Amarisoft gNB + Open5GS on Cloud
The purpose of this tutorial is to show you how to setup an opensource 5G Core called Open5GS on a local Virtual Machine and how to use it as a whole or in combination with Amarisoft Core (mme).
The purpose of this tutorial is to show you how to setup a non-Amarisoft Core (Open5GS) on Google Cloud Virtual Machine and configure Callbox (gNB) connected to the 5G Core on Cloud. The purpose of this tutorial is to show a sample case where a non-Amarisoft Core is installed on a cloud which is located far away from RAN. This kind of the setup would introduce some factors that does not come into play in regular setup where RAN and Core are installed on the same PC. Those factors are as follows : My motivation was to check if all of these factors (challenges) are properly handled and overcome.
- Large delay between RAN and Core. When I was testing this setup, RAN (Amarisoft gNB/eNB) was at my home and Core was installed on Cloud which is about 500 km away from my home. It will introduce much larger delay (both C-plane and U-plane) comparing to regular setup (i.e, RAN + Core in the same box)
- Network Address Translation. In this setup, the RAN PC was connected to internet over WiFi at my home which need to go through IP translation between the local IP at my home and global IP assigned to WiFi router. Also the IP on the cloud was configured to be translated between internal IP and External IP.
- Firewall Requirement on Cloud. The network setup on the cloud is not confired for this kind of application by default. So it need to be reconfigured to pass through all the protocols (e.g, SCTP) which are required for communication between RAN and Core.
Table of Contents
Introduction
The rapid evolution of 5G technology has driven the need for flexible and scalable mobile network architectures. Open5GS is a prominent open-source implementation of 5G core network functions, providing a modular and compliant platform for both research and commercial deployments. This tutorial focuses on deploying Open5GS on a cloud-based Virtual Machine (VM), specifically on Google Cloud, and configuring connectivity with a remote Radio Access Network (RAN) Amarisoft Callbox(gNB), situated hundreds of kilometers away. Unlike traditional setups where the 5G Core and RAN reside on the same physical machine or local network, this distributed architecture introduces unique challenges, including significant data-plane and control-plane latency, complex Network Address Translation (NAT) scenarios, and stringent firewall configurations. The Open5GS core, comprising modular network functions such as AMF, SMF, UPF, and others, communicates with the RAN over standardized 3GPP interfaces (e.g., NGAP over SCTP), making interoperability and network configuration critical for successful deployment. The significance of this architecture lies in its ability to demonstrate real-world cloud-native 5G core deployments, reflecting modern carrier network trends where core and RAN are often geographically and logically separated. This tutorial offers a practical, step-by-step guide to setting up Open5GS in the cloud, addressing the technical hurdles encountered when integrating with remote RAN equipment and highlighting the role of cloud infrastructure in next-generation mobile networks.
-
Context and Background
- Open5GS: An open-source 5G core network platform, compliant with 3GPP standards and designed for flexibility in both experimental and production environments.
- Cloud-Native 5G Core Deployment: Deploying the 5G Core on a cloud VM (Google Cloud) mirrors real-world telecom architectures, offering scalability, resilience, and geographic distribution.
- RAN Integration: Amarisoft Callbox(gNB) physically located far from the core introduces real network conditions such as high latency and NAT traversal, which must be addressed for reliable operation.
- Architectural Overview: Demonstrates integration of distributed 5G Core and RAN over the internet, utilizing protocols like SCTP and managing firewall/NAT configurations to enable seamless communication.
-
Relevance and Importance
- Illustrates a proof-of-concept for deploying non-Amarisoft core solutions in the cloud, a scenario increasingly common in modern telecom deployments.
- Addresses key technical challenges such as long-distance latency, NAT, and firewall traversal, providing insights applicable to real-world 5G network rollouts.
- Offers practical knowledge for integrating open-source core networks with commercial and open RAN platforms.
-
Learning Outcomes
- Step-by-step guidance on deploying Open5GS on a Google Cloud Virtual Machine.
- Configuration of firewall and NAT settings to enable communication between cloud-based 5G Core and remote RAN (Callbox gNB).
- Understanding of key 5G core network components and their roles in a distributed network architecture.
- Troubleshooting strategies for common connectivity and interoperability challenges.
- Familiarity with real-world deployment scenarios that differ from lab-based, co-located setups.
-
Prerequisite Knowledge and Skills
- Basic understanding of 5G network architecture and core network functions.
- Experience with Linux-based system administration and networking concepts.
- Familiarity with cloud infrastructure, especially Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resource provisioning and network configuration.
- Knowledge of RAN concepts and connectivity basics (gNB/eNB).
- Comfort working with firewalls, NAT, and IP networking.
Summary of the Tutorial
This tutorial outlines the test setup and procedures for validating interoperability between Amarisoft gNB and Open5GS as the 5G core network in a cloud-based environment. The test leverages Amarisoft UEsim as a test UE, focusing on configuration flexibility and compatibility with Open5GS network slicing.
-
Test Setup Overview:
- Virtual Machine running Ubuntu OS (specifically Ubuntu Server 20.04 for Open5GS compatibility).
- Open5GS installed as the 5G core network, with configuration and log directories specified.
- Amarisoft UEsim configured to match Open5GS default network slice and APN settings.
- Firewall settings on the cloud VM adjusted to allow necessary signaling traffic between the callbox and Open5GS core.
- Network Address Translation configured between public and private IP addresses as necessary.
-
Key Configuration Steps:
- Open5GS core: Only three configuration files (amf, ausf, udm) are modified from default for this test; after modification, associated services are restarted using systemctl commands.
- Callbox/gNB: The gnb-sa-open5gs-cloud.cfg file is used and customized as needed, particularly for IP addressing and network slicing.
- UEsim: Configuration is matched to the Open5GS subscriber database, including USIM, APN, and network slicing parameters.
- Open5GS User Database: Subscriber information is added or edited via the Open5GS WebUI, which may require access from a remote PC if the VM is cloud-hosted.
-
Test Procedure:
- Restart the LTE service on the callbox and verify the gNB's basic configuration and cell setup (specific cell parameters are not critical for this test).
- Verify that the gNB is connected to the Open5GS core network on the virtual machine.
- Restart the LTE service on UEsim and power it on, initiating registration with the network.
