LTE PDCCH Order
This tutorial shows how to trigger a PDCCH Order based RACH procedure from the callbox. In live network and UE, PDCCH Order transmission would happen when the connection gets Out of Sync and there is some data available for Network to send, but it would not be easy to create such a situation in lab settings. So in this tutorial, I will use RemoteAPI to trigger PDCCH order. The main purpose of this tutorial is to show how to configure PDCCH Order related parameters in configuration file and check if UE properly responds to the PDCCH order.
In most case, RACH is triggered by UE side decision, but there is some mechanism by which network (eNB) force UE to initiate RACH. In idle mode, Paging is such a mechanism and in connected mode PDCCH order is such a mechanism. PDCCH order is a mechanism in which network (eNB) order UE to initiate RACH by sending a specific format of DCI. The DCI format used for this purpose is DCI Format 1A with a specific value assigned to PRACH Mask Index field.
The PRACH procedure can be an Contention Based or Contention Free. The PDCCH order instruct which type of RACH procedure should be initiated by configuring specific preamble index values.
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Physical Downlink Control Channel (PDCCH) Order-based Random Access Channel (RACH) procedure is a critical mechanism in LTE networks that allows the evolved Node B (eNB) to directly command a User Equipment (UE) to initiate random access. Unlike typical RACH procedures, which are usually triggered by the UE in response to connectivity needs or synchronization loss, the PDCCH order enables the network to take proactive control, particularly in scenarios where the UE is in RRC_CONNECTED state but has lost uplink synchronization. This mechanism is fundamental for maintaining robust network operations, ensuring timely recovery from out-of-sync conditions, and guaranteeing the delivery of downlink data. The PDCCH order utilizes a specially formatted Downlink Control Information (DCI), specifically DCI Format 1A with a defined PRACH Mask Index, to signal the UE to begin either contention-based or contention-free RACH procedures. Understanding how to configure, trigger, and verify the PDCCH order process is essential for engineers and testers working with LTE radio access networks, especially in controlled environments where replicating real-world out-of-sync scenarios can be challenging. This tutorial leverages RemoteAPI to simulate and trigger the PDCCH order from a callbox, providing hands-on experience with configuration parameters and response verification, and deepening comprehension of the LTE RACH architecture and its operational significance within the mobile network ecosystem.
-
Context of the Technology
- The PDCCH order is a core feature within the LTE radio access network, facilitating direct network-initiated random access for UEs.
- It addresses scenarios where the UE loses uplink synchronization but remains in RRC_CONNECTED state, ensuring uninterrupted service delivery and network reliability.
- This mechanism is especially important in automated testing and lab environments, where realistic simulation of network behaviors is required.
-
Relevance and Importance of the Tutorial Topic
- Demonstrates practical methods to trigger and observe PDCCH order-based RACH, which is otherwise difficult to reproduce in laboratory settings.
- Equips learners with knowledge on configuring essential parameters in the callbox and test environment to mimic real network conditions.
- Highlights the architectural role of PDCCH and RACH in LTE connectivity, network recovery, and system resilience.
-
Learning Outcomes
- Understand the technical principles and signaling involved in PDCCH order-based RACH procedures.
- Gain hands-on experience with RemoteAPI to trigger PDCCH orders in a controlled test setup.
- Learn how to configure and verify PDCCH order-related parameters in configuration files.
- Acquire the ability to interpret UE responses and validate correct behavior in response to network commands.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge and Skills
- Basic understanding of LTE architecture, including eNB, UE, and radio protocol stack.
- Familiarity with RACH procedures and LTE control channels (especially PDCCH and DCI formats).
- Experience with network testing tools, callbox operation, and configuration file management.
- Working knowledge of RemoteAPI or equivalent test automation frameworks is beneficial.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial demonstrates two test procedures focusing on PDCCH Order-triggered RACH in LTE systems, covering both contention-based and contention-free approaches. The tests highlight configuration steps, test execution, and log analysis methodologies.
-
Test 1: Contention Based PDCCH Order
-
Configuration Steps:
- Modify
enb-pdcch-order-cb.cfg(copied from the default eNB configuration). -
Set the following key parameters:
- pdcch_order_prach to "cb_random" to trigger contention-based RACH via PDCCH Order.
- inactivity_timer to 600000 (10 minutes) to allow sufficient time for Remote API operations.
- Use the default
mme-ims.cfgconfiguration for MME.
- Modify
-
Test Execution:
- Start trace logging on the Callbox.
