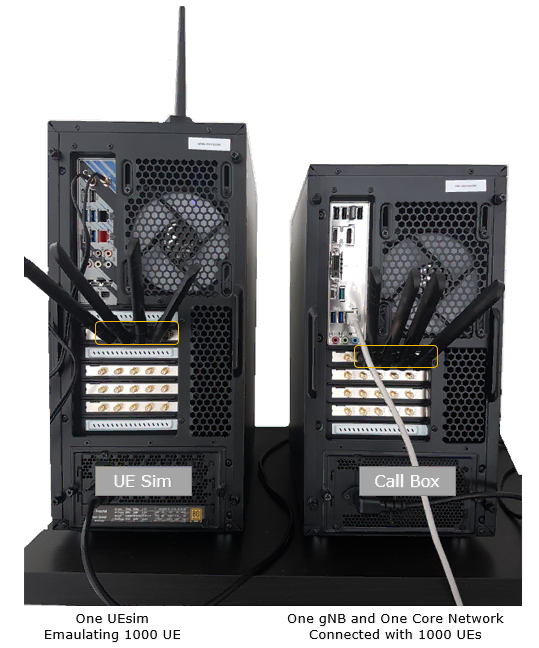
Case 1
: In this setup, one callbox (gNB) and one UEsim is used. The single UEsim can emulate multiple UEs (1000 UEs in this tutorial).

Case 2
In stead of using UEsim, you can use multiple of real mobilephones for the same test. With this setup, you can share one test equipment with many DUTs and do various function test (e.g, initial call setup, data connectivity, IMS etc) or you can use this setup as private network if you add external radio head to increase the coverage.

Key Configuration Parameters
Followings are important configuration parameters for this tutorial. You may click on the items for the descriptions from Amarisoft documents.
- UEsim
- Callbox
Test 1 : Test with Configuration File Only
In this test, I will show you how to test 1000 UE with configuration file only. It mean that the information (USIM information) for each and every UE is prepared in advance in configuration file. (
Configuration
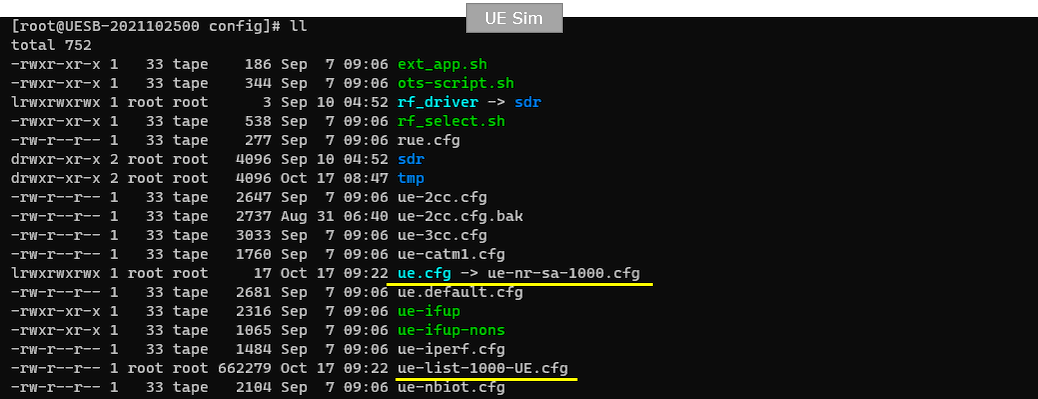
On UEsim, I used the ue-nr-sa-1000.cfg which is similar to ue-nr-sa.cfg. The configuration includes ue-list-1000-UE.cfg in it.
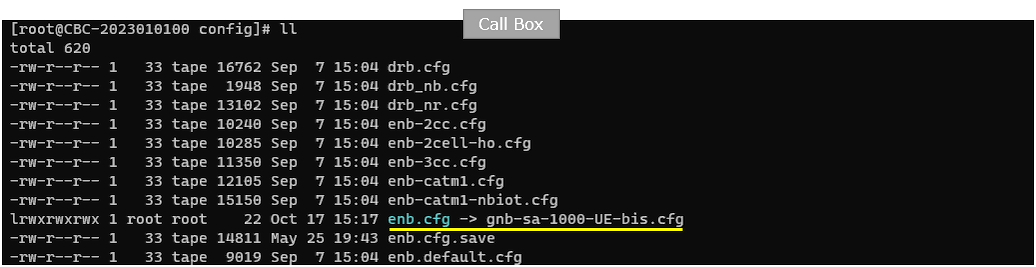
On callbox, I used gnb-sa-1000-UE-bis.cfg which is similar to gnb-sa.cfg.
To configure such a many UEs, we need to use special configurations for core network. For this purpose, I used the mme-ims-1000.cfg which is copied and modeified from mme-ims.cfg. In mme-ims-1000.cfg, an external ue_db file ue_db_1000-UE.cfg is included.