- Confirm successful UE registration and IP address assignment by checking callbox logs and using relevant callbox commands (e.g., 't' and 'ue').
- Attempt to ping the UE from the cloud (Open5GS core) to verify end-to-end connectivity.
- Analyze logs to confirm NGAP connection establishment between gNB and Open5GS (look for NGAP connection to the external IP of the VM).
Note: The tutorial assumes familiarity with basic VM setup, Open5GS installation, and Amarisoft configuration procedures. Configuration details unique to other test scenarios (if applicable) would be specified under their respective sections.
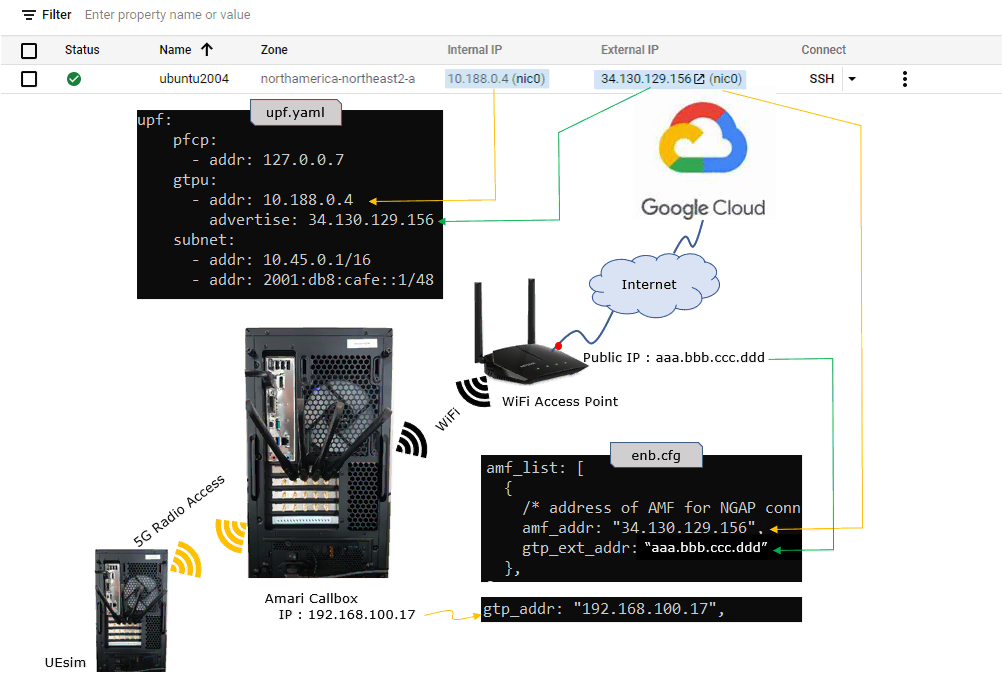
Test Setup
Test setup for this tutorial is as shown below. I assume that you would know on how to setup the Virtual Machine and run an instances of operating system (Ubuntu in this tutorial) and I would not explain on the procedure of those installation procedure.
Key Configuration Parameters
Followings are important configuration parameters for this tutorial. You may click on the items for the descriptions from Amarisoft documents.
- gNB Configuration
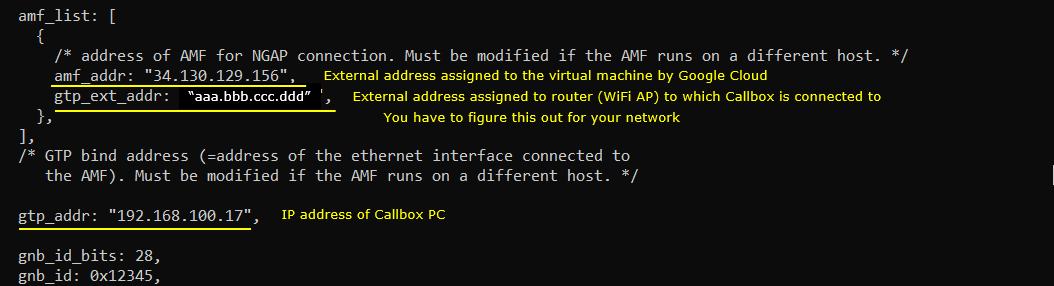
- gtp_addr
- gtp_ext_addr (enb)
- UEsim Configuration
- sim_algo
- imsi
- opc
- amf
- sqn
- K
- apn
- attach_pdn_type
- default_pdu_session_snssai
- sst
- sd
- default_nssai
- sst
- sd
Configuration
In this section, I will show the configurations for various components in the test setup that will be commonly used for every test cases in this tutorial. The configurations that is specific to each test case will be described in the configuration section under each test case.
Cloud
First thing you need to make it sure is to configure all the necessary firwall setting to allow the signaling traffic to go through between the callbox at home/office and core network on Cloud.
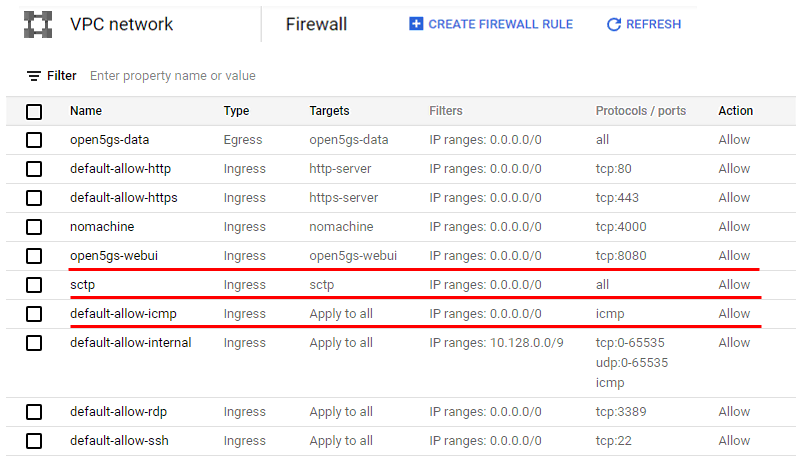
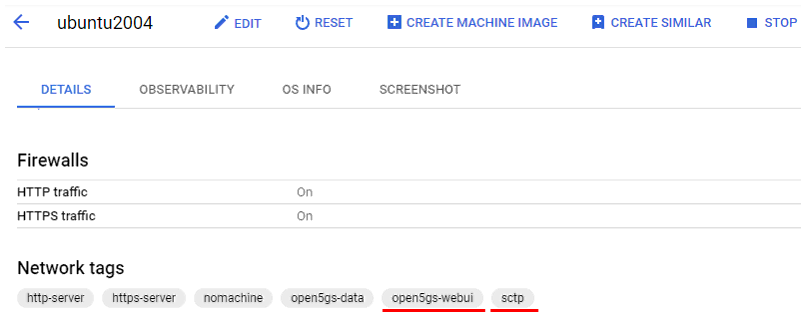
Following is all the firewall setting on the my cloud setup. For this tutorial, you should add at least three items underlined in red as shown below in addition to the default firewall setting.
