NR CMAS
This tutorial shows how to test NR CMAS on Amari Callbox with a commercial phone. CMAS stands for Commercial Mobile Alert System. It is a type of PWS (Public Warning System). Basic RAN Process of NR CMAS is as follows :
- Transmit SIB8 with CMAS Message
In real deployment, this process is controlled by CMAS server in core network side. It is the CMAS server and Core Network which are triggering the whole CMAS process and RAN to transmit the message.
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Commercial Mobile Alert System (CMAS), also known as Wireless Emergency Alerts (WEA) in the United States, is a critical component of the broader Public Warning System (PWS) designed to deliver timely emergency notifications to mobile users over cellular networks. In 5G New Radio (NR) networks, PWS capabilities are enhanced to provide robust, efficient, and reliable dissemination of public safety messages, leveraging advanced radio access network (RAN) features and spectrum efficiency. Unlike legacy 2G/3G technologies, where cell broadcast relied on dedicated channels like CTCH over FACH-SCCPCH, NR (and LTE) PWS implementations utilize broadcast channels such as BCCH mapped onto the physical downlink shared channel (PDSCH), eliminating the need for dedicated cell broadcasting resources. The architecture involves a PWS/CMAS server within the core network, which interfaces with the RAN to trigger SIB8 transmissions containing the alert payload. Amari Callbox, a versatile test platform, enables users to emulate NR network functions and validate CMAS delivery with commercial handsets, providing a controlled environment for testing message encoding, scheduling, and device reception in compliance with 3GPP standards. Mastery of these procedures is essential for engineers and operators seeking to ensure the reliability and compliance of public warning solutions in next-generation mobile networks.
-
Context and Background
- CMAS is part of the Public Warning System (PWS) infrastructure standardized by 3GPP, intended for rapid dissemination of emergency alerts such as severe weather, AMBER alerts, and presidential notifications.
- 5G NR introduces architectural enhancements and radio protocol optimizations, allowing more flexible, scalable, and efficient broadcast of public warning messages compared to legacy systems.
- Testing platforms like Amari Callbox simulate end-to-end network scenarios, enabling validation of alert delivery mechanisms without the need to access live commercial networks.
-
Relevance and Importance
- Ensuring that CMAS alerts are delivered reliably and promptly is fundamental for public safety and regulatory compliance.
- Understanding the differences in broadcast mechanisms between legacy and modern networks is crucial for effective deployment, troubleshooting, and innovation in emergency communication systems.
- Laboratory testing with commercial devices provides practical insights into user experience, device compatibility, and network configuration impacts.
-
Tutorial Objectives
- Demonstrate how to configure and use Amari Callbox to emulate NR CMAS scenarios with a commercial phone.
- Explain the end-to-end process of CMAS message delivery over NR, including SIB8 broadcasting and device reception.
- Highlight the architectural and procedural differences compared to legacy cell broadcast systems.
- Equip learners with the knowledge to verify and troubleshoot CMAS functionalities in a test environment.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge and Skills
- Familiarity with 3GPP radio access network architecture, especially NR and LTE concepts.
- Basic understanding of broadcast mechanisms in mobile networks and the role of SIB messages.
- Hands-on experience with network emulation tools such as Amari Callbox or similar platforms is beneficial, but not strictly required.
- General knowledge of emergency communication standards and regulatory requirements is advantageous.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial describes the procedure to test the Cell Broadcast Message Service (CMAS) functionality on a test setup using an Amarisoft platform. The following summarizes the key test procedures, steps, and methodologies:
-
Test Setup Preparation:
- Use the SIM card delivered with the system for the test; refer to the Configuration Guide for SIM card changes.
- The setup includes a callbox and a UE as shown in the provided diagram.
