LTE Roaming
The purpose of this tutorial is to show you how to perform Roaming Tests with LTE network.
This tutorial shows how to test Cell Reselection on Amari Callbox and a commercial UE. Cell Reselection is a mechanism where UE can change the cell in Idle mode. The idle mode cell change happens in several different situations as listed below. When we say 'Cell Reselection', it usually mean the first two cases, but people say in a little different way depending on context.
- UE changes cell to another cell which has higher cell power with the same PLMN as the current cell.
- UE changes cell to another cell which has higher priorities. This priorities may be configured in SIB or RRC Release message.
- UE lost signal from the current cell and change to another cell with selectable cell. Strictly speaking this is more like a cell selection, but it can be considered as a type of reselection.
- UE first attached to a visiting PLMN and changes to another cell with Home PLMN and vice versa. Strictly speaking this is called Roaming.
- UE attached to a cell and Network (eNB) explcitely direct UE to change to another cell via RRCConnectionRelease message. This is called Cell Redirection.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Cell Reselection and Roaming are core mechanisms in Long Term Evolution (LTE) networks, enabling User Equipment (UE) to optimize connectivity and maintain service continuity as radio and network conditions change. LTE, standardized by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), employs a layered architecture in which UEs interact with radio access nodes (eNodeBs) and core network entities to facilitate seamless mobility, efficient spectrum usage, and robust subscriber experiences. Cell Reselection governs the process by which an idle-mode UE autonomously selects the most suitable cell, based on parameters such as received signal quality, priority configurations, and PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) identity. This process is crucial for maintaining coverage, optimizing battery life, and ensuring rapid service reacquisition. Roaming, on the other hand, allows UEs to access services outside their home network, involving identity management and inter-PLMN procedures. While the full roaming architecture includes complex inter-core interfaces (such as S6a between VPLMN and HPLMN MMEs), this tutorial focuses on the foundational aspects of cell reselection and basic roaming procedures from the radio and PLMN perspectives. By leveraging tools like the Amari Callbox and commercial UEs, practitioners can simulate and analyze these behaviors, gaining insight into LTE mobility management, network selection logic, and the interplay between system information broadcasts and UE decision-making. The significance of mastering these procedures extends from device validation and network optimization to ensuring compliance with global roaming standards, making this knowledge essential for engineers, testers, and network operators working within the LTE ecosystem.
-
Context and Scope
- This tutorial addresses LTE mobility management, specifically focusing on cell reselection and roaming behaviors using Amari Callbox and a commercial UE.
- It explores how UEs autonomously select and switch cells in idle mode, examines the criteria influencing these decisions, and explains the limited-scope roaming tested here, distinct from full core network roaming architecture.
- The content is relevant for radio interface validation, device testing, and understanding fundamental LTE mobility procedures.
-
Relevance and Importance
- Understanding cell reselection is vital for optimizing network performance, improving user experience, and ensuring device interoperability in multi-cell and multi-PLMN environments.
- Roaming procedures covered here are foundational for confirming device readiness for international or multi-operator deployment, even if the full core roaming architecture is out of scope for this exercise.
- Mastery of these mechanisms supports efficient troubleshooting, network planning, and standards compliance.
-
Learning Outcomes
- Gain practical experience in setting up and executing LTE cell reselection and roaming tests using a controlled test environment.
- Comprehend the architectural roles of eNodeB, PLMN, and UE in idle mode mobility and network selection.
- Interpret system information configurations (such as SIBs) and understand their impact on UE behavior.
- Recognize the limitations of radio-level roaming testing versus full core network roaming deployment.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge and Skills
- Familiarity with LTE architecture, including eNodeB, UE, PLMN, and mobility management concepts.
- Basic understanding of radio resource management, idle mode procedures, and system information broadcasts.
- Experience with radio network testing tools (e.g., Amari Callbox) and access to a compatible commercial UE.
- General technical proficiency in wireless communications and network protocol analysis is recommended.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial outlines a procedure for testing LTE roaming between two PLMNs using a setup with one eNB supporting two PLMNs, two independently operating MMEs, and IMSs. The test focuses on verifying the UE's ability to roam between HPLMN and VPLMN cells and to observe the corresponding attachment and roaming behaviors.
-
Test Setup:
- All network components (eNB, MMEs, IMSs) are launched automatically by the LTE service and are accessible via the 'screen' window.