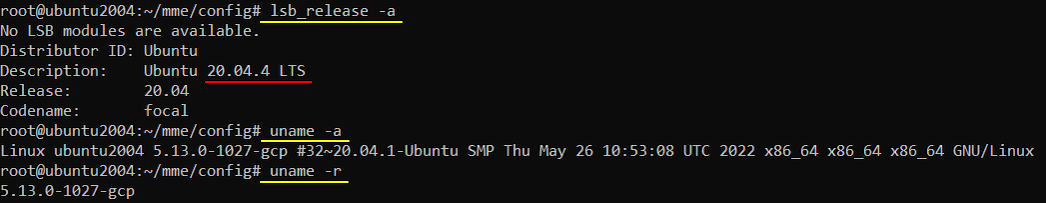
Some OS related information that I used in this tutorial is as shown below. Just for Amarisoft MME, you may use various other Linux distribution, but I am using the specific Linux distribution as shown below in order to use it not only for Amarisoft MME but also for the opensource core network called open5gs (As of Jun 2022, it seems open5gs works only in Ubuntu Server 20.04. I have tried with Ubuntu Server 22.04 but installation didn't go through. Ubuntu Desktop didn't work either for Open5GS)
Open5GS
I assume that you know how to install open5gs and would not explain about the detailed installation procedure. If you are not familiar with open5gs installation procedure, refer to the QuickStart of Open5gs official site or a note in sharetechnote.
Once you successfully installed the open5gs on the virtual machine, you would get the configuration as shown below.
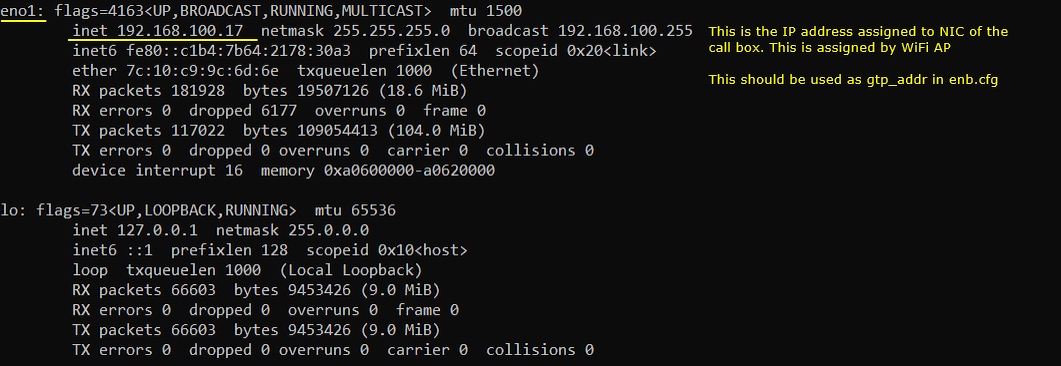
The NIC and IP configuration after the installation of open5gs on the virtual machine is as shown below.
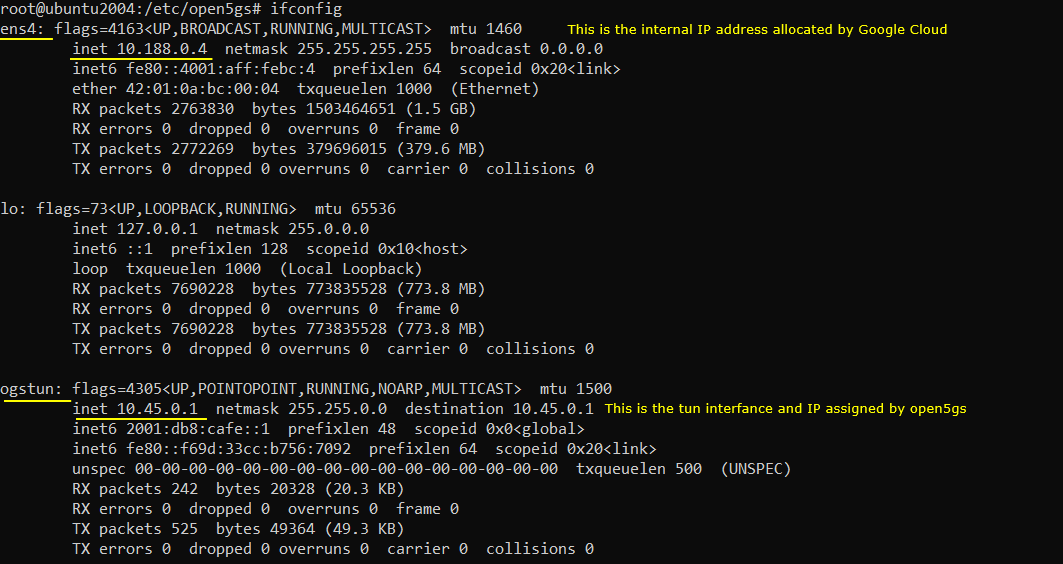
Following is the directory (/etc/open5gs) where the configuration files of open5gs are located.
Following is the directory (/var/log/open5gs) where the log files of open5gs are stored.