-
Configuration of Key Parameters:
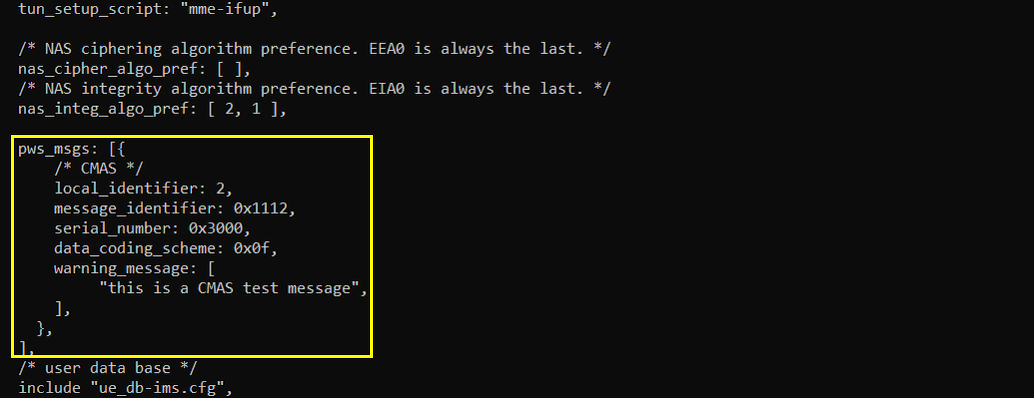
- Identify and configure essential parameters in pws_msgs, such as:
- local_identifier
- message_identifier
- serial_number
- data_coding_scheme
- repetition_period
- warning_type
- warning_message
- warning_message_hex
- send_warning_indication
- warning_area_list
- Use the default gnb-sa.cfg (NR SA configuration) without modification.
- Modify mme-ims-cmas.cfg (copied from mme-ims.cfg) to include the pws_msgs configuration with the required parameters.
- Identify and configure essential parameters in pws_msgs, such as:
-
Test Execution Procedure:
- Start LTE service and verify that the cell is properly configured as an NR cell.
- Power on the UE and allow it to attach to the cell.
- Confirm successful UE attachment to the core network (mmel).
- Send a CMAS message using the pws_write command, specifying the local_identifier parameter.
- Verify that the UE receives the CMAS message and emits an alarm sound. Both the visual text message and the audio alarm are required for successful test completion.
- To stop sending the CMAS message, use the pws_kill command, again specifying the relevant local_identifier.
-
Log Analysis Methodology:
- Capture logs with BCCH, RRC, and NGAP enabled to analyze the CMAS broadcast procedure.
- Configure the log viewer to display the relevant protocol layers for easier analysis.
- When the CMAS message is triggered by the pws_write command, verify that the core network sends the corresponding NGAP message for CMAS.
- Check that the CMAS message is broadcast via SIB8, and confirm the presence of fields such as messageIdentifier, serialNumber, warningMessageSegmentType, warningMessageSegmentNumber, warningMessageSegment, and dataCodingScheme.
- When stopping the CMAS message (via pws_kill), ensure the core network sends the appropriate NGAP message to terminate the broadcast.
This procedure ensures comprehensive testing of the CMAS functionality, including configuration, message transmission, UE reception and alarm verification, and detailed log analysis, while maintaining the required parameterization and network signaling flows.
Test Setup
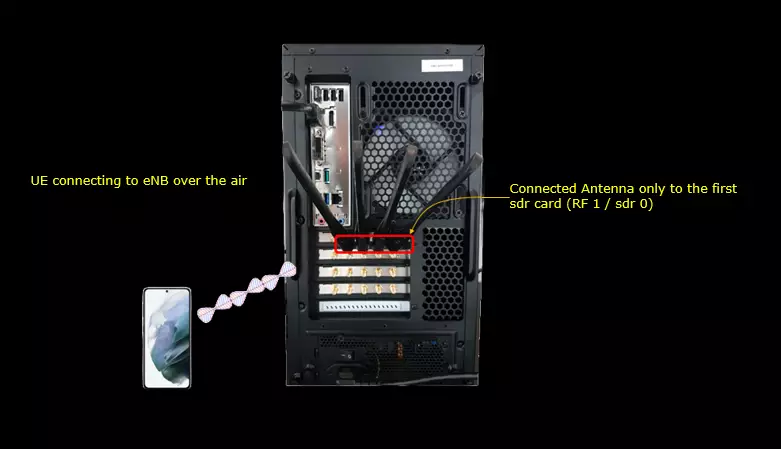
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below.
