NR NSA Split Bearer
The purpose of this tutorial is to show you how to test Uplink Splitbearer functionality in NSA. In this tutorial, it is assumed that you are faimiliar with basic operations of Amari Callbox operation. So in this tutorial, I will explain only about the configuration and analyzing the test result in the WebGUI log.
In NSA, user data goes through both LTE and NR. That is, a stream of user data may split between LTE chain and NR chain. This way of splitting user data into two different radio bearer (i.e, LTE bearer and NR bearer) is called Split bearer. In theory, we can think of the split bearer for both downlink and uplink, but in terms of 3GPP only uplink spit bearer is specified and downlink split is up to the implementation of network equipment manufacturer. In terms of Uplink Split Bearer, there are roughly three options as follows.
Option 1 : 100% going through LTE
Option 2 : 100% going through NR
Option 3 : data going through both NR and LTE (the ratio of split is configurable)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Uplink Split Bearer functionality in Non-Standalone (NSA) 5G networks represents a key advancement in the evolution of mobile communications, enabling simultaneous utilization of both LTE (Long-Term Evolution) and NR (New Radio, 5G) networks for user data transmission. This architecture, commonly referred to as Dual Connectivity (DC), allows a user device to maintain connections with both LTE and NR radio access technologies, facilitating enhanced throughput, reliability, and seamless mobility. In NSA deployments, the master eNB (LTE anchor) and secondary gNB (5G node) collaborate through the X2 interface to coordinate data paths and control signaling. The split bearer mechanism specifically addresses the uplink direction by enabling data packets originated by the user equipment (UE) to be distributed dynamically or statically between LTE and NR bearers, optimizing radio resource utilization and improving overall network performance. 3GPP specifications define uplink split bearer operation, while downlink splitting is left to vendor implementation, making uplink split bearer a standardized and critical feature for real-world NSA scenarios. Understanding and validating this functionality is essential for network engineers and testers, as it directly impacts end-user experience, network efficiency, and the ability to meet diverse service requirements in the 5G era. This tutorial focuses on guiding users through the configuration and evaluation of uplink split bearer behavior using the Amari Callbox platform, providing practical insights into test setup, WebGUI-based analysis, and interpretation of results within the NSA architecture.
-
Context and Background
- Non-Standalone (NSA) 5G leverages existing LTE infrastructure as an anchor while introducing 5G NR to achieve higher data rates and reduced latency.
- Dual Connectivity (DC) enables a single UE to connect to both LTE and NR, managed by distinct base stations (eNB for LTE, gNB for NR).
- Split Bearer Concept allows user-plane data to be split at the PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol) layer, offering multiple routing options for uplink traffic.
- The Amari Callbox is a comprehensive testing platform widely used for simulating and validating 4G/5G network scenarios, including NSA configurations.
-
Relevance and Importance
- Uplink split bearer functionality is critical for maximizing spectral efficiency and ensuring seamless service continuity during the transition from LTE to 5G NR.
- Testing and analyzing split bearer behavior is essential for verifying network compliance with 3GPP standards and for troubleshooting interoperability issues.
- The tutorial addresses practical aspects of configuration and log analysis, empowering network professionals to validate and optimize real-world NSA deployments.
-
Learning Outcomes
- Understand the architectural principles behind uplink split bearer in NSA networks.
- Gain hands-on experience configuring split bearer scenarios using the Amari Callbox WebGUI.
- Learn to interpret test results and logs to assess split bearer performance and behavior.
- Develop troubleshooting skills relevant to multi-radio, multi-bearer 5G environments.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge and Skills
- Familiarity with basic Amari Callbox operations and user interface navigation.
- Understanding of LTE and 5G NR concepts, including radio bearers and protocol stack fundamentals.
- General knowledge of 3GPP NSA architecture and dual connectivity principles.
- Basic skills in interpreting network logs and analyzing test output.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial guides through the procedures for testing split bearer configurations in an NR NSA (Non-Standalone) environment using Amarisoft Callbox, focusing on the configuration and verification of uplink (UL) traffic splitting between LTE and NR. The summary below outlines the test methodologies, key configuration steps, and verification procedures while maintaining the original content's structure and formatting.
-
Test Setup
- Use the SIM card provided with the system, unless reconfiguration is needed (see Configuration Guide).
- Internet access is configured to allow use of public services (e.g., Speedtest) for generating IP traffic.
- Several options are provided for connecting the CallBox to the internet; Case 4 is used here (direct wired, WiFi, or via another PC).
- For WiFi connectivity on a Linux (CLI) system, nmcli commands are provided to manage WiFi interfaces:
- # nmcli dev status
- # nmcli radio wifi
- # nmcli device wifi rescan
- # nmcli dev wifi list
- # nmcli dev wifi connect network-ssid password "network-password"
-
Key Configuration Parameters
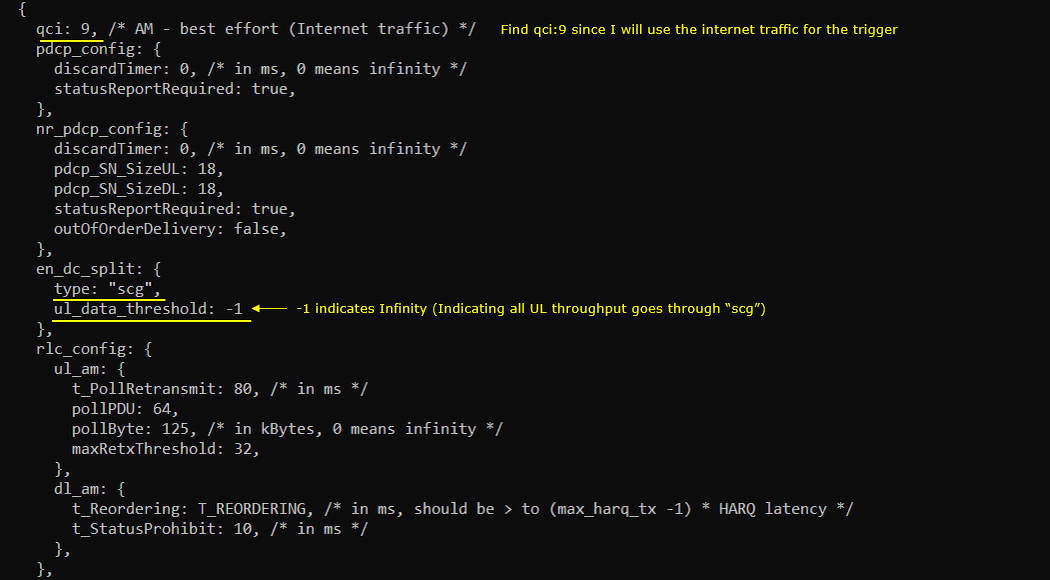
- Critical parameter: en_dc_split in drb-splitbearer.cfg
- Elements: type, ul_data_threshold, secondary_path_dl_ratio
- Critical parameter: en_dc_split in drb-splitbearer.cfg
-
Configuration Steps
- Use gnb-nsa-splitbearer.cfg (modified from gnb-nsa.cfg).