Open5GS - User DataBase
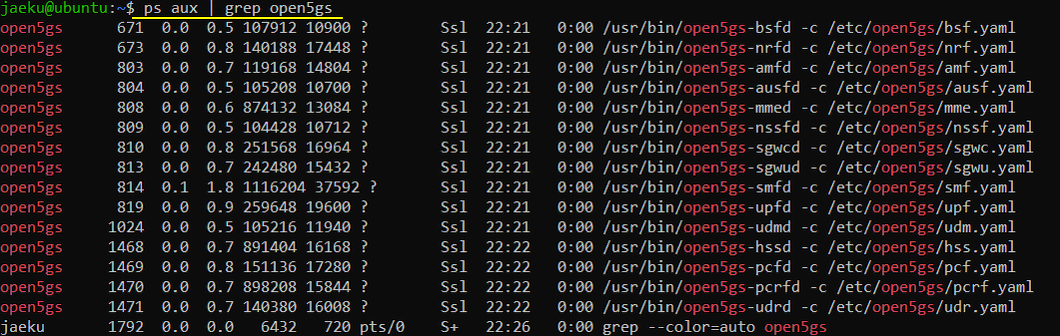
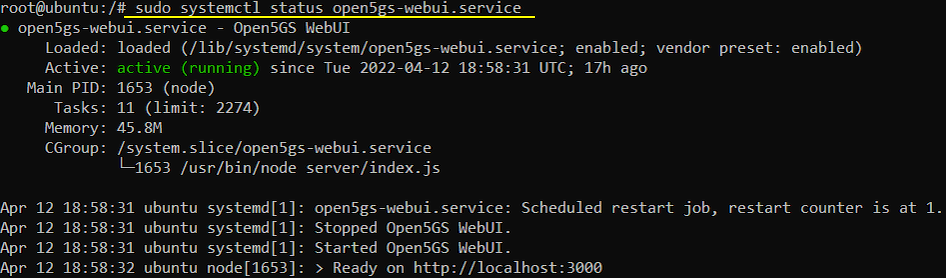
First make it sure that open5gs is running as shown below. (If web-ui is properly installed but not running, you may run it with the command : sudo systemctl restart open5gs-webui.service).
Then with the web browser, you can add a subscriber information to open5gs User Database as below. (If you are not familiar with WebUI setup, refer to this note from sharetechnote).
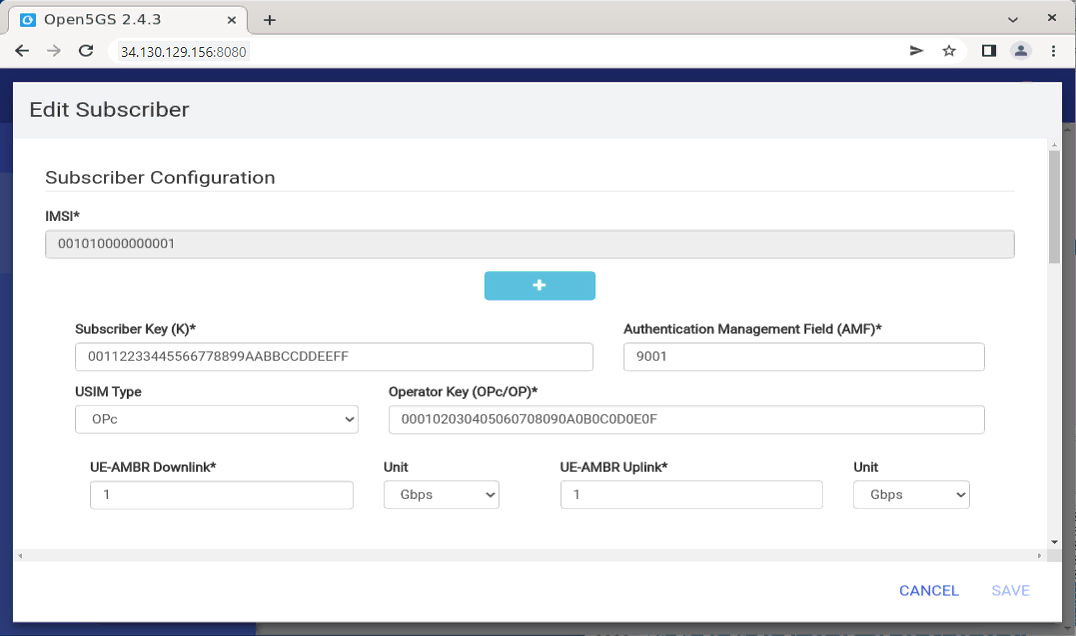
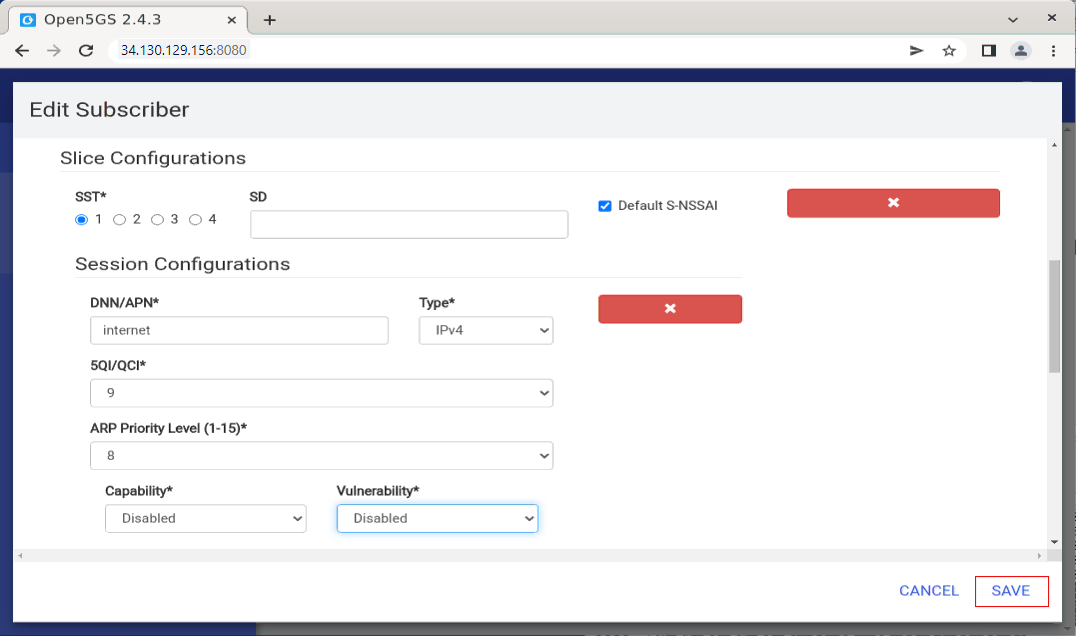
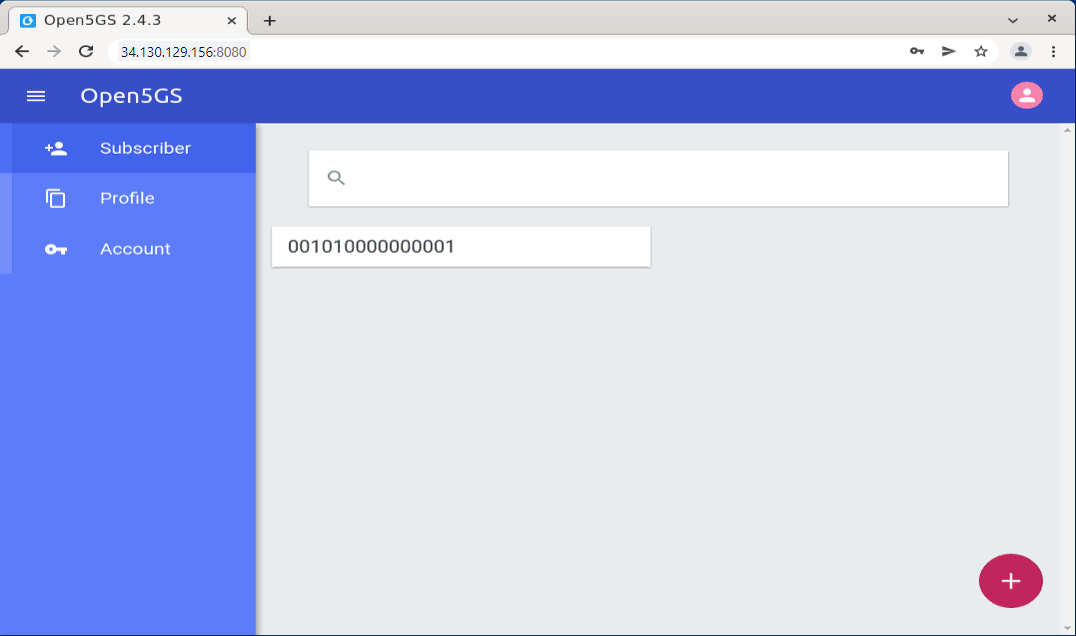
If you want to change the information for an existing UE, you can modify it with [Edit] menu as shown below.
