NR Rrc Inactive
The purpose of this tutorial is to show you how to test RrcInactive status. In this tutorial, I assume that you are familiar with basic operations of callbox and I would not explain the very basic operational procedure. I will just explain about the important configurations and how you can confirm on those configuration from the log.
RrcInactive in NR is a mechanism to park the communication in a kind of dormant mode without releasing RRC. The advantage of putting the communication into this mode comparing to releasing RRC is that it can switch back to the normal communication mode much more quickly then the case of RrcRelease.
Overall procedure (statemachine) for switching back and forth between RRC Connected and RRC Inactive is as follows.
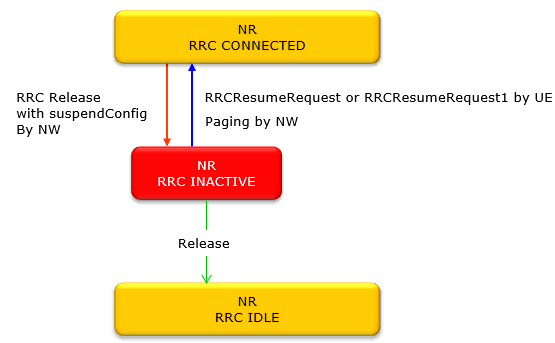
Image Source : Sharetechnote
Table of Contents
Introduction
RRC Inactive is a pivotal feature introduced in 5G New Radio (NR) systems, designed to enhance both user experience and network efficiency by introducing a new state in the Radio Resource Control (RRC) state machine. Unlike legacy LTE systems, where mobile devices transition between RRC Connected and RRC Idle states, 5G NR leverages the RRC Inactive state to allow User Equipment (UE) to remain in a semi-dormant mode, conserving signaling overhead and reducing latency for state transitions. Architecturally, this innovation addresses the need for ultra-fast resumption of data sessions while minimizing battery consumption and network resource utilization, especially in scenarios characterized by frequent but sporadic data exchanges such as IoT applications or instant messaging. The RRC Inactive state maintains essential UE context at both the gNodeB (next-generation NodeB) and the Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF), enabling rapid state transitions without the need for full connection establishment procedures. This mechanism is crucial in supporting 5G use cases that demand high mobility, low latency, and efficient network operation. Understanding and testing RRC Inactive status is therefore essential for engineers and network operators aiming to optimize 5G deployments, troubleshoot state transition behaviors, and ensure compliance with 3GPP standards. This tutorial provides an in-depth examination of the RRC Inactive state, focusing on the procedural aspects, configuration parameters, and log verification techniques necessary for effective testing in a controlled environment.
-
Context and Background
- RRC Inactive is a new state introduced in the 5G NR RRC state machine to bridge the gap between RRC Connected and RRC Idle.
- It is designed to optimize signaling efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and enable fast state transitions for UEs.
- The architecture relies on maintaining UE context at both the gNodeB and the core network (AMF), allowing session resumption without complete re-establishment procedures.
-
Relevance and Importance of This Tutorial
- Testing RRC Inactive status is critical for verifying network implementations and UE behavior in compliance with 5G standards.
- Proper understanding and configuration of RRC Inactive improves network efficiency, reduces latency, and enhances user experience.
- Operators and engineers benefit from reduced signaling load and improved battery life for connected devices.
-
What You Will Learn
- Key configuration parameters involved in enabling and testing RRC Inactive state on a callbox environment.
- Procedural steps for transitioning UEs between RRC Connected and RRC Inactive, and methods for confirming state transitions using logs.
- Best practices for interpreting log data to verify correct network and UE behavior during state transitions.
- Architectural insights into how RRC Inactive supports advanced 5G use cases and optimizes network resource management.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge
- Familiarity with basic callbox operations and test equipment procedures.
- Understanding of 5G NR architecture, including gNodeB, AMF, and RRC protocol fundamentals.
- Ability to interpret network logs and basic troubleshooting skills in a radio access network environment.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial demonstrates the test procedure for verifying the NR RRC Inactive feature using a callbox and a UE (User Equipment). The process involves configuring both the gNB and MME, connecting the UE, and observing RRC state transitions, particularly focusing on the RRC Inactive and Resume mechanisms.
-
Test Setup:
- Use the provided SIM card unless configuration change is required.
- Refer to the Configuration Guide for any changes to the setup.
-
Key Configuration Parameters:
- Configure rrc_inactive and its associated parameters in the gNB configuration file, including:
- use_full_resume_id
- rna_cell_list (with plmn and cell_id_list)
- rna_ranac_list (with tac and ranac_list)
- ran_paging_cycle
- t380_mins
- inactivity_timer
- release_timer_mins
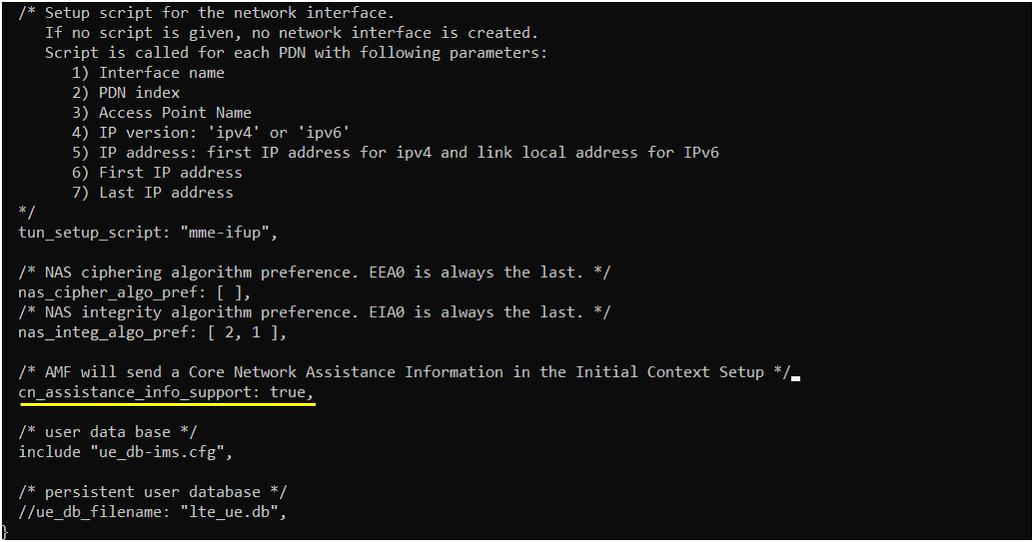
- In the MME configuration, enable cn_assistance_info_support to support RRC Inactive.
