Connecting to External MME
The purpose of this tutorial is to show you how to run MME in an external PC (in a virtual box on an external PC). In ordinary usage of Amarisoft Callbox, we run eNB/gNB on a same PC. Motivation for this tutorial was for the case where non-Amarisoft RAN and Amarisoft Core are used, but I don't have any non-Amarisoft RAN to play with and I tried with Amarisoft RAN and Amarisoft Core but they are in different location. However, you can apply the concept of this tutorial to the case for Amarisoft RAN + Non-Amarisoft Core and for Non-Amarisoft RAN + Amarisoft Core. It is relatively simple to combine the heterogenious components, the only parameters that you need to pay attention to are amf_addr and gtp_addr.
Table of Contents
- Connecting to External MME
Introduction
In the evolving landscape of mobile network architectures, the separation and virtualization of network functions have become fundamental to deploying flexible, scalable, and interoperable solutions. The Mobility Management Entity (MME) plays a crucial role in the LTE Evolved Packet Core (EPC) as the key control-plane node responsible for mobility management, session handling, and signaling between the radio access network (RAN) and core network elements. Traditionally, solutions like Amarisoft Callbox integrate both the radio (eNB/gNB) and core components on a single system for ease of use and rapid prototyping. However, as real-world deployments increasingly demand interoperability between heterogeneous RAN and core network elements—sometimes from different vendors or situated in physically distinct environments—there is a strong motivation to decouple and virtualize core functions such as the MME. This tutorial demonstrates how to configure and run the MME in a virtualized environment (such as a VirtualBox instance) on an external PC, enabling flexible combinations like Amarisoft RAN with a third-party core (or vice versa). The approach leverages standardized interfaces and configurable parameters, notably amf_addr (Access and Mobility Function address) and gtp_addr (GPRS Tunneling Protocol address), to ensure seamless interconnection between distributed network components. Understanding this setup is vital for engineers, researchers, and operators aiming to test, deploy, or interoperate with multi-vendor or geographically distributed 4G/5G network architectures.
-
Context and Background
- The MME is a fundamental component of LTE EPC, managing user mobility, authentication, session management, and signaling between the RAN (eNB/gNB) and the core.
- Amarisoft Callbox is a comprehensive software-based LTE/5G platform enabling rapid prototyping and testing, often with both RAN and core components on a single host.
- Modern network deployments require the flexibility to interconnect RAN and core components across different hardware or virtualized environments to support heterogeneous and geographically distributed setups.
-
Relevance and Importance
- This tutorial addresses real-world scenarios where the RAN and core are provided by different vendors or need to reside on separate physical or virtualized platforms.
- It enables advanced testing, development, and integration workflows essential for multi-vendor interoperability, network slicing, and distributed network functions in 4G/5G networks.
-
Learning Outcomes
- Understand the architectural principles behind decoupling RAN and core network elements.
- Gain practical knowledge on configuring and running the MME in a virtualized environment external to the RAN host.
- Learn to identify and set key configuration parameters (amf_addr and gtp_addr) for successful interconnection.
- Acquire troubleshooting skills for common challenges encountered in distributed network setups.
-
Prerequisites
- Basic understanding of LTE/EPC architecture, including the roles of RAN, MME, and core network elements.
- Familiarity with Amarisoft Callbox or similar software-based RAN/core solutions.
- Experience with virtualization platforms (e.g., VirtualBox) and network configuration.
- General knowledge of IP networking and protocol configuration.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial outlines the procedure for setting up and testing a 5G/4G network environment where the MME (Mobility Management Entity) is hosted externally on a separate PC. The steps are organized into setup, configuration, execution of the test, and log analysis.
-
Test Setup:
- Install callbox software on an external PC running Fedora to serve as the external MME.
- Ensure proper network connectivity between the callbox (acting as gNB/eNB) and the external MME PC.
-
Configuration:
- Use and modify gnb-sa-external-mme.cfg on the callbox, ensuring amf_addr is set to the external MME PC IP address and gtp_addr to the callbox NIC with access to the external PC.
- On the external MME PC, use mme-ims-external.cfg for MME configuration, specifying gtp_addr as the IP address of the NIC that connects to the rest of the network.