- The eNB is configured to support two PLMNs, with each PLMN associated with a separate MME.
-
Configuration:
- The setup and configuration follow the guidelines from the Multiple MME tutorial, enabling support for multiple PLMNs and MMEs as depicted in the setup diagram.
-
Test Procedure:
- Start with the UE powered on. Disable Mobile Data for both HPLMN and VPLMN cells to allow the UE to enter and remain in the idle state, which is preferred for the roaming test.
- On the eNB screen, confirm that the UE initially attaches to Cell 1 (HPLMN).
- Turn off the HPLMN Cell, leaving only the VPLMN cell (ENB1) active.
- Wait for the UE to camp on to the VPLMN cell. This process may take a few minutes. Verify the presence of the roaming icon on the UE and confirm attachment to Cell 2 (VPLMN).
- Power on the HPLMN Cell again so that both HPLMN and VPLMN cells are active. The UE should still be registered to the VPLMN cell at this stage.
- Wait for the UE to detect and camp back to the HPLMN cell, typically requiring several minutes as the UE searches for the higher-priority HPLMN.
- Observe and confirm that the UE reattaches to Cell 1 (HPLMN) and the HPLMN icon is displayed on the device.
-
Log Analysis:
- Rather than analyzing individual protocol messages, log verification is performed by checking the cell attachment status across different stages of the test.
- Initially, confirm in the logs that the UE is attached to Cell 1 (HPLMN).
- After roaming, verify that the UE is attached to Cell 2 (VPLMN).
- Following reversion to the HPLMN, check that the UE is once again attached to Cell 1.
This methodology validates the UE's roaming capabilities between HPLMN and VPLMN environments and ensures correct cell attachment and roaming behavior through both direct observation and log verification.
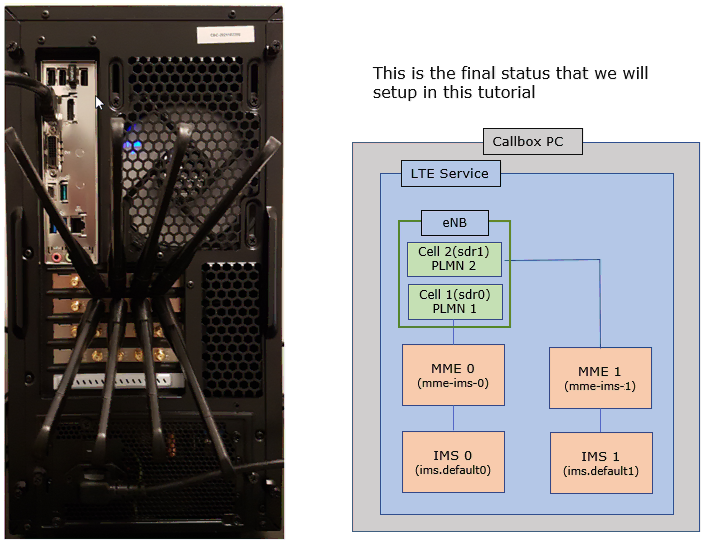
Test Setup
In this tutorial, you may use two types of as shown below. All the components will launch automatically by lte service and all the components will be automatically added to 'screen' window as well.
Configuration
For this tutorial, you can use two types of the setup as below.
: eNB with two PLMN, two MME and IMSs are running indepentaly as illustrated above, so configuration is pretty complicated. I used the exact same configuration as in the tutorial : Multiple MME.