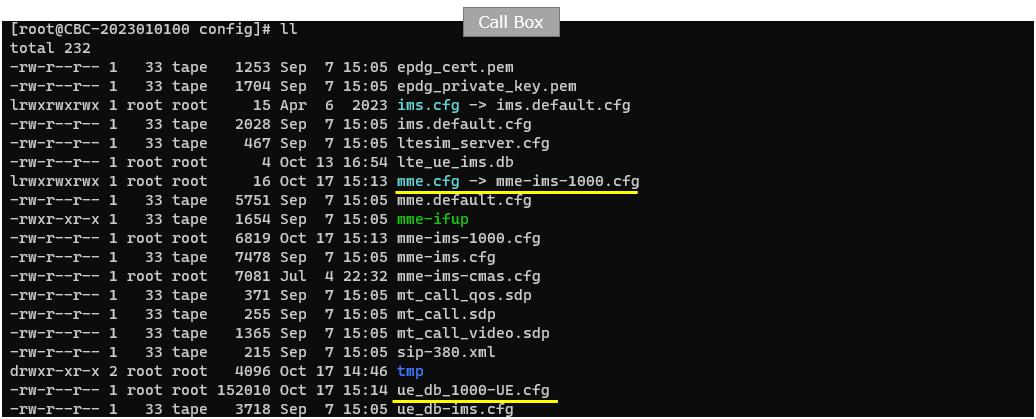
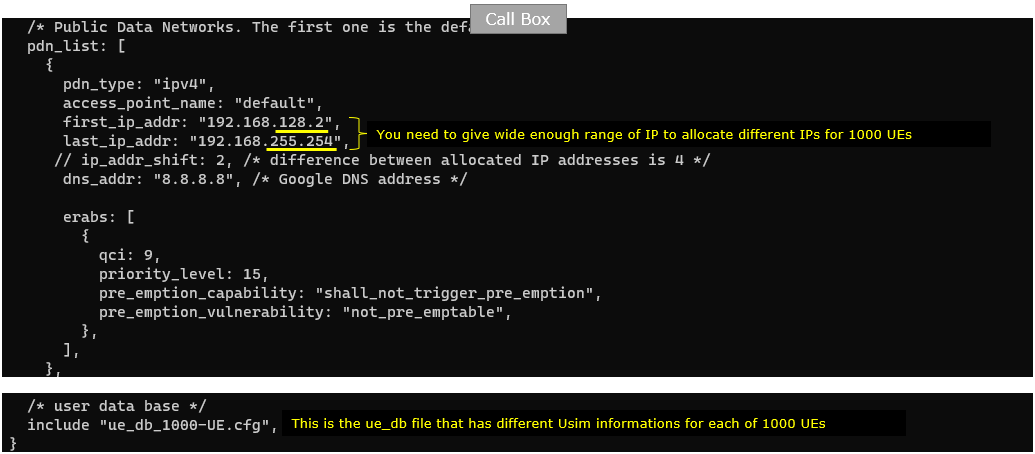
In the mme-ims-1000.cfg a few parameters are modified specifically to handle huge numbers of UEs as highlighted below. The point here is to specify the wide enough ranges of ip addresses (range determined by first_ip_addr and last_ip_addr) to accommodate over 1000 UEs. Another thing to note is that the predefined ue configuration (ue_db_1000-UE.cfg) is included in mme configuration.
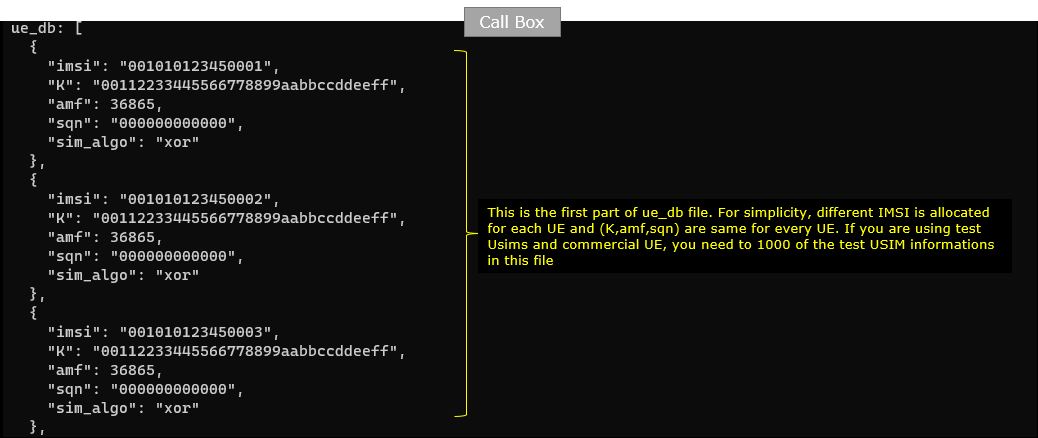
In this tutorial, following SIM information will be used within ue_db_1000-UE.cfg . Make it sure to configure the same parameters on UE side as well. As you see, ue_db is just the accumulation (list) of USIM parameters like imsi, K, amf, sqn, sim_algo. If you are using Amarisoft UEsim instead of commerical UEs and use "xor" for sim_algo, UEsim has functionality to generate this file automatically. It just increment imsi value with all other parameters set to be same.
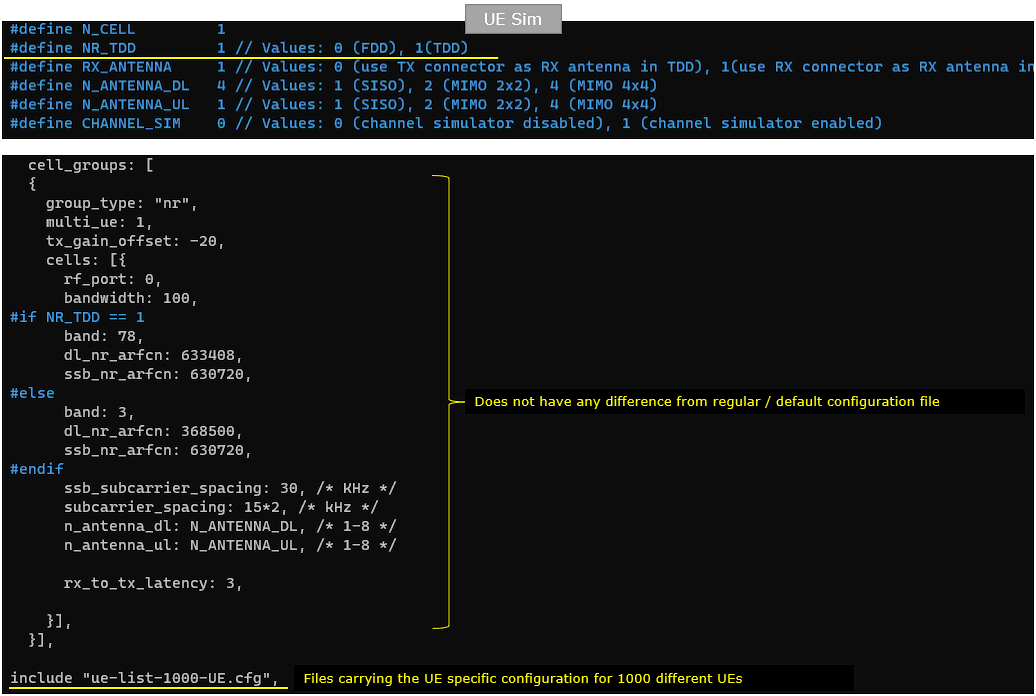
In ue-nr-sa-1000.cfg on UEsim, Notice that all the individual UE information is included as a separate file named ue-list-1000-UE.cfg.