- Configure rrc_inactive and its associated parameters in the gNB configuration file, including:
-
Configuration Steps:
- Start from gnb-sa.cfg and modify it to create gnb-sa-rrc-inactive.cfg with the necessary RRC Inactive settings.
- Edit mme-ims.cfg to produce mme-ims-cn-assistance.cfg and set cn_assistance_info_support to true.
- Add the rrc_inactive object in the gNB configuration, ensuring cell_id_list is correctly set (28-bit binary from concatenated gNB and Cell IDs).
-
Test Execution Procedure:
- Verify cell configuration using cell phy and cell commands, and ensure compatibility with the UE.
- Power on the UE and ensure it attaches to the cell.
- Confirm the UE is registered to the MME and has at least one IP address assigned.
- Wait for the UE to enter the RRC Inactive state when there is no traffic; this is indicated by "[inactive]" in the trace log.
- Trigger RRC Resume by initiating user data (e.g., ping command) from the callbox. The first ping reply may be delayed due to the Resume process, which includes RAN Paging and other procedures.
- Observe the RRC Resume process, where the UE transitions back to RRC Connected upon user data activity.
-
Log Analysis:
- Check the UE capability information to ensure RRC Inactive support is advertised.
- If no higher layer data traffic is present for the configured duration, the network triggers the switch to RRC Inactive (RrcRelease with suspendConfig).
- While in RRC Inactive, triggering data traffic (e.g., ping) initiates the Resume process. Proper ue-Identity must be used, matching the suspendConfig.
- Upon paging, the UE sends a Resume Request (with resumeIdentity matching suspendConfig).
- The gNB responds with an RRC Resume message, containing all necessary configuration to reestablish the connection.
- If the UE receives and applies the RRC Resume message, it sends an RRC Resume Complete message.
- Repeated inactivity will again transition the UE to RRC Inactive; subsequent user activity will repeat the resume process.
Key Points:
- Correct configuration of both the gNB and MME is essential for RRC Inactive functionality.
- UE capability for RRC Inactive must be verified before running the test.
- The test validates the state transitions between RRC Connected, RRC Inactive, and back to Connected, triggered by user data activity and network inactivity timers.
- Log analysis focuses on confirming state transitions and matching identities used throughout the suspend and resume procedures.
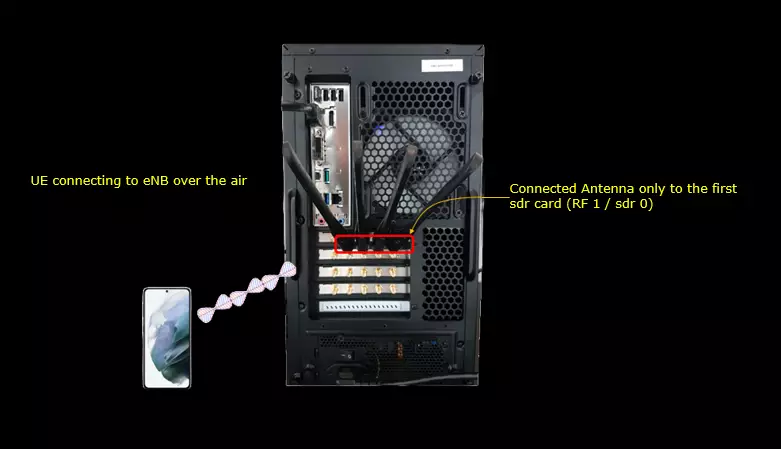
Test Setup
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below. (NOTE: Since TDD UL/DL configuration gets configured into SIB1 message and you may not need to get UE connected to the callbox if you just want to check the SIB1 as in this tutorial)
- SIM Card used in this tutorial is the one delivered with the system as it is.
- If you want to change the configuration, The tutorial Configuration Guide would help

Key Configuration Parameters
Followings are important configuration parameters for this tutorial. You may click on the items for the descriptions from Amarisoft documents.
- rrc_inactive : In this link, you will get the descriptions for all items listed below.
- use_full_resume_id
- rna_cell_list
- plmn
- cell_id_list
- rna_ranac_list
- tac
- ranac_list
- ran_paging_cycle
- t380_mins
- inactivity_timer
- release_timer_mins
Configuration
I used the configuration gnb-sa-rrc-inactive.cfg which is copied from gnb-sa.cfg and modified for this tutorial.
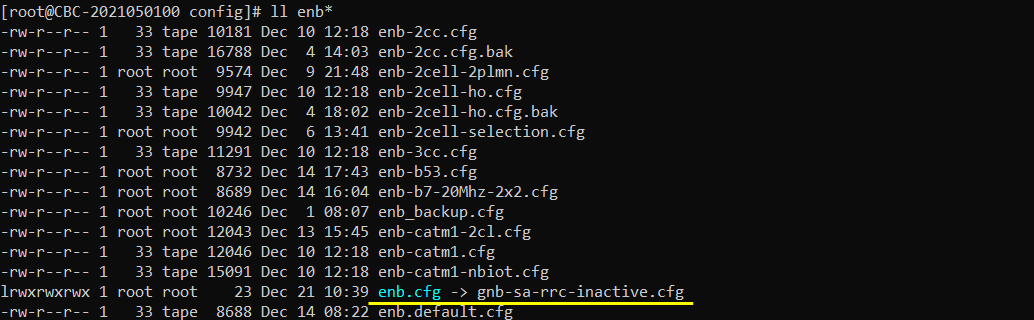
I have used mme-ims-cn-assistance.cfg which is copied from mme-ims.cfg and modified. RRC Inactive involves core network feature as well as gNB configuration, so I created a special configuration file for mme configuration as well.