- Power on the UE and allow it to complete the attach procedure.
- While the UE is in the connected state, send the Remote API command:
./ws.js enb '{"message":"pdcch_order_prach",:enb_ue_id":1}' - Verify the correct
enb_ue_idusing the trace window. - Observe that the PRACH is triggered by the PDCCH Order.
-
Log Analysis:
- Confirm that the RACH is triggered by the PDCCH order in the logs.
- Verify that the PDCCH contains 'pdcch_order,' indicating it is intended to trigger RACH.
- Observe the 4-step RACH procedure, which signifies a contention-based process.
-
Configuration Steps:
-
Test 2: Contention Free PDCCH Order
-
Configuration Steps:
- Modify
enb-pdcch-order-cf.cfg(copied from the default eNB configuration). -
Set the following key parameters:
- pdcch_order_prach to "cf_random" to trigger contention-free RACH via PDCCH Order.
- inactivity_timer to 600000 (10 minutes).
- Use the default
mme-ims.cfgconfiguration for MME.
- Modify
-
Test Execution:
- Start trace logging on the Callbox.
- Power on the UE and allow it to complete the attach procedure.
- While the UE is in the connected state, send the Remote API command:
./ws.js enb '{"message":"pdcch_order_prach",:enb_ue_id":1}' - Verify the correct
enb_ue_idusing the trace window. - Observe the PRACH triggered by the PDCCH order.
-
Log Analysis:
- Verify that the SIB2 message contains the preamble sequence index, confirming the contention-free RACH process.
- Check the number of RA-Preambles in rach-ConfigCommon for confirmation.
- Confirm the 'pdcch_order' indication in PDCCH and the triggered RACH procedure in the logs.
-
Configuration Steps:
Both tests utilize the Callbox and UE setup with specific SIM card and configuration parameters. The procedures emphasize configuration changes, execution steps using Remote API, and careful log verification to validate the RACH triggering process and its contention type.
Test Setup
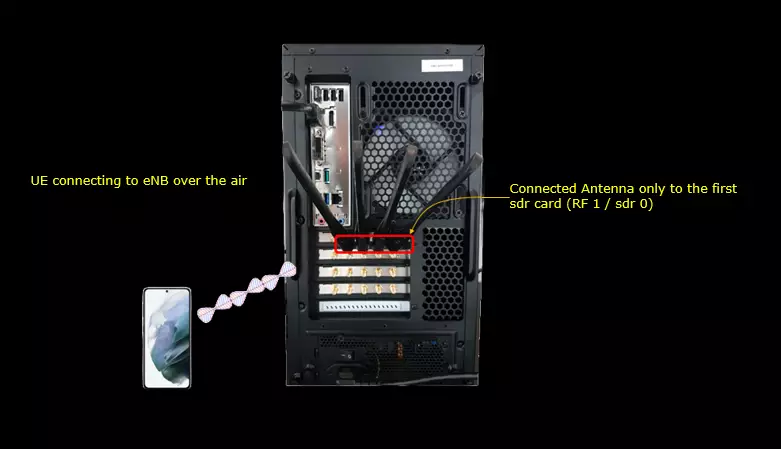
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below.
- SIM Card used in this tutorial is the one delivered with the system as it is.
- If you want to change the configuration, The tutorial Configuration Guide would help

Key Configuration Parameters
Followings are important configuration parameters for this tutorial. You may click on the items for the descriptions from Amarisoft documents.
Test 1 : Contention Based PDCCH Order
This test is to show how to configure contention based PDCCH Order and varify it.
Configuration
I used enb-pdcch-order-cb.cfg which is copied and modified from the default eNB configuration (enb.default.cfg).