- SIM Card used in this tutorial is the one delivered with the system as it is.
- If you want to change the configuration, The tutorial Configuration Guide would help

Key Configuration Parameters
Followings are important configuration parameters for this tutorial. You may click on the items for the descriptions from Amarisoft documents.
- pws_msgs : In this link, you would get the descriptions for all the items listed below. In the document, there are much more parameters (optional parameters) than the list below
- local_identifier
- message_identifier
- serial_number
- data_coding_scheme
- repetition_period
- warning_type
- warning_message
- warning_message_hex
- send_warning_indication
- warning_area_list
Configuration
I used the gnb-sa.cfg (NR SA default configuration) as it is without changing any contents in it.
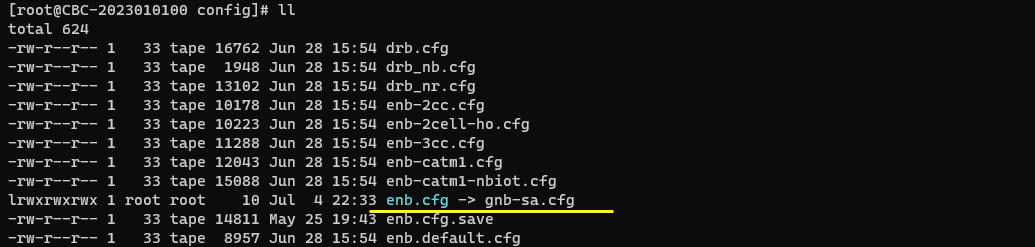
I also used mme-ims-cmas.cfg which was copied and modified from mme-ims.cfg.
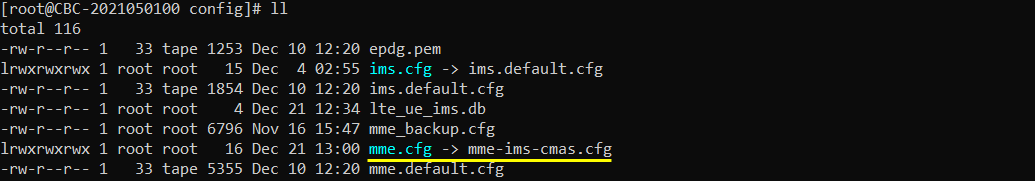
In mme-ims-cmas.cfg I have added the following configuration. Just add pws_msgs configuration and specify the details like local_identifier, message_identifier, serial_number, data_coding_scheme, warning_message etc.
Perform the test
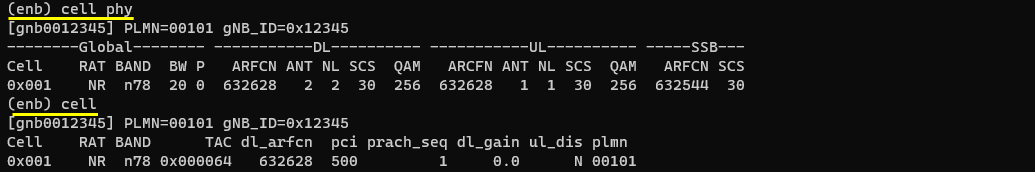
Start LTE service and check basic cell configuration. Any cell configuration is OK as long as it is NR cell.