The initial part of the configuration is to configure the basic physical information for the cell that the UE has to camp on. If you are using commercial UE instead of Amarisoft UEsim, you don't need this configuration since commercial UE detect the cell automatically during cell selection process.
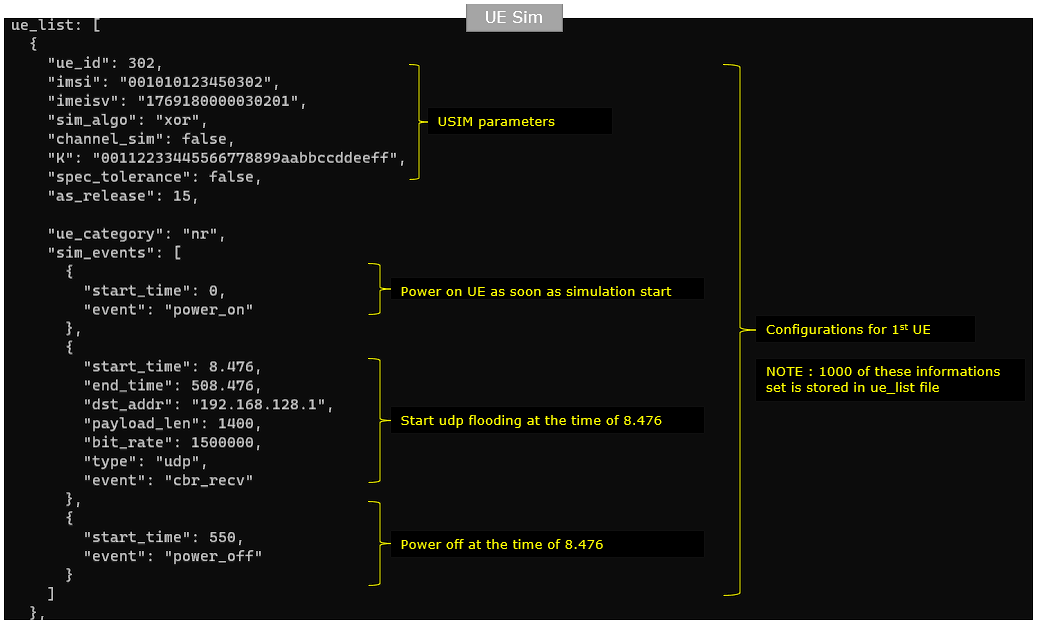
Note that at the end of the configuration, you see the ue-list file(ue-list-1000-UE.cfg) included. It mean you need to prepare the file,
You should prepare the ue_list file in a form as follows. In this file, you need to provide a set of parameters for 1000 different UEs, meaning that you need to put 1000 copies of the following parameter sets configured differently for each UE.
The initial segment is for USIM information and basic access capability and next segment (sim_events) to configure the behavior of each UE for example, when to powr on, when to start IP traffic (udp in this example) and when to power off.
Following is the configuration in gnb-sa-1000-UE-bis.cfg
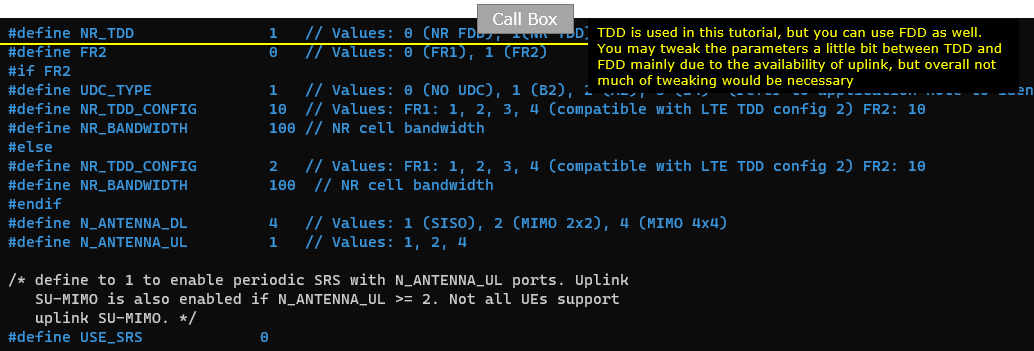
At first, I set NR_TDD = 1 indicating that I will use NR TDD in this test. You can use TDD or FDD as you like without changing much of other parameters.