Perform the test
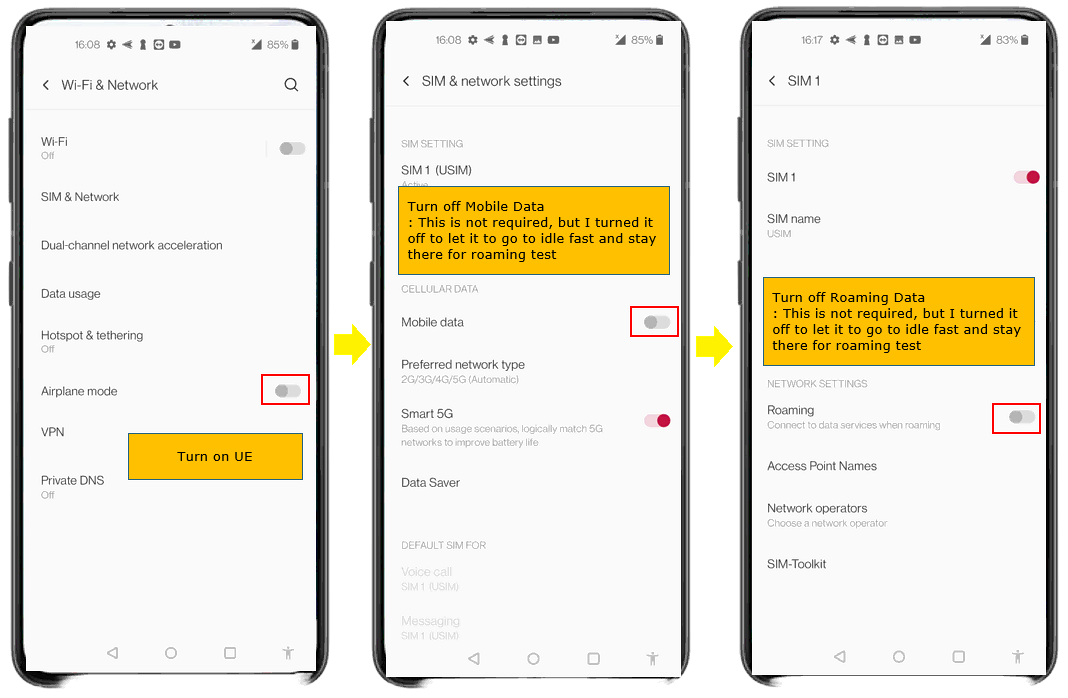
First with UE, power on UE and disable Mobile Data for both HPLMN cell and VPLMN Cell. (
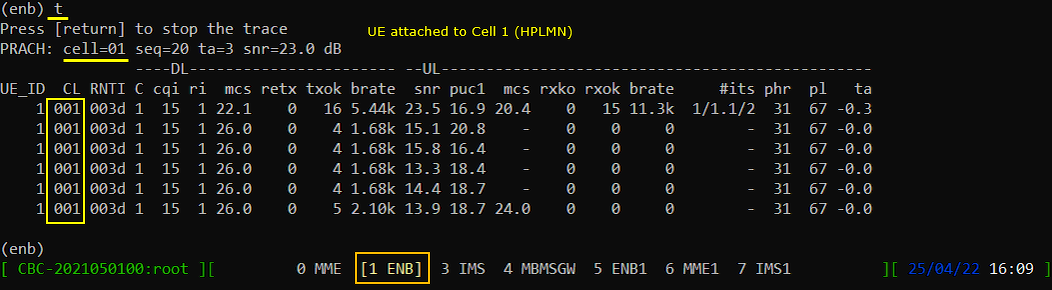
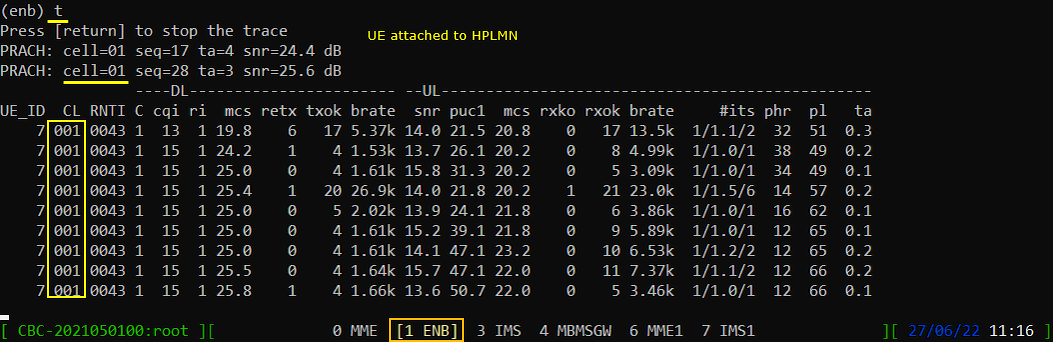
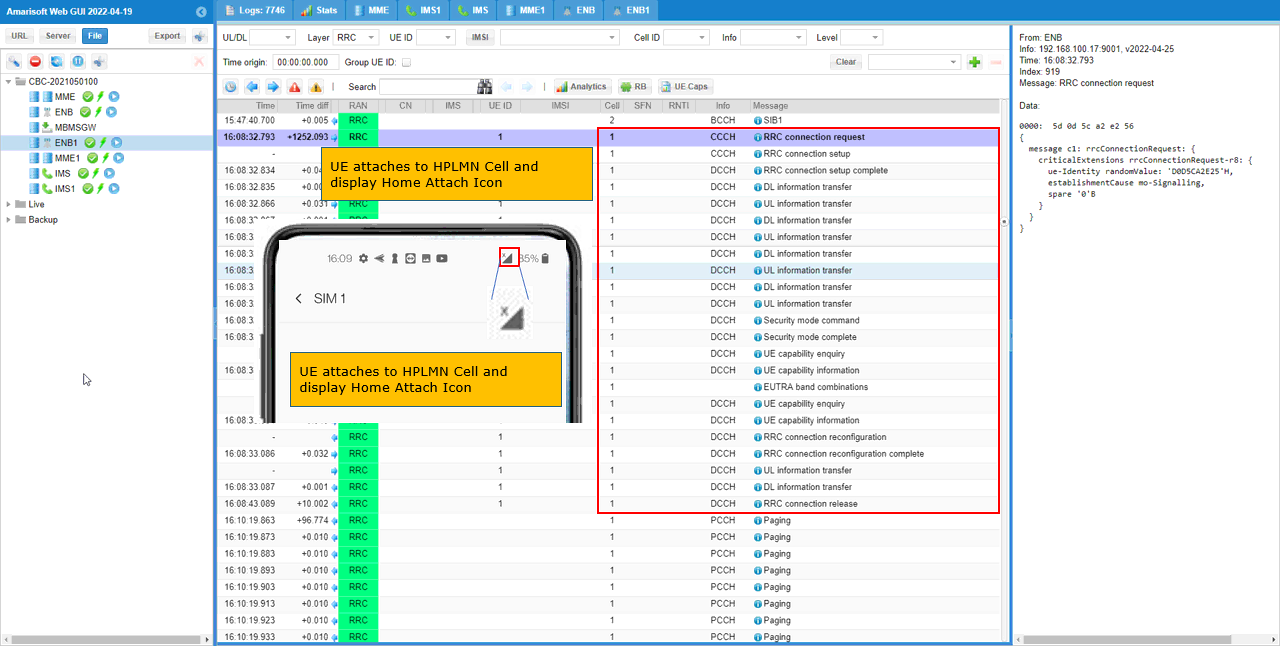
Go to [1 ENB] screen and confirm that UE attaches to Cell 1 (HPLMN).