- drb-splitbearer.cfg is set in the configuration to control split bearer behavior.
- Modify drb_config parameter to use drb-splitbearer.cfg instead of the default.
- Set en_dc_split in drb-splitbearer.cfg:
- Configure type and ul_data_threshold for each test scenario.
- Adapt configuration for device-specific requirements (e.g., TDD/FDD support).
-
Pre-Test Checks
- Ensure the network interface with internet connectivity and tun0,1,2,3 interfaces are up.
- Check the routing table for proper routing through tun interfaces.
- Verify internet connectivity from CallBox by pinging an external IP (e.g., 8.8.8.8) and a URL (to check DNS resolution).
- [Optional] Use nslookup or similar to resolve URLs and verify with a direct IP ping.
-
General Test Procedure
- Disable UE WiFi to ensure traffic is routed through cellular.
- Attach the UE and confirm successful connection to Callbox.
- Verify UE receives an IP address.
- Ping the UE from Callbox to confirm network reachability.
- Test internet browsing from UE.
- Generate high data rate traffic using an online speed test site (ensure both uplink and downlink are tested).
-
Test 1: Split Ratio Decided by UE Side Decision
- Objective: Demonstrate UL traffic split between LTE and NR based on UE's decision (typically 50-50).
- Configuration:
- Set split type to "scg".
- Set ul_data_threshold to 0 (b0), enabling UE-side split decision.
- Verification:
- Confirm configuration is reflected in the signaling messages (pdcp-Config).
- Observe equal UL throughput on both LTE and NR connections, indicating a 50-50 split.
- Check both downlink and uplink traffic are present on LTE and NR.
-
Test 2: All UL Traffic Goes Through NR (scg)
- Objective: Demonstrate all UL traffic is routed exclusively via NR (no split).
- Configuration:
- Set split type to "scg".
- Set ul_data_threshold to -1 (infinity), disabling splitting and forcing all UL through NR.
- Verification:
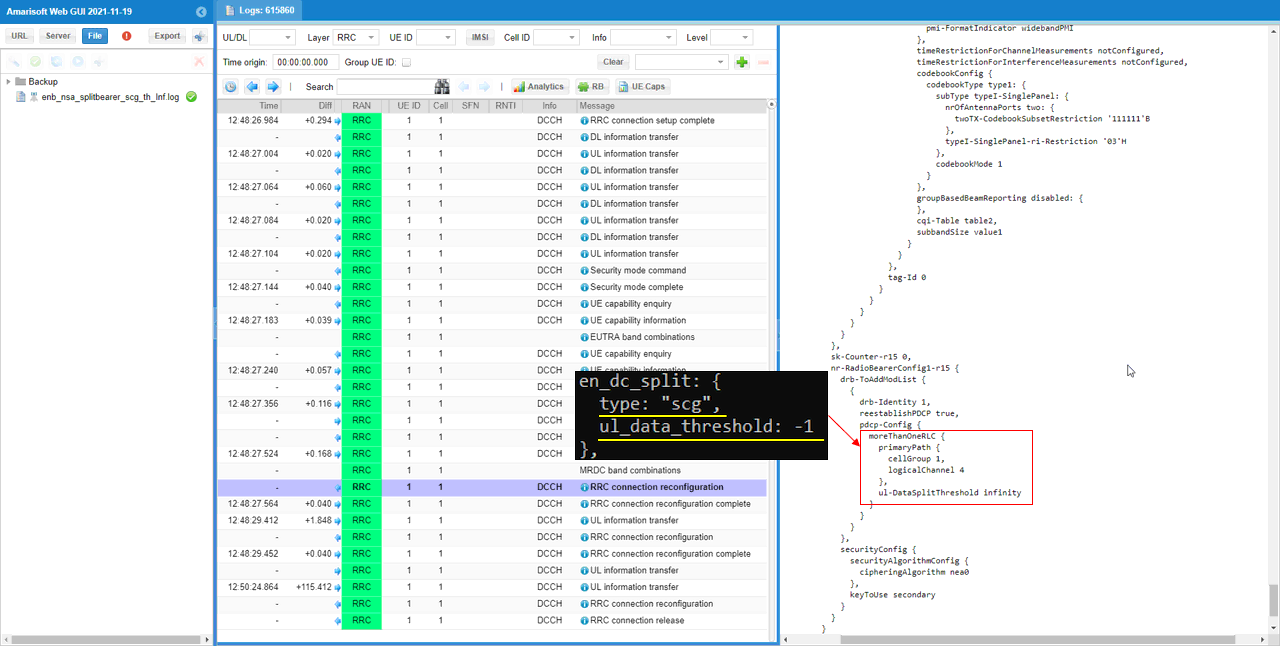
- Confirm configuration in signaling messages (cellGroup 1 and ul-DataSplitThreshold infinity).