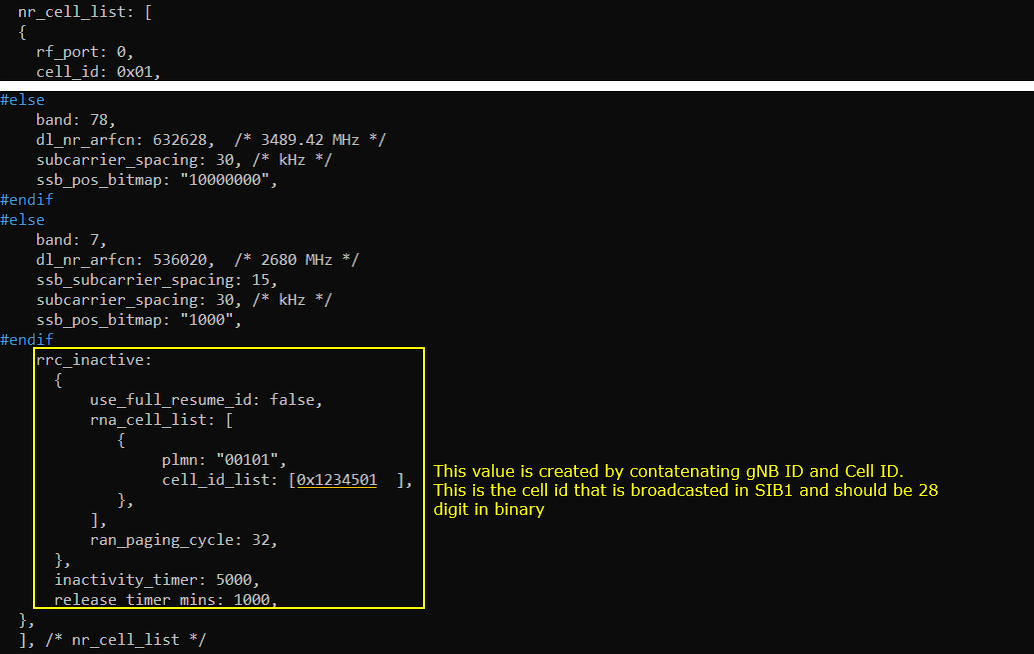
In gnb-sa-rrc-inactive.cfg, add rrc_inactive object as shown below. Configuration for RRC inactive for gNB is set by rrc_inactive parameter. rna_cell_list, inactivity_timer and release_timer_mins are important parameters in this configuration. cell_id_list within rna_cell_list should be 28 digit in binary and you can create the value by concatenating gNB ID and Cell ID.
In mme-ims-cn-assistance.cfg , add the parameter cn_assistance_info_support as show below. It is important to set cn_assistance_info_support to true in order to enable RRCinactive functionality.
Perform the Test
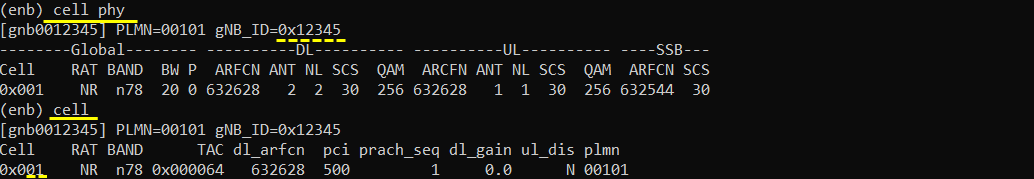
Check basic cell configuration with 'cell phy' and cell command, and make it sure that it is configured as per your UE capability. gNB_ID and Cell ID with dotted line is used to make up the number in cell_id_list[] in the configuration file shown before.
Power on UE and Get the UE attached to cell
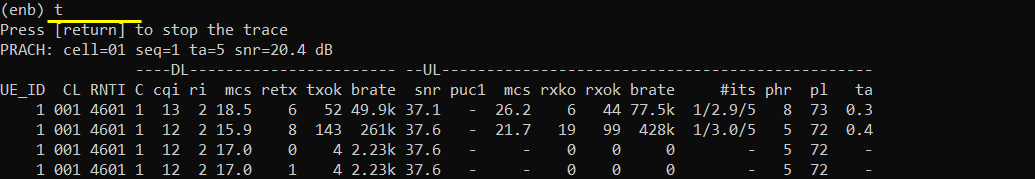
Make it sure that UE is registered to mme. Make it sure that at least one IP is assigned to the UE.

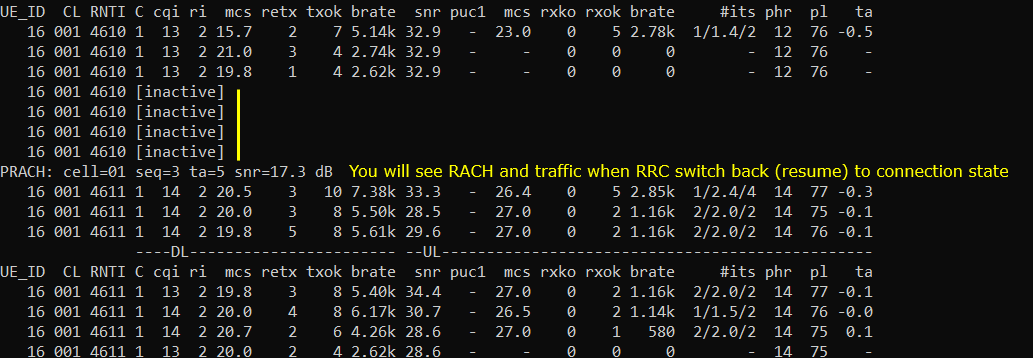
When there is no traffic, RRC goes into [inactive] as shown below. When the call status goes into RRCinactive, [inactive] is printed in the trace log.