-
Use ots.default.cfg in the
/root/ots/configdirectory on the external MME PC. No additional configuration files are strictly necessary due to the minor changes required. - Additional configuration is performed in mme.cfg and ots.cfg files as shown, ensuring correct addressing and network parameters.
-
Test Execution:
-
On the callbox (enb) screen, run the
ngcommand to verify the MME IP address the gNB is connected to. -
On the external MME PC, use the
ng_rancommand to check the IP address of the gNB to which the MME is connected. -
On the callbox, use
cellandcell phycommands to confirm the gNB (cell) is configured as intended. Any SA configuration can be used for this test. - Power on the UE and allow it to complete the attach process. Verify that the UE successfully registers to the external MME and is assigned an IP address.
- From the external MME PC, ping the UE to confirm end-to-end connectivity.
-
On the callbox (enb) screen, run the
-
Log Analysis:
- On the external MME, update the MME IP address and increase the maximum log size for all components to ensure full data traffic headers are captured.
- Increase the max log size on the eNB/callbox for troubleshooting purposes.
- Confirm via logs that the gNB is successfully connected to the external MME.
- Power on the UE and check protocol sequence logs to ensure that all signaling and data flows are working as expected.
The entire process verifies proper integration and operation of an external MME in a test network, focusing on network setup, configuration validation, protocol registration, connectivity checks, and log-based troubleshooting.
Test Setup
In this setup, I installed callbox software on an external PC with fedora to use it as the external MME.

Configuration
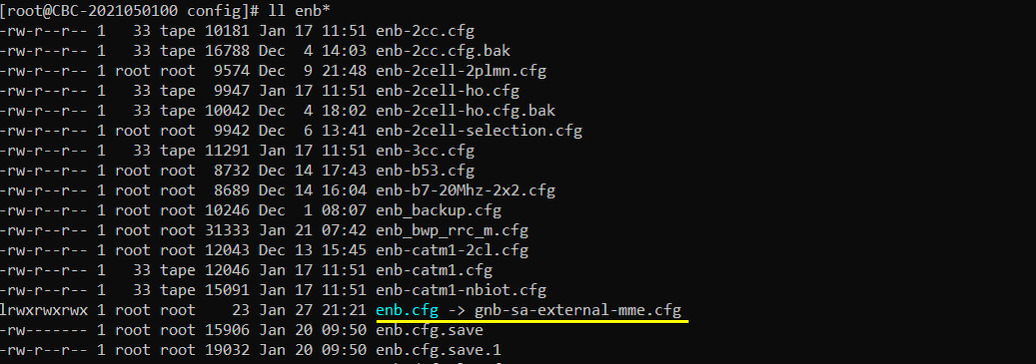
I used gnb-sa-external-mme.cfg which is copied and modified from gnb-sa.cfg.
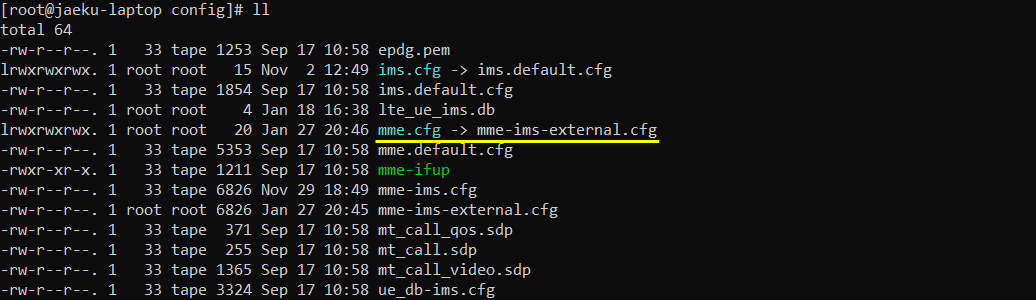
I used mme-ims-external.cfg on the external MME PC which is copied from mme-ims.cfg.
I used ots.default.cfg file in /root/ots/config directory on the external MME PC. I haven't created any additional config file for this because the change will be very minor and may not be mandatory.