Power on UE and let UE attach to the cell
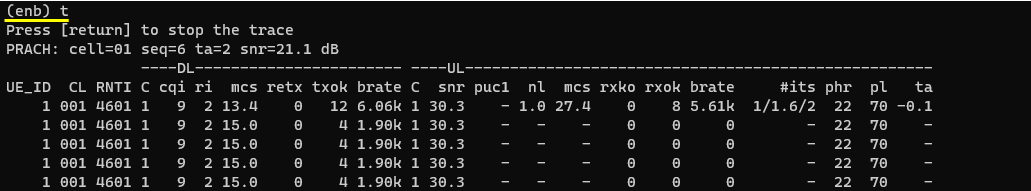
Confirm that UE is attached to mmel

Send CMAS using pws_write command as shown below. (

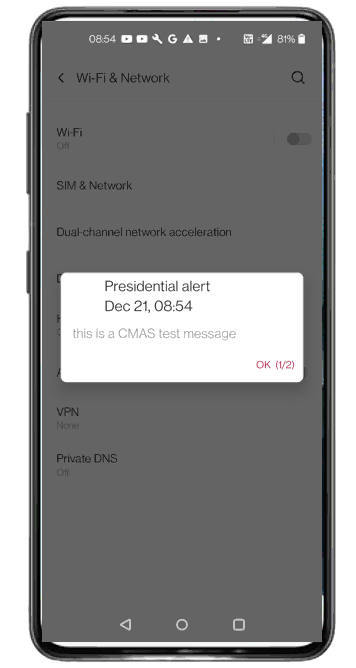
Check if you get CMAS message as shown below. You should hear alarm sound from the UE as well. Both text message and Alarm sound is requirement for the test.
You can stop cmas message using the following command. (

Log Analysis
Since CMAS message is broadcast by SIB message triggered by Core Network, the first step for CMAS log analysis is to capture the log with BCCH, RRC and NGAP enabled as shown below.
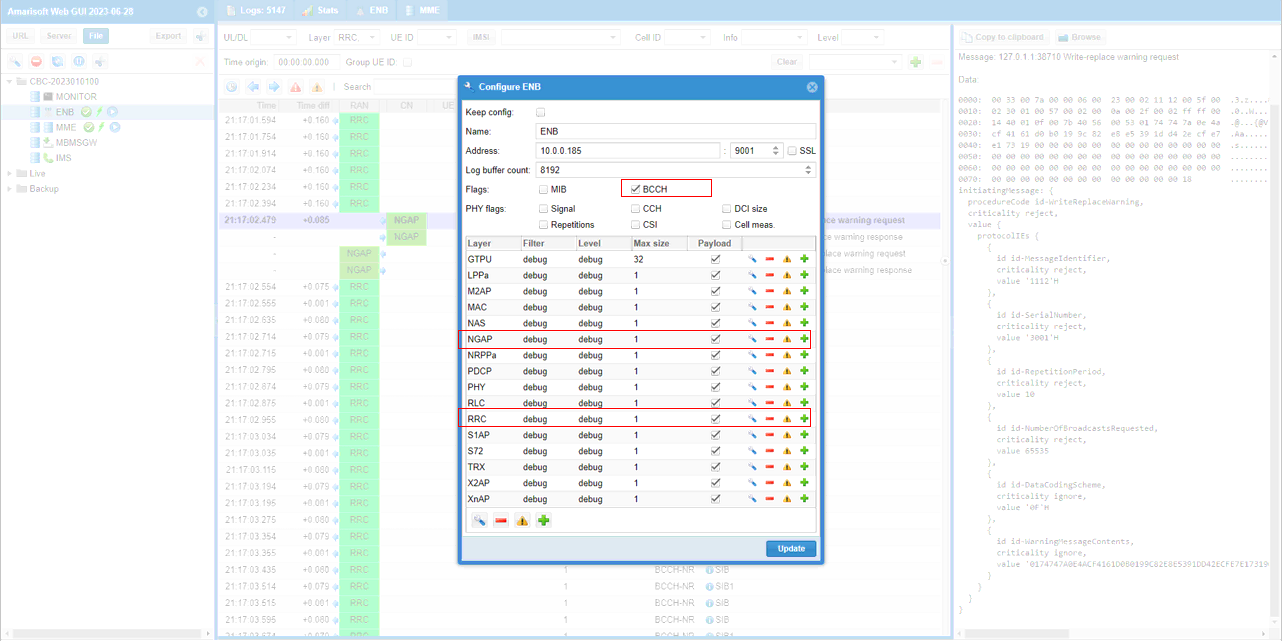
Set the layer as shown below for the convinience of the log analysis.