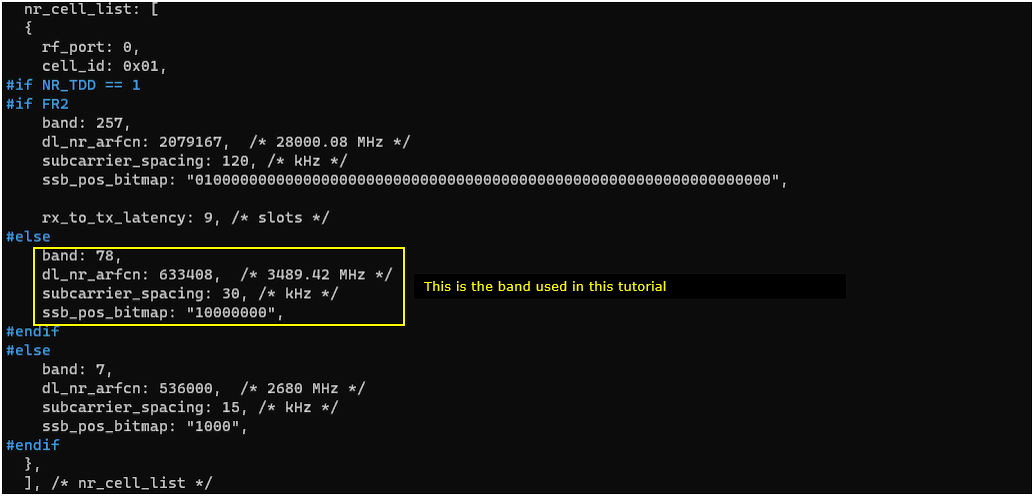
In this tutorial, I used NR band 78, scs(subcarrier spacing) 30Khz and ssb bitmap "100000000". It doesn't matter much on how you change these parameters. You can change band, dl_nr_arfcn, subcarrier_spacing, ssb_pos_bitmap in any way you like as long as it complies with 3GPP specification.
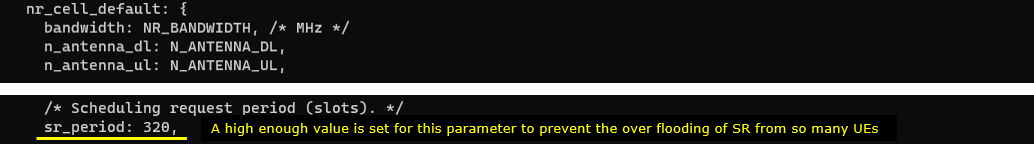
In nr_cell_default, the first thing that I did is to increase the value of sr_period. The default is 40 and I increased this to 320. This is to prevent too many UEs from sending too many SR requestion. In other words, this is to prevent SR flooding from too many UEs.
For the applications like 1000 UEs, there should be enough PRACH resources for those many UEs. You can do this with the combination of msg1_fdm, ssb_per_prach_occasion, cb_preambles_per_ssb, In this tutorial, I just increased cb_preambles_per_ssb to allow many UEs to map to the same SSB and RACH occasion. This does not mean that it allows the contention. It is just to allow many UEs to attempt PRACH without waiting too long. (You may check out this note for further details on meaning of msg1_fdm, ssb_per_prach_occasion, cb_preambles_per_ssb)
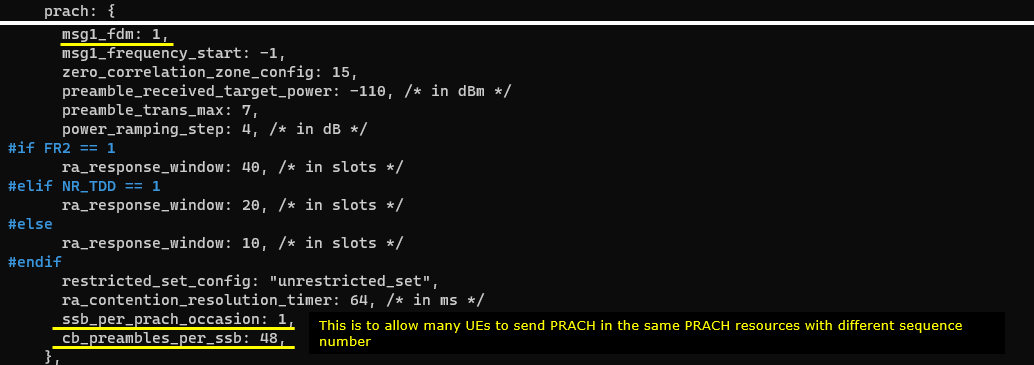
For this kind of use case handling so many UEs, gNB should be able to send a lot of PDCCH(DCI) within a slot. It mean that there should be enough physical resources to transmit many PDCCH. This is why I increased the value for duration parameter as shown below.