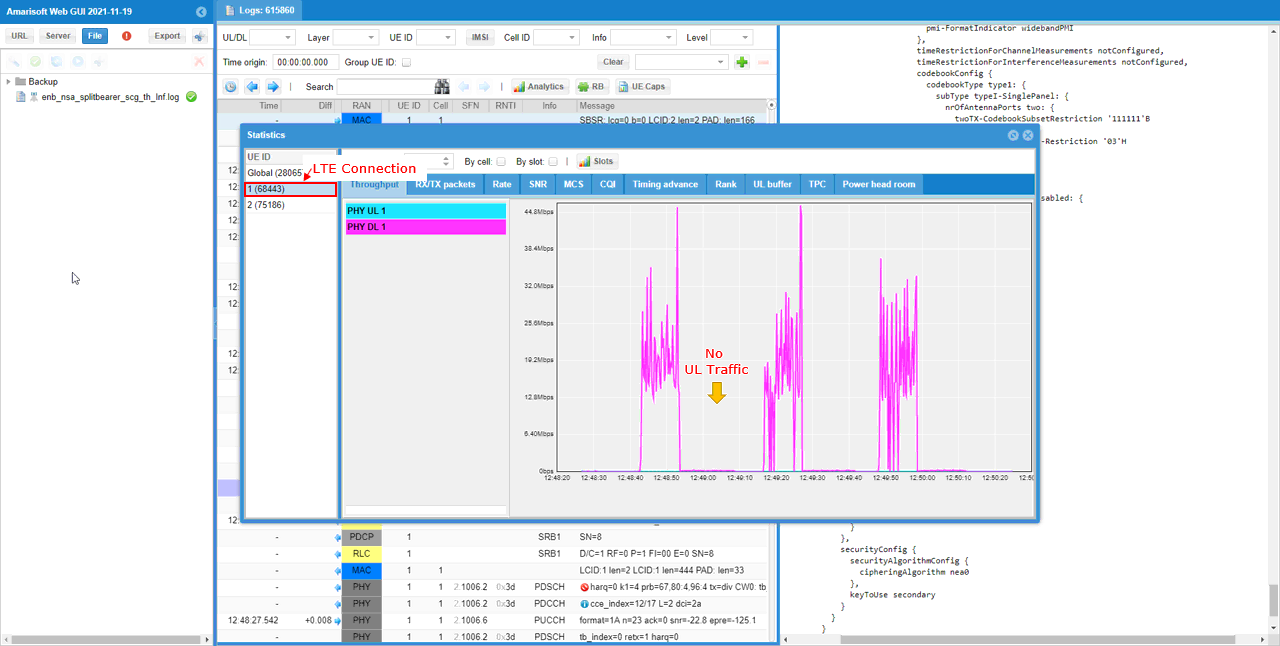
- Observe downlink traffic on LTE, but no uplink traffic.
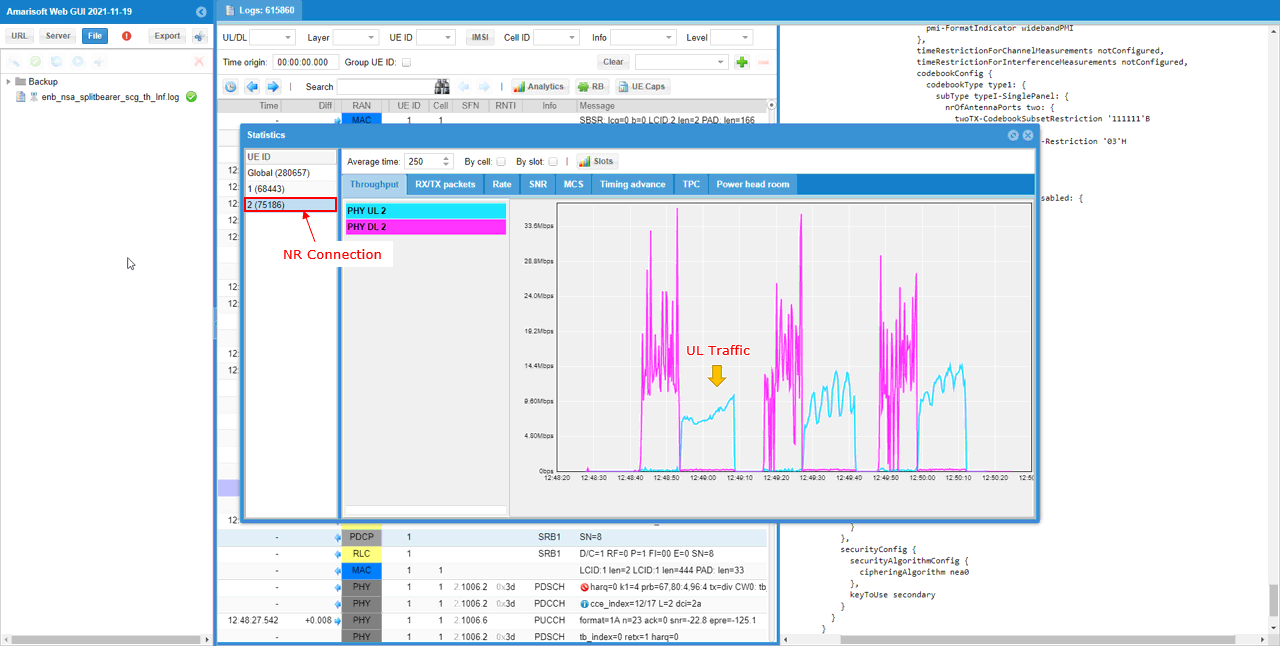
- See both uplink and downlink on NR, with 100% of UL traffic routed via NR.
This tutorial emphasizes configuration of split bearer parameters, connectivity verification, and observation of traffic distribution to validate split bearer and uplink routing behavior in an NR NSA environment. The procedures outlined support both flexible and exclusive routing of uplink data, with methodologies suitable for varied user equipment and test environments.
Test Setup
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below. (
- SIM Card used in this tutorial is the one delivered with the system as it is.
- If you want to change the configuration, The tutorial Configuration Guide would help

There are several many ways to provide internet access to your CallBox. Followings are some of them I can think of. In this tutorial, I used the Case 4.
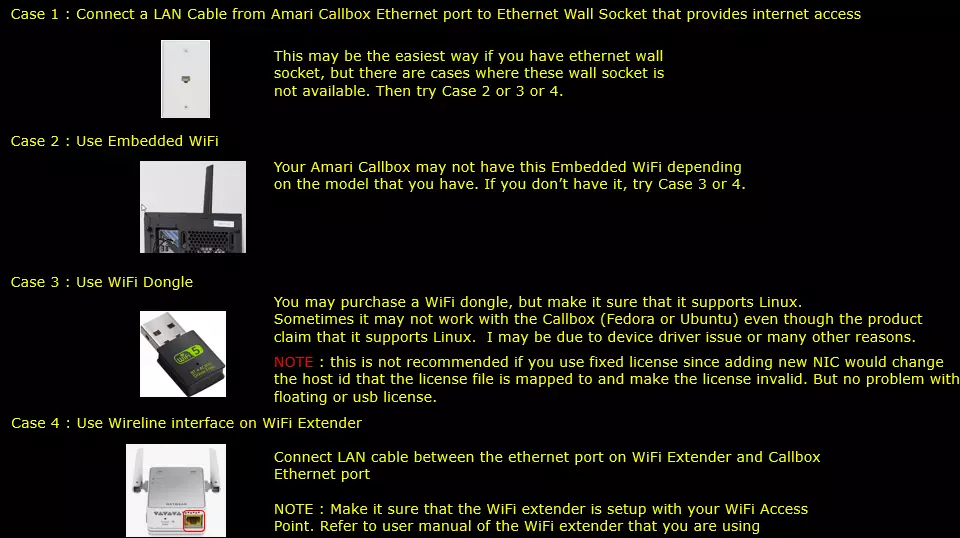
If you decided to use Case 2 and Case 3, following tips would be helpful.