Now turn off HPLMN Cell. VPLMN cell (ENB1) remain active.
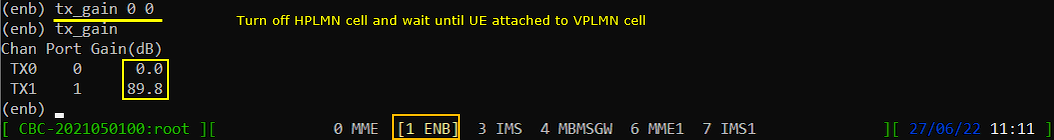
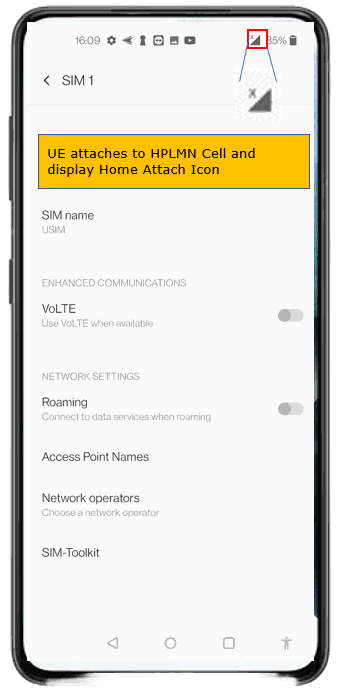
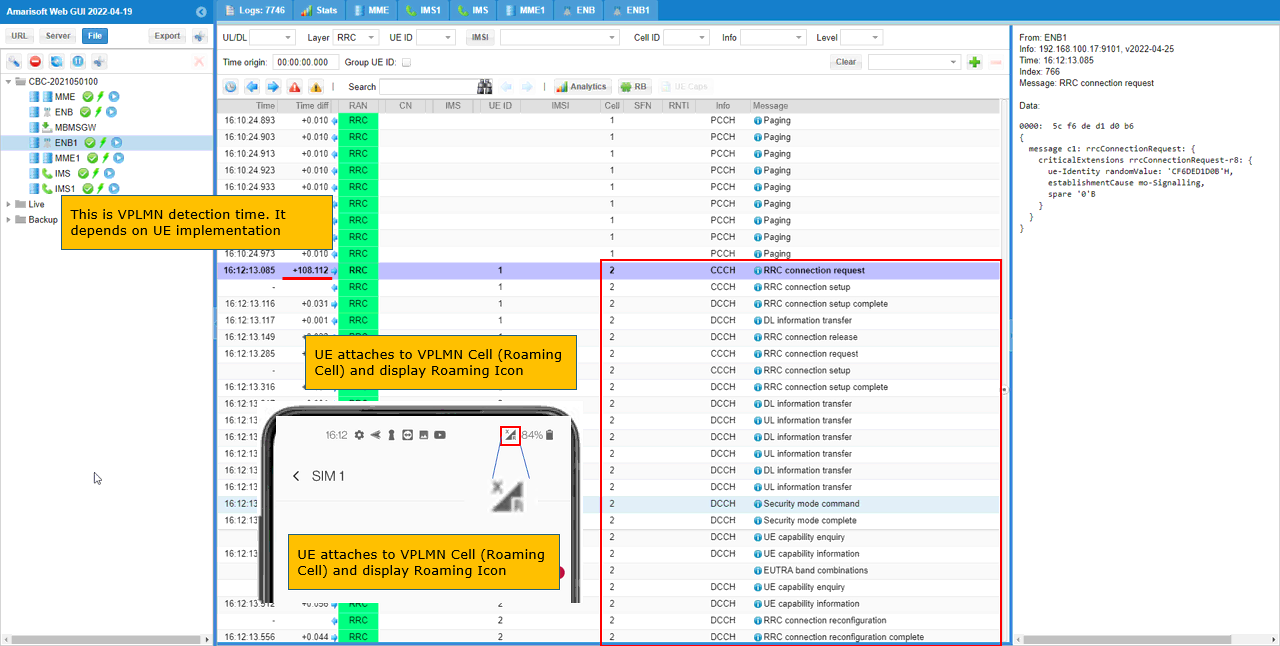
Make it sure that UE attaches to VPLMN cell. This takes a while (a few min) for UE to camp on to VPLMN Cell. You would see Roaming Icon displayed on the phone.