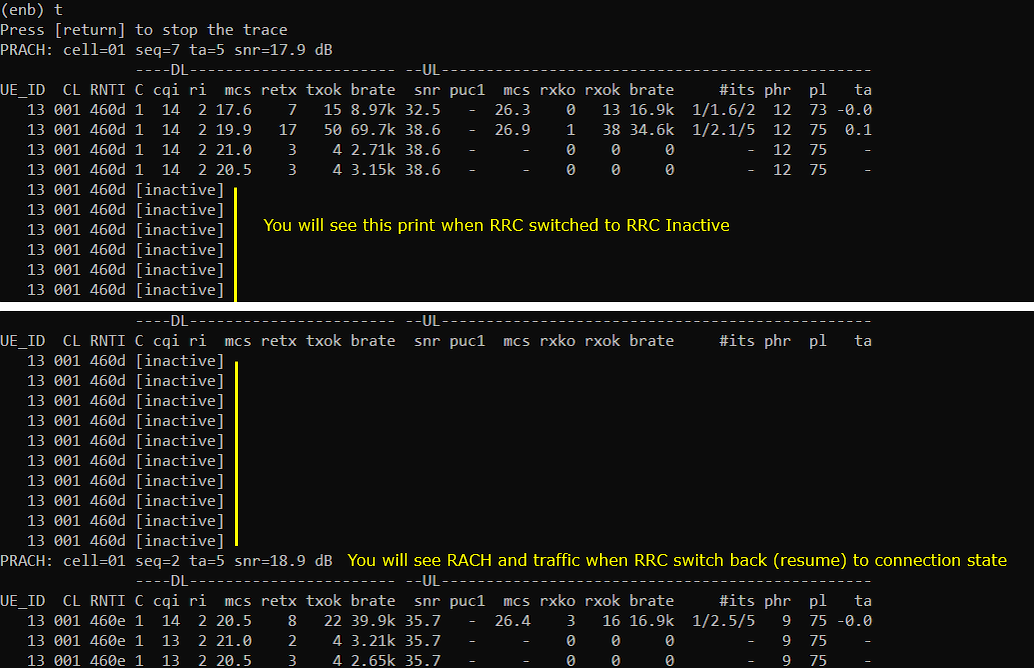
When the RRC is in Inactive state, you can let Callbox to trigger Resume by sending ping as below. Usually the 'time' value for the first ping reply would be very long since it has to wait until the Resume process gets completed. During the resume process, RAN Paging and a few additional procedures should be completed and these steps are the main factors of the delay.
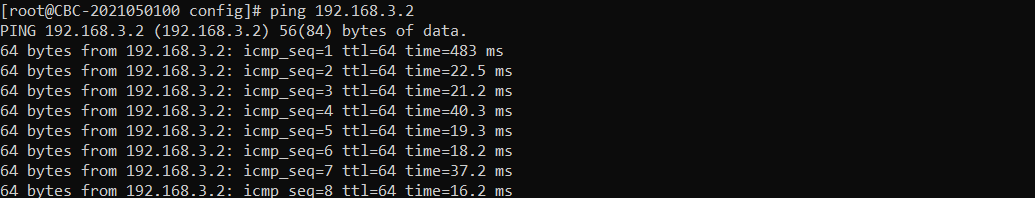
Rrc resumes as shown below as the user traffic (ping data in this case). When higher layer triggers RRC Resume, you would see that RACH process is triggered in trace log.
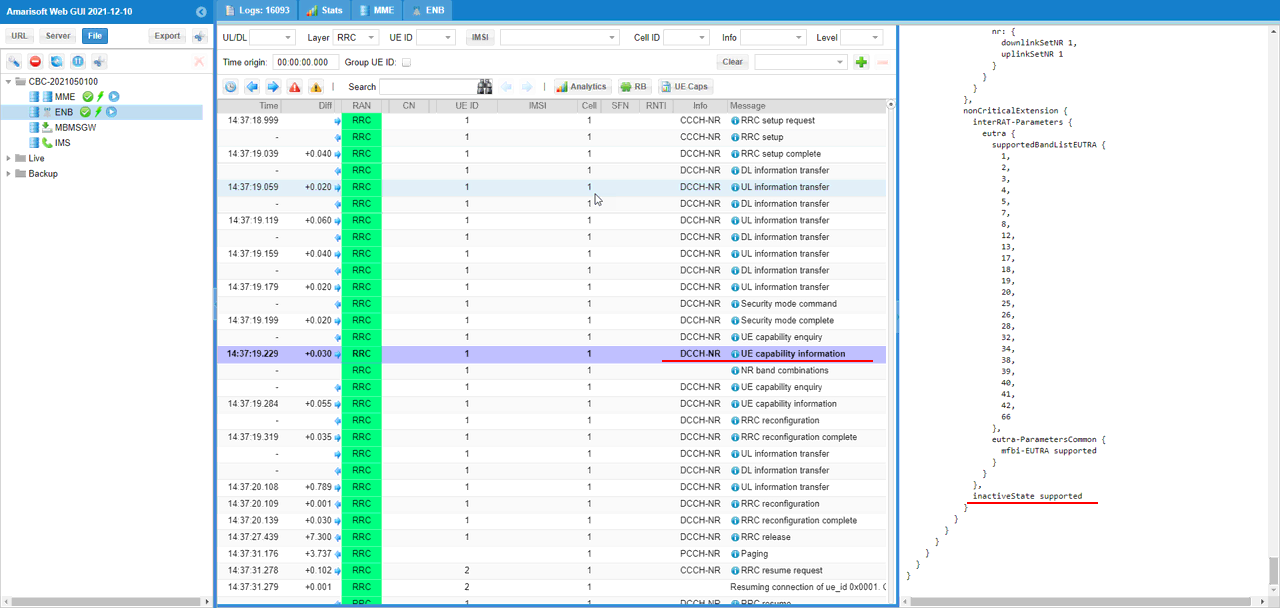
Log Analysis
First to check if UE support Rrc Inactive states from UE capability information message. If UE does not notify inactiveState, gNB and MME would not trigger RRC inactive process.