In gnb-sa-external-mme.cfg on Callbox, I made the following modification. Note that I changed amf_addr to point to the external MME PC IP address and gtp_addr to point to the IP address of NIC on Callbox which has access to external PC.
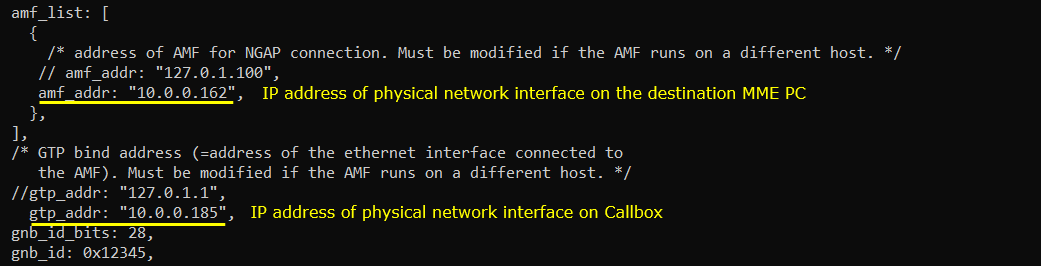
Configure as follows in /root/mme/config/mme.cfg (mme-ims-external.cfg ) on the external MME PC. gtp_addr here is the IP address of NIC which has access to other PCs.
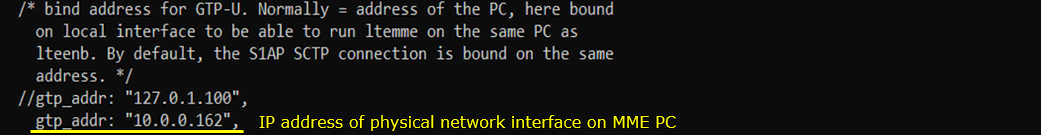
Configure as follows in /root/ots/config/ots.cfg on the external MME PC

Perform the test
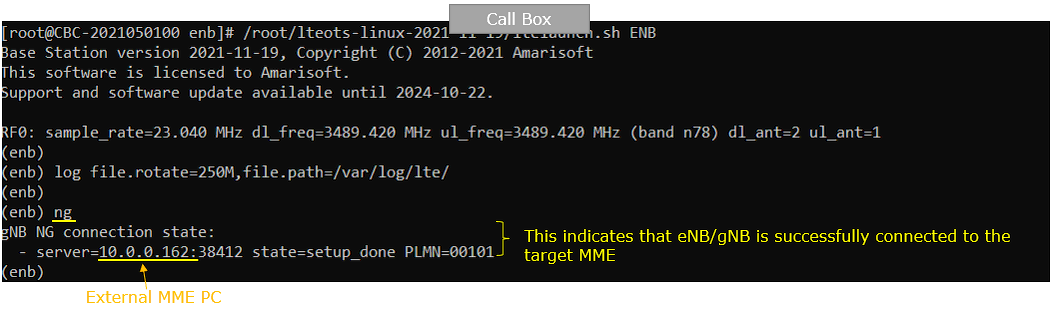
On Callbox (enb) screen, run the command : ng. this shows the IP address of the MME IP which the gNB is connected to.
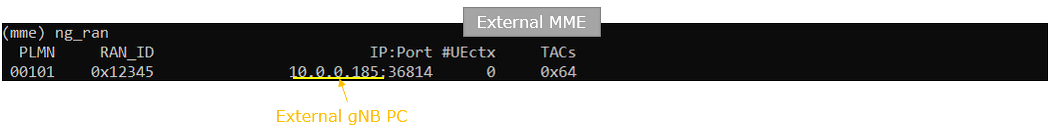
On the external MME PC, you can check the IP address of gNB which the MME is connected to using the command ng_ran in (mme) screen window.