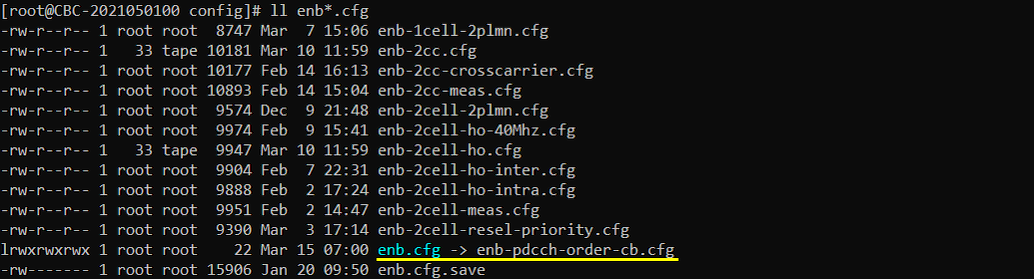
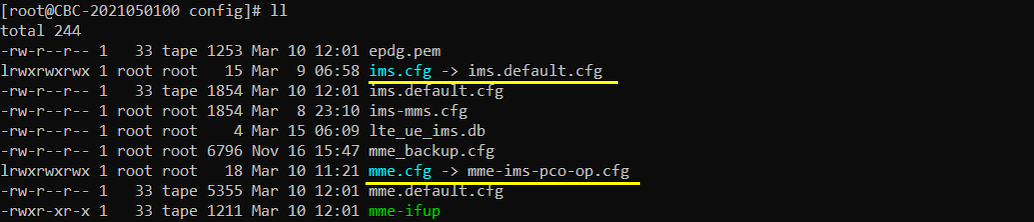
I used the default configuration mme-ims.cfg .
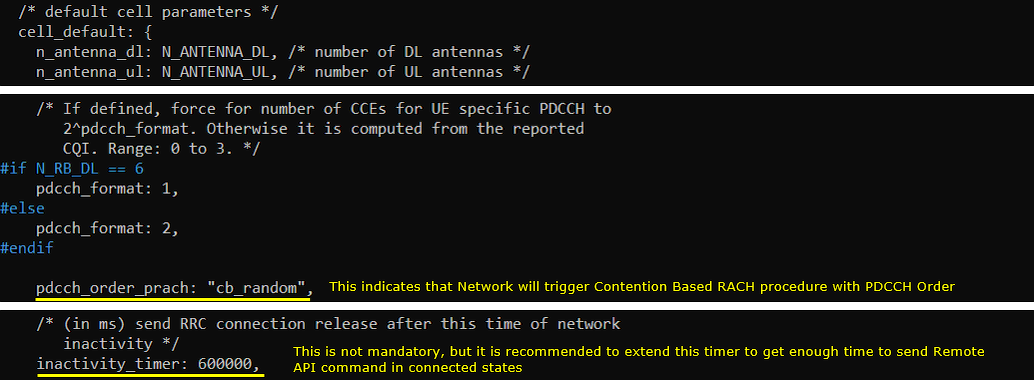
In enb-pdcch-order-cb.cfg, parameters are set as follows. The required configuration is to set pdcch_order_prach to "cb_random" which indicates that Network will trigger the contention based RACH with PDCCH Order. In addition, inactivity_timer is set to 600000 (10 min) to give enough time to type in Remote API command in connected states.
Perform the Test
First, Start trace logging on Callbox, Power on UE and let it complete the attach.
While call is in connected state, Send the RemoteAPI command by running ./ws.js enb '{"message":"pdcch_order_prach",:enb_ue_id":1}'