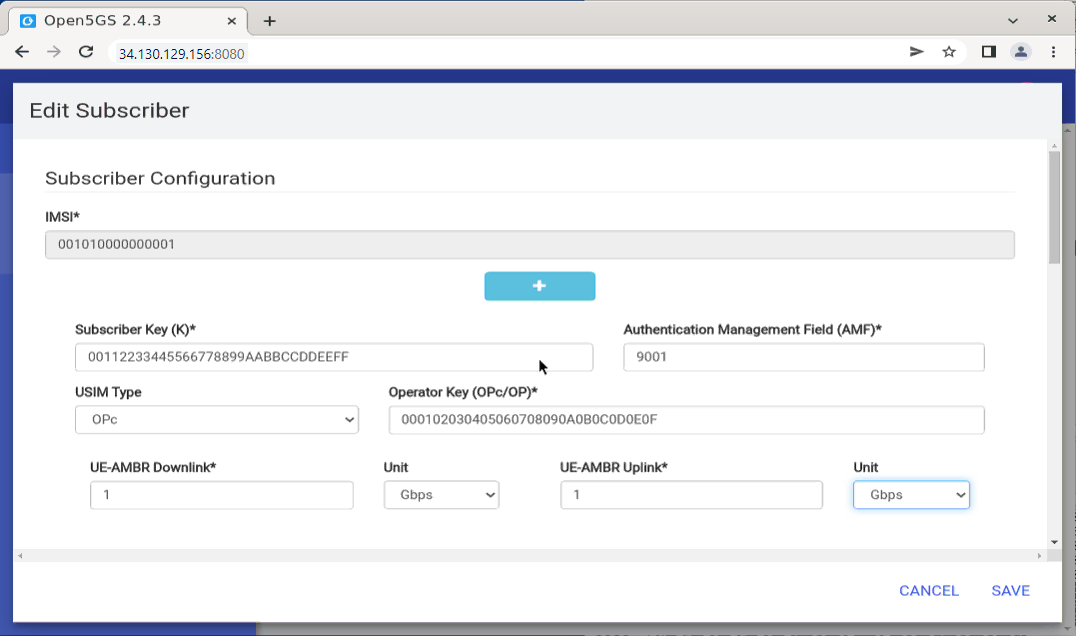
Callbox
The detailed callbox configuration would very for each test case, so the detailed configuration will be described under each test case, but following network configuration would stay same for all the test case in my setup.
(
UEsim
I will be using the same UE sim configuration for all the test cases in this tutorial.
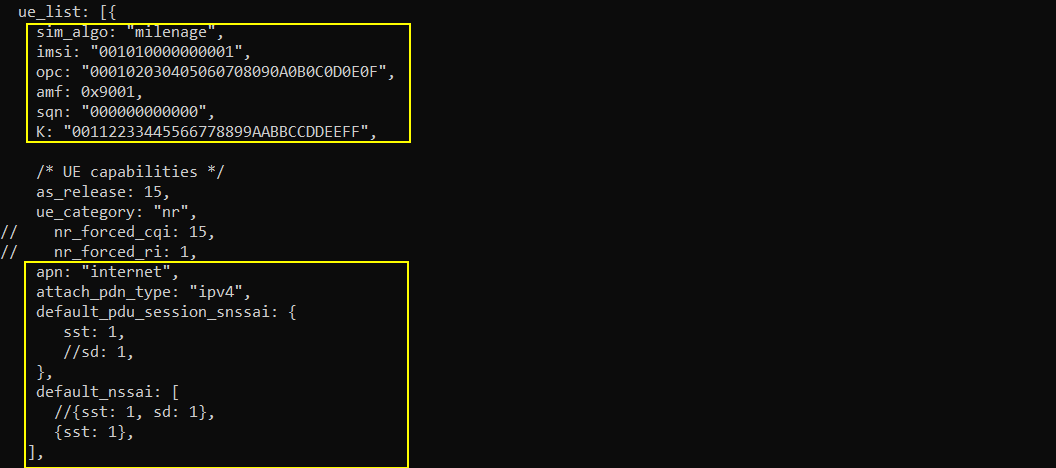
Following is the UE information configured in ue-nr-sa-open5gs.cfg which is copied and modified from ue-nr.cfg. I configured USIM information of open5gs UE DB to match with this configuration and I added apn, network slicing information to match with the default configuration of open5gs default network slice information.