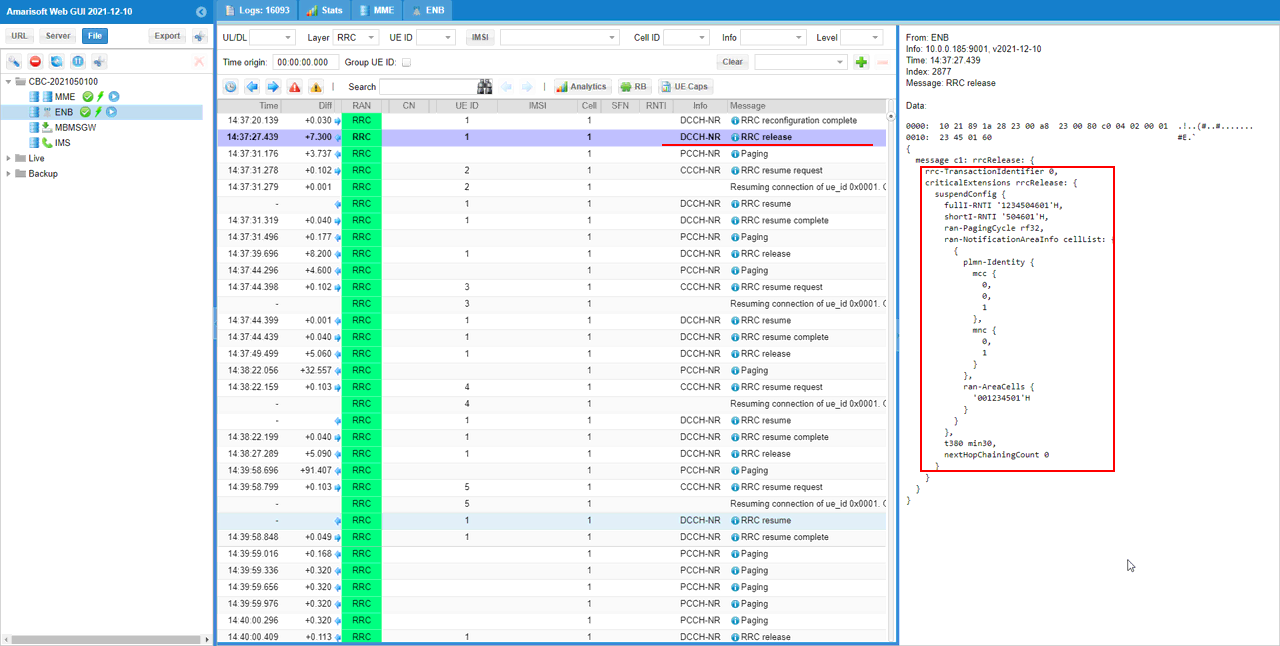
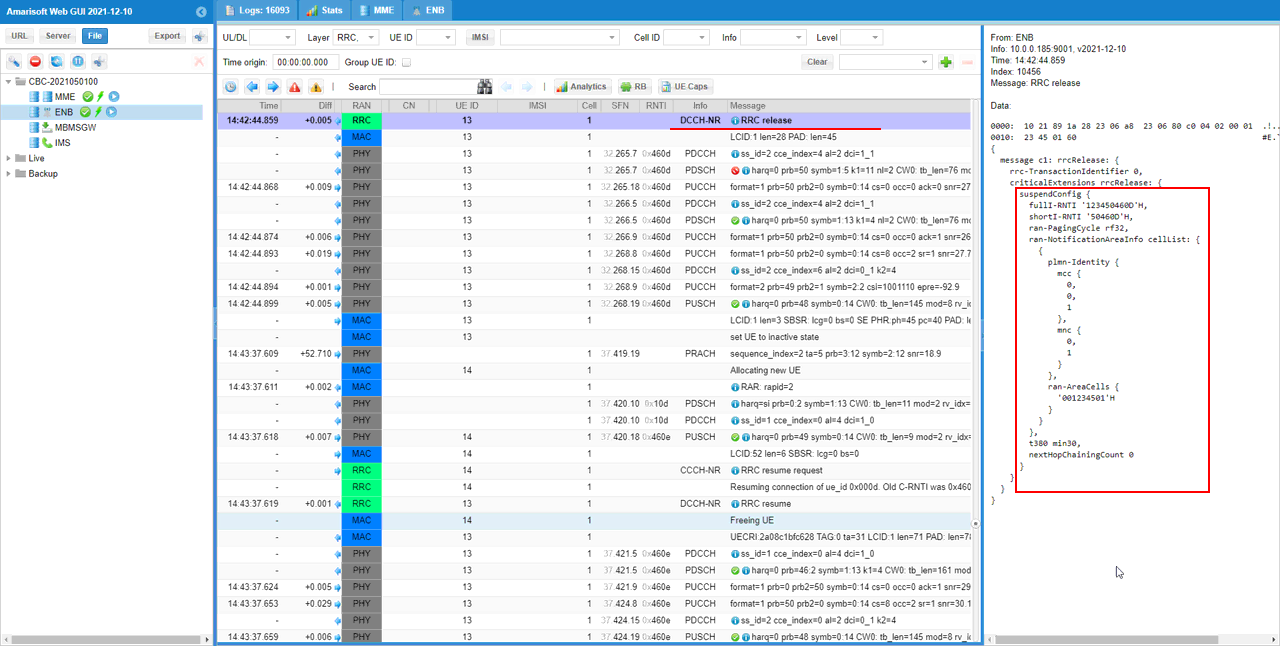
If there is no higher layer data traffic for a certain duration set in the configuration file. Network would trigger switching to RRC INACTIVE as shown below. RRC message to switch to RRCinactive is rrcRelease message with suspendConfig IE. The suspendConfig IE provide the required information to resume the connection when needed.