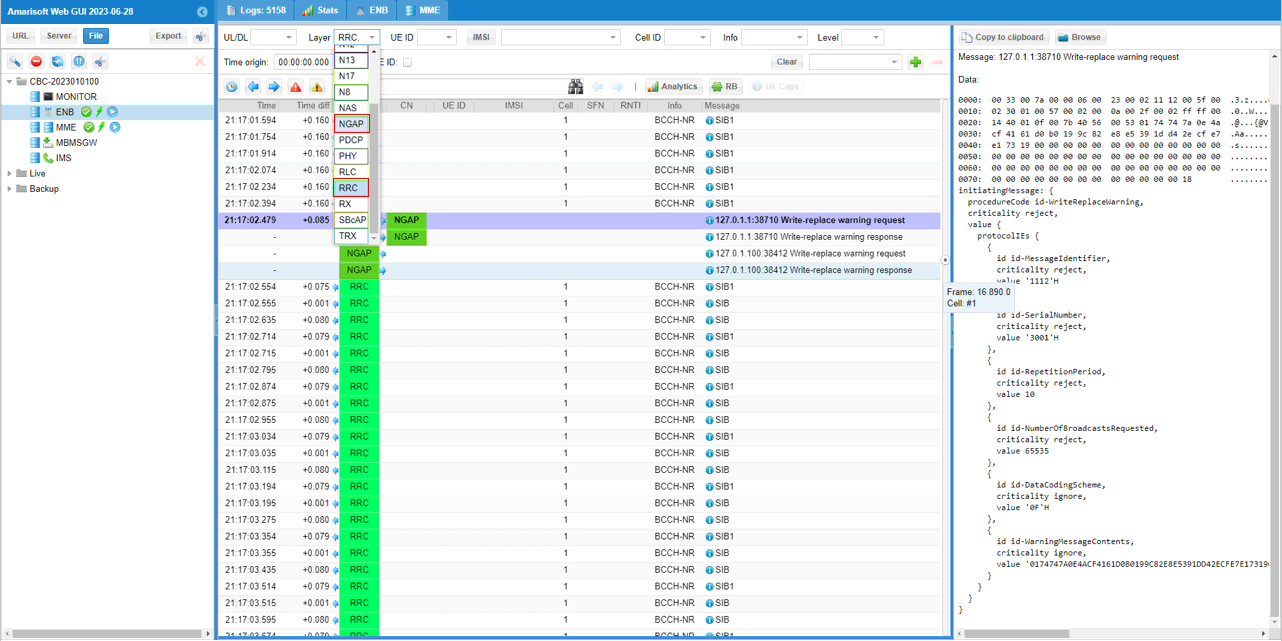
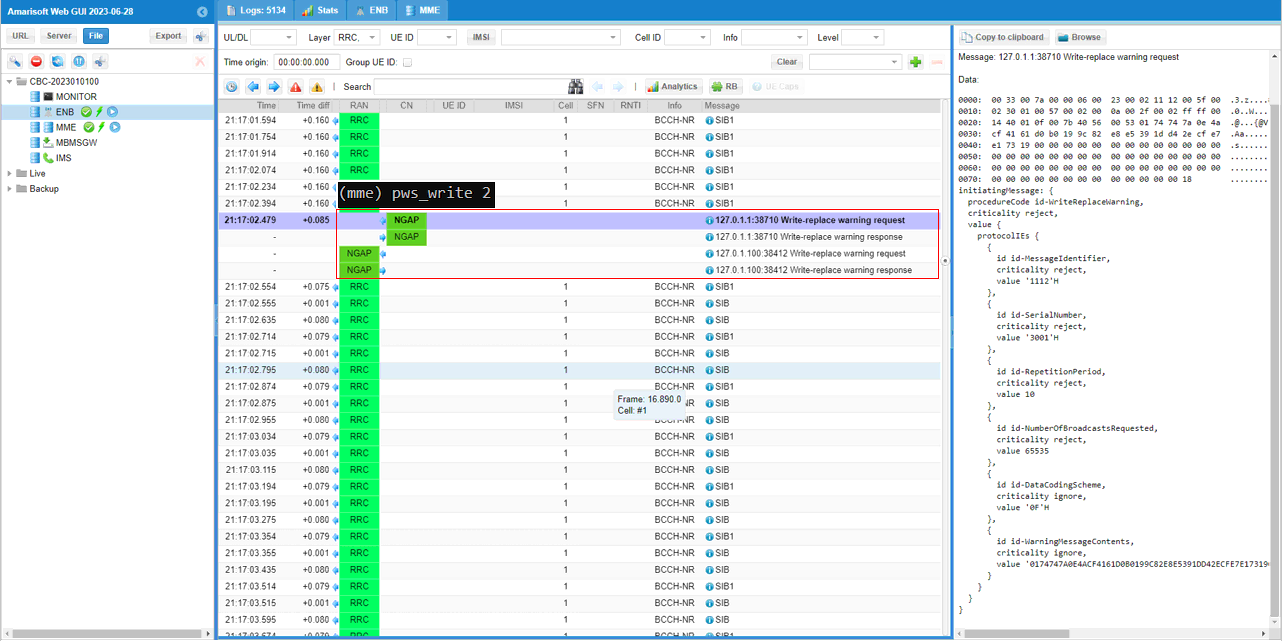
When you send the CMAS message message (triggered by mme command 'pws_write'), Core Network send NGAP message for CMAS as shown below.|
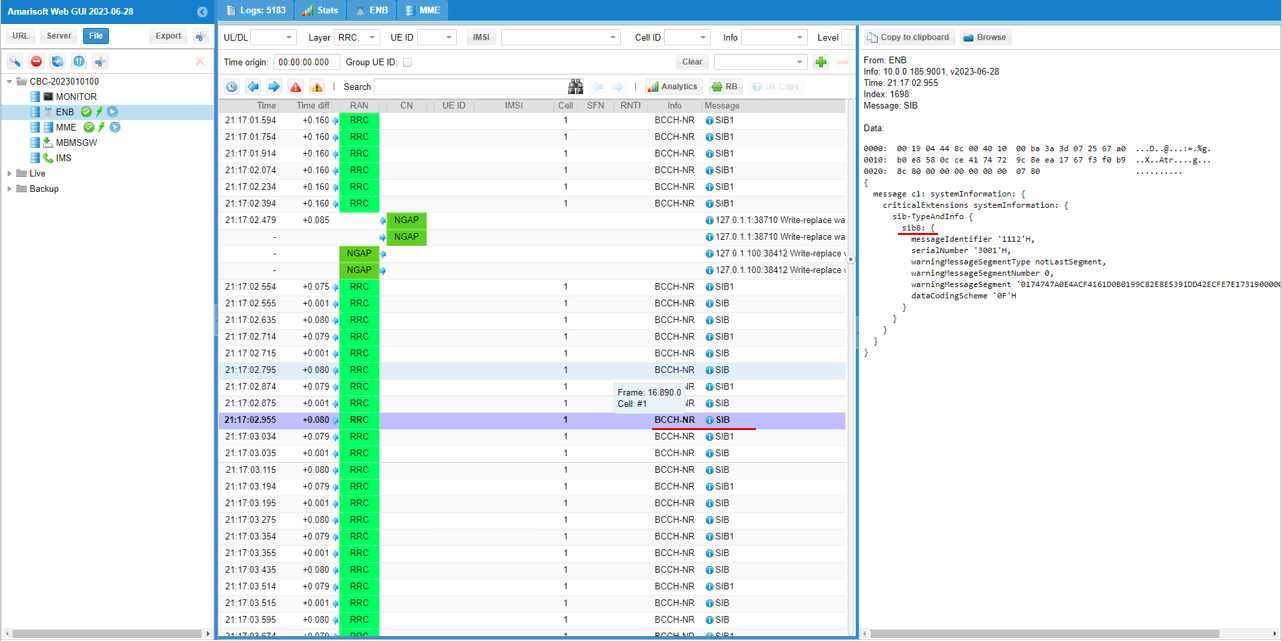
CMAS message is broadcast via sib8. In this SIB you can check out the details of CMAS contents : messageIdentifier, serialNumber, warningMessageSegmentType, warningMessageSegmentNumber, warningMessageSegment, dataCodingScheme.