Test 1 : Amari gNB + Open5GS
In this test, I will show you a case where Amarisoft callbox is used as 5G/NR RAN only and Open5GS as a whole core network (i.e, AMF + AUSF + UDM + SMF + UPF and everything else).
Configuration
Open5gs
In this test, only three configuration files of open5gs has been modified from the default as shown below. All other configuration remain as default.
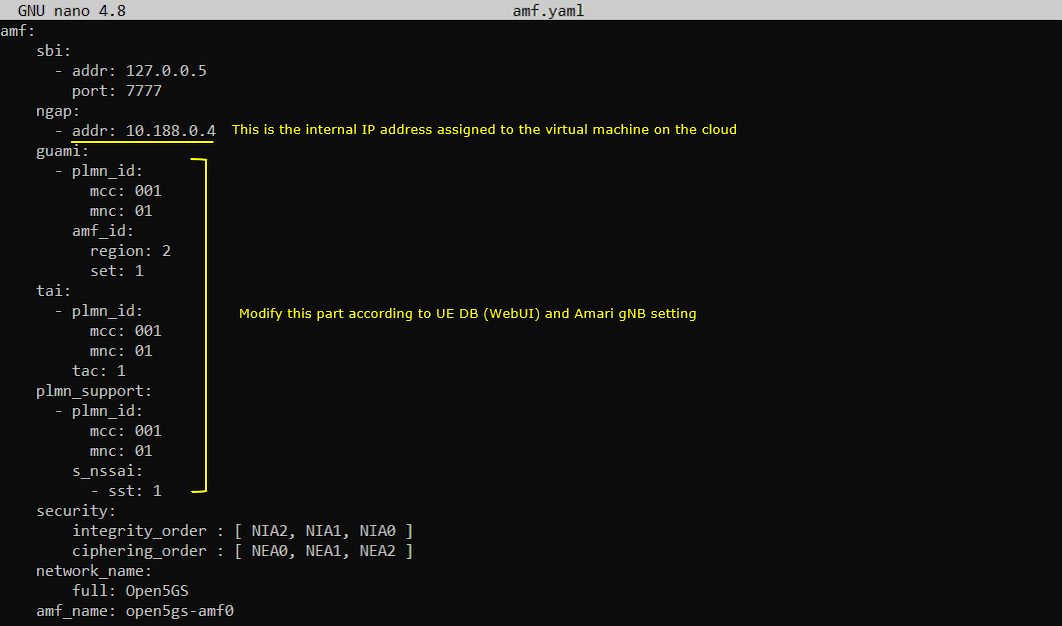
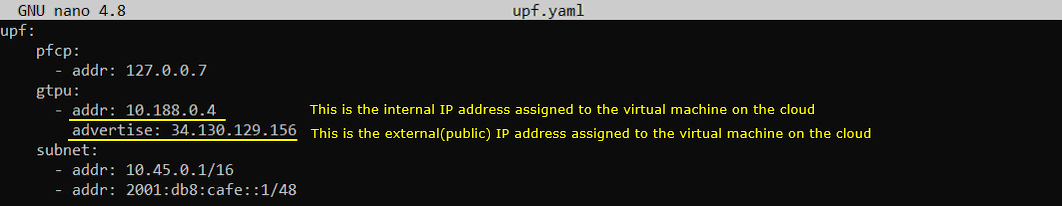
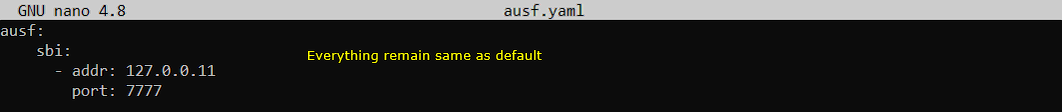
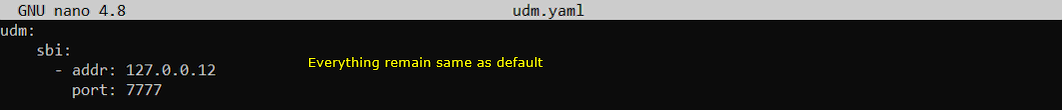
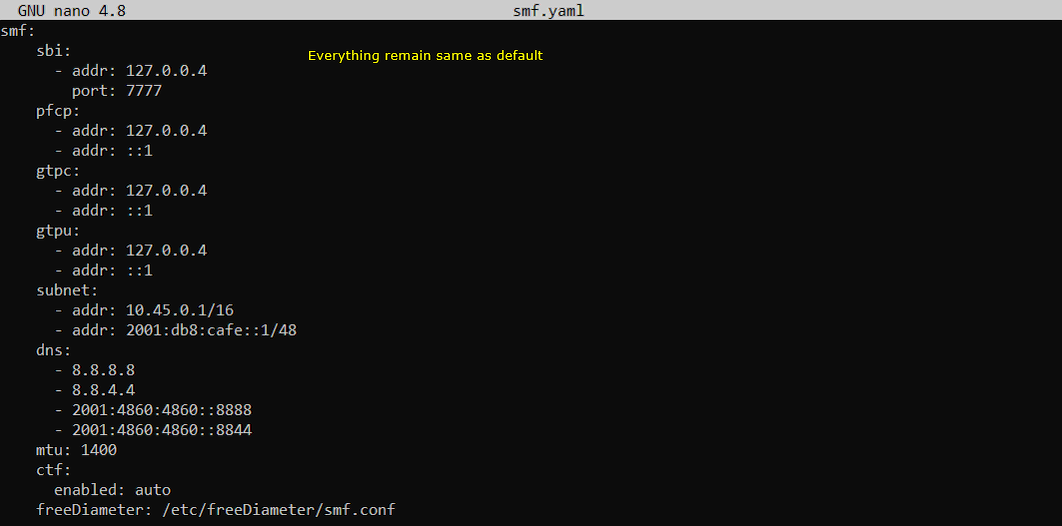
Once you change anything for a network component, you have to restart the components which is associated with the configuration file as below.
|
$ sudo systemctl restart open5gs-amfd $ sudo systemctl restart open5gs-ausfd $ sudo systemctl restart open5gs-upfd $ sudo systemctl restart open5gs-udmd |
Callbox
In this test, gnb-sa-open5gs-cloud.cfg is used as gNB configuration and it is copied and modified from gnb-sa.cfg.