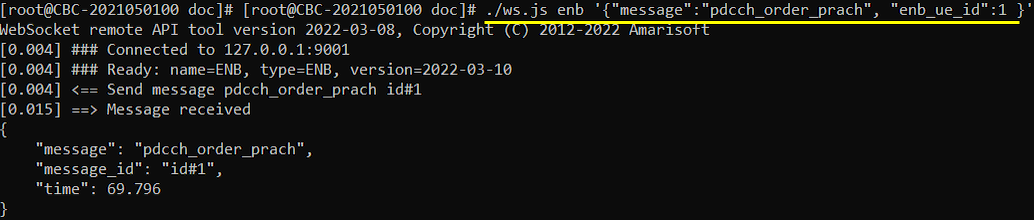
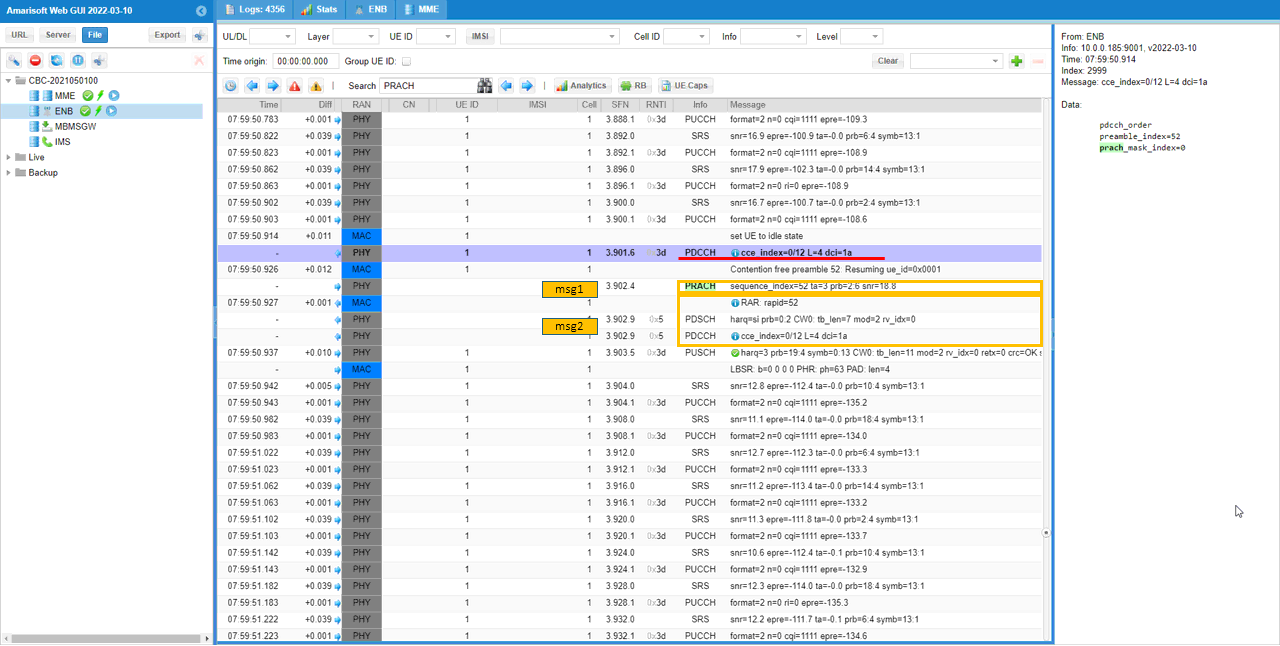
You would get the PRACH triggered by PDCCH order as shown below.
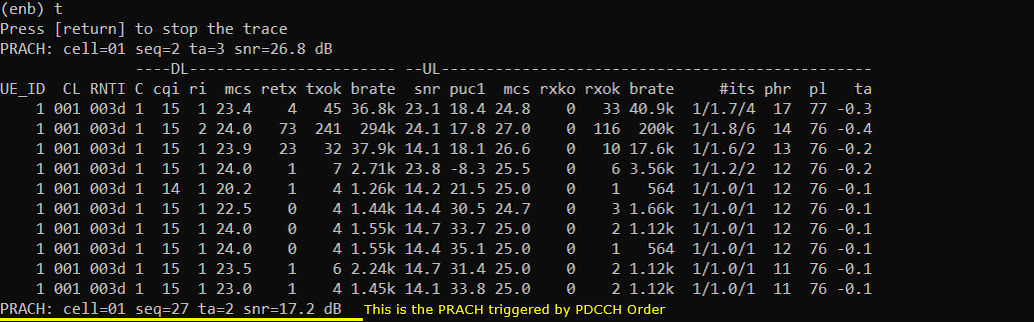
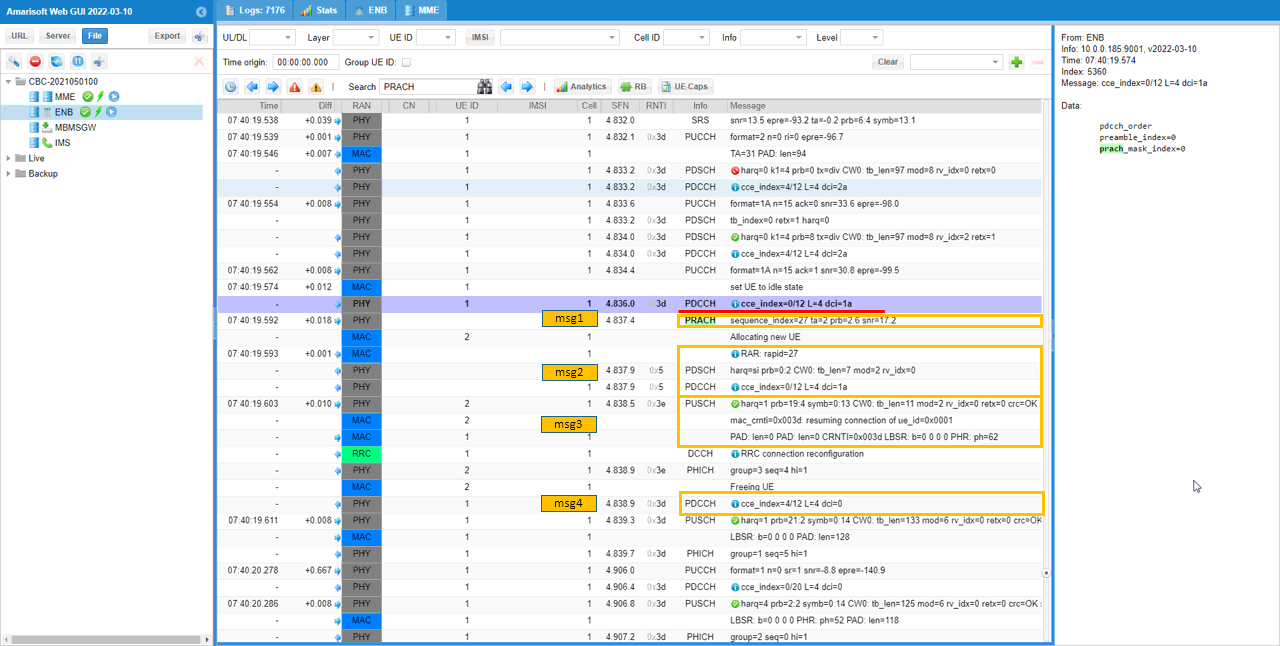
Log Analysis
Check out the RACH procedure which is triggered by pdcch_order. In the data of PDCCH, you see 'pdcch_order' which mean this is to trigger RACH, not for scheduling and you see 4 step RACH procedure which indicates it is contention based process.
Test 2 : Contention Free PDCCH Order
This test is to show how to configure contention based PDCCH Order and varify it.
Configuration