If you trigger data traffic (e.g, ping) while in Rrc Inactive, the callbox(gNB) would send ping to trigger Resume process. The ping should carry the ue-Identity that is same as the one configured in suspendConfig of rrcRelease message.
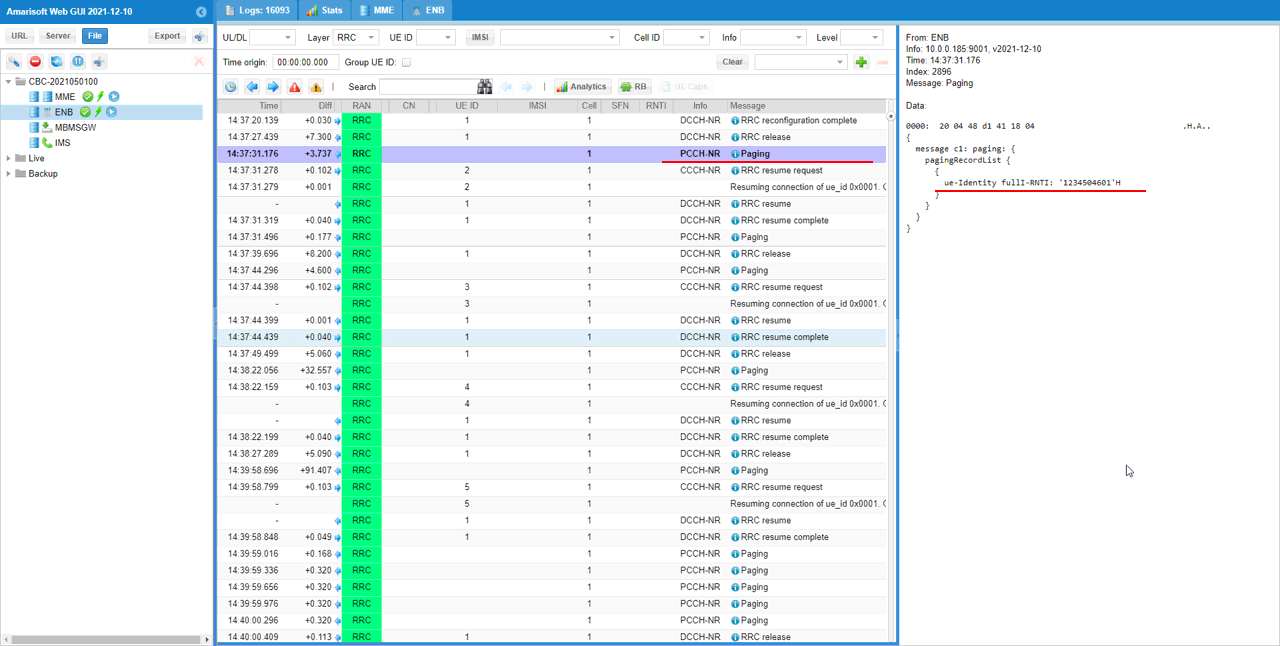
In response to the paging, UE will send resume request. In rrcResumeRequest message, you see resumeIdentity IE which is associated with RNTI that is configured in suspendConfig.
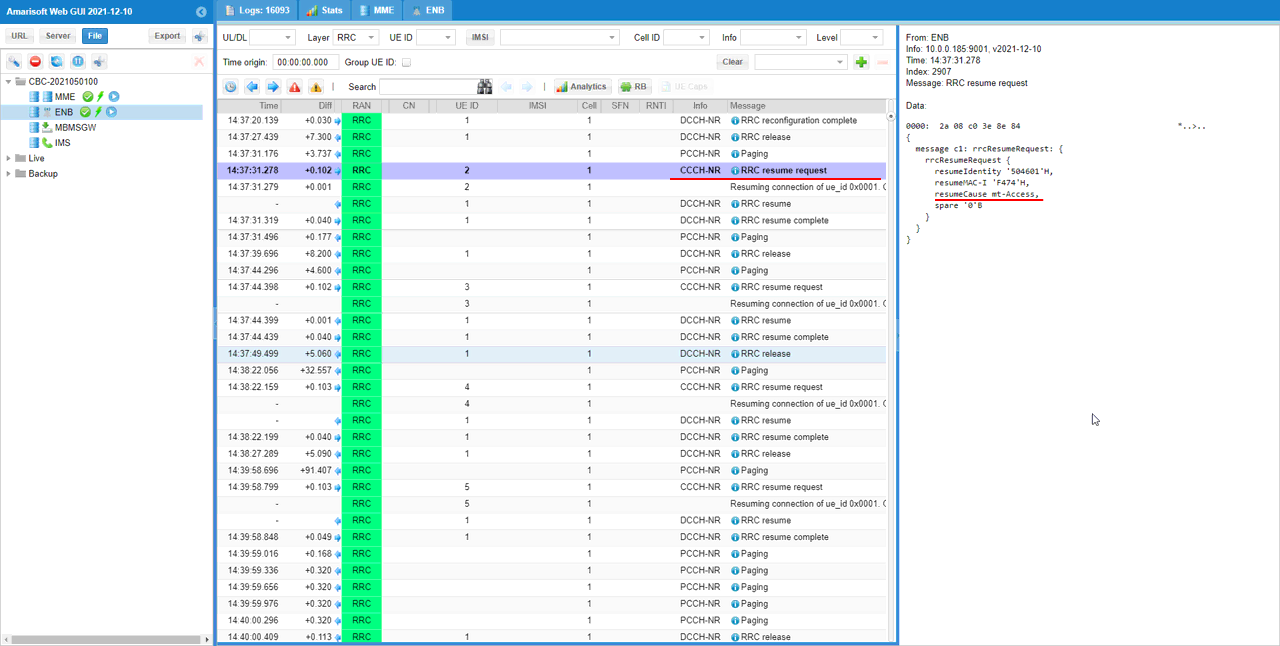
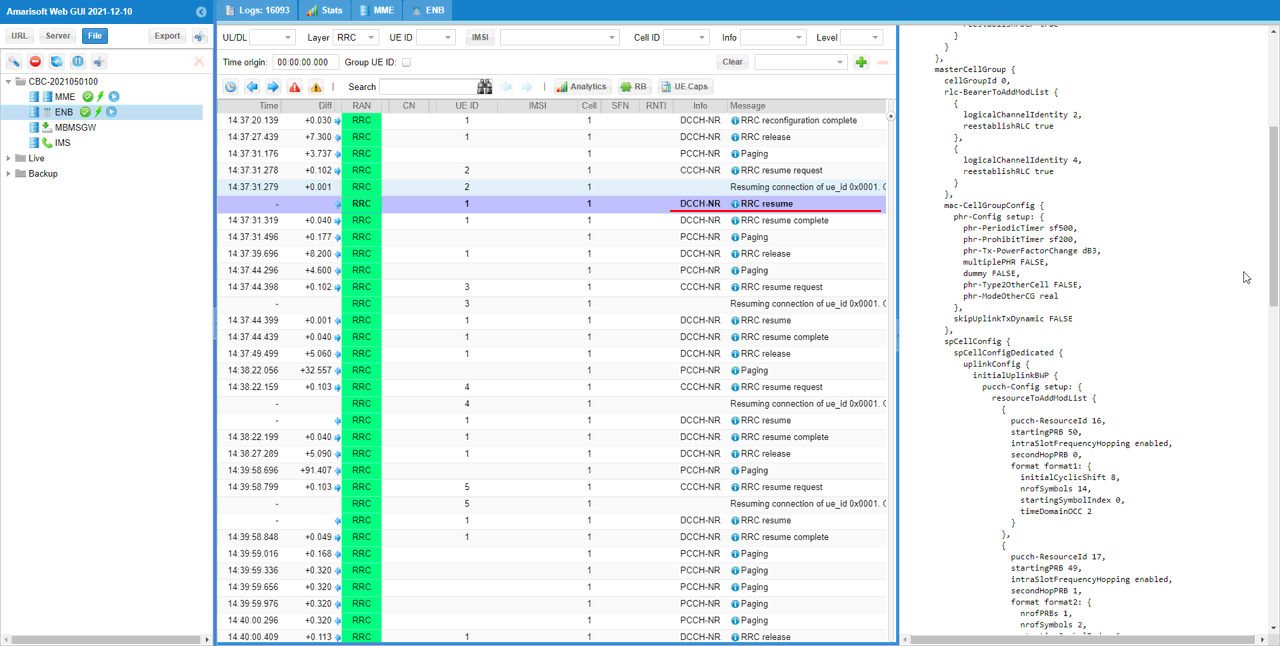
Callbox send Rrc Resume with the necessary Rrc Configuration to switch back to Rrc Connected state. If UE recieves the paging, it send Rrc Resume Request. If gNB recieves rrcResumeRequest from the UE, it send RRC resume message. In terms of functionality and the information it carries, RRC resume message is similar to RRC setup message. It should carry all the radio protocol parameter to reestablish the call connection.
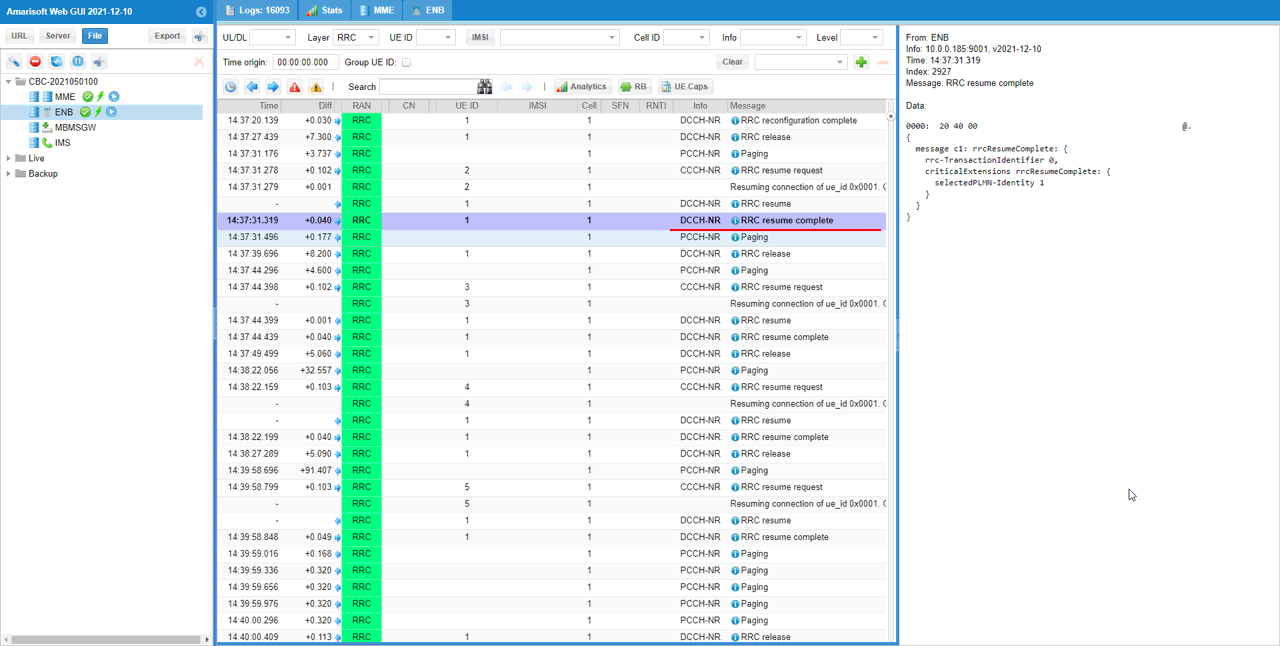