Since Amari Callbox is running command line mode of Linux (Fedora or Ubuntu) NOT on GUI , it is not straightforward to enable / connect WiFi.
Followings are some of the command line command you would need to get WiFi connectivity. You may search these commands on internet for the detailed usage.
# nmcli dev status
# nmcli radio wifi
# nmcli device wifi rescan
# nmcli dev wifi list
# nmcli dev wifi connect network-ssid password "network-password"
Key Configuration Parameters
Followings are important configuration parameters for this tutorial. You may click on the items for the descriptions from Amarisoft documents.
- en_dc_split : In this link, you will get the descriptions for all items listed below.
- type
- ul_data_threshold
- secondary_path_dl_ratio
Configuration
I have used gnb-nsa-splitbearer.cfg which is copied and modified from gnb-nsa.cfg.
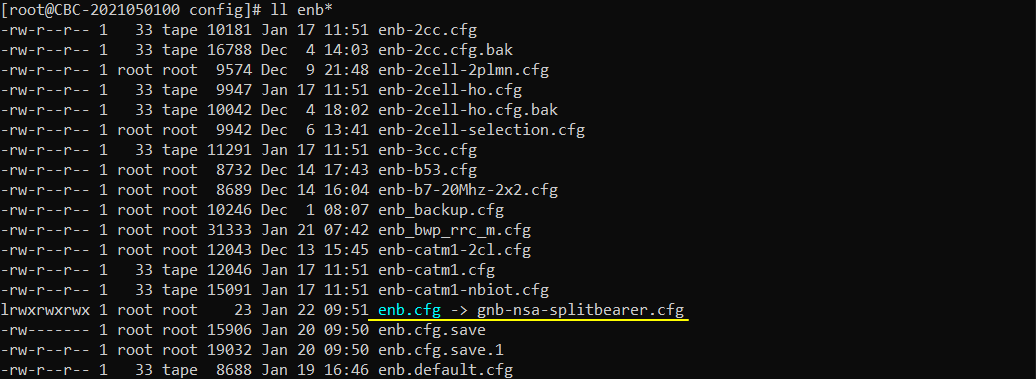
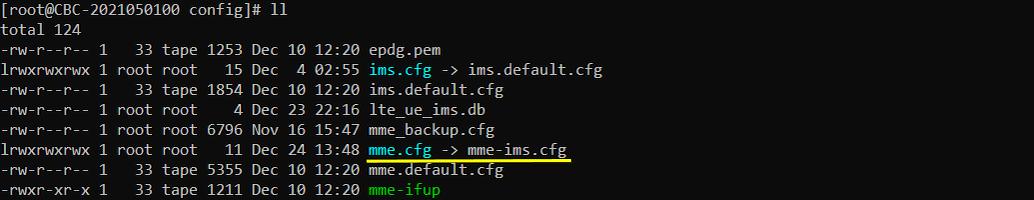
I am using the default mme, ims config as shown below.
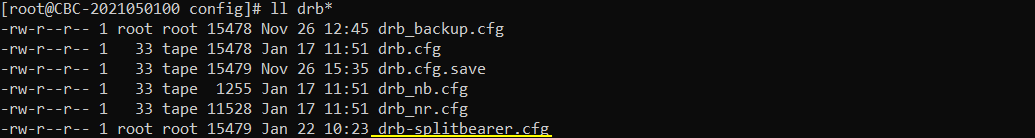
I used drb-splitbearer.cfg which is copied from drb.cfg
In gnb-nsa-splitbearer.cfg, I made a modification as follows (this is because the commercial UE that I have support TDD only. You may use whatever configuration that your UE support)
I changed the drb_config parameter as below so that drb-splitbearer.cfg is used instead of drb.cfg

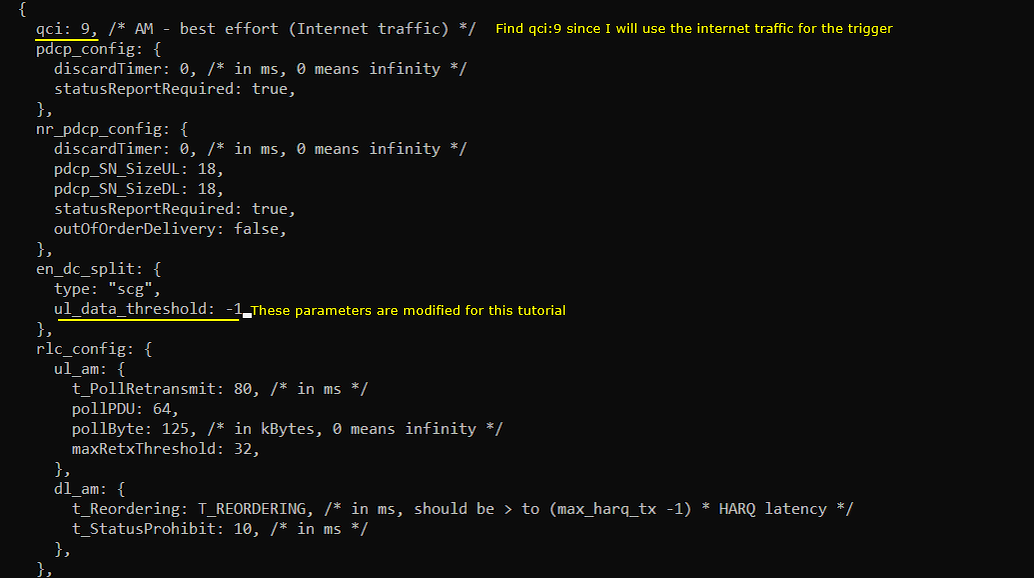
The major configuration parameter for this tutorial is en_dc_split specified in drb-splitbearer.cfg. The property of the split is configured by the parameter end_dc_split. The en_dc_split has two elements type and ul_data_threshold. In this tutorial, these two configurations modified for each different test.
Check Up before trying UE connection
Before you trying internet connection with UE, you need to check several basic things shown in this section and make it sure everything works as shown here, otherwise Internet connection from UE may not work.