I used enb-pdcch-order-cf.cfg which is copied and modified from the default eNB configuration (enb.default.cfg).
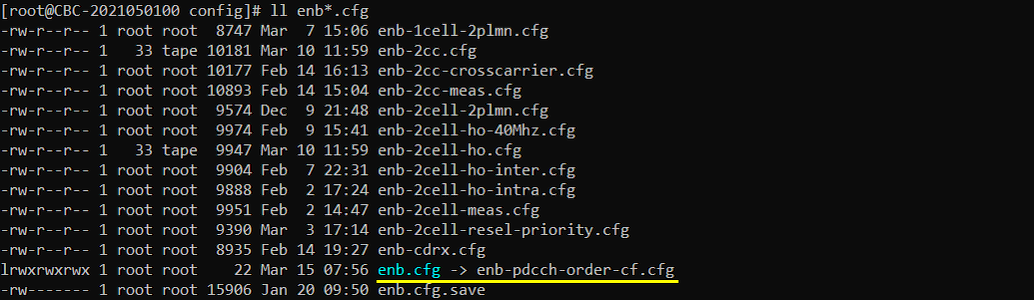
I used the default configuration mme-ims.cfg .

In enb-pdcch-order-cf.cfg, parameters are set as follows. The required configuration is to set pdcch_order_prach to "cf_random" which indicates that Network will trigger the contention free RACH with PDCCH Order. In addition, inactivity_timer is set to 600000 (10 min) to give enough time to type in Remote API command in connected states.
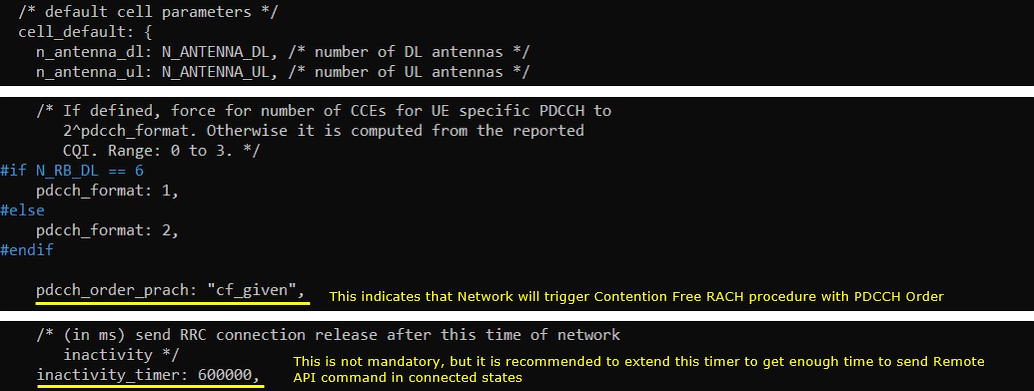
Perform the Test
First, Start trace logging on Callbox, Power on UE and let it complete the attach.