If UE properly recieves RRC resume message and applied all the parameters properly, UE send Rrc Resume Complete
If there is no data traffic at higher layer for a certain duration. Network would trigger switching to RRC INACTIVE as shown below
If UE trigger data traffic (e.g, browsing) while in Rrc Inactive, the UE would send ResumeRequest to trigger Resume process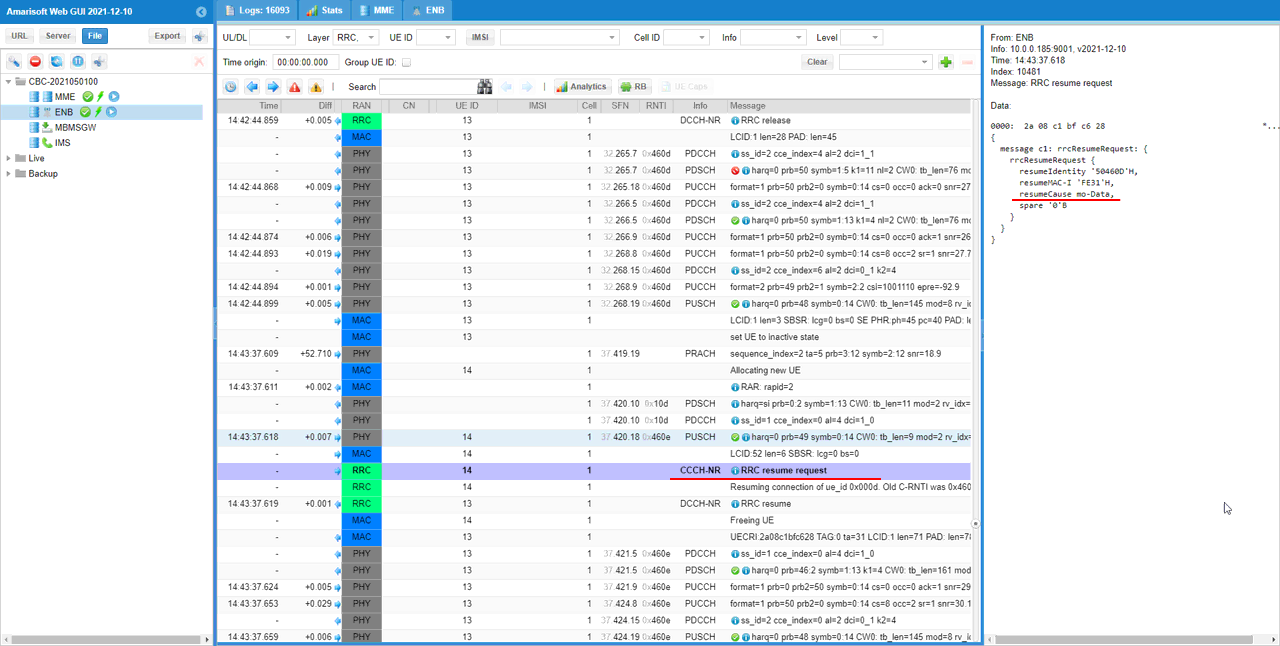
RRC / NAS Signaling
RrcRelease (SA)
: This is the RrcRelease message sent by gNB to switch to Rrc Inactive Status. (
{
message c1: rrcRelease: {
rrc-TransactionIdentifier 0,
criticalExtensions rrcRelease: {
suspendConfig {
fullI-RNTI '1234504601'H,
shortI-RNTI '504601'H,
ran-PagingCycle rf32,
ran-NotificationAreaInfo cellList: {
{
plmn-Identity {
mcc {
0,
0,
1
},
mnc {
0,
1
}
},
ran-AreaCells {
'001234501'H
}
}
},
t380 min30,
nextHopChainingCount 0
}
}
}
}
Paging (SA)
: This is the Paging message sent by gNB to trigger UE to wake up from the inactive status. (
{
message c1: paging: {
pagingRecordList {
{
ue-Identity fullI-RNTI: '1234504601'H