Make it sure that the network interface with internet connectivity is up and tun0,1,2,3 are up.
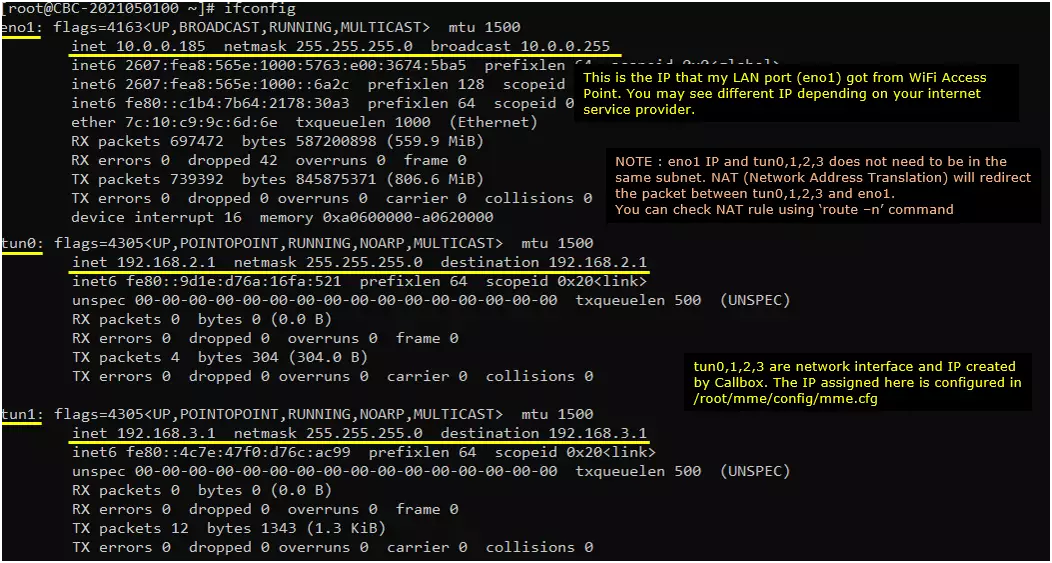
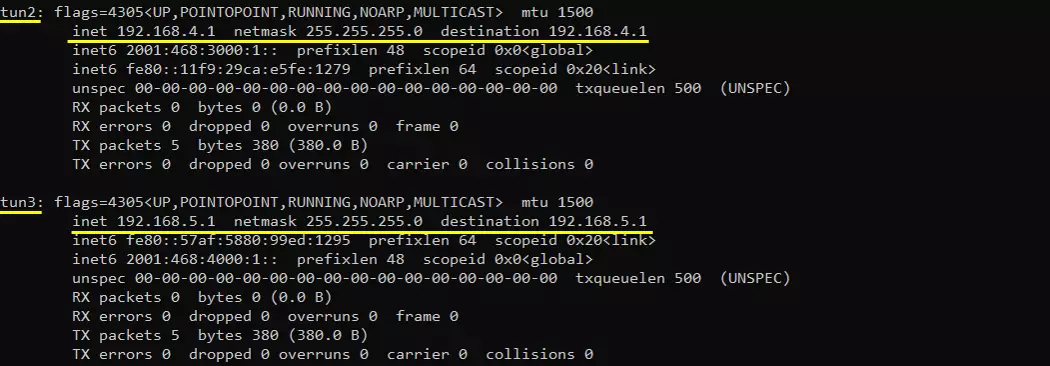
Check up the routing table on CallBox PC. It would usually be as follows. (NOTE : The gateway Iface name may be different on your system depending on your system configuration. But you should see tun0, tun1, tun2, tun3 as shown below)
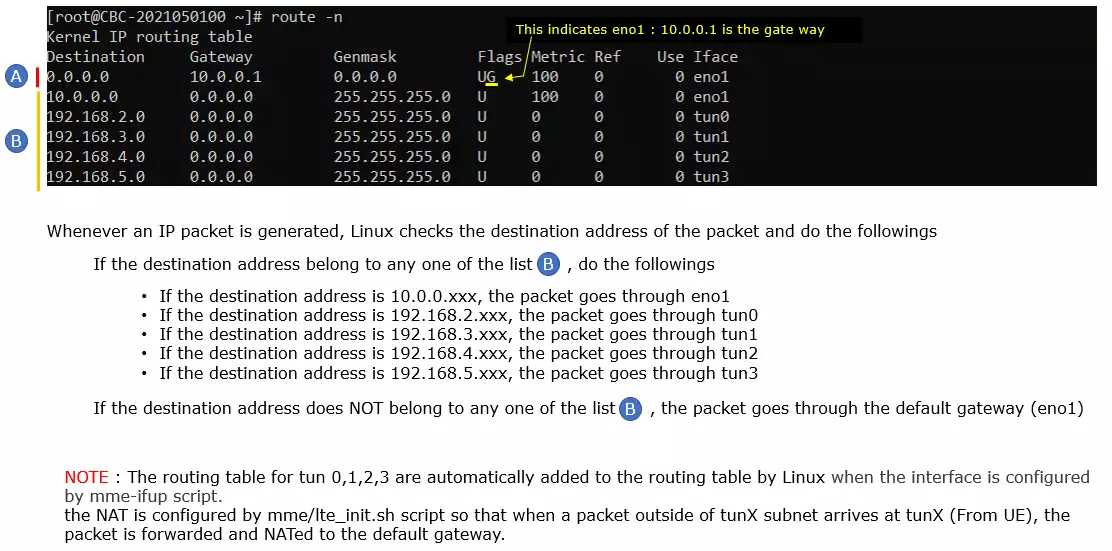
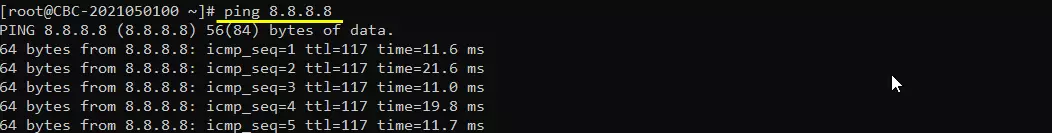
Make it sure that the call box can reach a server over the internet. I am checking the connectivity as follows
Try ping to 8.8.8.8. This is google DNS and this is configured as DNS by default in mme.cfg
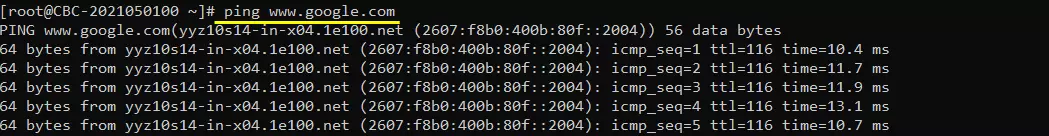
Try ping to a url to check the DNS is working
[Optional] you may find the IP address to a specific url and try ping to the server with both in direct IP and url

Perform the Test
I will try with a few different split bearer settings but the test procedure is all the same as described in this section. I turn off WiFi so that UE can get access to data traffic through cellular instead of WiFi. In most of commercial UE, WiFi has higher priority for data traffic.