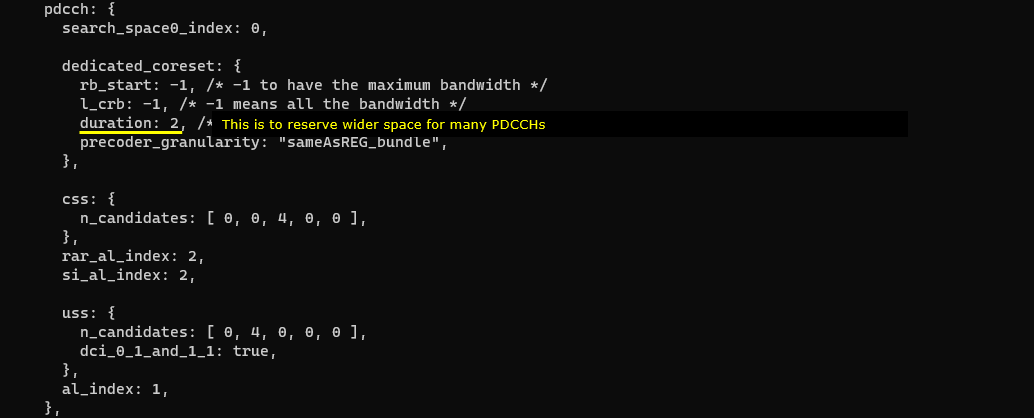
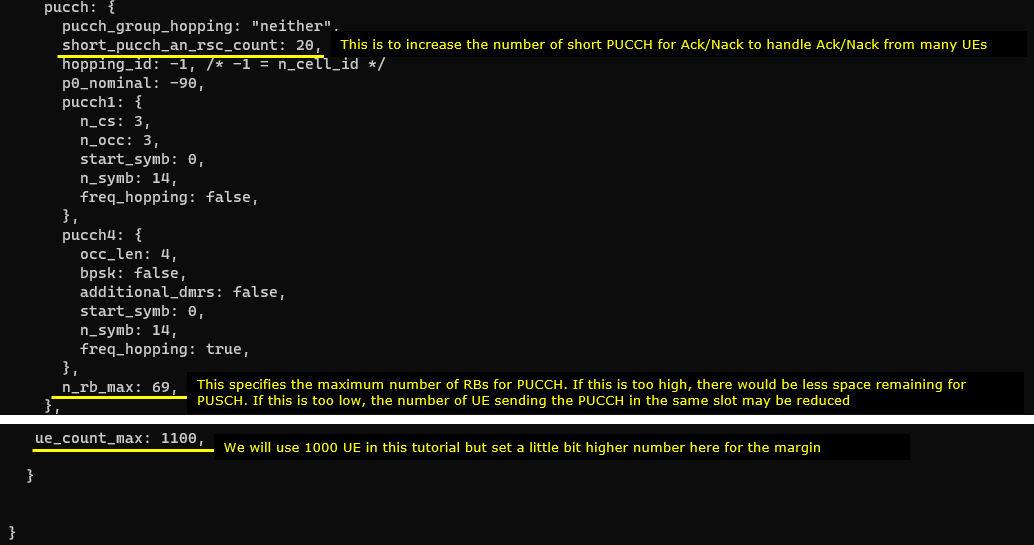
Not only for Downlink control channel, but also for uplink control channel we need to assign enough physical resources to handle such a many uplink control information. For this, I increased the value for short_pucch_an_rsc_count to increase the number of short PUCCH for Ack/Nack to handle Ack/Nack simultaneously sent by many UEs. For allow PUCCH from many UEs we need wide uplink physical resources, but the gNB should not allocate all of the uplink resoures for PUCCH. In that case, it would not have any remaining space for PUSCH. To prevent PUCCH from consuming the whole UL resources, we need to set a certain limit for PUCCH space with the parameter n_rb_max.
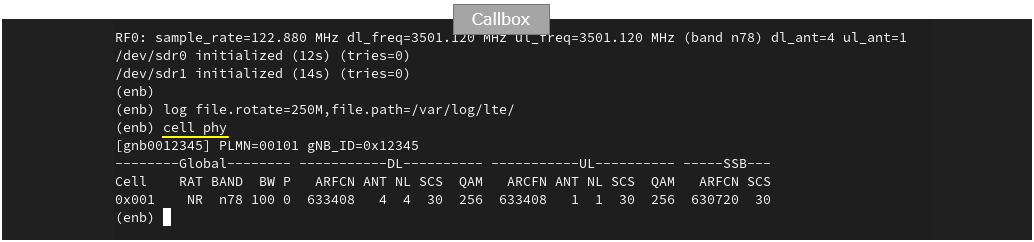
Perform the test
Check out cell phy configuration and make it sure the cell is configured as intended.
Start UEsim and run 't' command. Make it sure that all the UE get registerred. You may try 't' command on Callbox as well. The key point is to wait until you see all UE IDs (1 through 1000 in this case) connected. If you are using commercial UEs for the test, you can confirm the same thing on Callbox also using 't' command.