While call is in connected state, Send the RemoteAPI command by running ./ws.js enb '{"message":"pdcch_order_prach",:enb_ue_id":1}'

You would get the PRACH triggered by PDCCH order as shown below.
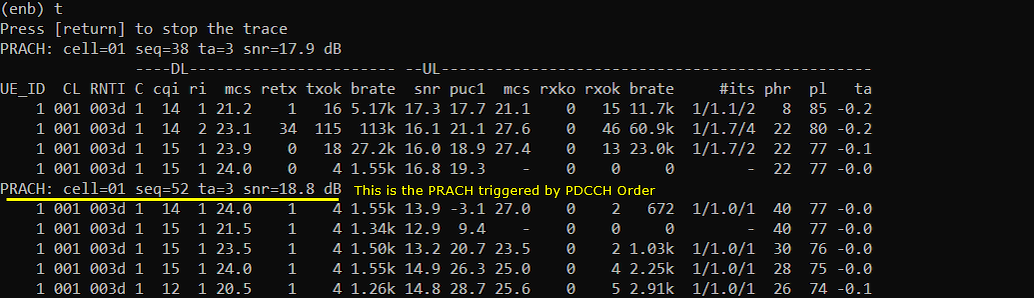
Log Analysis
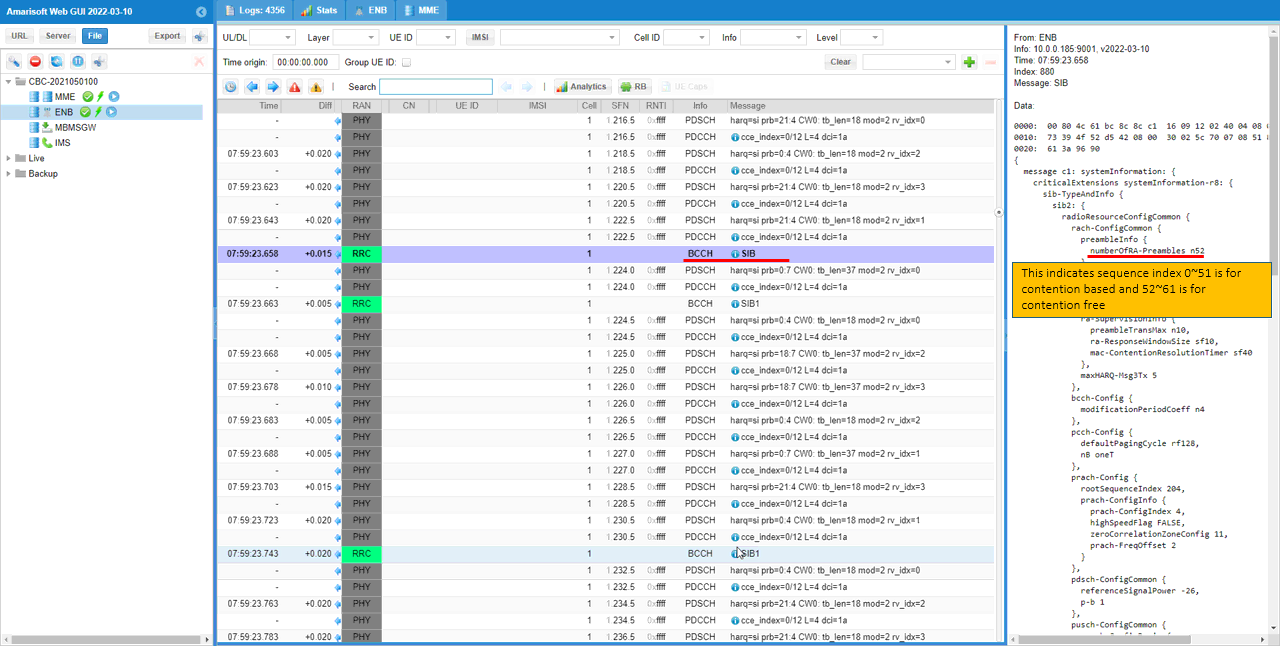
In case of contention free RACH, there should be some preamble sequence index which can be used for contention free process. You can confirm this in SIB2 message by checking numberofRA-Rreambles in rach-ConfigCommon.
Check out the RACH procedure which is triggered by pdcch_order. In the data of PDCCH, you see 'pdcch_order' which mean this is to trigger RACH, not for scheduling and you see 4 step RACH procedure which indicates it is contention based process.