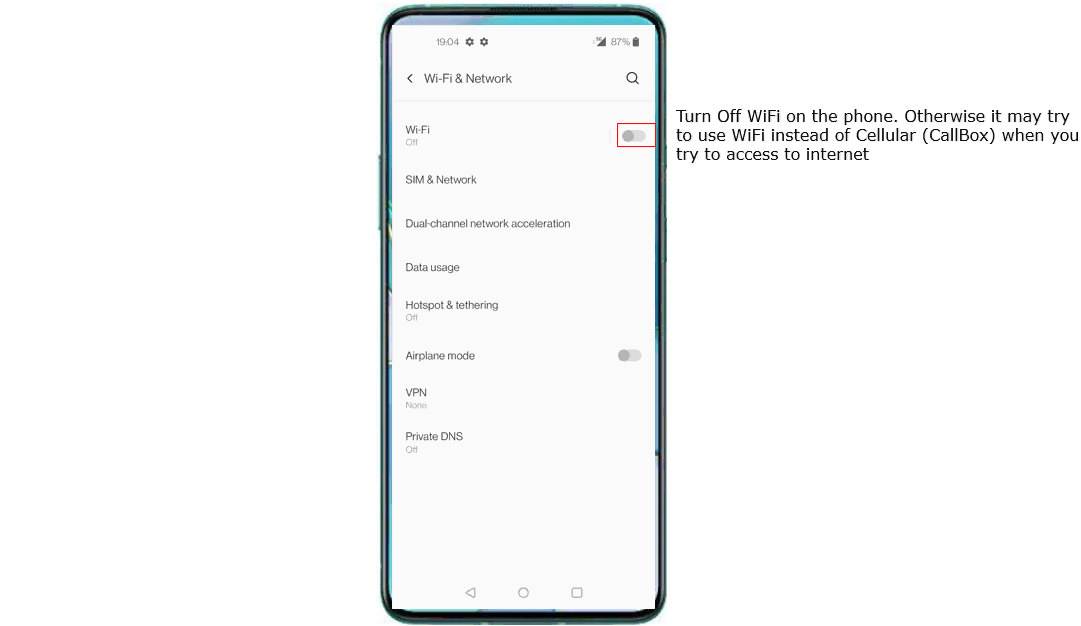
Do the initial attach and confirm that UE is connected to Callbox.
Confirm that UE is assigned with an IP

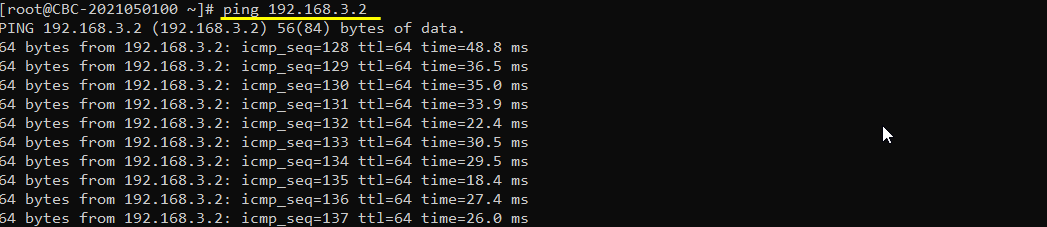
Ping from Callbox to UE and confirm that ping works
Try Browsing and make it sure that internet access works.
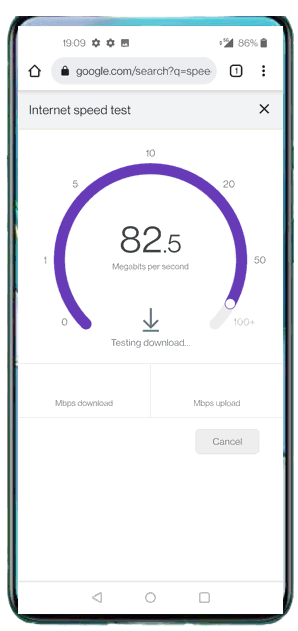
Go to speedtest site and generate high data rate of traffic. You may use any speed test site, but make it sure that the site test uplink speed test as well as downlink speed test
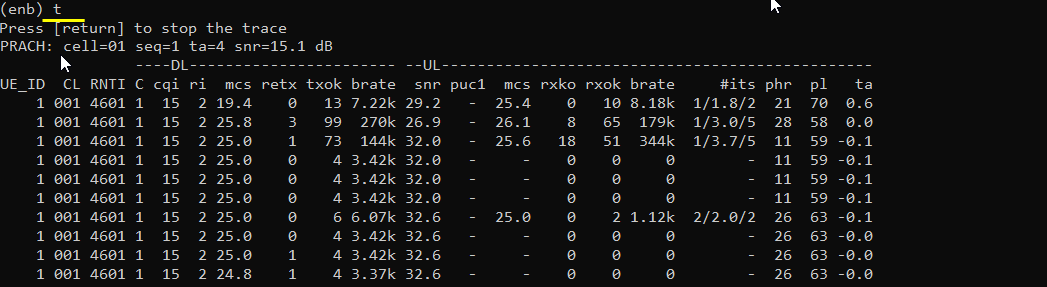
Test 1 : Split ratio decided by UE side decision
This test is to show the case where UL throughput gets splitted between LTE and NR based on UE side decision. In many case, UE split the UL traffic 50-50 in this configuration.
In this test, I set the split type and threshold as follows. split type is set to "scg" and ul_data_threshold is set to 0. ul_data_threshold 0 inidcates b0 which implies that the split is determined by UE side decision.