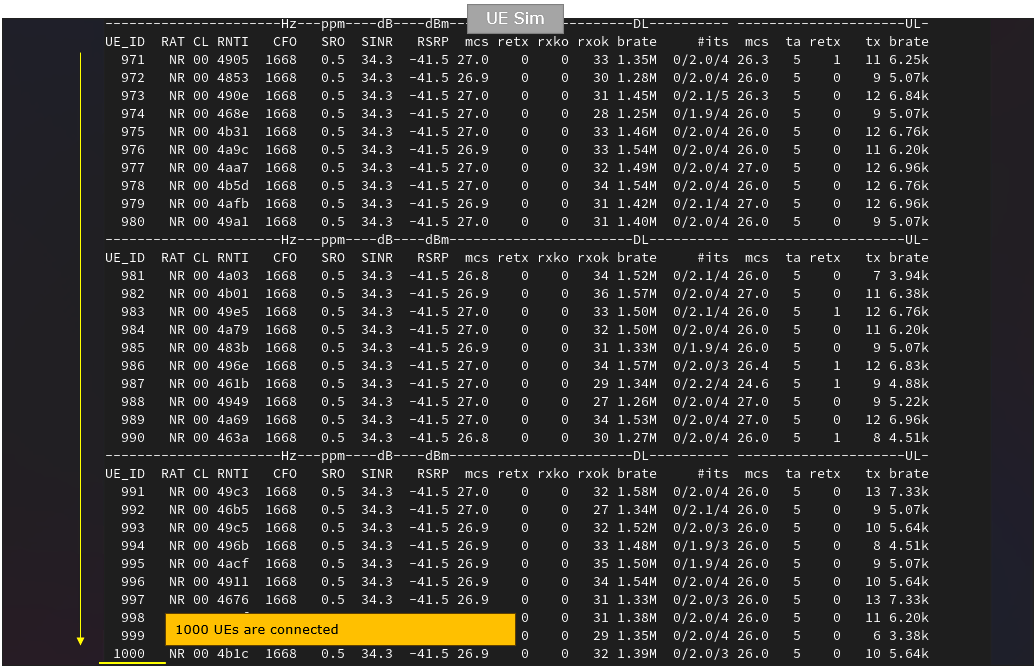
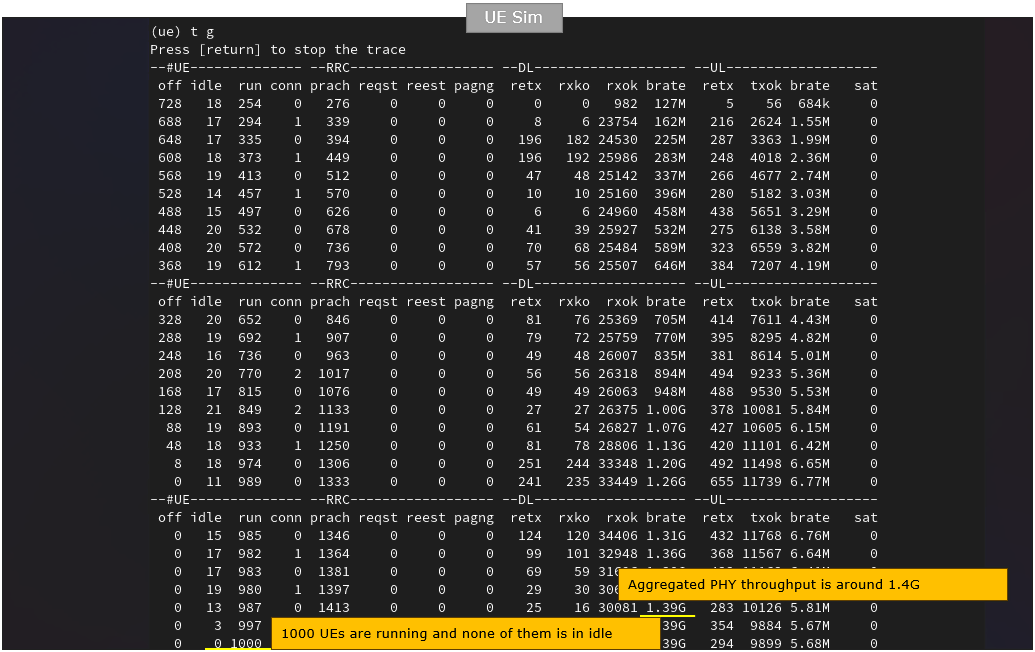
You can also get some global statistics using "t g" command as shown below. With this command, you can find out high level statics like how many UEs are in idle('idle' colum), how many UEs are off ('off' colum) and how many UEs are in connection ('conn' colum).
Log Analysis
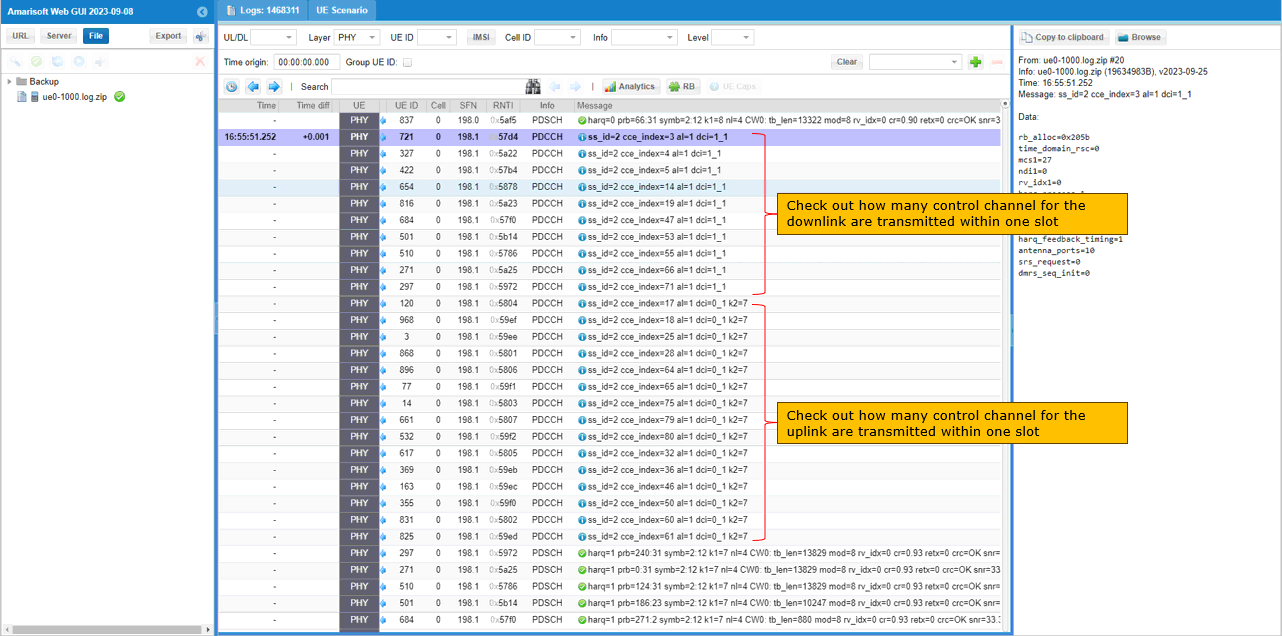
While UEs are in connected state, you can check out how many UEs and which UEs are scheduled for each slot as shown below. You may check out the same thing on gNB log as well. In this log, I would not look much into signaling process because basically they are typical initial attach sequence. What I want to highlight is about lower layer scheduling and see how gNB allocates physical resources to handle such a large amount of UEs.
First let's check how gNB transmit control information. As you can see below, a lot of PDCCHs are transmitted within single slot (SFN 198 and slot 1 in this case). Among these PDCCHs are many dci 1_1 (DL schedule) and dci 0_1(UL schedule).