}
}
}
}
RrcResumeRequest (SA)
: This is the RrcResumeRequest message sent by UE to trigger UE to wake up from the inactive status. (
{
message c1: rrcResumeRequest: {
rrcResumeRequest {
resumeIdentity '504601'H,
resumeMAC-I 'F474'H,
resumeCause mt-Access,
spare '0'B
}
}
}
RrcResume (SA)
: This is the RrcResume message sent by gNB to setup RRC. (
{
message c1: rrcResume: {
rrc-TransactionIdentifier 0,
criticalExtensions rrcResume: {
radioBearerConfig {
..
},
masterCellGroup {
cellGroupId 0,
rlc-BearerToAddModList {
..
},
mac-CellGroupConfig {
..
},
spCellConfig {
spCellConfigDedicated {
uplinkConfig {
initialUplinkBWP {
pucch-Config setup: {
..
},
resourceToReleaseList {
..
},
schedulingRequestResourceToAddModList {
..
}
},
srs-Config setup: {
...
}
}
},
csi-MeasConfig setup: {
...
},
tag-Id 0
}
}
}
}
}
}
RrcResumeComplete (SA)
: This is the RrcResumeComplete message sent by UE. (
{
message c1: rrcResumeComplete: {
rrc-TransactionIdentifier 0,
criticalExtensions rrcResumeComplete: {
selectedPLMN-Identity 1
}
}
}