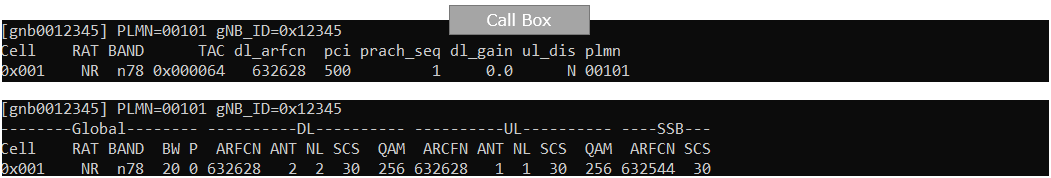
On the Callbox, confirm the gNB (cell) is configured as intended using 'cell' and 'cell phy' command. The defailed configuration is not important for this tutorial. You may use any kind of SA configuration for this tutorial.
Now Power On UE and let it complete the attach process and check if UE is successfully registerred to the external MME and IP address is assigned to the UE
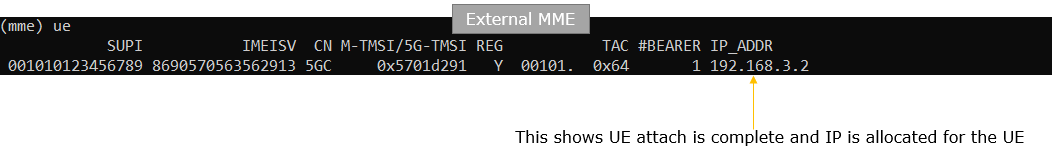
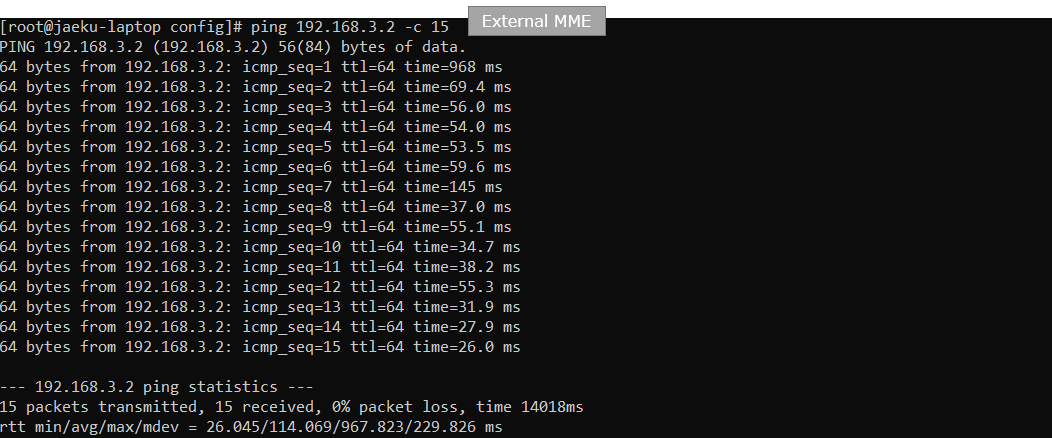
Try ping from the external MME PC to UE and confirm that ping goes through.