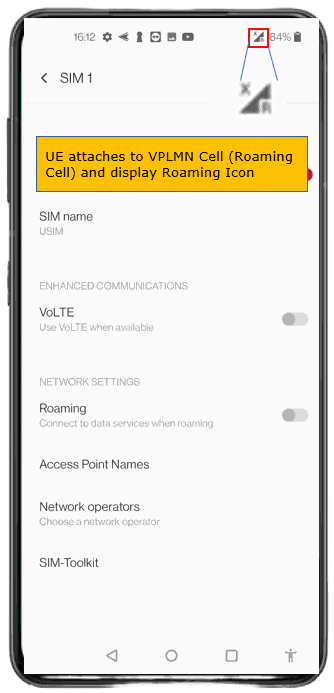
Confirm that UE attaches to Cell 2 (VPLMN).
Now power on HPLMN Cell gain. At this moment, both HPLMN and VPLMN cell are active and UE is registered to VPLMN Cell.
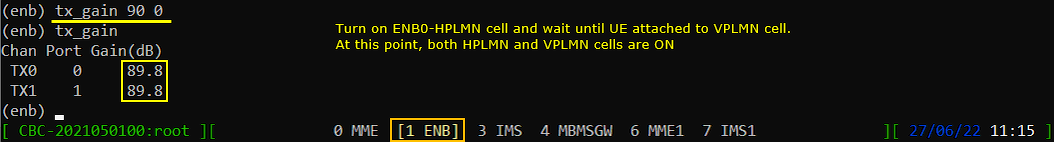
Wait until UE camp on to HPLMN Cell. This would take several minutes for UE to search for High Priority PLMN (HPLMN) cell.