Based on DL scheduling shown above, corresponding PDSCHs are transmitted by gNB as shown below. Since k0 for all dci 1_1 is 0 by default (meaning k0 for all dci 1_1 are same), you should see the same number of PDSCHs as the number of dci 1_1 within single slot.
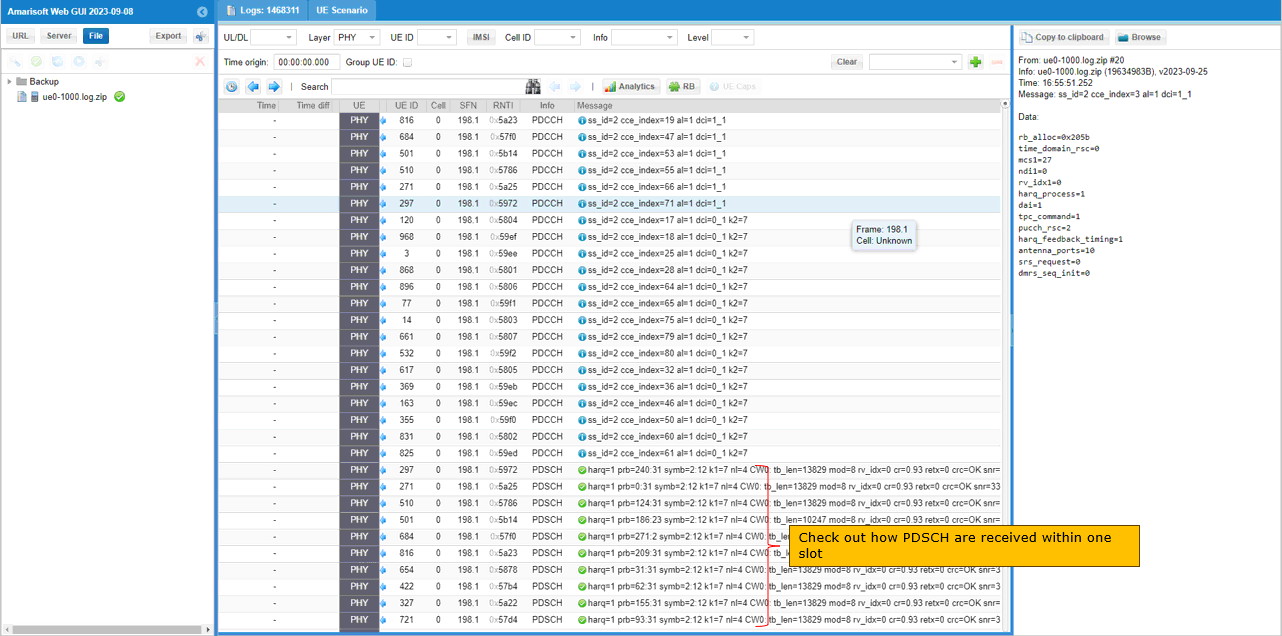
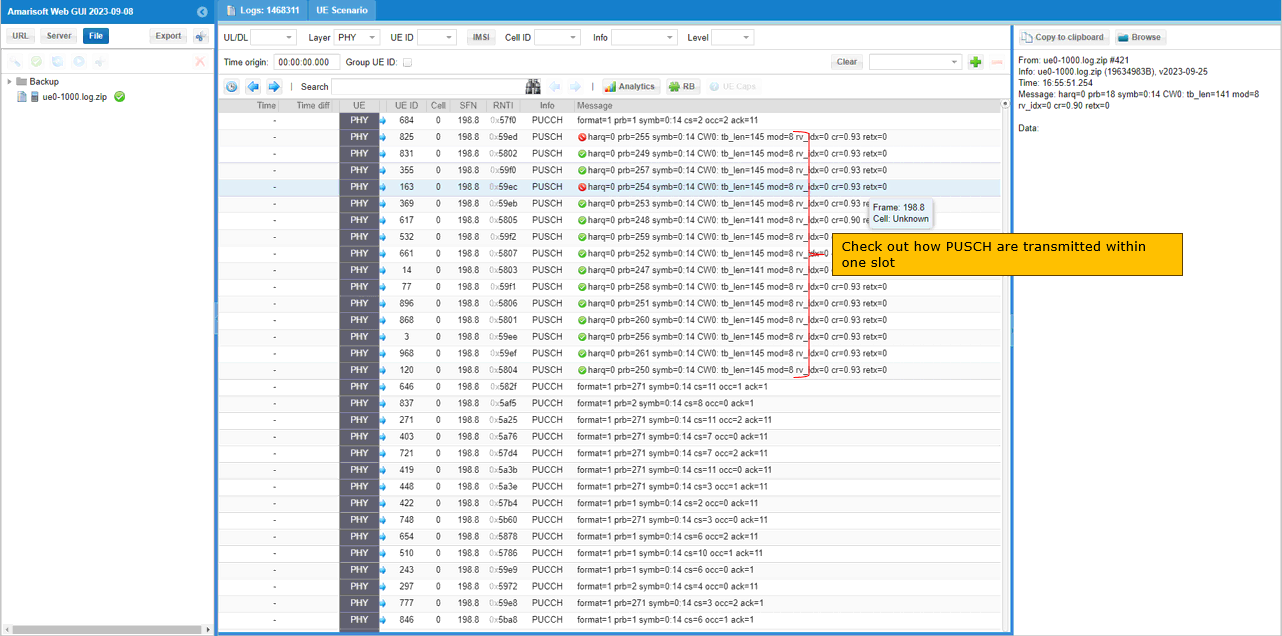
Based on UL scheduling shown above, corresponding PUSCHs are transmitted by UE as shown below. Since k2 for all dci 0_1 is all 7 (meaning k7 for all dci 1_1 are same), you should see the same number of PUSCHs as the number of dci 0_1 within single slot.