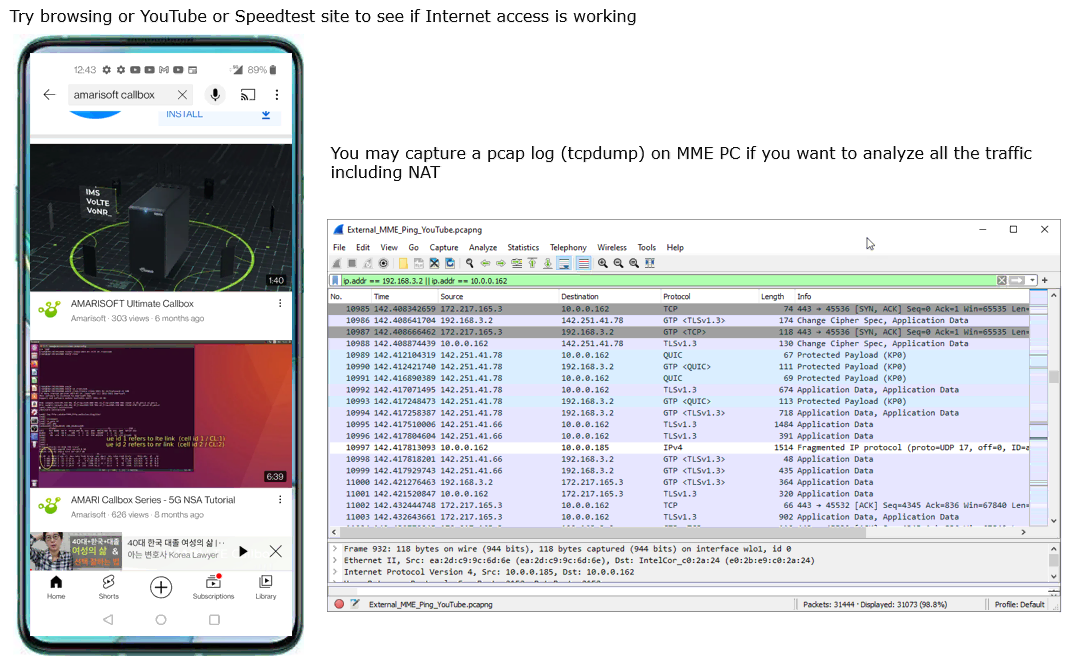
Log Analysis
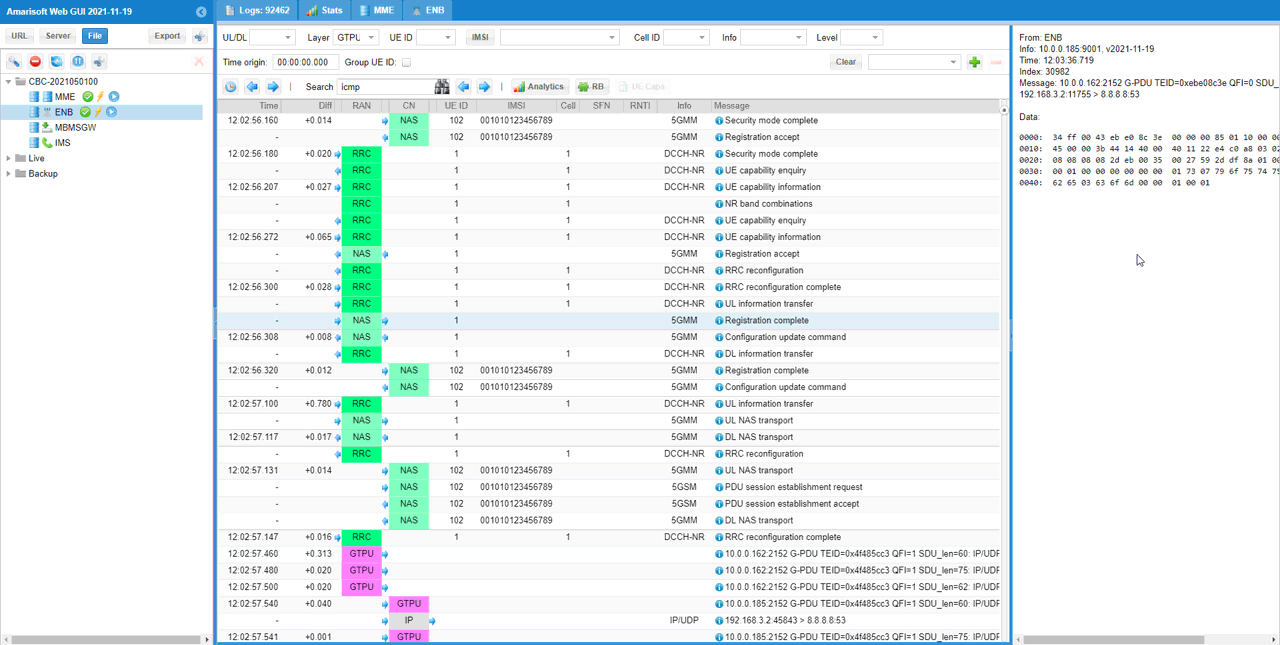
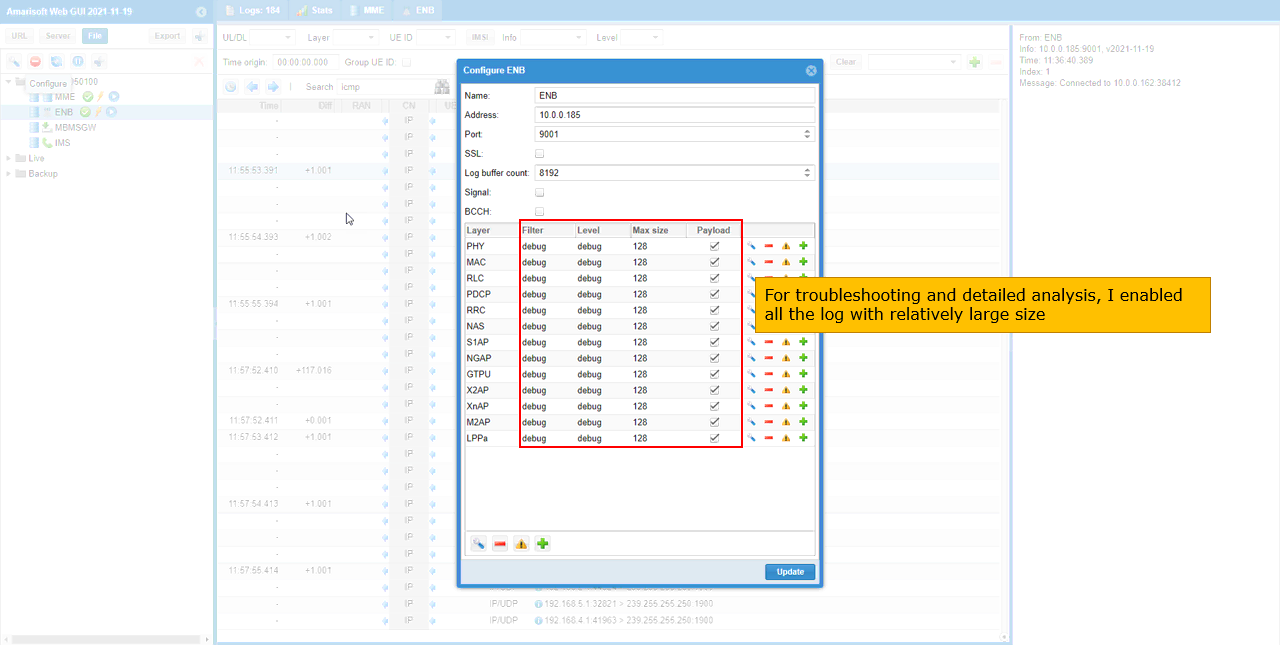
Since the MME is running on external PC, I changed IP address of MME as shown below and increased the Max size of all the components to capture the full header of data traffic.