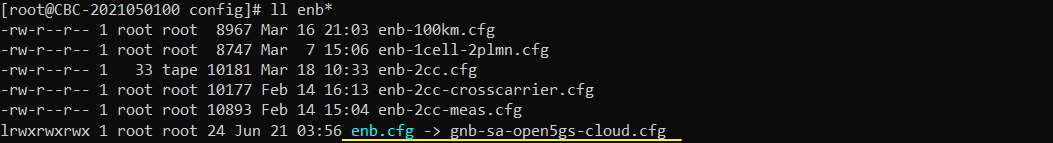
For mme, no special configurations are used. Everything is used as default configuration. (
The configuration in gnb-sa-open5gs-cloud.cfg are set as follows (
Perform the Test
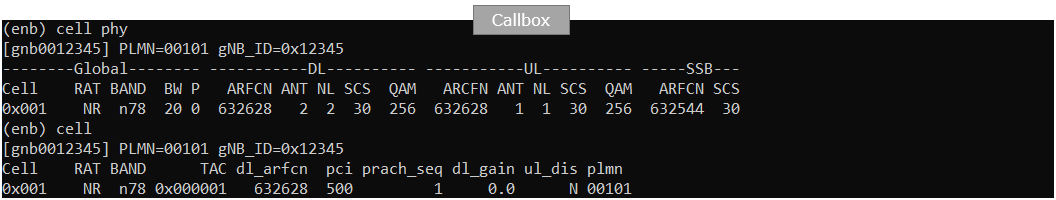
First restart lte service on callbox and check basic configuration of gNB as shown below. Actually cell configuration is not so important for this test. Configure the cell in any way you like.
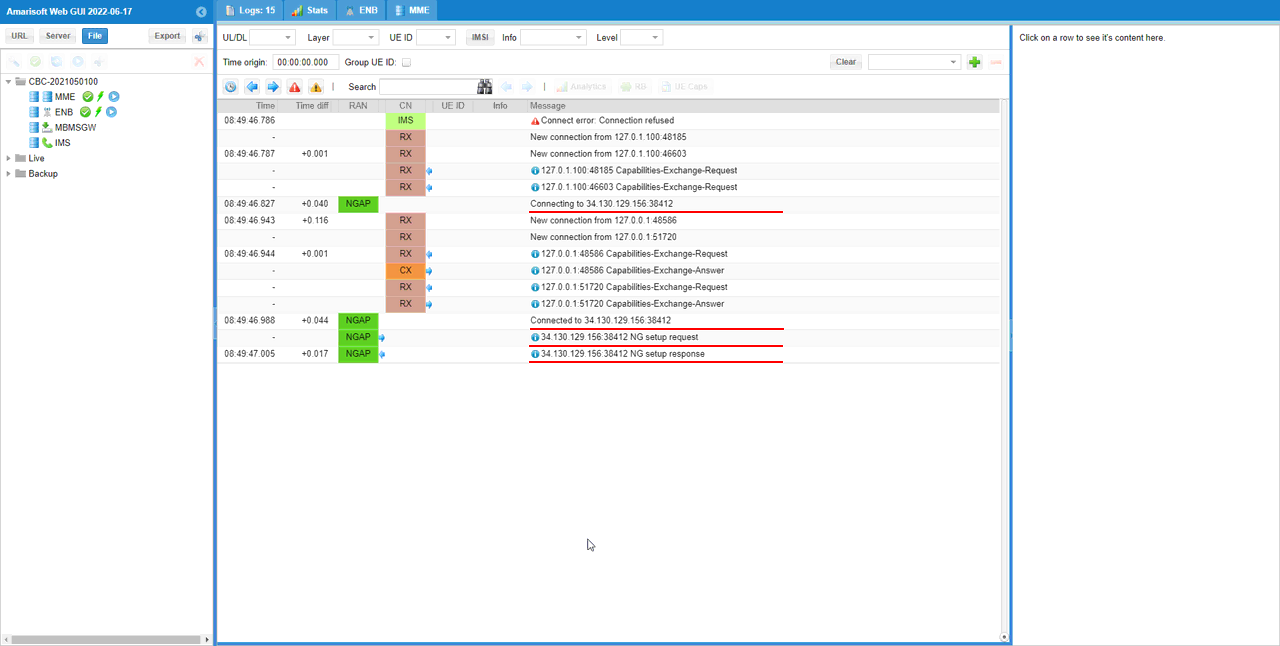
Check on the core network to which the gNB is connected. You should see the core network on the virtual machine connected as shown below.

Now restart lte service on UE sim and power on the UE.