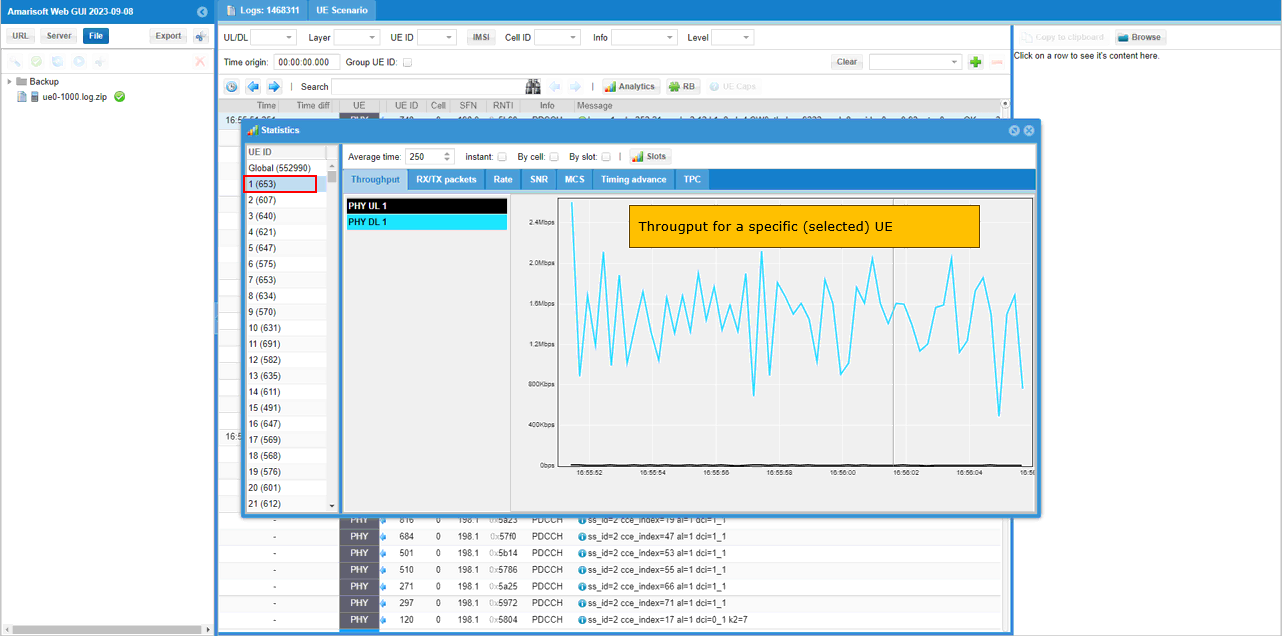
While UEs are in connected state, you can check out the total throughput (aggregated throughput) of all the connected UEs and throughput for each individual UE. You may check out the same thing on gNB log as well.
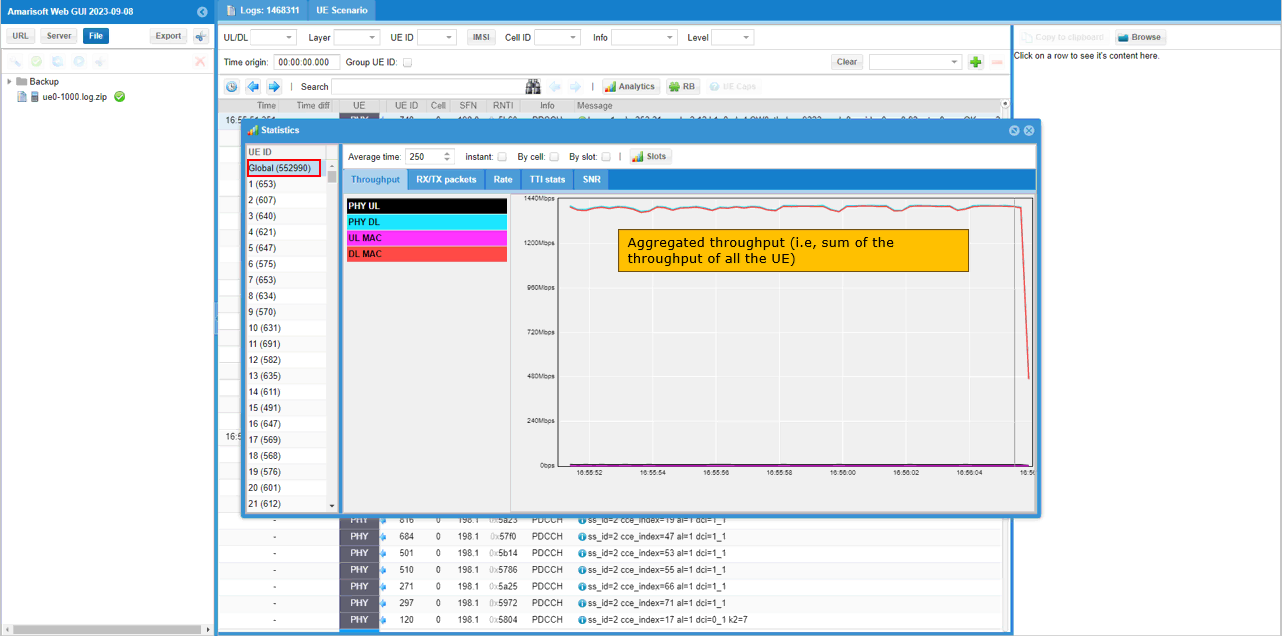
While UEs are in connected state, you can check out the total throughput (aggregated throughput) of all the connected UEs and throughput for each individual UE. You may check out the same thing on gNB log as well.
While UEs are in connected state, you can check out the total physical resource allocation (aggregated resource allocation) of all the connected UEs. You may check out the same thing on gNB log as well.