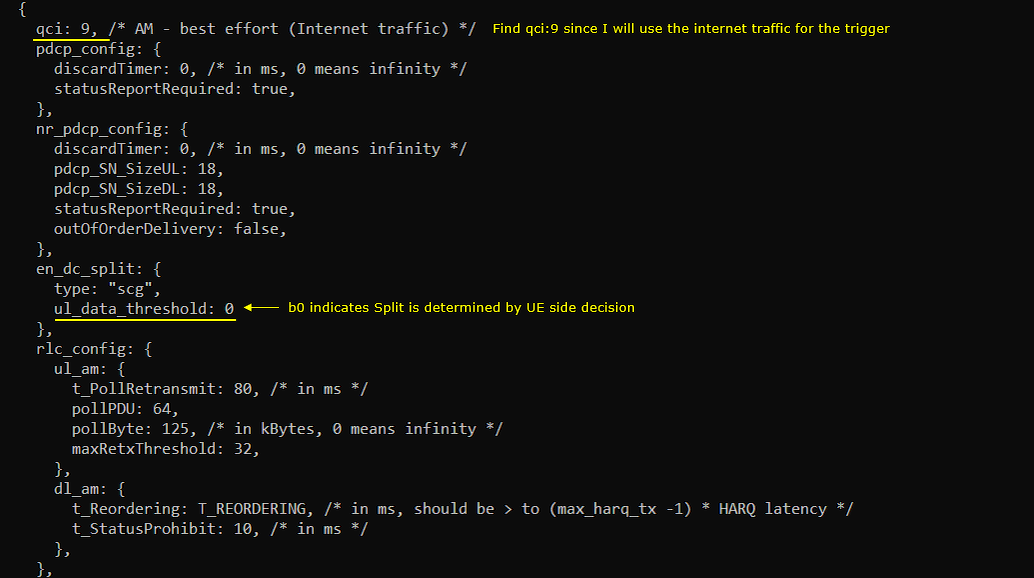
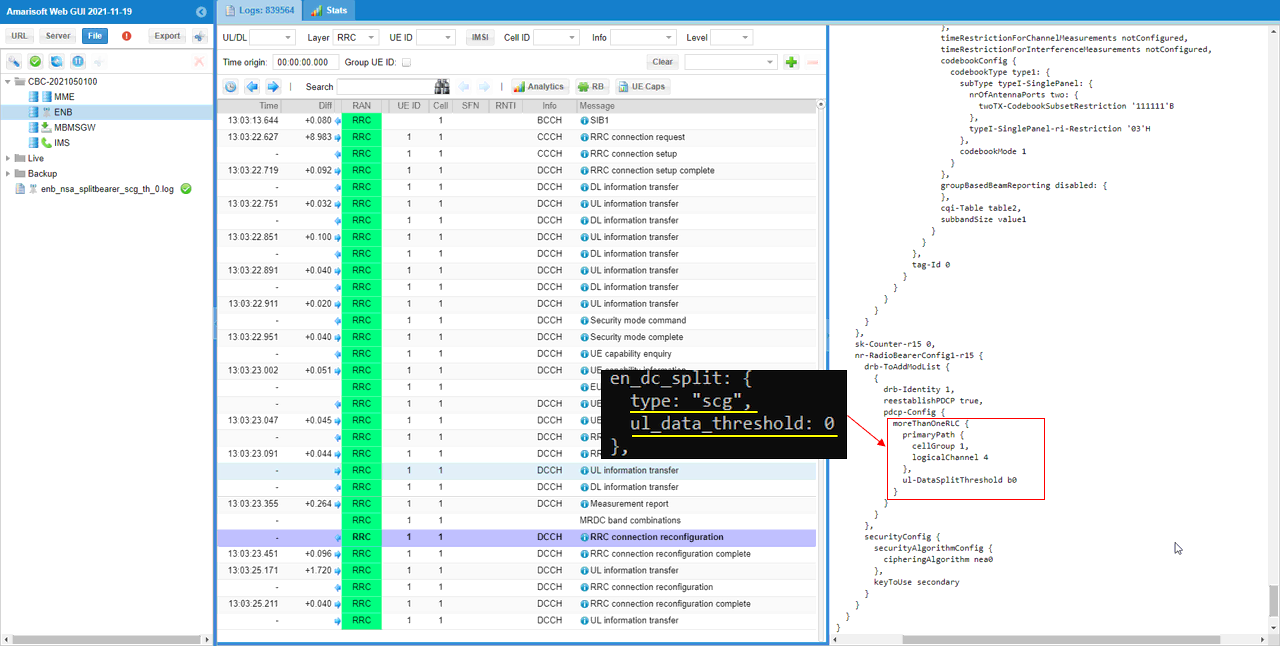
You can confirm your configuration is reflected in rrc message as shown below. split setting is configured in pdcp-Config of nr-RadioBearerConfig-r15. cellGroup IE is configured by 'type' parameter and ul-DataSplitThreshold IE is configured by ul_data_threshold parameter. cellGroup 0 means MCG and 1 means SCG.
Check how ul traffic gets splitted between LTE (mcg) and NR(scg).
In LTE connection, you see both downlink and uplink traffic.
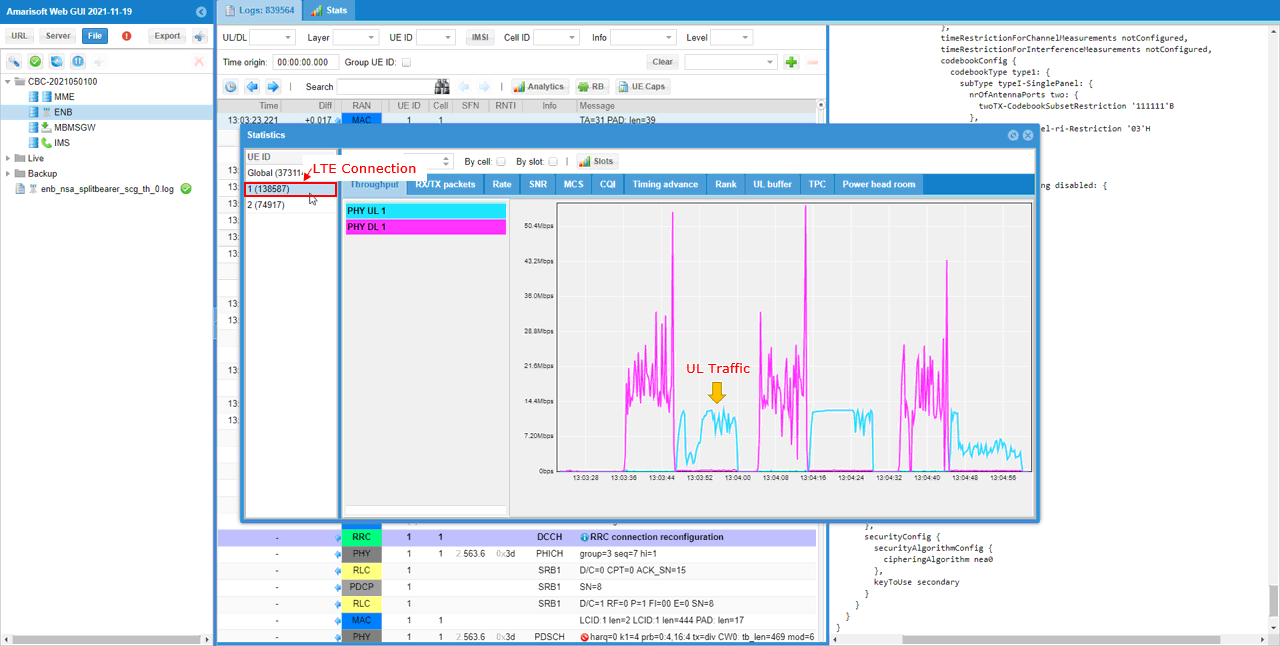
In NR connection, you see both downlink and uplink traffic with almost same throughput as in LTE. It means that UL traffic is split 50-50.