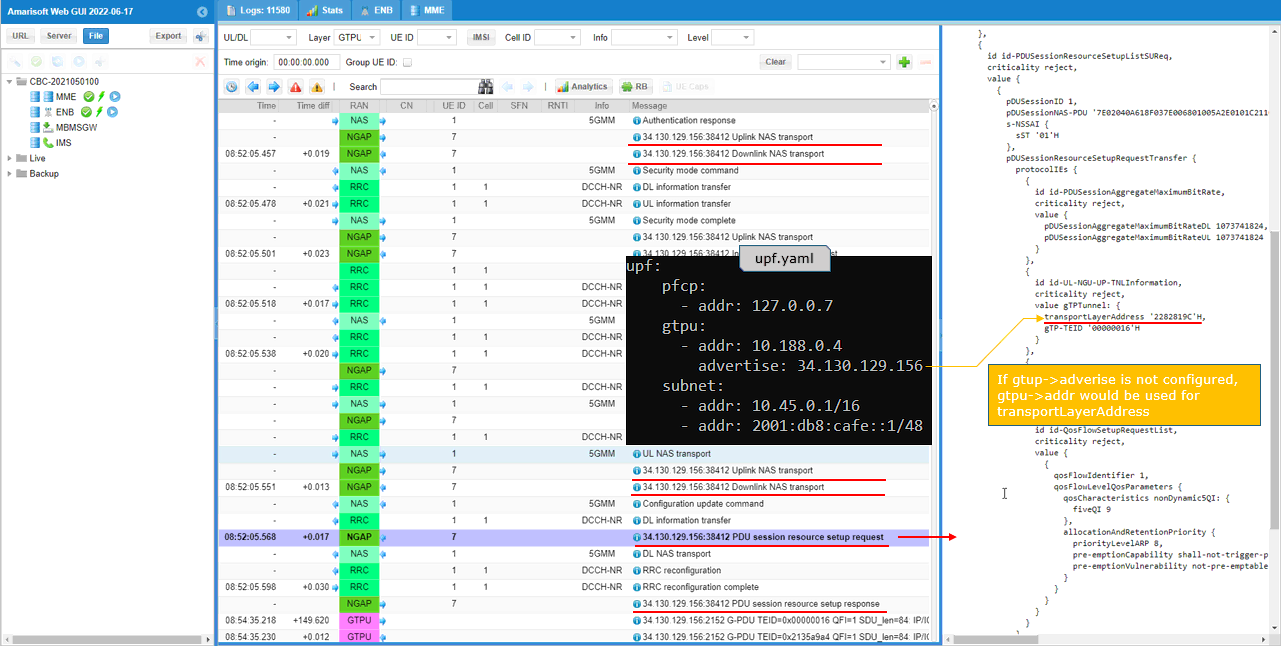
If the connection is successfully completed, you should see UE is registered and assigned with IP as shown below.

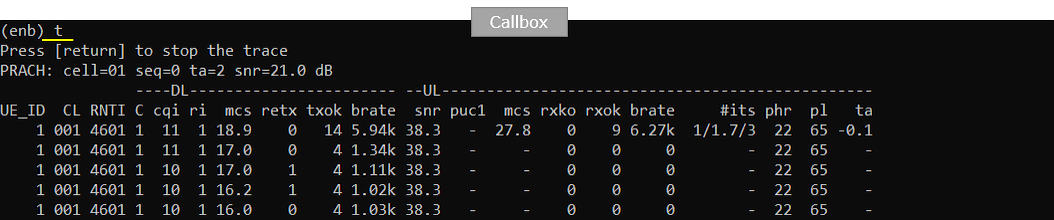
You can confirm on the UE connection with 't' command and 'ue' command in callbox as shown below

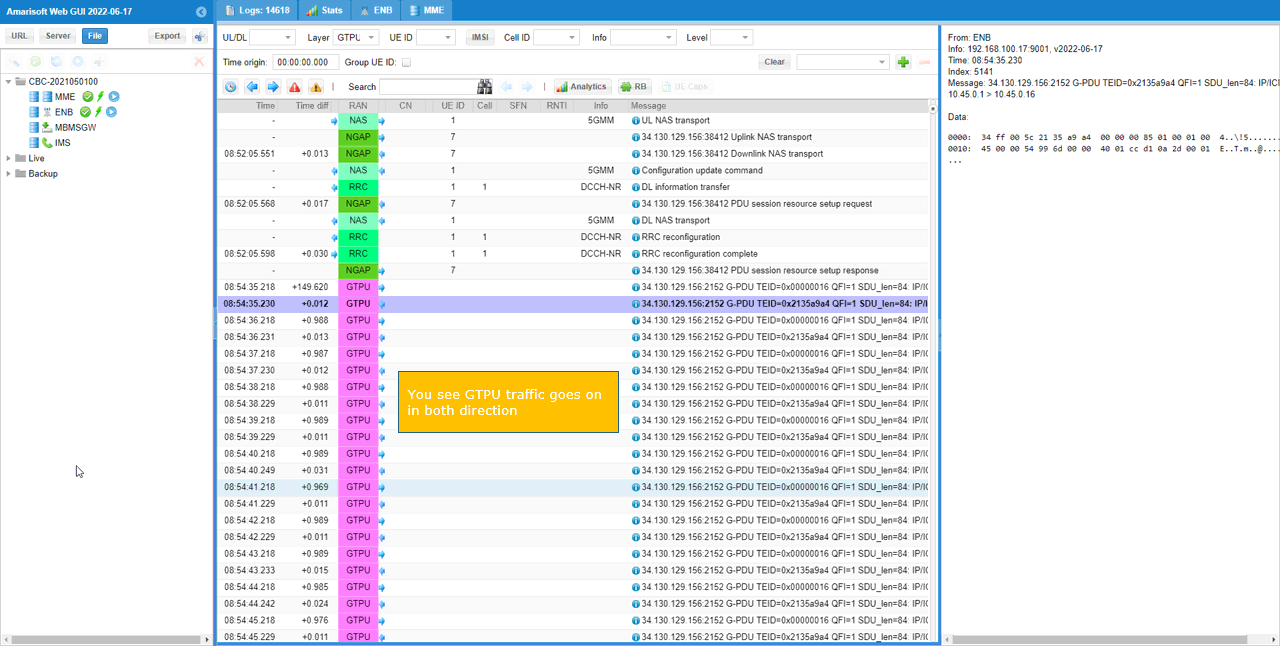
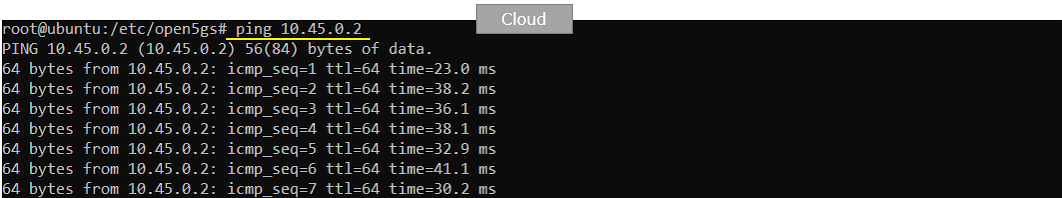
Try ping from Cloud(open5gs) to UE as shown below.
Log Analysis
As soon as you start the lte service on the callbox and if the gNB is successfully connected to the mme on Cloud, you should see the NGAP connection as shown below (You should see the NGAP is connected to the external IP of the virtual machine on the Cloud).