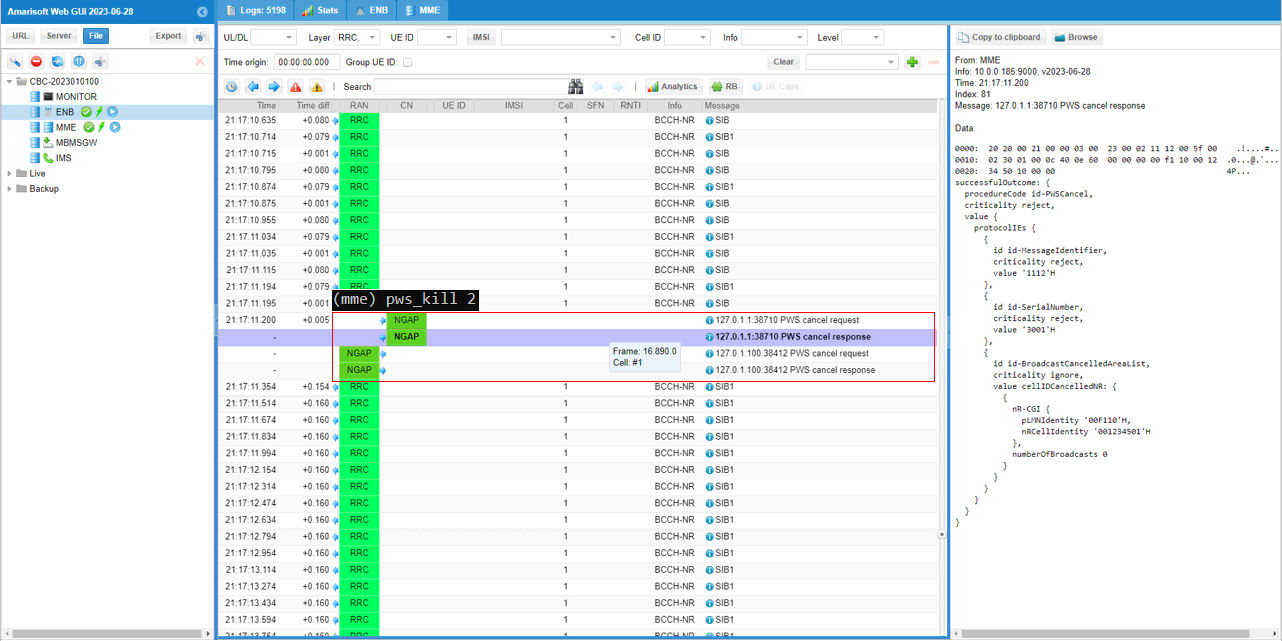
When you stop the CMAS message message (triggered by mme command 'pws_kill'), Core Network send NGAP message for CMAS as shown below.|
RRC / NAS Signaling
SIB 8
: This is the SIB 8 message sent by gNB to configure CMAS. (
{
message c1: systemInformation: {
criticalExtensions systemInformation: {
sib-TypeAndInfo {
sib8: {
messageIdentifier '1112'H,
serialNumber '3001'H,
warningMessageSegmentType notLastSegment,
warningMessageSegmentNumber 0,
warningMessageSegment '0174747A0E4ACF4161D0B0199C82E8E5391DD42ECFE7E1731900000000000000'H,
dataCodingScheme '0F'H
}
}
}
}
}