Now you would see the HPLMN icons on UE when it completes the attach to the HPLMN Cell.
Log Analysis
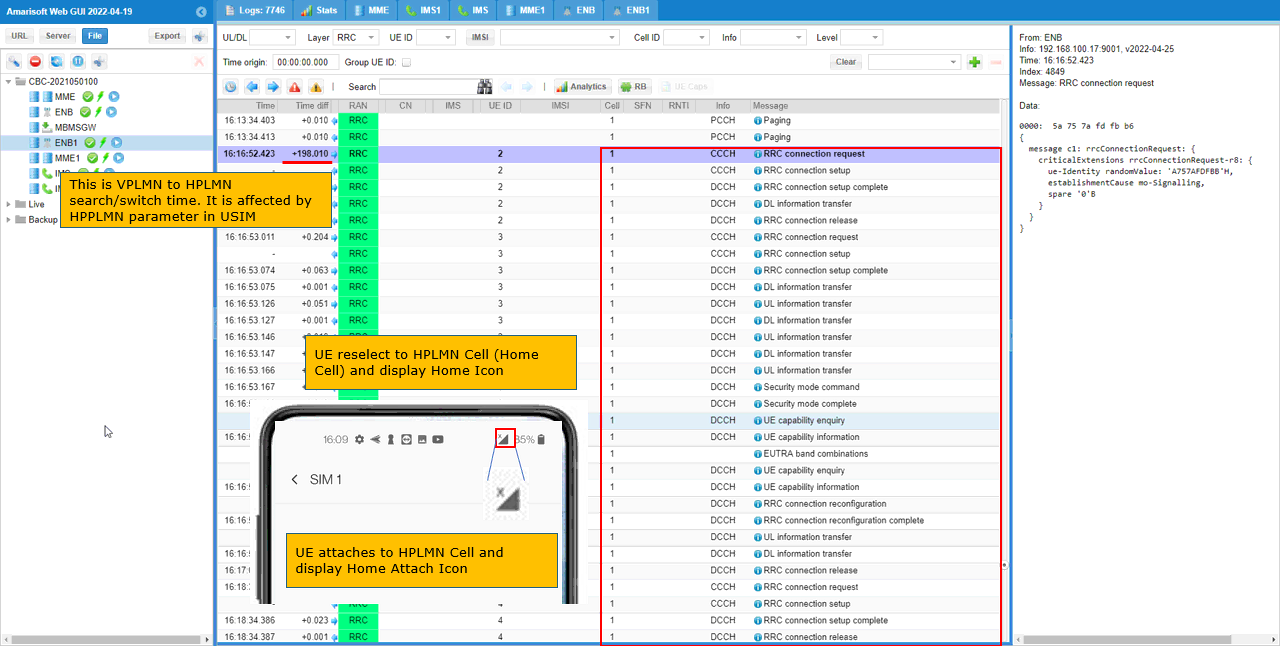
In this log, I would not look into any specific message. I will just take a look at a few blocks of messages to check to which cell the UE is connected.
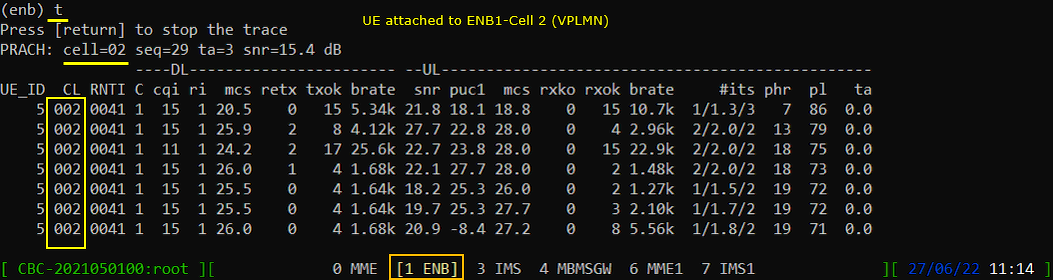
First, Confirm that UE is connected to the first cell (HPLMN Cell). You can identify the cell by checking the number in 'Cell' column.
Once the UE is roamed to VPLMN cell, you should see that the UE is now connected to Cell 2.
After roaming back to HPLMN cell, you should see that UE is attached to Cell 1.