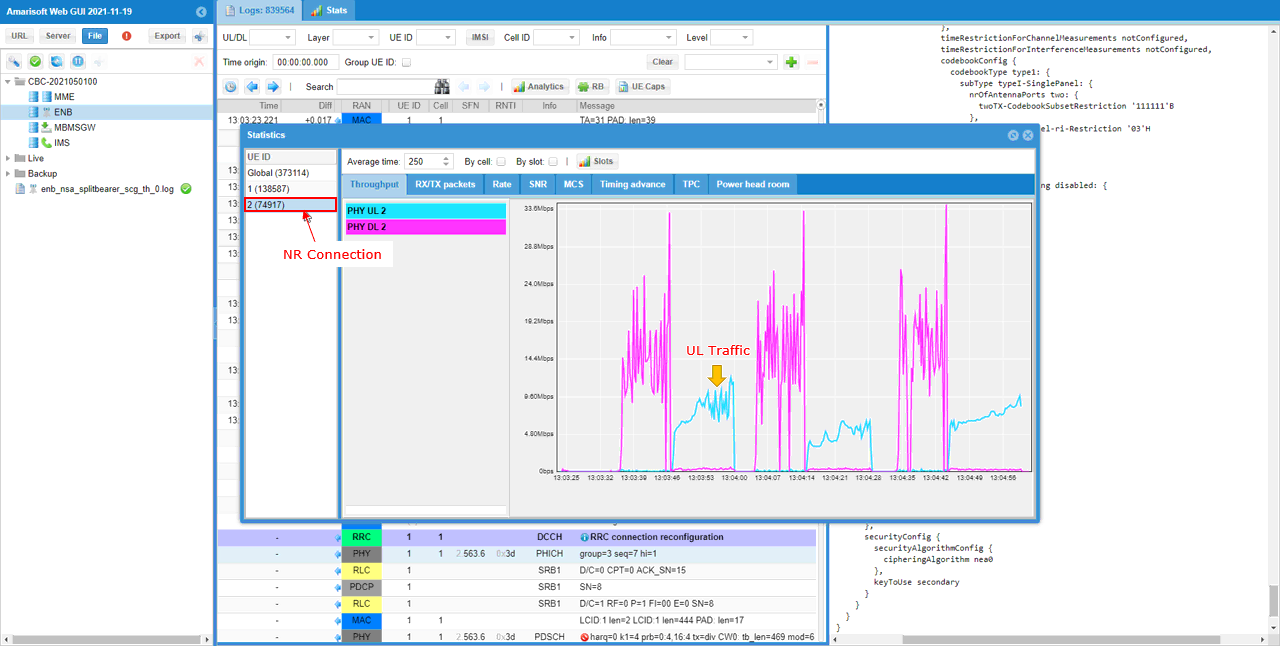
Test 2 : All UL traffic goes through NR (scg)
This test is to show the case where UL throughput does get splitted between LTE and NR, and goes through NR cell only.
In this test, I set the split type and threshold as follows. split type is set to "scg" and ul_data_threshold is set to -1. ul_data_threshold -1 inidcates 'infinity' which implies that the split does not happen and all the throughput goes through the channel specified by 'type'.
You can confirm your configuration is reflected in rrc message as shown below. split setting is configured in pdcp-Config of nr-RadioBearerConfig-r15. cellGroup IE is configured by 'type' parameter and ul-DataSplitThreshold IE is configured by ul_data_threshold parameter. cellGroup 0 means MCG and 1 means SCG. cellGroup 1 and ul-DataSplitThreshold infinity means that all the UL throughput goes through SCG only.
Check how ul traffic gets splitted between LTE (mcg) and NR(scg).
In LTE connection, you see downlink traffic but does not show any Uplink traffic.
In NR connection, you see both DL and UL traffic. Comparing to the traffic pattern of LTE channel, you would notice that 100% UL traffic goes though NR channel only.
RRC / NAS Signaling
: This section is to show you the overall structure of important Rrc messages and Information IE (IE) that are related to this tutorial. It is not intended to describe the details on every RRC/NAS Information elements. With the overall structure and key IEs shown here, it hope it would be easier / clearer to go through the sample log provided in this tutorial or any logs that you captured from your own test setup or live network.
rrcConnectionReconfiguration for NR Addition
: This is the RRC message sent by eNB (LTE) to add NR. (
message c1: rrcConnectionReconfiguration: {
rrc-TransactionIdentifier 0,
criticalExtensions c1: rrcConnectionReconfiguration-r8: {
....
nonCriticalExtension {
nonCriticalExtension {
nonCriticalExtension {
nonCriticalExtension {
nonCriticalExtension {
nonCriticalExtension {
nonCriticalExtension {
nonCriticalExtension {
nr-Config-r15 setup: {
endc-ReleaseAndAdd-r15 FALSE,
nr-SecondaryCellGroupConfig-r15 {
rrc-TransactionIdentifier 0,
criticalExtensions rrcReconfiguration: {
....
nr-RadioBearerConfig1-r15 {
drb-ToAddModList {
{
drb-Identity 1,
reestablishPDCP true,
pdcp-Config {
moreThanOneRLC {
primaryPath {
cellGroup 1,
logicalChannel 4
},
ul-DataSplitThreshold b0
}
}
}
},
securityConfig {
...
}