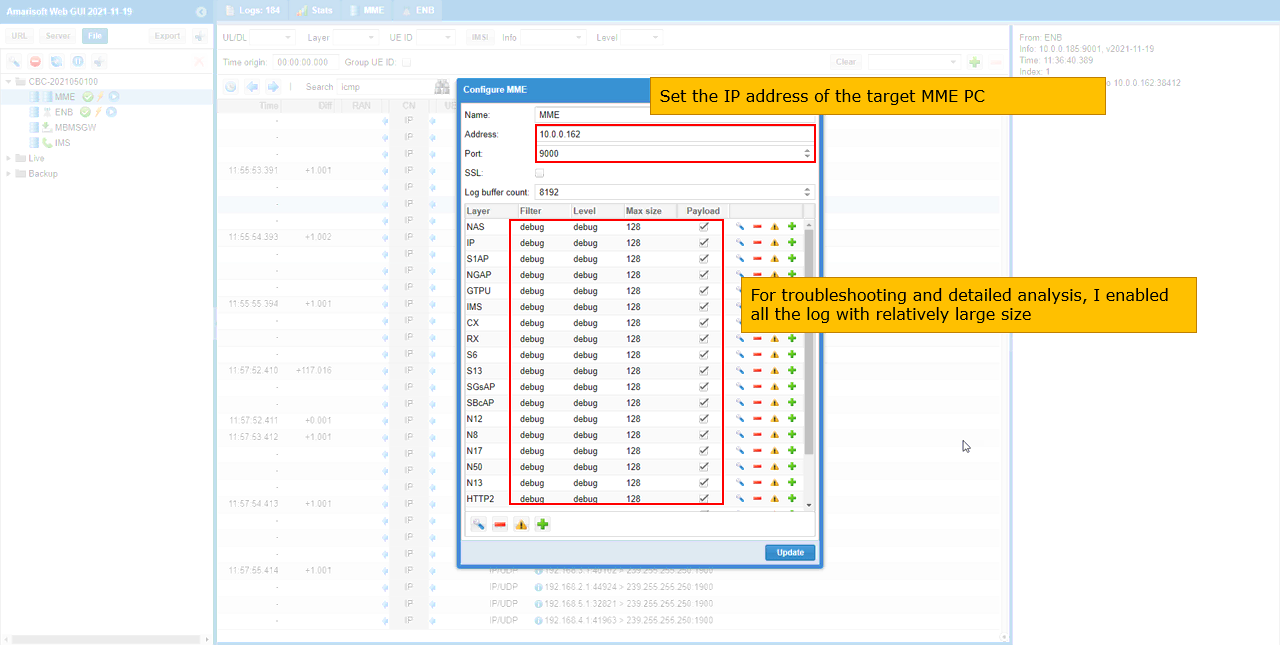
Increase the max size of all the components on eNB for troubleshooting
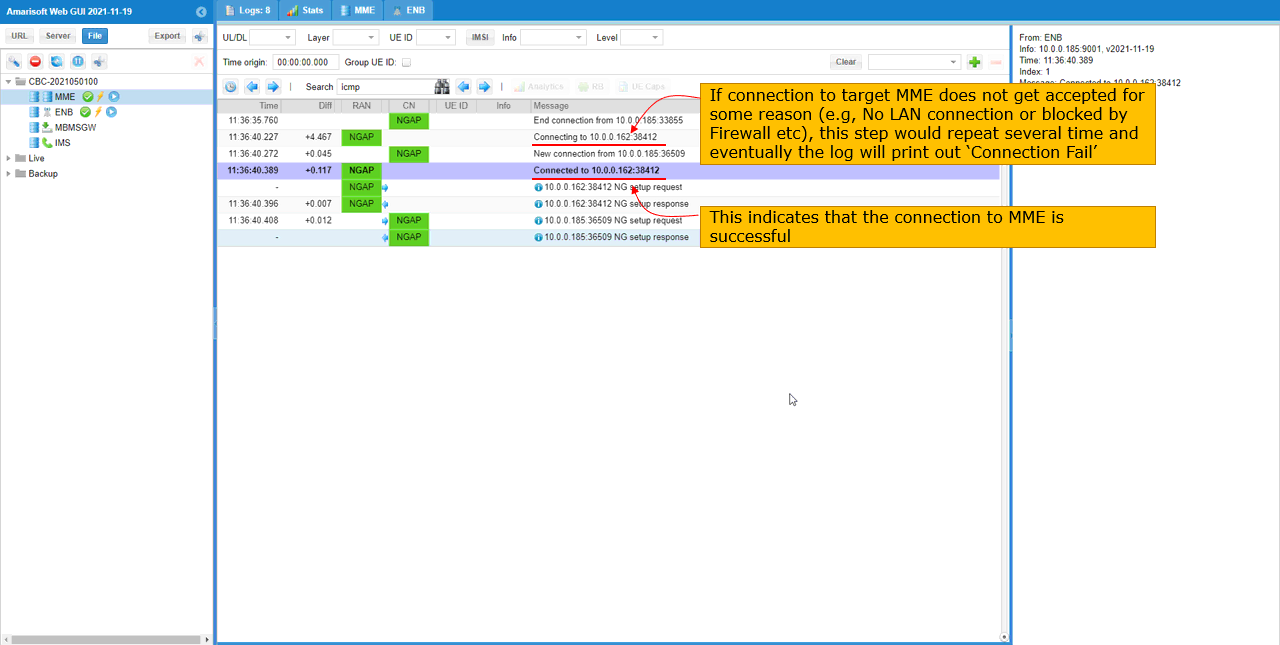
You can check if the gNB is successfully connected to the external MME
Power on UE and check if all the protocol sequence is properly going through